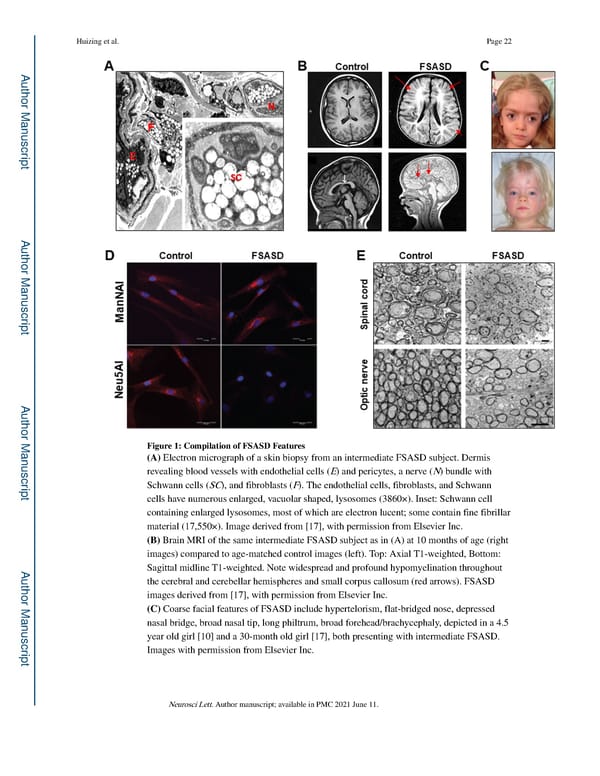
Huizing et al. Page 22 A uthor Man uscr ipt A uthor Man uscr ipt A uthor Man Figure 1: Compilation of FSASD Features (A) Electron micrograph of a skin biopsy from an intermediate FSASD subject. Dermis uscr revealing blood vessels with endothelial cells (E) and pericytes, a nerve (N) bundle with ipt Schwann cells (SC), and fibroblasts (F). The endothelial cells, fibroblasts, and Schwann cells have numerous enlarged, vacuolar shaped, lysosomes (3860×). Inset: Schwann cell containing enlarged lysosomes, most of which are electron lucent; some contain fine fibrillar material (17,550×). Image derived from [17], with permission from Elsevier Inc. (B) Brain MRI of the same intermediate FSASD subject as in (A) at 10 months of age (right images) compared to age-matched control images (left). Top: Axial T1-weighted, Bottom: A Sagittal midline T1-weighted. Note widespread and profound hypomyelination throughout uthor Man the cerebral and cerebellar hemispheres and small corpus callosum (red arrows). FSASD images derived from [17], with permission from Elsevier Inc. (C) Coarse facial features of FSASD include hypertelorism, flat-bridged nose, depressed nasal bridge, broad nasal tip, long philtrum, broad forehead/brachycephaly, depicted in a 4.5 uscr year old girl [10] and a 30-month old girl [17], both presenting with intermediate FSASD. ipt Images with permission from Elsevier Inc. Neurosci Lett. Author manuscript; available in PMC 2021 June 11.
 Free Sialic Acid Storage Disorder: Progress and Promise Page 21 Page 23
Free Sialic Acid Storage Disorder: Progress and Promise Page 21 Page 23