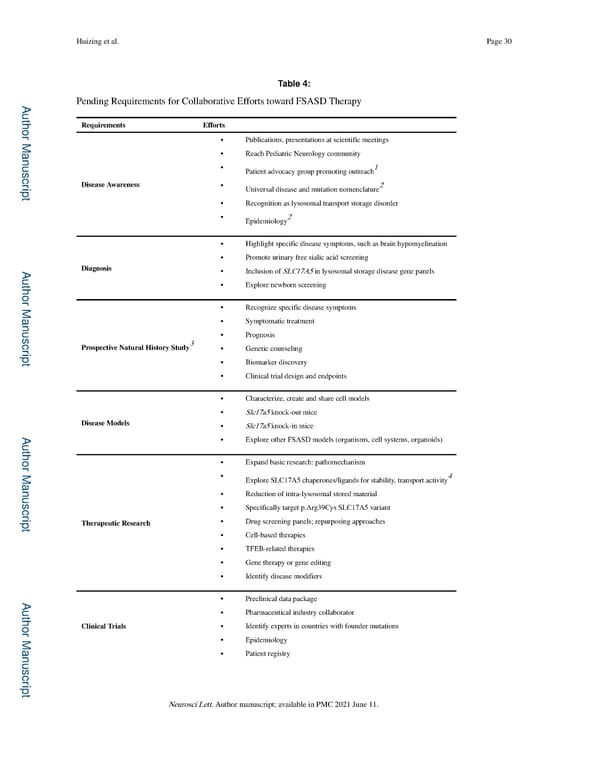
Huizing et al. Page 30 Table 4: Pending Requirements for Collaborative Efforts toward FSASD Therapy A uthor Man Requirements Efforts • Publications, presentations at scientific meetings • Reach Pediatric Neurology community uscr • 1 Patient advocacy group promoting outreach ipt Disease Awareness • Universal disease and mutation nomenclature2 • Recognition as lysosomal transport storage disorder • Epidemiology2 • Highlight specific disease symptoms, such as brain hypomyelination • Promote urinary free sialic acid screening A Diagnosis • Inclusion of SLC17A5 in lysosomal storage disease gene panels uthor Man • Explore newborn screening • Recognize specific disease symptoms • Symptomatic treatment uscr 3 • Prognosis Prospective Natural History Study • Genetic counseling ipt • Biomarker discovery • Clinical trial design and endpoints • Characterize, create and share cell models • Slc17a5 knock-out mice Disease Models • Slc17a5 knock-in mice A • Explore other FSASD models (organisms, cell systems, organoids) uthor Man • Expand basic research: pathomechanism • Explore SLC17A5 chaperones/ligands for stability, transport activity4 uscr • Reduction of intra-lysosomal stored material • Specifically target p.Arg39Cys SLC17A5 variant ipt Therapeutic Research • Drug screening panels; repurposing approaches • Cell-based therapies • TFEB-related therapies • Gene therapy or gene editing • Identify disease modifiers A • Preclinical data package uthor Man • Pharmaceutical industry collaborator Clinical Trials • Identify experts in countries with founder mutations • Epidemiology • Patient registry uscr ipt Neurosci Lett. Author manuscript; available in PMC 2021 June 11.
 Free Sialic Acid Storage Disorder: Progress and Promise Page 29 Page 31
Free Sialic Acid Storage Disorder: Progress and Promise Page 29 Page 31