BNY Mellon ESG Report
ENTERPRISE ESG REPORT 2021
BNY MELLON ENTERPRISE ESG 2 ABOUT THIS REPORT ABOUT THIS REPORT This is BNY Mellon’s 15th report covering environmental, social and governance (ESG) topics. Our annual updates in this report are not just about our company’s environmental and social impact, but also about how we view and integrate ESG considerations throughout our operations, leveraging opportunities and mitigating risks cross-functionally and across our lines of business. We publish our Enterprise ESG report annually, generally in the second quarter, on www.bnymellon. com/futurefirst . Unless otherwise noted, this report includes data and activities from BNY Mellon’s global operations for the calendar year 2021, and all data is as of 12/31/2021 and covers The Bank of New York Mellon Corporation and its subsidiaries. The report also provides select data from past years in order to facilitate year-over-year analysis. The methodologies, assumptions and estimates used to calculate climate- related data (including greenhouse gas emissions) throughout the industry are continuing to develop and are likely to change in future periods, including as a result of regulatory or other developments. As such, this could result in changes to the data, scope and time periods presented. This is our 13th report using the Global Reporting Initiative (GRI) Standards, a leading sustainability reporting framework. This report has been prepared in accordance with the GRI Standards Comprehensive option. NEW IN THIS REPORT This report describes our progress toward reporting against the Task Force on Climate-related Financial Disclosures (TCFD) recommendations and serves as an update to our Considering Climate at BNY Mellon report, released in February 2021. Reflecting our integrated approach to the TCFD recommendations, the related content is contained throughout this report. A TCFD Index indicates the location of relevant public information in both this report and others. United Nations Global Compact As a participant of the UN Global Compact, our commitment to a culture of integrity is supported at the highest level. We report on our alignment with the Ten Principals of the UN Global Compact through our Communication on Progress , which is included in this report. As part of our pledge to the UN Global Compact , we continue to support broader societal goals, such as the UN Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs). From our administration of green bond issuances to our efforts to build the workforce of the future, we contribute in tangible ways to achieving a more sustainable world. In this report, we highlight the SDGs that correspond to each of our Enterprise ESG pillars. Glossary of Key Terms Finally, to advance transparency and consistency in ESG disclosures, this report includes a glossary of key terms related to ESG issues and responsible investing. We believe that sharing these definitions with our stakeholders will contribute to achieving consistent terminology and shared understanding. We welcome your comments about this or any of our reports via the contact form on our website. Task Force on Climate-related Financial Disclosures (TCFD)

This is a modal window.
BNY MELLON ENTERPRISE ESG 3 ABOUT THIS REPORT BNY MELLON OVERVIEW BNY Mellon plays a critical role as a central orchestrator in the global financial ecosystem, touching in excess of 20% of investable assets globally. We are the world’s largest custodian, with over $45 trillion in assets under custody and/or administration (AUC/A); we clear about $10 trillion of securities and process over $2 trillion of payments per day; and we manage $2.3 trillion of assets on behalf of our Investment and Wealth Management clients. As global markets become increasingly complex and data-centric, this unique view across the financial industry helps us deliver valuable insights, identify trends and innovate new ideas to help improve outcomes for clients and the industry as a whole. Built on a legacy of trust and innovation, BNY Mellon is committed to using our reach, convening power and resources to address pressing global ESG issues. We strive to contribute to sustainable economic growth that helps protect healthy markets; enhances our own business resiliency and longevity; and aims to deliver positive impact for clients, employees, shareholders and communities. We power individuals and institutions to succeed across the financial world. Our Global Reach Assets Under Management $2.3* trillion Assets Under Custody and/or Administration $45.5* trillion 35 countries 38% of 2021 revenue generated outside United States Workforce 49,100 employees 50% based outside United States * As of March 31, 2022
BNY MELLON ENTERPRISE ESG 4 ABOUT THIS REPORT 2021 ESG PERFORMANCE HIGHLIGHTS At BNY Mellon, we are committed to the principles of ESG $1.9 trillion 1 Assets managed by investment firms that are signatories to the PRI $62 billion 2 Green debt under administration One of the Leading Trustees 2 for green bond deals in 2021 And we put the Future First SM in how we run our business ENVIRONMENTAL Carbon neutral 3 in our operations since 2015 Paper neutral in the U.S. and India since 2017 Reduction in GHG 4 emissions from 2018 baseline for Scopes 1 & 2 12% SOCIAL ISO/IEC 27001:2013 Certified Information Security Management System 40% Female globally 36% Diverse backgrounds, U.S. $34.5M Corporate, foundation and employee community support GOVERNANCE 100% Active employees certified on Code of Conduct provisions 36% 5 Women on board of directors 96% Stockholder approval on say-on- pay during the prior three years 1 A UM figure represents the aggregate total of investment firm PRI signatories’ assets under management at December 31, 2021. Includes Alcentra, ARX Investimentos, Insight Investment (including North America), Mellon Investments Corporation, Newton Investment Management (including North America) and Walter Scott & Partners. It does not include assets managed by investment firm personnel as dual officers of The Bank of New York Mellon and The Dreyfus Corporation. Siguler Guff AUM is not included in this calculation, given the minority interest in the firm held by BNY Mellon. Insight’s AUM is represented by the market value of cash, securities and derivatives held in client accounts. Where a client mandate requires Insight to manage some or all of a client’s liabilities, and Insight is to be paid an investment management fee based upon the value of such liabilities, the AUM for the account will be based on the value of the liabilities plus the gross notional value of any derivatives used in the management thereof. 2 Da ta reflective of FY 2021; Dealogic and Refinitiv. 3 F or Scope 1 and Scope 2 greenhouse gas emissions, including our data centers, as well as Scope 3 business travel emissions, through the use of renewable energy and carbon offsets. 4 Since 2018, including data centers. 5 The fig ure provided is based on Board membership following the 2022 Annual Meeting of Stockholders. ESG Awards and Recognition Dow Jones Sustainability North America Index (DJSI) 8 consecutive years CDP A List for climate management leadership 9 consecutive years FTSE4Good Global Benchmark Index 10 consecutive years Perfect score on the Corporate Equality Index for LGBTQ workplace equality, Human Rights Campaign Foundation 14 consecutive years Bloomberg Gender- Equality Index 7 consecutive years BNY Mellon Awards and Recognition
BNY MELLON ENTERPRISE ESG 5 ABOUT THIS REPORT TABLE OF CONTENTS Message From Our CEO 6 Approach 7 Putting the Future First SM 8 Future First SM ESG 8 Enterprise ESG Implementation 11 How We Consider Climate 17 Culture and Purpose 18 Diversity, Equity and Inclusion 19 Leadership and Development 26 Employee Engagement, Retention and Wellbeing 30 Our Community Impact 35 Responsible Business 41 Risk Management 42 Strong Governance 48 ESG and Responsible Investment Client Solutions 52 Global Citizenship 68 Managing Climate Change 69 Environmental Sustainability 79 Supply Chain 83 Advocacy and Political Engagement 85 Protecting Human Rights 86 Appendix 90 Global Reporting Initiative (GRI) Index 91 UN Global Compact Communication on Progress (COP) 107 Task Force on Climate-Related Financial Disclosures Recommendations Index 109 Glossary 112 Le gal Notices 117
BNY MELLON ENTERPRISE ESG 6 ABOUT THIS REPORT The challenges facing business and society are more complex than ever. As a leading global financial institution, we believe that BNY Mellon has a significant opportunity to make a positive impact and contribute to a more sustainable future. Through our culture and purpose, and responsible business and global citizenship initiatives, we strive to be a catalyst for the betterment of our stakeholders. It is these values that inspired us to take action in March to help those impacted by the war in Ukraine. Our employees gave generously and we matched their donations to further humanitarian efforts in the region. Along with financial contributions, our team in Poland has been providing tireless support, compassion and community to Ukrainians since the war began, assisting with refugee efforts and in many cases welcoming those in need into their homes. This is just one example of the many ways we advanced our environmental, social and governance (ESG) efforts in 2021. The Future First SM ESG framework, which was introduced last year, is another. It guides our own enterprise practices and conduct, underpins the strength of our client solutions and establishes a platform for thought leadership. 6 F or Scope 1 and Scope 2 emissions, including our data centers, as well as Scope 3 business travel emissions. Additionally, we introduced global caregiver leave that provides ten days of paid leave to care for immediate and extended family members. This is the second year we outline progress against our Enterprise ESG goals, which we remain focused on achieving by 2025. Our ESG strategy will continue to evolve to reflect new challenges and needs. As it does, we will embrace our responsibilities, and strive to contribute to sustainable economic growth—helping to protect healthy markets, enhancing our own business resiliency, and aiming to deliver positive impact for our clients, employees, shareholders and communities. MESSAGE FROM OUR CEO We also achieved carbon neutrality 6 in our operations for the seventh consecutive year by reducing energy use, procuring renewable electricity through the use of RECs, the accepted market-based legal instruments that represent the rights to renewable energy generation, and purchasing carbon offsets. Further, we achieved paper neutrality in our operations globally in 2021 via a certified offset program. With this report, we reaffirm our support of the T en P rinciples of the United Nations Global Compact in the areas of human rights, labor, environment and anti- corruption. This serves as our initial communication on progress, describing our actions to integrate the Global Compact and its principles into our strategy, culture and daily operations. Furthermore, we are committed to sharing this information in our 2022 Enterprise ESG Report, to be published next year. A Message from Todd Gibbons, CEO, BNY Mellon
BNY MELLON ENTERPRISE ESG 7 APPROACH APPROACH
BNY MELLON ENTERPRISE ESG 8 APPROACH PUTTING THE FUTURE FIRST SM At BNY Mellon, we’re committed to putting the Future First by using our global reach, influence and resources not just to power success today, but to help safeguard the future. Our approach, termed Future First , starts with our own ESG practices and conduct referred to as Enterprise ESG, then extends that thinking to the way we serve clients through our ESG and Responsible Investment Client Solutions. As a key participant of the global financial system, we believe it is part of our responsibility to help build the infrastructure that can facilitate investing with an ESG, responsible and sustainable lens. BNY Mellon is well positioned to help clients across the value chain. Our ESG approach empowers clients with strategies, data and analytics for every phase of the investment life cycle. Because our clients’ needs include ever-evolving ESG demands, our solutions are multifaceted. FUTURE FIRST ESG At BNY Mellon, we utilize a twofold approach to managing our ESG impact. Through Enterprise ESG —“Who we are” — we seek to integrate an ESG lens across our enterprise. Delivering on our ESG framework, we Consider Everything SM , starting with our own enterprise-wide practices, considering our business impacts on global issues and contributing to opportunities that help communities thrive. Through our ESG and Responsible Investment Client Solutions — “What we do” — we create and deliver ESG and Responsible Investment products and services . In this way, we expand on our actions by providing leading products and services that can help our clients meet their own ESG investment objectives and contribute progress toward ESG goals. We believe this approach leverages our reach, market influence and resources. Our actions can more powerfully drive shared value and significant progress toward global issues while simultaneously supporting our business objectives. Our Enterprise Environmental, Social and Governance (ESG) Commitment Statement articulates how we address these responsibilities and how we work to mitigate risks and capitalize on opportunities related to ESG. Adopted in September 2021, this statement aligns with existing BNY Mellon ESG-related statements and policies. Fu ture First SM — Our ESG Framework Who we are: Enterprise ESG What we do: ESG Client Solutions We firmly believe the strength of our client solutions is underpinned by our own actions and behavior as an enterprise. Culture and Purpose Responsible Investment Responsible Business Data and Analytics Global Citizenship Financing and Payments
BNY MELLON ENTERPRISE ESG 9 APPROACH Enterprise ESG Strategy BNY Mellon’s Enterprise ESG strategy is built on three pillars that correspond with what is currently most relevant to the company and our clients, employees, shareholders and the communities in which we operate. Culture and Purpose, Responsible Business and Global Citizenship. These pillars, and the dimensions within them, guide us in prioritizing how we integrate ESG considerations into our operations to address risks and opportunities across our business and are updated as necessary. Most recently, we have increased our focus on climate change within our Enterprise ESG strategy. We take both an inside-out approach, considering how our business impacts ESG issues and considerations, and outside-in, considering how ESG risks and opportunities impact our business. BNY Mellon is guided by global standards, frameworks and principles as we stay abreast of the rapidly evolving ESG landscape. They also guided the development of our 2025 Enterprise ESG Goals and key performance indicators, which are underpinned by mechanisms for monitoring our progress. Our strategy is implemented by an Enterprise ESG team and was guided in 2021 by a cross-functional Enterprise ESG Steering Council composed of senior leaders. Our strategy takes into account stakeholder input, global trends, business objectives and the results of enterprise-wide analyses to establish ESG priorities. Culture and Purpose Responsible Business Global Citizenship Diversity, Equity and Inclusion Leadership & Development Employee Engagement & Wellbeing Community Impact Risk Management Governance ESG and Responsible Investment Client Solutions Technology Climate Change Environmental Sustainability Supply Chain Public Policy Human Rights Various guidelines, such as the United Nations Global Compact (UNGC), Principles for Responsible Investment (PRI), Sustainability Accounting Standards Board (SASB) standards, the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs), and rating and ranking frameworks, also influence our Enterprise ESG strategy. The Task Force on Climate- related Financial Disclosures (TCFD) recommendations inform our climate strategy, which is encompassed under our broader Enterprise ESG strategy. ESG and Responsible Investment Client Solutions 7 As of March 31, 2022. While BNY Mellon is a global enterprise with 49,100 employees located in 35 countries, our financial services activities have an even broader reach. As the world’s largest custodian, with $45.5 7 trillion in assets under custody and/or administration, we have an exceptional view of ESG investment trends and an outsized ability to help clients positively affect the long term. With our size, scale and significance at the heart of the financial system, we touch many points along the financial value chain — which means we are well positioned to collaborate with clients to establish market best practices and create innovative ESG solutions.
