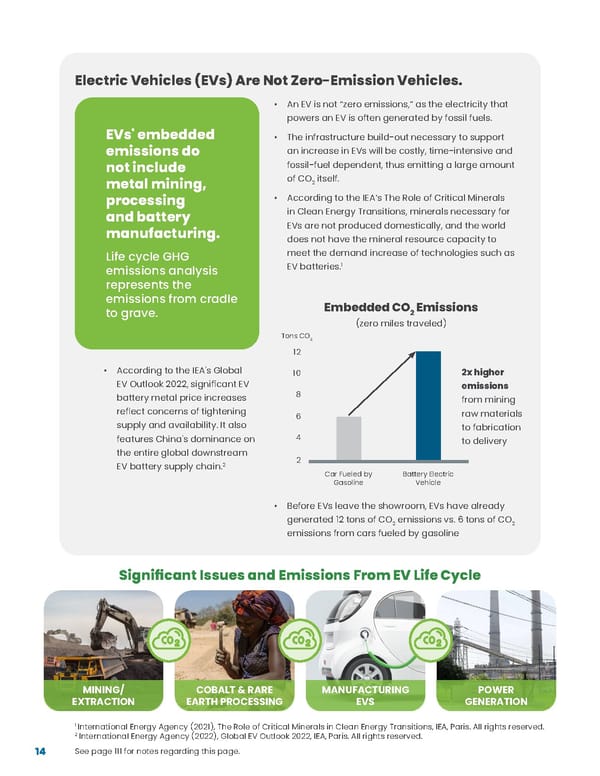
14 Electric Vehicles (EVs) Are Not Zero-Emission Vehicles. See page 111 for notes regarding this page. MINING/ EXTRACTION COBALT & RARE EARTH PROCESSING MANUFACTURING EVS POWER GENERATION Significant Issues and Emissions From EV Life Cycle Embedded CO 2 Emissions (zero miles traveled) Car Fueled by Gasoline Battery Electric Vehicle 2x higher emissions from mining raw materials to fabrication to delivery 10 8 6 4 2 Tons CO 2 12 EVs' embedded emissions do not include metal mining, processing and battery manufacturing. Life cycle GHG emissions analysis represents the emissions from cradle to grave. 1 International Energy Agency (2021), The Role of Critical Minerals in Clean Energy Transitions, IEA, Paris. All rights reserved. 2 International Energy Agency (2022), Global EV Outlook 2022, IEA, Paris. All rights reserved. • An EV is not “zero emissions,” as the electricity that powers an EV is often generated by fossil fuels. • The infrastructure build-out necessary to support an increase in EVs will be costly, time-intensive and fossil-fuel dependent, thus emitting a large amount of CO 2 itself. • According to the IEA’s The Role of Critical Minerals in Clean Energy Transitions, minerals necessary for EVs are not produced domestically, and the world does not have the mineral resource capacity to meet the demand increase of technologies such as EV batteries. 1 • According to the IEA's Global EV Outlook 2022, significant EV battery metal price increases reflect concerns of tightening supply and availability. It also features China's dominance on the entire global downstream EV battery supply chain. 2 • Before EVs leave the showroom, EVs have already generated 12 tons of CO 2 emissions vs. 6 tons of CO 2 emissions from cars fueled by gasoline
 Valero ESG Report Page 13 Page 15
Valero ESG Report Page 13 Page 15