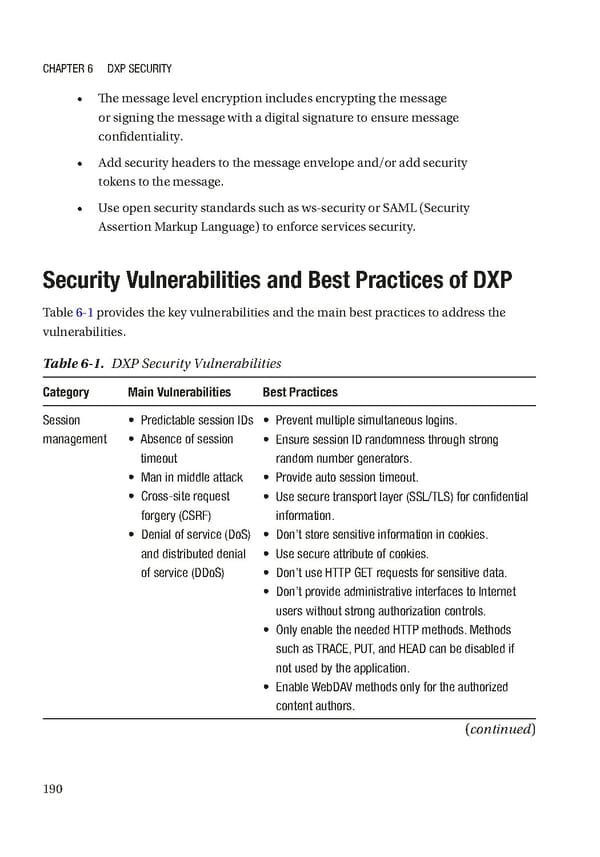
Chapter 6 DXp SeCurity • The message level encryption includes encrypting the message or signing the message with a digital signature to ensure message confidentiality. • Add security headers to the message envelope and/or add security tokens to the message. • Use open security standards such as ws-security or SAML (Security Assertion Markup Language) to enforce services security. Security Vulnerabilities and Best Practices of DXP Table 6-1 provides the key vulnerabilities and the main best practices to address the vulnerabilities. Table 6-1. DXP Security Vulnerabilities Category Main Vulnerabilities Best Practices Session • predictable session iDs • prevent multiple simultaneous logins. management • absence of session • ensure session iD randomness through strong timeout random number generators. • Man in middle attack • provide auto session timeout. • Cross-site request • use secure transport layer (SSL/tLS) for confidential forgery (CSrF) information. • Denial of service (DoS) • Don’t store sensitive information in cookies. and distributed denial • use secure attribute of cookies. of service (DDoS) • Don’t use http Get requests for sensitive data. • Don’t provide administrative interfaces to internet users without strong authorization controls. • Only enable the needed http methods. Methods such as traCe, put, and heaD can be disabled if not used by the application. • enable WebDaV methods only for the authorized content authors. (continued) 190
 Building Digital Experience Platforms Page 204 Page 206
Building Digital Experience Platforms Page 204 Page 206