BNY MELLON ENTERPRISE ESG 10 APPROACH We are meeting client and investor demand to elevate the scope and focus of our collaboration with clients, and our focus on Responsible Investment. We expect Responsible Investment to expand significantly as asset managers increasingly understand that it is no longer possible to successfully manage portfolios without a comprehensive analysis of the risks and opportunities associated with the transition to a more sustainable future. Additionally, we see the role of stewardship of capital as profoundly changing. Businesses without a sustainable model may cease to be attractive to customers, employees and ultimately investors. We believe that in the long run, investments will be expected to deliver a twin benefit of financial returns and a positive impact to society. Because our clients’ needs must respond to ever-evolving ESG demands, our solutions are multifaceted and fall into three categories: Responsible Investment: BNY Mellon offers a range of Responsible Investment options and advice for professional and personal investors to help them achieve their investment goals. Empowering Investors Through ESG Data and Analytics: Our breakthrough tools and analytics capabilities power investment processes and portfolio reviews for asset owners and asset managers, helping them to achieve their ESG goals. Enabling ESG Financing and Payments: We offer an end- to-end suite of ESG financing and payments solutions through our global market infrastructure, Issuer Services and Treasury Services. Learn more about our ESG and Responsible Investment Client Solutions . SPOTLIGHT Innovations for Future Value Leveraging our leading position in the global capital markets, BNY Mellon convened clients and other stakeholders at our inaugural Future First Forum in May 2021. BNY Mellon leaders and industry experts discussed the innovations that are helping companies have a positive impact on people, communities and the planet while also driving long-term value. As BNY Mellon CEO Todd Gibbons noted, the pandemic has accelerated the need for widespread adoption of ESG principles and responsible investing. Over the course of the day, various perspectives pointed to a key theme: Participants saw an urgent need for clarity, consistency and transparency in how the financial industry addresses ESG considerations — whether via predictable policy, more transparent ESG data, or consistent frameworks for measuring impact. However, it will take time, innovation and initiative to accelerate the evolution of ESG to deliver positive global impact. Future First Insights Series As we work with our clients to help them achieve their ESG and responsible investment goals, we gain insights into key issues and share those through our Future First Insights thought leadership series. Authored by experts across the organization, these articles have addressed topics such as fixed income and responsible investing, helping investors understand climate risk, key ESG trends in retail investing, and addressing the challenges of ESG data.
BNY MELLON ENTERPRISE ESG 11 APPROACH ENTERPRISE ESG IMPLEMENTATION The Enterprise ESG function is composed of four main focus areas: strategy setting, reporting, disclosures and stakeholder engagement. Each of these focus areas relies on strong cross-functional collaboration across the enterprise and ESG integration across the lines of business and functions. In 2021, we placed a particular focus on climate change, having built out our climate change strategy and issued our first stand-alone report, Considering Climate at BNY Mellon , dedicated to how we’re considering the risks and opportunities brought on by climate change effects. Learn how we are Managing Climate Change . ESG Materiality We focus on what matters most and where we can drive business transformation. Thus, BNY Mellon periodically adjusts our approach to remain current with stakeholder concerns, global trends and our own business strategies. In 2020, we increased alignment of our ESG efforts both within our organization and with external reporting frameworks. In addition to updating our Enterprise ESG strategy, we introduced goals and key performance indicators (KPIs) to guide our actions from 2020 through 2025. Our Enterprise ESG strategy and goals are based on research and stakeholder input gathered through an ESG materiality assessment process conducted in 2019 that helped us determine the most relevant ESG issues for BNY Mellon. 8 8 2020 Enterprise ESG Report , page 10 ESG MATERIALITY ASSESSMENT KEY THEMES Technological Resilience: Information security and resilience to cyberattacks represent a key intersection of societal needs and BNY Mellon business priorities. The Importance of the Employee: Employee issues such as diversity & inclusion, talent attraction, retention and development, and gender pay equity can help differentiate BNY Mellon in an increasingly competitive business environment. Climate Readiness & Response: The impending impacts from climate change require every institution to act. In financial services, frameworks such as the TCFD recommended disclosures help facilitate a robust and substantive assessment of climate-related vulnerabilities and opportunities. Integrating ESG: Increasing evidence of the benefit of systematically integrating environmental, social and governance considerations into the investment process is bolstering demand for such products and services. Tr u s t & Tr a n s p a r e n c y : Board oversight, responsiveness and transparency regarding evolving sustainability challenges are important to respond to stakeholder expectations. We consider the impact of the choices we make and the decisions we take — and report on those enterprise-wide practices. The commitments we make at the global level guide the execution of our Enterprise ESG and climate change strategies, and the reporting of our performance. Enterprise ESG impacts the culture at BNY Mellon, informs our responsible business practices, and inspires our global citizenship. We contribute to sustainable economic growth that helps protect healthy markets, enhances our own business resiliency, and aims to deliver positive impact for key stakeholders.
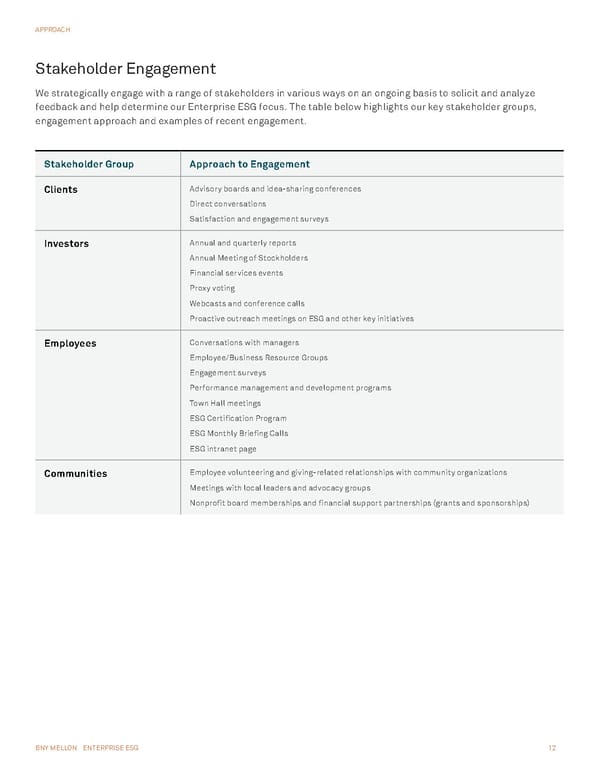
BNY MELLON ENTERPRISE ESG 12 APPROACH Stakeholder Engagement We strategically engage with a range of stakeholders in various ways on an ongoing basis to solicit and analyze feedback and help determine our Enterprise ESG focus. The table below highlights our key stakeholder groups, engagement approach and examples of recent engagement. Stakeholder Group Approach to Engagement Clients Advisory boards and idea-sharing conferences Direct conversations Satisfaction and engagement surveys Investors Annual and quarterly reports Annual Meeting of Stockholders Financial services events Proxy voting Webcasts and conference calls Proactive outreach meetings on ESG and other key initiatives Employees Conversations with managers Employee/Business Resource Groups Engagement surveys Performance management and development programs Town Hall meetings ESG Certification Program ESG Monthly Briefing Calls ESG intranet page Communities Employee volunteering and giving-related relationships with community organizations Meetings with local leaders and advocacy groups Nonprofit board memberships and financial support partnerships (grants and sponsorships)
BNY MELLON ENTERPRISE ESG 13 APPROACH Enterprise ESG 2025 Goals and Progress We continue to report against the goals and key performance indicators (KPIs) that we announced in 2019 to guide our actions from 2020 through 2025. Our ESG performance is reported regularly to our Executive Committee and to the Corporate Governance Nominating and Social Responsibility (CGNSR) Committee of our Board of Directors. Culture and Purpose 2025 Goals and Key Performance Indicators Diversity, Equity and Inclusion GOAL: Drive a culture of inclusion and advance diverse representation In progress Increase senior leadership positions held by women and ethnically and racially diverse employees with unique percentage point targets by Executive Committee member Increase percentage of participation in Employee/Business Resource Groups (E/BRGs), as evidenced by employee registered membership in at least one group, by 3% year over year, starting from the 2019 baseline year Consistently rank among the top employers for leadership in the field of diversity, equity and inclusion Leadership & Development GOAL: Drive a culture of high productivity, engagement and commitment to continuous learning and development to support successful leaders, managers and their teams In progress Improve manager effectiveness score by 5% year over year, as measured through Manager Upward Feedback process Increase the number of discrete employees participating in/utilizing nonmandatory learning programs, on a year-over-year basis Employee Engagement & Wellbeing GOAL: Support a culture of wellbeing through a holistic program focused on engaging employees and developing key management behaviors to decrease health risk In progress Increase positive response to employee health survey question “Do you think your workplace supports a culture of health and wellbeing?” by 5% Offer at least two wellbeing programs that meet or exceed market benchmarks; increase enrollment and/or active participation by 10% year over year Community Impact GOAL: Leverage the company’s resources and employee talent to significantly increase impact of community support in the regions and countries in which BNY Mellon operates In progress Direct 65% of corporate grants and sponsorship giving donations to organizations and causes that are aligned with our strategic focus of developing the workforce of the future Facilitate 130,000+ hours of employee volunteerism annually Increase total hours of Signature Pro Bono consulting delivered to nonprofits by 10% over the 2019 baseline year Achieve a skills-based volunteering target of 40% of total employee volunteer hours, ensuring that a significant portion of volunteer efforts leverage employees’ professional experience
BNY MELLON ENTERPRISE ESG 14 APPROACH Responsible Business 2025 Goals and Key Performance Indicators Risk Management * GOAL: Risk Framework - Continue to evolve and fortify our risk infrastructure's integration into BAU practices across the organization In progress Promote consistent and aligned utilization of the risk lifecycle (identification, measurement, mitigation, monitoring) across the company as a key factor in risk/reward decisions for product, client and geography prioritization GOAL: Risk Culture - Sustain strong global risk and compliance culture focused on risk awareness, ownership and ethical behavior In progress Drive active employee engagement and ownership of risk and compliance requirements through ongoing strategic communication and development Technology GOAL: Continually evolve business protocols to help ensure systems continuity in every jurisdiction in which we operate, and across borders In progress Expand our information security management system based on an internationally recognized specification (i.e., ISO 27001) for all critical applications and business services GOAL: Evolve business protocols to provide technology knowledge, resilience and business continuity In progress Cultivate a globally competitive level of workforce awareness concerning information systems security Governance GOAL: As part of the director recruitment and refreshment efforts for our Board of Directors, continue to ensure that candidate slates include individuals with diverse backgrounds and perspectives in order to maintain the Board’s diverse composition In progress Review at least annually, the diversity criteria applied by the Board in its process of evaluating the qualifications of potential candidates Integrate into the evaluation of external search firms’ performance a review of such firms’ capabilities in developing diverse candidate pools GOAL: Formalize proactive outreach program to engage shareholders on ESG performance In progress Increase proactive engagement with top shareholders on ESG topics Enhance integration of ESG content in public reporting, including but not limited to BNY Mellon’s Proxy materials ESG and Responsible Investment Client Solutions GOAL: Provide best-in-class client solutions to the global ESG community by enabling ESG financing In progress Increase assets managed by investment firms that are signatories to the UNPRI Increase number of clients who use our ESG Global Risk Solutions, and Data and Analytics solutions Increase volume of new green bonds administered Demonstrate ESG thought leadership and proof points as measured by industry recognition and client satisfaction metrics * Language in the goals were refined to provide clarity
BNY MELLON ENTERPRISE ESG 15 APPROACH Responsible Business 2025 Goals and Key Performance Indicators Environmental Sustainability GOAL: Maintain commitment to environmental sustainability, including effectively managing natural resource usage, such as energy and greenhouse gas emissions, waste, paper and water In progress Reduce greenhouse gas emissions by 20% from a 2018 base year, for Scopes 1 & 2 including data centers, in line with Science Based Targets (SBTi) methodology Maintain carbon neutrality commitment Divert 80% of office waste from landfills Target zero waste to landfills for technology equipment Achieve paper neutrality in the U.S. and India Drive water use reduction in building operations Supply Chain GOAL: Build a Supplier Diversity Program that has longevity, consistent with BNY Mellon’s value proposition and diversity initiatives In progress Refine program resources to improve program processes and increase efficiencies Implement a company-wide sustainable training program on supplier diversity Increase outreach with diverse suppliers through supplier development and education experiences Public Policy GOAL: Continue to engage with stakeholders on key regulatory and legislative issues important to BNY Mellon In progress Expand internal awareness of regulatory and legislative impacts and trends Strategically advocate on priority legislative and regulatory issues affecting BNY Mellon Human Rights GOAL: Continue the commitment to preventing modern slavery and human trafficking in our operations, supply chain and communities In progress Conduct due diligence and training practices to promote understanding of Modern Slavery Act principles
BNY MELLON ENTERPRISE ESG 16 APPROACH Enterprise ESG Governance A clear governance structure drives the integration of our Enterprise ESG strategy throughout our company and helps to align our activities with our business goals and cultural values. Our governance mechanisms balance the interests of our varied stakeholders and help inform our policies, practices, reporting and disclosure. Enterprise ESG Governance Structure Corporate Governance, Nominating and Social Responsibility (CGNSR) Committee of the Board of Directors Provides primary oversight of BNY Mellon’s ESG efforts. Consists of independent directors who regularly review our Enterprise ESG performance, monitor progress against goals, and provide guidance to management Read more in the CGNSR Committee Charter . Executive Committee Responsible for ESG progress and success; monitors progress on goals, anticipates market trends and future client needs, and drives business innovation Enterprise ESG Steering Council Composed of senior employees spanning our business functions, was active in 2021 to help integrate ESG globally and regionally ESG and Responsible Investment Client Solutions Working Group Composed of senior employees spanning our business functions, was active in 2021 to help integrate ESG globally and regionally Enterprise ESG Team Leads strategy development and governance processes, provides subject matter expertise, collaborates with company functions and departments to assist in development of ESG integration initiatives, manages public reporting and disclosures related to ESG activities, facilitates external stakeholder input, and collaborates with experts and facilitates thought leadership Working Groups Ad hoc as needed Subject Matter Experts Staff across varying areas of the company who execute ESG-related policies, practices and programs Employee Groups Employee/Business Resource Groups (E/ BRGs), sustainability ambassadors, and volunteer and philanthropic fundraising committees that support social or environmental impact initiatives Learn more about Enterprise ESG .
BNY MELLON ENTERPRISE ESG 17 APPROACH HOW WE CONSIDER CLIMATE BNY Mellon is developing a framework to consider climate-related risks, which often manifest in the long term, as well as opportunities throughout our business. In 2019, we signed on to support the TCFD recommendations, in part to guide the execution of that framework. In addition, four of the investment firms in our Investment Management business have also signed on as supporters. Additionally, across our business, we maintain numerous affiliations with industry and thought leadership initiatives to support corporate considerations of climate change and climate risk. We utilize the TCFD recommendations to inform our climate-related disclosure to provide investors, lenders, insurers and other stakeholders the necessary information on our approach to considering our climate-related risks and opportunities. This provides a framework for substantive conversations about our analysis, action plans and work to embed climate- related matters into our business strategy. The consideration of climate risks and opportunities is part of our larger body of work to address the integration of ESG into the way we operate and serve our clients and is thus embedded in our Enterprise ESG strategy and approach. We seek to respond to climate risks and opportunities throughout our business strategy and across our entire enterprise. Thus, additional information about our management of climate-related risks can be found throughout this report, primarily in Risk Management , Managing Climate Change and Environmental Sustainability . In early 2021, building on our support of TCFD, in early 2021 we published our first stand-alone climate-related report, Considering Climate at BNY Mellon . In that report, we outlined our approach, plan and actions to address climate-related risk and opportunities. In this Enterprise ESG report, we provide an update on our progress. It is not meant to be an exhaustive account of our work, but rather examples of areas where we have initiatives in place related to climate risks and opportunities. Our most recent progress is flagged by “New in 2021” headings.
CULTURE AND PURPOSE Culture is the driving force behind our success as a global leader in financial services. We maintain a high-performance culture by engaging across our global team, leveraging the rich diversity of our people and equipping them to contribute to our shared purpose: powering individuals and institutions to succeed across the financial world. In our communities we prepare young people to prosper in the workplace of the future, and fund programs that teach students next-generation business and technology skills. United by the common values of Passion for Excellence, Integrity, Strength in Diversity and Courage to Lead, our people demonstrate behaviors that enable us to deliver on purpose-driven growth. By enabling people to thrive, we contribute to the following SDGs:
BNY MELLON ENTERPRISE ESG 19 CULTURE AND PURPOSE DIVERSITY, EQUITY AND INCLUSION The unequal impacts of the pandemic and climate change have shone a light on how these issues disproportionately fall on the underserved and marginalized in our communities. Ongoing racial disparities and serious social justice issues weigh not just on the lives of individuals but also on society as a whole. These unresolved issues emphasize the importance of making our diverse society more equitable and inclusive. In an interconnected world, shaped and accelerated by globalization, having a diverse workforce improves social equity and inclusion as well as creates a competitive business advantage. Research shows that the business case for diversity remains robust and that organizations benefit when they adopt systematic, business-led approaches to inclusion and diversity. 9 Embracing diversity, advancing equity and fostering inclusion can drive organizational performance by enabling individuals to achieve their full potential and contribute to the success of a company. Our Opportunity and Approach Diversity, Equity and Inclusion (DEI) at BNY Mellon is integral to our business strategy. We invest in attracting, developing, advancing, supporting and retaining top and high-potential talent. With Strength in Diversity as one of our four core values, we actively seek diversity of thought, perspectives and problem-solving. We strive to create an ecosystem and environment that unleashes the power of diverse backgrounds, experience and expertise to produce better ideas and business outcomes. We deliver programs, adjust our practices and create policies that embed DEI in our operating and governance models and throughout the talent life cycle. We are strengthening our culture to promote a sense of belonging and support wellbeing — whether working in the office or virtually — that enables us to do our best work, build great careers and lead fulfilling lives. 9 Diversity Wins: How Inclusion Matters , McKinsey 2020 2021 ACHIEVEMENTS Workforce Diversity: Increased women among new hires, senior leaders globally and Board of Directors, and increased ethnic/racial representation in our U.S. workforce among senior and mid-level leaders and on our Board, when compared to 2020. Executive Development: Graduated the first cohort of 23 diverse, high-potential candidates from our flagship Executive Sponsorship program. Disability Inclusion: Achieved 100% on the Disability Equality Index and named a Best Place to Work for Disability Inclusion. * Inclusive Workplace: Ranked among the top 20 Fortune 500 Companies on Diversity and Inclusion, ** achieved 100% on the HRC Corporate Equality Index, named a Best Place to Work for LGBTQ+ Equality and included in the Bloomberg Gender-Equality Index. *** * BNY Mellon Named to 2021 Disability Equality Index , July 14, 2021 ** The top 20 Fortune 500 companies on diversity and inclusion , June 2, 2021 *** BNY Mellon Recognized for Championing a Culture of Inclusion and Equity , January 27, 2022
BNY MELLON ENTERPRISE ESG 20 CULTURE AND PURPOSE Strategy and Governance Diversity, equity and inclusion (DEI) is integral to who we are as a company, what our people experience as members of our global team, and how we serve all our stakeholders. From the time people join our organization, we work to welcome them into a culture that is respectful, equitable and fosters a sense of belonging. We appreciate the differences and unique contributions of our employees and seek to offer them opportunities for advancement. These values are codified in policies such as our Equal Opportunity Policy in the United States and our global Code of Conduct, which prohibits discrimination. Our four-pillar DEI strategy is embedded in our business strategy, operating model, talent experience and client value proposition. The Global Head of Diversity, Equity and Inclusion engages with Executive Committee members and the Board of Directors on DEI goals, progress and challenges. Executive Committee members’ variable compensation is informed by performance against these and other goals. Our global head and regional leads, covering the Americas, EMEA, APAC and India, work with other subject matter professionals to develop the global DEI strategy. The team then consults and collaborates with Human Resources colleagues, business leaders and the Executive Committee to adapt the DEI strategy locally. Employees across the company bring fresh perspectives to our work through their membership in, and leadership of, our Employee/Business Resource Groups (E/BRGs) and by serving on various business-line and regional DEI councils. DIVERSITY, EQUITY AND INCLUSION STRATEGY Our global strategy stands on a foundation of four pillars: Business Imperative Enable businesses to leverage DEI to improve and differentiate performance Ta l e n t Build the best global team, reflecting the rich diversity of our talent and client markets and the communities we serve Inclusive Culture Ensure our culture is respectful, equitable and fosters a sense of belonging Market Leadership Set a high bar for our company and our people to actively champion and drive DEI progress
BNY MELLON ENTERPRISE ESG 21 CULTURE AND PURPOSE Addressing Racial Injustice BNY Mellon continues to enact programs, policies and actions to address social inequities and systemic racial disparities. Our momentum grows as diversity, equity and inclusion are woven more deeply into the fabric of our organization. Some progress has been made, but we are by no means satisfied. While we have accelerated planned DEI actions, we realize that meaningful results arise from sustained action over time. In the U.S., we continue to work toward representation goals in our most underrepresented ethnic/racial talent populations. We aim to achieve these increases from a 2020 baseline by year-end 2023 by improving outcomes in diverse hiring, advancement and retention. • Achieve a 15% increase in overall Black representation to 12% • Achieve a 30% increase in Black representation of Senior Leaders (Directors and Managing Directors) to over 4% • Achieve a 15% increase in overall Hispanic/Latinx representation to almost 8% • Achieve a 30% increase in Hispanic/Latinx representation of Senior Leaders (Directors and Managing Directors) to over 5.5% We have also publicly pledged to increase senior women representation among Directors and Managing Directors across our EMEA region from 28% to 33% by year-end 2025. A Business Imperative We believe that our entire workforce shares responsibility in building a culture where all people feel a sense of belonging. Thus, each employee has a DEI goal in their performance management plan. Our people come from all races, ethnicities, cultures, genders, sexual orientations, ages, abilities and backgrounds. To ensure that diversity advances and continues to inform how we grow our business and serve our clients, we embed DEI in every stage of the talent life cycle and partner with lines of business to enhance performance, innovation and impact by leveraging DEI. For example, through an expansion of our relationship with a federally designated Minority Depository Institution, we intend to do more work with underserved community banks to help close gaps in racial wealth and access to capital. GLOBAL GENDER DIVERSITY The events of the past year, including the COVID-19 pandemic, acutely affected women, as more women than men are opting to leave the workforce or downshifting their careers. Working mothers, women in senior management positions and Black women are experiencing some of the largest challenges. 10 While attrition among women at BNY Mellon is up year over year, bright spots include an increase in the proportion of women among new hires and representation of women in our senior leadership ranks and on our Board of Directors at the end of 2021. While many of our DEI initiatives contribute to the increased representation of women at all grades across the company, several initiatives are intended to advance women in the organization. These efforts include improved candidate sourcing, including from existing employees, through the utilization of software, and enhanced recruiting expertise and pipeline affiliates. In addition, we are paying attention to internal talent pipelines, supporting high-potential employees with development plans, and increasing the inclusion of women in our candidate and promotion slates and talent referrals. To bolster retention and advancement, we promote a culture of sponsorship, whereby senior leaders act as sponsors to advocate for and empower high-potential employees to position themselves as protégés. Development plans should have promotion-readiness objectives and may include sponsorship or coaching to support top women to advance their careers. We have recently expanded and added employee benefits and programs that support life balance, including our global Caregiver Leave Policy, providing employees up to 10 days of paid leave to prioritize planned and unplanned family care circumstances. 10 COVID-19’s Impact on Women’s Employment , McKinsey.
BNY MELLON ENTERPRISE ESG 22 CULTURE AND PURPOSE The visibility of underrepresented employees in senior positions can improve gender and intersectional diversity throughout an organization as it creates role models for others. Our intentional progress toward advancing women in leadership positions was recognized by American Banker when four BNY Mellon leaders were again included in its 2021 Most Powerful Women program and four other employees were named to the 2021 HERoes Women Role Models Lists. GLOBAL GENDER DIVERSITY* % women U.S. Workforce 2020 44% 2021 43% Global Workforce 2020 41% 2021 40% New Hires 2020 39% 2021 40% Mid-level Leaders 2020 35% 2021 35% Senior Leaders 2020 29% 2021 30% Executive Leaders 2020 29% 2021 26% Board of Directors 2020 27% 2021 31% Among U.S.-based BNY Mellon employees, overall representation of individuals from underrepresented ethnic/racial backgrounds rose to 36% in 2021 from 35% the previous year. Continuing a multiyear trend, ethnic/ racial diversity also improved year over year in our senior and mid-level leadership ranks, up to 26% and 34%, respectively. Additional details can be found in the EE01 Report at the end of this report. U.S. ETHNICITY* % of U.S. workforce from underrepresented ethnic/racial backgrounds U.S. Workforce 2020 35% 2021 36% U.S. New Hires 2020 44% 2021 44% Executive Leaders 2020 20% 2021 18% Senior Leaders 2020 25% 2021 26% Mid-Level Leaders 2020 33% 2021 34% Board of Directors 2020 36% 2021 38% * “Mid-l evel leaders” are inclusive of BNY Mellon’s vice president-level employees, “Senior leaders” are inclusive of BNY Mellon’s director-level and above employees, excluding executive leaders, and “Executive leaders” are inclusive of BNY Mellon’s Executive Committee. Data is based on employee voluntary disclosures, as of 31 December 2021. Current, accurate data provides visibility into the composition of our workforce. The BNY Mellon People Analytics team maintains and publishes workforce representation data, conducts analyses and facilitates workforce planning activities, which enables us to track diversity, identify changes and improve representation throughout the talent life cycle.
BNY MELLON ENTERPRISE ESG 23 CULTURE AND PURPOSE Attracting and Retaining Diverse Talent To broaden our talent pool diversity, we have forged strategic alliances with professional associations, educational institutions, think tanks and nonprofits that reach Black, Hispanic/Latinx, Asian, LGBTQ+, people with disabilities, neurodiverse individuals, veterans and other talent from backgrounds currently underrepresented in our workforce. We aim for fair opportunity by requiring diverse candidate slates, creating inclusive job descriptions and involving diverse interview panels. We engage nontraditional candidates such as those reentering the workforce after an extended leave of absence. We took a number of steps in 2021 so our recruitment process engages and includes candidates from diverse backgrounds and offers equitable access to our job openings. We equipped hiring managers with resources, tools and training, such as a recruitment process checklist and an Inclusive Hiring course, so our hiring process is more inclusive of a broadly diverse talent pool. BNY Mellon has incorporated an artificial-intelligence-powered platform that enhances our ability to identify promising candidates and reach our diversity hiring goals. The platform is now live, and we are beginning to collect data and metrics that reveal efficacy of different methods, approaches, communications and external affiliates in increasing the diversity of applicants and hires. PAY E Q U I T Y BNY Mellon is committed to providing equal pay for equal work. To achieve our goal, we periodically review our pay practices and processes and publicly share the results. This transparency holds us accountable to our stakeholders and contributes to change. Earlier in 2022, we once again voluntarily published the results of our most recent pay practices review and adjusted median pay gap and unadjusted median pay data. The adjusted median pay gap analysis measures whether we are paying employees, regardless of gender or race/ ethnicity, comparably for doing the same/similar work. In this adjusted median pay gap analysis, we account for legitimate factors, including geography, level and job. Unadjusted median pay compares the 50th percentile of pay of a defined group (women or racial/ethnic group) against the 50th percentile of pay for the comparison group (men or majority group). In this analysis, pay is unadjusted, meaning that we do not adjust pay for any factors like job, geography or job level. Our recent pay practices review, based on 2021 total compensation data (which includes incentive compensation paid in early 2022), found that compensation for both women globally and U.S. employees from underrepresented ethnic/racial backgrounds are, on average, 100% of their respective counterparts. We also published our 2021 UK Gender Pay Gap Report in accordance with the UK Government’s criteria, our fifth such report. Measuring a gender pay gap is not the same as measuring equal pay. This report provides an overview of the difference between the average earnings of men and women in our largest UK employing entity, notes the drivers behind any gaps, and describes the steps we are taking to improve gender representation at all levels of the company. Finally, we aim to compensate employees fairly and competitively. Learn more about Fair Pay . DIVERSITY AT ALL LEVELS As workforce representation is an outcome of successful talent retention, we are proactively enhancing programs, practices and policies to reduce voluntary attrition, particularly among talent from underrepresented groups, and increase diversity at all levels in our organization, especially at the senior levels. We embed DEI in succession bench criteria and design development plans that improve promotion readiness, offer sponsorship and advance talent diversity. In its second year, our Sponsor Ready course continues to build awareness and skill in sponsoring colleagues. Open to all employees, this course is creating a sponsorship culture that will contribute to sustained knowledge sharing, skill building, diversity of thought, talent advancement and retention, and competitive advantage across our businesses. In 2022, the first cohort of 23 diverse, high-potential candidates graduated from our flagship Executive Sponsorship program. Initiated by our executive leaders, the first phase of the program engaged Black and Hispanic/Latinx high performers. Candidates in this inaugural cohort were each paired with a member of
BNY MELLON ENTERPRISE ESG 24 CULTURE AND PURPOSE BNY Mellon’s Executive Committee and participated in programmatic engagement and development of inclusion as a differentiated skill, including the five-week Sponsor Ready e-learning course, speaker series and peer- networking/coaching forums. Participants learned to strengthen a culture of sponsorship across the company that engages and elevates more of our underrepresented top talent. In addition to this formal program, we provide other resources to support the development and retention of diverse talent and improve managers’ inclusive leadership competency. While we hold a common set of core values across our enterprise and work toward a shared DEI strategy, the implementation approach is often adapted to take into account regional context. India. The Maximizing Personal and Professional Potential (MP3) talent development program helps women in mid-management build skills to weather challenges with resilience. Successful candidates complete group mentoring sessions and then are coached by sponsors for role readiness. EMEA. This region has set a goal to increase the representation of women in senior management roles across EMEA from 28% in 2020 to 33% by the end of 2025. We have made progress, as women held 29% of senior management roles in that region, as of December 9, 2021. This builds on the achievement of an earlier goal set upon signing the HM Treasury Women in Finance Charter. In 2016, BNY Mellon UK set a goal that a minimum of 30% of all hires in the region be women and/ or diverse across all job levels by the end of 2017. We met that goal ahead of the target date. RACE ACTION IN THE UK AND EMEA In the UK, we have implemented an array of measures aimed at improving equity and outcomes for employees from underrepresented racial and ethnic groups, including collecting employee ethnicity/race data, and increased participation in voluntary self-identification surveys by UK employees. Using a combination of data analyses and focus group feedback, we launched a UK Race Action Plan to enhance the employee experience and support employee growth, development and retention. We will continue to track and report UK employee ethnicity data to monitor progress and the impact of the Plan. Across the region, our EMEA Business Inclusion Council strives to enhance an inclusive culture by embedding DEI into the way we operate. Since it was formed in 2020, this council has developed plans to expand employee self-identification options beyond gender and beyond the UK, and conducted campaigns to encourage employees to share their demographic information. The council has also created and promoted resources to build and measure inclusion and has identified techniques to attract, develop and retain employees from underrepresented groups. DISABILITY INCLUSION AT WORK As we continue our work to be an even more inclusive employer, we seek to reach people with disabilities, the largest and most diverse underrepresented group globally. HEART, our diverse abilities employee resource group, drives change by increasing awareness and understanding of visible and invisible disabilities and health-related conditions. These include physical and mental health issues, chronic ill health and neurodiversity. To assess and benchmark our efforts, we participated in the Disability Equality Index for the third time in 2021 and scored 100% for the second consecutive year. 11 BNY Mellon was also named to the Disability Equality Index ® “Best Places to Work” list by Disability:IN and the American Association of People with Disabilities. 11 BNY Mellon Named to 2021 Disability Equality Index, July 14, 2021
BNY MELLON ENTERPRISE ESG 25 CULTURE AND PURPOSE SPOTLIGHT Autism@Work Our efforts to seek out and include individuals with diverse abilities includes our Autism@Work pilot program, through which we recruited diverse talent on the autism spectrum to take part in an apprenticeship and ultimately work full-time at BNY Mellon. Five of eight apprentices in 2021 accepted full-time positions with our Global Operations and Technology team. We believe that this neurodiversity initiative accelerates innovation, adds significant business value and helps us harness the power of difference. In addition to Autism@Work, BNY Mellon’s Enterprise Quality Engineering team engages contract workers who are neurodiverse. Company plans for 2022 include expanding our neurodiversity initiative to more parts of our business and other regions, including Ireland and India. We are also rebranding the program as Neurodiversity Inclusion@BNY Mellon, signaling our intention to engage capable talent with other forms of neurodiversity, such as attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) and dyslexia. Through these initiatives and others, we are fulfilling our pledge as a member of the Valuable 500, a CEO-led movement committed to disability inclusion, including neurodiversity. EMPLOYEE-LED INCLUSION As remote working and social distancing continued for a second year, our employees took advantage of the level playing field of digital, truly global engagement to gain deeper appreciation for the value of connection and inclusion. E/BRG membership continues to grow year over year. With nearly 400 leaders and 11,500 unique members, one in four BNY Mellon employees is a member of an E/BRG. Our six E/BRGs help us achieve enterprise DEI goals through initiatives that provide a supplemental support system, community of belonging and peer network for our people throughout their career journey. For example, E/BRGs lead mentoring and reverse mentoring programs that create exposure to different thinking, which benefits both emerging leaders and experienced, established leaders. In BNY Mellon India, the Inclusion Ambassador program fosters experiential learning for the Inclusion Ambassadors to enable them drive a culture of inclusion and belonging across their respective teams. Enterprise ESG 2025 Diversity, Equity and Inclusion Goal Drive a culture of inclusion and advance diverse representation KPI: Increase percentage of participation in E/BRGs, as evidenced by employee registered membership in at least one group, by 3% year over year, starting from the 2019 baseline year Progress: Membership in BNY Mellon’s six E/BRGs grew from 11,408 to 11,500 in 2021, an increase of 5% ADDITIONAL DIMENSIONS OF REPRESENTATION (BNY MELLON IN THE U.S. AND UK) Data based on employee voluntary disclosures, as of 31 December 2021 People with Disabilities LGBTQ+ Veterans 5 .1% U.S. Workforce 1.5% U.S. Workforce 1.8% U.S. Workforce 0.3% UK Workforce 2.0% UK Workforce 0.0% UK Workforce
BNY MELLON ENTERPRISE ESG 26 CULTURE AND PURPOSE Driving DEI Change in Our Industry BNY Mellon serves as a powerful catalyst for change when we join with other organizations in making public diversity goals and working toward them collectively. Our support for the following initiatives underpins our long- term commitment to help drive DEI progress across our industry and society more broadly. We are a signatory to: • Association of Business Service Leaders’ #WorkingTogether Pledge, Poland • Chartre De La Diversite, Luxembourg • Gender Equality Charter, Belgium • HM Treasury Women in Finance Charter • Social Mobility Pledge • United Nations Standards of Conduct for Business Tackling Discrimination against Lesbian, Gay, Bi, Trans, and Intersex People • Valuable 500 • Women in Finance Charter, Ireland Enterprise ESG 2025 Diversity, Equity and Inclusion Goal Goal: Drive a culture of inclusion and advance diverse representation KPI: Consistently rank among the top employers for leadership in the field of diversity, equity and inclusion Progress: 2022 Bloomberg Gender- Equality Index 2021 Disability Equality Index, 100% score Human Rights Campaign Foundation 2021 Corporate Equality Index, 100% Score Ranked #15 of the Fortune 500 companies on diversity and inclusion A listing of additional DEI awards and recognition is available on our website. LEADERSHIP AND DEVELOPMENT Offering robust and varied experiences for continuous learning and development provides a competitive advantage for organizations seeking to attract and retain the best talent. With the talent shortage and focus on the candidate-centric market, organizations will be required to devote more attention to internal mobility, reskilling and upskilling existing employees. They will need to keep sustainability at their core to attract, develop and retain the right talent to help drive ESG strategy and outcomes. Dynamic learning journeys give existing employees avenues for building skills and capabilities, preparing them to meet the changing needs of our organization and preparing them for the future of work. Our Opportunity and Approach BNY Mellon continuously reviews learning and development trends and collaborates with industry- leading vendors to ensure that our offerings are highly competitive and aligned to employee interests and expectations for professional growth. In particular, the concepts of employee scarcity and sustainability 12 have shaped our 2021 workforce strategy and continue to inform our learning and development strategy. Our organization supports employees’ development as individual contributors and leaders. We strive to create a lifelong learning culture that provides opportunities for them to acquire new skills and competencies at every stage of their BNY Mellon journey. 12 Future of Work Trends in 2022: The new era of humanity , Korn/Ferry
BNY MELLON ENTERPRISE ESG 27 CULTURE AND PURPOSE 2021 ACHIEVEMENTS Return to Office: Prepared managers for workplace transition through information sessions and a toolkit on adapting and adjusting to employees’ return to office. Purpose-Driven Growth: Equipped leaders and managers at all levels to advance our vision for the future by embedding our new values into the BNY Mellon culture. Developing Digitally: Introduced multiple new learning and development experiences to develop employees’ technical and digital knowledge and skills. Connecting Virtually and Learning Digitally Now in its second year, our Leadership and Professional Development Academy online learning platform enables our global workforce to connect virtually and learn digitally. The platform’s social functionalities, learning cohorts and points system also support a collaborative and engaging learning environment. The 24/7 Resource Library, composed of videos and brief articles, facilitates immediate learning on a topic. As employees continue to navigate the ongoing public health crisis, our Remote Work Bootcamp and Leading in the New Normal courses, as well as our Virtual Leadership journey, help them improve their work on virtual platforms. Managers’ and leaders’ success starts with their transition to a new role. Our first-line managers and directors participate in comprehensive leadership development programming that sets them up for success. Enterprise ESG 2025 Leadership and Development Drive a culture of high productivity, engagement and commitment to continuous learning and development to support successful leaders and managers and their teams KPI: Increase the number of discrete employees participating in/utilizing nonmandatory learning programs, on a year-over-year basis Progress Year 2020 2021 YoY change Total elective learning hours (excludes mandatory courses) 390,801 4 0 9 ,14 5 5% Average hours per year 9 8 -11% Distinct count of courses completed 7, 3 0 2 8,657 19% % of year-end active employee population that completed nonmandatory training 91% 98% 8% KPI: Improve manager effectiveness score by 5% year over year, as measured through Manager Upward Feedback process Progress: Due to systems updates, there was no Upward Feedback process conducted in 2021
BNY MELLON ENTERPRISE ESG 28 CULTURE AND PURPOSE EXPANDING OPPORTUNITIES FOR GROWTH BNY Mellon provides a wealth of development opportunities to help people advance their careers and progress within our organization. We believe the strength of our offerings contributes to the fact that 33% of open positions were filled by internal candidates in 2021. However, in recognition of the need to stay current with changing workplace dynamics and worker expectations, we made several additions and changes during 2021. BNY Mellon encourages employees to continue their education by reimbursing certain expenses related to educational courses through a tuition assistance program. In addition to tuition reimbursement discounts and school savings, the program also includes access to education coaches who can provide expert academic and college financing advice and help with choosing the best path for furthering education. At the enterprise level, our new DEI Academy is developing leadership acumen and building critical skills to drive purpose-driven growth and a values- based culture. More than 99% of employees completed the foundational unconscious bias course, and we have added modules on Inclusive Leadership, Inclusive Hiring and Inclusive Performance Management. Our increasingly inclusive culture arises not only from formal training but also the efforts of our leaders as they seek to model behaviors that create a sense of belonging and psychological safety. We introduced training to equip managers and senior leaders with the skills to create an effective work environment that aligns with current workforce needs and the direction of our future of work. In response to our employees returning to the office, we proactively prepared our managers to meet the needs of their employees. We provided a comprehensive toolkit, including frameworks for team working arrangements and exceptions, and a discussion guide, talking points and FAQs to guide the dialogue. We provided training on our Purpose-Driven Growth Agenda, which connects the company’s purpose and vision to build a culture that is both high performing and human centered. Targeted training was delivered to all senior leaders to equip them to hold culture activation sessions that engage teams to discuss how the new values can be applied and integrated into daily performance. SPOTLIGHT ESG-Aware Employees We introduced an ESG Certification program to help all employees build and advance their knowledge of the management and integration of ESG factors into business operations and the investment process. In addition to an introductory video, the three ESG-focused modules cover ESG fundamentals, client solutions and the regulatory landscape. This new offering supports our ESG objectives by enhancing our ability to deliver a powerful and differentiated client experience. ADOPTING A DIGITAL FOCUS To evolve our training delivery, we accelerated our approach to blended learning through the expansion and availability of online learning. For example, we introduced a technology workforce development platform to offer easy access to technical and digital training to a wider audience. We increased our investment in developing employees’ technical and digital capabilities by introducing multiple new learning and development opportunities, including the following: Technology Role-Based Learning Pathways. We provide 56 role-targeted learning pathways to help employees advance skills in their current role or begin to cross-train for future roles. Global Payments, Treasury, Issuer Services and Markets Learning Hub. This new online portal provides directed learning recommendations based on identified skill development for select individual contributors, people managers and directors in our Operations business. The hub provides exciting and innovative learning content, sourced from external vendors, where employees can aim to develop the skills and behaviors required for their current and future roles. Tour de Learning. This innovative seven-week gamified learning event delivers technology and digital learning to our Global Operations and Technology organization.
BNY MELLON ENTERPRISE ESG 29 CULTURE AND PURPOSE EMERGING TALENT PROGRAMS Attracting outstanding individuals from all backgrounds to our organization is vital to achieving our corporate value “passion for excellence” and remaining a global leader in financial services. We invest in our coordinated suite of programs for individuals at key transition points in their career progression. These opportunities, which are structured to attract qualified individuals to our organization and advance career growth, range from one-day Sophomore Summits and summer internships to one- and two-year rotational and immersion programs. In tandem, our philanthropic focus on developing the workforce of the future synergistically aligns our commitments to DEI, digital transformation and Community Impact giving and employee volunteering. United States. Our 2021 campus recruiting season utilized a virtual format, including eight Historically Black Colleges and Universities as well as three Hispanic Serving Institutions. We also strengthened outreach to diverse candidates by collaborating with and sponsoring the Society of Hispanic Engineers, National Society of Black Engineers and Grace Hopper (a female engineering conference). EMEA. Our EMEA Business Inclusion Council strives to embed DEI in the way we operate in that region. The council identifies ways to improve access to diverse talent to tap into more diverse talent pools. For example, in the UK we engage with Black Young Professionals, the largest UK network of Black professionals, to promote vacancies and participate in the #10000BlackInterns program. India. A fellowship program in India utilizes a six- month internship program to attract underrepresented individuals, e.g., those with disabilities, returning women, LGBTQ+ and veterans. The internships offer a learning pathway, buddy and mentor, and regular assessments, followed by the opportunity for qualified candidates to convert to full-time roles upon completion. SPOTLIGHT Cultivating Technology Talent BNY Mellon prepares and recruits future technology talent through a growing system of campus recruiting and training. In 2021, Campus Recruiting and Global Operations and Technology launched two bespoke mentor-to-intern-to- full-time-hire pathways to our existing summer internship and 18-month full-time program for new full-time technology hires. These new routes include the Student Technology and Readiness Training Upskill Program (S.T.A.R.T.U.P.), a school- year mentorship program with the City University of New York (CUNY) as well as The Community College of Allegheny County (CCAC), and a summer internship Technology Future Talent program for second-year students in associate and bachelor’s degree programs. Through this continuum of training, we are advancing technology talent in the financial services industry and increasing our access to qualified candidates in a competitive marketplace. PREPARING NEW YORKERS FOR WORK As a cofounder of the 30-member New York Jobs CEO Council, BNY Mellon is addressing employer needs for skilled employees by training and hiring New Yorkers, with a focus on Black, Hispanic/Latinx and Asian communities. In collaboration with CUNY, a BNY Mellon philanthropic partner, the New York City Department of Education and other groups, the council aims to hire 100,000 New Yorkers by 2030, including 25,000 CUNY students. The program offers EverUp Micro-Credentials in eight prioritized job areas to provide participants with a competitive boost at landing jobs and internships at Jobs Council companies. In 2021, the program engaged more than 1,600 students in information sessions, and 820 CUNY students completed EverUp Micro-Credential Skills Training. In addition, five redesigned degree programs were codeveloped by CUNY faculty and over 30 company subject matter experts.
BNY MELLON ENTERPRISE ESG 30 CULTURE AND PURPOSE Performance Management Our performance management process plays a critical role in building a high-performance culture and facilitates the alignment of individual contributions with enterprise strategy. Manager and team member conversations create a rich feedback loop to reinforce performance standards and to fuel ongoing professional development. DEI goals are included in the performance management plans of all employees, placing on them the responsibility to help build inclusive teams and an equitable culture that enable all members to thrive. By elevating inclusion as a leadership competency, we have made inclusive leadership an imperative for anyone responsible for managing, or who aspires to manage, high-performance teams. In 2021 we embedded our corporate values in our annual performance management process as part of our Values and Behaviors initiative. This sets the expectation for not only what we do, but also how we do it and why. Values and Behaviors conversations are now more deeply embedded into performance reviews and development conversations. For example, for the first time, performance ratings include two separate ratings, one for results and one for behaviors. EMPLOYEE ENGAGEMENT, RETENTION AND WELLBEING Employees in job markets globally left their jobs at record rates in 2021, many citing a lack of connection to their organization as a primary reason. Feeling burned out and undervalued, workers reported a desire to restore life balance and the ability to prioritize their physical, mental, emotional and social wellbeing. Successful employers are evolving by listening to understand employees’ perspectives and increasing employee engagement. In addition to encouraging employees to embrace corporate values and purpose, employers are equipping workers with the skills to manage their personal growth and life balance, and boost their resilience and overall wellbeing. 13 Our Opportunity and Approach We continue to build a distinctive people experience to engage BNY Mellon employees. Our offerings cover the full life cycle of our relationship, from first contact through alumni status. Employees want a supportive workplace that meets them in their life moments. We continually evaluate our employee engagement and wellbeing offerings to better realize those expectations. Engaged employees are critical to our success: When employees are at their best, they are more productive, creative, purpose-driven and collaborative members of our workforce. We strive to maintain a listening culture that is open to varying employee needs and respond by addressing employees’ physical, emotional, social and financial wellbeing. 13 The Great Attrition: The power of adaptability , McKinsey Organization Blog, Nov. 22, 2021
BNY MELLON ENTERPRISE ESG 31 CULTURE AND PURPOSE 2021 ACHIEVEMENTS Employee Engagement: Introduced a digitally powered program to equip managers with real- time insights on employee sentiment. Higher Wages: Increased the minimum hourly salary rate for employees based in the U.S. from $16.50 to $18.00. Life Balance: Introduced global Caregiver Leave Policy: 10 days of paid time off to manage planned and unplanned family care circumstances. Enhanced Time Off: Introduced U.S. enhanced paid sick and safe-time of 13 days, inclusive of both physical and mental health needs. Employee Engagement and Retention Employees are BNY Mellon’s most valuable resource. Our people generate the innovations, administer the programs and deliver the services that enable our success day by day and year to year. It follows that their continued engagement as members of a highly inclusive, diverse and collaborative community is essential to our continued business success. We support engagement by: • Connecting the work of our employees to company success in the context of an inclusive culture of recognition and appreciation • Providing platforms for employee opinions and ideas • Catalyzing personal and professional growth • Supporting physical, mental, social and financial wellbeing • Establishing a comprehensive set of competitive benefits and compensation to equitably compensate strong performance and meaningful work Establishing a highly competitive employee value proposition is another critical element of hiring and retaining top talent. We have articulated an employee value proposition to guide our engagement with current and future employees and make a compelling case as to why top employees should choose to build a career with us. Toward that end, in 2021 BNY Mellon engaged in an extensive review of our employer brand and value proposition. We evaluated existing messaging and resourcing, interviewed employees and benchmarked key competitors. Key findings provide insights about how BNY Mellon has a differentiated advantage as an innovative culture, our strong commitment to diversity, and the range and strength of our benefit and wellbeing offerings. We are now focused on implementing strategic recommendations in 2022. Our work in this space is intended to provide focused messaging and positioning of BNY Mellon as an employer of choice that is both realistic and aspirational for attracting future generations of talent while also helping to retain and engage our current employee base. PURPOSE-DRIVEN GROWTH A foundational component of engaging and retaining employees is our Purpose-Driven Growth Agenda, which is centered on the core purpose of “powering individuals and institutions to succeed across the financial world.” Introduced in 2021, this agenda aims to help each employee to connect what they do to broader efforts at the team, line of business and enterprise levels. Our shared purpose is informed by our vision “to define what it means to be the trusted financial institution for the next generation of clients and employees.” It builds on our Values and Behaviors Initiative, which was launched in December 2020. Through this initiative we have been encouraging employees to have the courage to lead from wherever they are, act with integrity always, and renew their passion for excellence . Our power flows from our strength in diversity . These values are activated by behaviors that are defined by role, from senior leaders to managers to frontline employees. Our goal is to help employees center their daily activities on our purpose and vision in practical, observable ways.
BNY MELLON ENTERPRISE ESG 32 CULTURE AND PURPOSE CELEBRATING ACHIEVEMENTS We have also built our Values and Behaviors into our company-wide recognition program, so that employee nominations are now aligned to the defined values and behaviors that we want to reinforce. This program acknowledges performance, celebrates service milestones and tracks wellbeing achievements to reinforce a purpose-driven culture of inclusion and belonging. Employee feedback on the tool has led to 2022 enhancements designed to improve the user experience and increase participation. EMPLOYEE RETENTION Retaining talented and skilled employees reflects the health of an organization and contributes to its success. Through our Values and Behaviors Initiative and Purpose- Driven Growth Agenda, we are helping employees understand their roles in our organization and conveying the important contribution they make to our shared success. To retain valued employees, we developed and implemented a global retention plan tailored to the workforce needs in each region. In addition, we provided extensive support and extended benefits to help support employees as they coped with the impacts of the pandemic. To monitor this important indicator, we track employee retention both globally and regionally. In 2021, our company-wide retention rate was 87%, which represents a 5% decrease from 2020. Employee Retention by Region Asia Pacific 2020 Female 91% 2021 Female 86% 2020 Male 91% 2021 Male 86% Europe, Middle East & Africa (EMEA) 2020 Female 93% 2021 Female 88% 2020 Male 94% 2021 Male 89% India 2020 Female 88% 2021 Female 83% 2020 Male 90% 2021 Male 83% Latin America 2020 Female 88% 2021 Female 89% 2020 Male 89% 2021 Male 79% U.S. & Canada 2020 Female 94% 2021 Female 89% 2020 Male 93% 2021 Male 89% To t a l 2020 Female 92% 2021 Female 87% 2020 Male 92% 2021 Male 87% 70% 8 0% 9 0% 1 00%
BNY MELLON ENTERPRISE ESG 33 CULTURE AND PURPOSE FA IR PAY Ensuring that our employees are compensated competitively and fairly is a priority for BNY Mellon. Supporting our employees’ financial wellbeing is important to retaining global talent and core to our company purpose of powering individuals to succeed across the financial world. We demonstrate our commitment by investing significant resources to achieve this goal, and in 2021, BNY Mellon increased the minimum hourly salary rate for employees based in the U.S. from $16.50 to $18.00 per hour. This is nearly two and a half times the federal minimum of $7.25. Additionally, BNY Mellon will also provide the greater of a 3% salary increase or a salary raise to $20.00 per hour to any U.S. employee earning between $18.00 and $20.00 per hour. In further evidence of our commitment to fair pay, we have received accreditation from the UK Living Wage Foundation (the Foundation) for paying the UK Living Wage , as defined by the Foundation, to all our UK employees and subcontractors and have worked closely with our UK suppliers to confirm they pay the Living Wage as well. We are committed to reviewing this annually to confirm whether the Living Wage remains our minimum payment for all UK employees, including our suppliers, each year. Learn about our performance on Pay Equity . LISTENING TO EMPLOYEE FEEDBACK Staying connected with our employees and understanding their concerns was one of our top priorities as we entered our second year of working remotely. Following an all-employee engagement survey in 2020, Executive Committee members and other employees have been leading workstreams focused on improving connectivity across the enterprise, organizational processes, life balance and career development. In 2021, we formalized a program that continuously gathers and summarizes employee feedback to provide managers with timely information on employee sentiment. In addition to this feedback tool, we gained additional insights through an E/BRG engagement survey of the approximately 1,000 people enrolled in these groups. Taken together, these offerings and communication promote empathetic conversations across BNY Mellon as return-to-office plans evolve, and bring new considerations and opportunities to our organization. Enterprise ESG 2025 Leadership & Development Goal Drive a culture of high productivity, engagement and commitment to continuous learning and development to support successful leaders, managers and their teams KPI: Run a new company-wide employee engagement survey in 2020 to establish baseline engagement scores Perform on target with benchmark engagement scores for financial services industry Progress: • Launched a comprehensive People Experience initiative to address this opportunity • Achieved a 24 Net Promoter Score on engagement, which exceeds the finance industry benchmark of 20 Employee Wellbeing BNY Mellon’s approach to benefits and wellbeing is designed to support the health of a vibrant workforce. Through our three-part Global Wellbeing Strategy, we provide a flexible set of resources for employees to manage and sustain their health goals, grow their personal tools to manage stress, support their families and reach their financial goals. When our people have the support they need in the moments that matter, they can be resilient, bring their best and deliver for our clients. Our wellbeing strategy centers around: Life Balance. Demonstrating a caring approach by acknowledging diverse life circumstances, including strong leave and absence policies and supportive workplace flexibility to facilitate life balance. Wellbeing Platform. Supporting total wellbeing through inclusive programs that allow people to thrive in all aspects of wellbeing, including physical and emotional health, financial wellness and family. Preventative Health. Encouraging early identification of health risks through simple access to relevant screenings, vaccinations and risk reduction tools.
BNY MELLON ENTERPRISE ESG 34 CULTURE AND PURPOSE CARING DURING COVID-19 As the pandemic continued, the wellbeing of our people remained a priority. We evolved our wellbeing strategy by expanding our resources for physical, emotional, social and financial wellbeing, with a particular focus on mental health. BNY Mellon continued to support employees through the personal and emotional impact of the pandemic, with a focus on Meeting you in your life moments . Tools, policy changes, programs, services, and a wide variety of training and learning opportunities regularly provide employees with ways to engage with each other and BNY Mellon on their wellbeing journey. We monitor employee satisfaction levels through a tool that uses the employee Net Promoter Score (eNPS) measurement technique. A result of these and other efforts, survey results for health and wellbeing indicate a three-point increase in eNPS score from February 2021 to February 2022 (34 to 37) measured by organizational support for health and wellbeing in the categories of physical, mental and social wellbeing. Our Global Operations and Technology (GOT) team established a Wellbeing Council to champion the employee experience and wellbeing. The cross- functional group encompasses the GOT Executive Council, Senior Leadership Forum and Human Resources, among others. The council seeks to help employees manage work-life integration, address family and personal needs, prioritize physical and mental health, and balance their workload with the needs of the business. Through the introduction of COVID-19 and mental health-related benefits and programs, we are helping employees achieve life balance by providing tools to conduct self-assessments and manage personal resilience factors. We delivered an It’s OK to Choose You mental health awareness and education campaign to mitigate stress and burnout. Employees and their families increasingly reached out for support from our Employee Assistance Program (EAP), indicating we are indeed making an impact in normalizing conversations around emotional wellbeing. In the U.S., offerings were expanded in 2021 by introducing enhanced paid sick and safe time of 13 days, for both physical and mental health needs. Internationally, we continue to align sick leave entitlements to market norms, with medical leave provisions available in many countries. We continue to provide access to medical expertise via briefings during town hall meetings and targeted education sessions around vaccinations and variant developments. Across all health matters, our Executive Committee participates in regular briefings from senior medical advisors, enabling decision-making around the firm’s responses to be data driven and grounded in science. Enterprise ESG 2025 Employee Engagement & Wellbeing Goal Support a culture of wellbeing through a holistic program focused on engaging employees and developing key management behaviors to decrease health risk KPI: Increase positive response to employee health survey question “Do you think your workplace supports a culture of health and wellbeing?” by 5% Progress: Enhancing employee sentiment that "the firm supports my health and wellbeing." Three-point increase from February 2021 to February 2022 (34 to 37) as measured by the eNPS score in the categories of physical, mental and social wellbeing KPI: Offer at least two wellbeing programs that meet or exceed market benchmarks; increase enrollment and/or active participation by 10% year over year Progress: Introduced Global caregiver leave that provides 10 days of paid leave when employees need to care for immediate and extended family members Continued our enhanced WOW recognition program, a one-stop-shop for recognizing performance, celebrating service milestones and tracking wellbeing achievements to reinforce a purpose-driven culture of recognition and belonging Continuing to reduce mental health stigma with our confidential support service supporting, on average, three times as many individuals during 2020 and 2021 compared to pre-pandemic levels
BNY MELLON ENTERPRISE ESG 35 CULTURE AND PURPOSE SPOTLIGHT Restoring Daily Lives in India As waves of COVID-19 cases strained India’s healthcare infrastructure in mid-2021, we instituted measures targeted at the personal and professional wellbeing of our employees in that country. These steps included supplemental COVID-19 care, on-site COVID-19 vaccination events, meals to the ill, 24/7 nurse support, equipment availability, support for families of employees who passed away, healthcare, assistance for childcare, and other health- and wellbeing-related resources. These market- specific benefits augmented the enterprise-wide COVID-19 relief measures described above. WORKPLACE HEALTH AND SAFETY In keeping with our commitment to social responsibility, BNY Mellon is invested in protecting the health and safety of our employees globally and asking that our suppliers commit to doing the same for their employees. Through our Code of Conduct, internal policies and initiatives, we strive to promote employee health, safety and wellbeing. See details in our Health and Safety Statement . OUR COMMUNITY IMPACT Ongoing humanitarian challenges have sharpened the urgency of addressing inequality. The dual health and economic challenges of the past two years have prompted not only a reevaluation of work and life, but also an understanding of how disparately those who are underserved are affected. Recovery from the pandemic and rebuilding in an equitable way will require effort from all sectors of society. With their financial and human capital, businesses can take the lead in rebuilding a future in which all can reach their full potential and participate in healthy, vibrant communities. Our Opportunity and Approach Our long-term success is linked to the strength of the global economy and the resiliency of our industry. To meet the needs of the moment and deliver on our core values, we actively support the communities where we live and work. By bringing the firm’s full resources to bear, we empower philanthropic organizations around the world to build their capacity and meet the emerging needs of the individuals they serve. To achieve the greatest impact, BNY Mellon 14 leverages our philanthropic funding along with the skills and expertise of our people and our leading role in the global financial services ecosystem. We address many issues important to our employees and our business — from the environment to human rights — with a strategic focus on developing a diverse workforce equipped to meet the demands of a technologically driven society. We also recognize that underserved communities have been disproportionately affected by the ongoing effects of COVID-19, and our response reflects our commitment to prioritize equitable health and financial relief and recovery. 14 BNY Mellon is the corporate brand name of The Bank of New York Mellon Corporation and may be used to reference the corporation as a whole and/or its various subsidiaries generally.
BNY MELLON ENTERPRISE ESG 36 CULTURE AND PURPOSE 2021 ACHIEVEMENTS Building the Future Workforce: Funded 75% of our $20 million pledge to academic and job training organizations for multiyear educational and workforce development programming. Empowering Nonprofits: Provided nearly 3,300 hours of pro bono technical assistance and strategic advising valued at more than $600,000.* Advancing Racial and Social Justice: Directed approximately $1.4 million in grants championing justice, advocacy, reform, human rights and equal protection under the law. Aiding Afghans: Facilitated relief to Afghan citizens and refugees through $250,000 in humanitarian aid , supported by employee giving and legal pro bono services. Supporting Recovery: Facilitated an additional $1.4 million in support to COVID-19 resiliency efforts, bringing total pandemic relief support to over $7.8 million since the start of the outbreak. Global Giving: Raised $1.4 million from more than 750 employees in 12 countries through a weeklong global employee Giving Tuesday campaign. * Valuation Guide: Giving in Numbers Survey , CECP. Strategy and Scope Our Global Impact Citizenship (GIC) office carries out the company’s strategy and drives social impact in three complementary areas: Corporate Giving, which provides grants and sponsorships; Community Impact, our year- round employee giving and volunteer platform; and Enterprise ESG, which leverages our reach and market influence to address pressing global issues. We believe that individuals from all backgrounds and communities can contribute and deserve to thrive in the digital economy. We work with nonprofits, academic institutions, and other organizations to help develop a future workforce that is equitable, diverse and innovative. Our strategic philanthropic investments are focused on meeting the needs of individuals from high school age to early career who are from groups that have traditionally been underrepresented in the business and technology fields. Our workforce of the future focus aligns with many of the UN Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs), most directly supporting SDG Goal 4: Quality Education (Ensure inclusive and equitable quality education and promote lifelong learning opportunities for all); and Goal 8: Decent Work and Economic Growth (Promote sustained, inclusive and sustainable economic growth, full and productive employment and decent work for all). Our entire approach recognizes the importance of collaboration and the unique role each sector has to play in achieving social impact, in line with Goal 17: Partnership for the Goals. Developing the Workforce of the Future Creating career pathways in business, technology and STEM LINK LEARN LIFT
BNY MELLON ENTERPRISE ESG 37 CULTURE AND PURPOSE In 2021, surpassing our KPI for strategic alignment of our corporate giving, we devoted a majority of our corporate grant funding to realize our strategy of building the workforce of the future in three primary areas. Link connects individuals from diverse backgrounds with innovative job training and skills, Learn provides equitable educational access through scholarships and paid internships, and Lift addresses racial and economic disparities and empowers communities to realize their potential in the future workforce and economy. Now in the third year of our $20 million commitment to fund the future workforce, we can report on the early impact of this bold initiative, which aims to create career pathways in business, technology and STEM. LINK In order to link diverse talent with innovative pathways to enduring careers, we direct funding to programs around the world that promote flexible educational opportunities that individuals can adapt to their availability, learning styles and professional needs. Examples of investments in this area include: • Pursuit, an intensive technology training program for high-need, high-potential individuals with no formal training in technology that has propelled diverse graduates into well-paying tech jobs • No-cost comprehensive technical training at Per Scholas — where 87% of participants are people of color — helping to close the tech skills divide • Jewish Vocational Service Bridges to College & Careers Business/Technology pathway, which helps students from diverse communities gain the necessary skills to find employment and build careers, while partnering with employers to hire, develop and retain a productive workforce • A grant to The Advance Leadership Institute to strengthen the institute’s programming and operations, including its Executive Leadership Academy, which cultivates Black leadership and fosters inclusion for companies, institutions and communities • Gen-E 2021, Europe’s largest festival for youth entrepreneurship, where 370,000 young entrepreneurs competed to become Company and Start Up of the Year We also seek to advance the field through thought leadership and capacity building. To that end, research facilitated by BNY Mellon through the Sutton Trust identified key barriers to a more diverse tech workforce and helped to refine its pathways to professions. And BNY Mellon funding and professional guidance created a faculty development program to enrich technology education for faculty members from engineering schools and polytechnics across India. LEARN In order to provide equitable access for individuals seeking to enter business, technology and STEM, we invest in the educational success of underserved populations. Our multiyear commitment to STEM- based programming that directly benefits students at the City University of New York (CUNY) and the Community College of Allegheny County (CCAC) is a cornerstone of the firm’s commitment to developing and investing in tomorrow’s talent. With BNY Mellon’s financial support, CUNY launched the NYC Future of Work Initiative providing education and training for high- demand jobs and expanded the BNY Mellon Transfer Scholarship program, which since its fall 2019 inception has supported associate degree earners who have transferred into a CUNY senior college to pursue their bachelor’s degrees. In addition, the firm’s investments have enabled CCAC’s BNY Mellon Early College in High School program to expand to include all schools and school districts in Allegheny County to provide even broader access to quality education. Students are able to earn a high school diploma as well as specialized certification(s) or an associate degree in a specified discipline. The program offers career pathways in business, accounting, information technology and digital support to underrepresented students in partnership with local school districts. In addition to the virtual campus, all students can access any of CCAC’s four campuses and four neighborhood centers to use the resources at those locations. Learn more in Cultivating Technology Talent .
BNY MELLON ENTERPRISE ESG 38 CULTURE AND PURPOSE Additional BNY Mellon scholarships supported: • Three of the most prominent Historically Black Colleges and Universities (HBCUs): Howard University, Morehouse College and Spelman College • The Hispanic Scholarship Fund for scholarships and wraparound support, such as mentoring, leadership development and career services • The Posse Boston STEM program, which annually identifies, selects, trains and supports a cohort, or posse, of young women pursuing an undergraduate education in the STEM fields LIFT To help them succeed on their journeys and thrive in their careers, individuals should live in safe, secure and thriving communities that support their development. Through investments that address racial and economic disparities, strengthen culture and arts, and promote economic development, we help to create conditions in which individuals can realize their potential in the future workforce and economy. Learn more about how we aim to protect human rights . We also help build stronger communities through financing affordable housing in low-income neighborhoods through our Community Reinvestment Act investments . Enterprise ESG 2025 Community Impact Goal Leverage the company’s resources and employee talent to help significantly increase impact of community support in the regions and countries in which BNY Mellon operates. KPI: Direct 65% of corporate grants and sponsorship giving donations to organizations and causes that are aligned with our strategic focus of developing the workforce of the future Progress: Aligned 74% of Global Impact Citizenship’s corporate grant and sponsorship giving with our strategic focus of developing the workforce of the future 2021 Community Support: $34.5 million* Employee Giving $3.0 million Company Matching Donations $5.3 million Foundation Giving $8.1 million Corporate Grants and Scholarships $17.4 million Value of pro bono volunteering ** $600,000 *** * All figures are rounded to the nearest 100,000. ** Valuation Guide: Giving in Numbers Survey, CECP. *** Data includes Signature and legal pro bono programs. SPOTLIGHT: Fierce Advocates for Justice BNY Mellon received a Community Leadership Award from John Jay College of Criminal Justice, a leader in educating for justice, for our work on building the workforce of the future. Through funding curricula and the STEM Acceleration Program, we provide support to exceptional individuals from underrepresented communities and broaden access to vital career fields.
BNY MELLON ENTERPRISE ESG 39 CULTURE AND PURPOSE COVID-19 RESILIENCY In light of the ongoing societal needs related to the pandemic and resulting economic hardships, Global Impact Citizenship facilitated funding for COVID-19 resiliency to key regional and international agencies. We targeted funding to nongovernmental relief organizations in areas where our employees live and work as well as to grant support to hospitals and organizations focusing on healthcare infrastructure, including: • A vaccine education initiative to strengthen and accelerate the business community’s response to COVID-19 with the Ad Council, leading businesses, and communications and public health organizations • Research at the New York Blood Center with the eventual goal of developing potential therapeutic targets as well as biomarkers for COVID-19 reinfection risk evaluation in people of color • The Hispanic Federation’s COVID-19 VIDA (Vaccination Immunization Dosage Awareness) Initiative to help Latino-led community health centers across the U.S. get Latinos vaccinated against the coronavirus Employee Giving and Volunteering We encourage our employees to volunteer and give back to the communities where they live and work and to support the causes and organizations about which they are passionate. BNY Mellon’s year-round Community Impact program offers our employees several ways to engage in purpose-driven volunteerism and increase the impact of their time and financial contributions. In 2021, BNY Mellon provided company matching donations up to $5,000 to approved charities for employee donations and matching donations of $25 per hour for volunteer time spent in support of approved charities. In addition, eligible employees may take up to three days of paid volunteer time per year with the company. While in-person and face-to-face volunteering was paused during the pandemic to protect the health and safety of our employees and our philanthropic partners, we facilitated employee involvement through a streamlined Community Impact Online platform. New functionality made it even easier for our employees to request a company match and find ways to volunteer virtually. To inspire employee participation in Giving Tuesday, the global giving movement for generosity, BNY Mellon launched a global, weeklong Giving Tuesday campaign. More than 750 employees in 12 countries participated, raising a total of $1.4 million for educational and charitable organizations, the company’s largest Giving Tuesday effort to date. PRO BONO ADVISING Delivering critical technical assistance and strategic advising services since 2017, the company’s corporate pro bono practice has a twofold benefit. First, philanthropic partners are able to leverage our employees’ expertise in areas such as technology, human resources and communications to increase their capacity and expand their reach. In addition, employees have the opportunity to apply their skills in a new context and develop as a result. Through the Signature Pro Bono program and the legal services work facilitated by our Legal Department, BNY Mellon capitalizes on our greatest resource — our people — for good. Following the COVID-19 pandemic and movement for racial justice and equality, our employees mobilized to
BNY MELLON ENTERPRISE ESG 40 CULTURE AND PURPOSE equip organizations through our Pro Bono Accelerator, the Signature Pro Bono program’s one-day consulting marathon. • Diversity, Equity & Inclusion professionals helped the youth mentorship organization SEEDS-Access Changes Everything to create an Anti-Racist Hiring Policy • Employees from the Enterprise Resiliency Office advised Getting Out and Staying Out, a nonprofit which fights recidivism, on developing a business continuity plan • A team of the company’s real estate experts drafted floor plans for The Food Project, helping the non- profit to envision its new community food center Our Cross-Sector Fellowship, the Signature Pro Bono Program’s multi-week consulting engagement, boasted its largest-ever global cohort in 2021. Cross-functional teams collaborated with nonprofit leaders to develop new products and processes that will have a sustainable impact on organizations’ reach and efficiency. As part of one Fellowship project, a team from Digital and Global Operations & Technology advised Lincoln Center for the Performing Arts on an enterprise technology transformation, which resulted in the organization hiring its first chief technology officer. Separately, in India, employees have devoted additional pro bono hours to developing mobile applications for the visually impaired and building a website for Cancer Institute (WIA), among other technology projects. In addition BNY Mellon employees donated their time and legal skills to address inequities and advance human rights . SKILLED VOLUNTEERING In addition to pro bono advising, BNY Mellon employees engaged in skills-based volunteering during 2021. Of the 45,000 hours of employee volunteering, 89% were skills- based, representing the highest percentage of skills- based volunteer hours contributed in one year since we began tracking this metric as a KPI in 2020. Using their general professional experience to mentor, coach and educate others, our people are helping to open possibilities for some of society’s most underserved populations. For example: • Employees helped immigrants prepare for their U.S. citizenship interview through Literacy Pittsburgh • Technology professionals served as hackathon coaches for young entrepreneurs from Title I high schools in New York City as part of Futures in Tech. Enterprise ESG 2025 Community Impact Goal Leverage the company’s resources and employee talent to help significantly increase impact of community support in the regions and countries in which BNY Mellon operates KPI: Facilitate 130,000+ hours of employee volunteerism annually Progress: Achieved over 45,000 hours of employee volunteerism, 35% of our goal, despite suspension of in-person volunteering for 2021 KPI: Increase total hours of Signature Pro Bono consulting delivered to nonprofits by 10% over the 2019 baseline year Progress: Increased total Signature Pro Bono consulting hours by 11% over 2019 baseline KPI: Achieve a skills- based volunteering target of 40% of total employee volunteer hours, ensuring that a significant portion of volunteer efforts leverage employees’ professional experience Progress: Achieved skills- based volunteering level of 89% of total volunteer hours
RESPONSIBLE BUSINESS For over 235 years, businesses, communities and global economies have relied on BNY Mellon as a trustworthy, dependable steward of financial operations around the world. We know our clients, we embody our goal to act responsibly, and we deliver Future First SM solutions designed to bene fit clients and to make a positive impact on people and the planet. Despite the fluctuation in the global markets since the onset of the pandemic, in 2021 we continued to support our clients, powered by responsible governance, effective risk management and technological innovation. As a resilient global financial services provider, we provide the continuity of operations our clients expect. Additionally, we offer a growing array of ESG and Responsible Investment products and services designed to help clients who seek to impact climate change, social inequity and other similar challenges. By conducting our business responsibly and offering ESG and Responsibl e Investment products and services, we contribute to the foll owing SDGs:
BNY MELLON ENTERPRISE ESG 42 RESPONSIBLE BUSINESS RISK MANAGEMENT Social, political, environmental and financial turbulence has continued to impact economies and communities. The global pandemic entered year two, climate change concerns escalated, and Russian aggression in Ukraine has heightened geopolitical instability and resulted in economic sanctions. In the face of these and other market disruptions, investors, regulators and the public alike scrutinize business operations, assessing companies’ ability to navigate pressing global challenges. Markets expect effective corporate governance, strong risk management, business continuity, and ethical and transparent workplace standards that enable organizations to thrive over the long term. Our Opportunity and Approach BNY Mellon plays a vital role in the global financial markets, and effective risk management is core to our success. Our customers and the financial markets depend on BNY Mellon for our financial strength. Around the world, we are recognized for our solid balance sheet, healthy risk culture, and commitment to financial stability in all market environments. We seek to manage risk responsibly and serve as a reliable custody and investment source. We maintain a comprehensive and strong risk management framework that is designed to make intelligent risk-based decisions by appropriately identifying, measuring and mitigating all material risks to support responsible growth. In that context, we are increasingly focused on climate change as a risk driver. BNY Mellon is taking proactive action to support sustainable growth, and we are evolving our Risk Management Framework to further embed the consideration, impact and management of climate- related risks. 2021 ACHIEVEMENTS Risk Management: Continued to implement holistic risk management principles through initiatives that drove a strong risk culture, clear risk ownership and comprehensive risk oversight. Climate Risk: Continued enhancing our global risk frameworks informed by the Task Force on Climate-related Financial Disclosures (TCFD) recommendations. Cultivating Leaders: Graduated our first cohort of 10 diverse, high-potential Risk & Compliance leaders from the Executive Development Program. Risk Training: Provided close to 200 risk and compliance learning courses to approximately 49,600 employees. Risk Management Principles Our holistic risk management principles provide a company-wide approach to effectively and appropriately managing risk. This approach includes: • A strong risk culture across the company • Clear risk ownership by the businesses and corporate functions • Comprehensive oversight by Risk & Compliance This approach enables us to better identify, monitor and manage our risk exposures across the enterprise and provide our Board with the information needed to exercise appropriate oversight. The holistic risk principles are foundational to our ability to achieve our strategic priorities, including scaling and digitizing our operating model, implementing ESG and climate risk considerations into the framework, and realizing growth opportunities. In 2021, we continued to make significant progress toward multiple priority initiatives including: Enterprise Limit Framework. We operationalized by business and legal entity the enterprise limit framework implemented in 2020, driving enterprise-wide consistency and strengthening the linkage between business risk management and corporate risk appetite.
BNY MELLON ENTERPRISE ESG 43 RESPONSIBLE BUSINESS Our risk appetite defines the limits on the level and nature of the risk we are willing to assume to meet our strategic objectives. Policy Governance. We transformed policy governance by implementing a new policy hierarchy. This included significantly reducing the number of policies, clarifying policy content and responsibilities, and launching a new policy platform for employees while retaining comprehensive coverage of requisite subject matter. Product Governance. We implemented a single, transparent approval pathway for new or modified products and services, accelerating time to market and supporting business growth. Enterprise ESG 2025 Risk Framework Goal Goal : Continue to evolve and fortify our risk infrastructure's integration into BAU practices across the organization* KPI: Promote consistent and aligned utilization of the risk lifecycle (identification, measurement, mitigation, monitoring) across the company as a key factor in risk/reward decisions for product, client and geography prioritization Progress: Global risk frameworks have been enhanced to require specific consideration of climate as a driver of risk, including assessment and management of potential impacts. • Enhanced risk appetite statement with climate change highlighted within broader ESG risk consideration • Identified core vulnerabilities and corporate climate risk profile • Tailored relevant risk policies and governance structures to support risk identification and management • Established specific climate risk requirements for primary risk categories and key risk assessment processes, and initiated stress testing and scenario analysis workstreams • Defined KRIs to measure climate risk impacts and to support monitoring relative to risk appetite • Completed foundational training and initial awareness building to key global teams and select boards Enterprise ESG 2025 Risk Culture Goal Goal: Sustain strong global risk and compliance culture focused on risk awareness, ownership and ethical behavior* KPI: Drive active employee engagement and ownership of risk and compliance requirements through ongoing strategic communication and development Progress: • Provided close to 200 risk and compliance learning courses to approximately 49,600 employees** • Promoted employee understanding and management of risk by regularly publishing leader blogs and news articles on important risk concepts, policies and practices, and sending a regular risk and compliance-focused newsletter to all employees * L anguage in the goal was refined to provide clarity * N umber is cumulative total of unique employees who received training throughout 2021. TYPES OF RISK Our primary risk categories include: Operational Risk (including Compliance & Financial Crimes and Technology & Resiliency Risk), Market Risk, Credit Risk, Liquidity Risk, Strategic Risk and Model Risk. BNY Mellon operates under one enterprise-wide framework for managing risk. Through our Enterprise Risk Management Framework and Policy, we have established common risk management practices that can be understood and consistently applied across the company. ESG issues and, in particular, climate change risk are considered drivers of risk. BNY Mellon recognizes the importance of maintaining a deep understanding of all risk drivers and vulnerabilities that may exist. Risk drivers may include the macroeconomic environment, changes to competitor and/or customer behavior, regulatory or legislative change, climate risks, and a range of other potential sources of risk that may have significant impacts on the global economy and the finance sector over the short, medium and long term. These drivers constitute a risk to BNY Mellon’s balance sheet, business model and future profitability. In summary, a risk driver is an overarching driver of risk that may impact any, and all, risk categories to which BNY Mellon is exposed through the ongoing execution of our business strategy.
BNY MELLON ENTERPRISE ESG 4 4 RESPONSIBLE BUSINESS RISK GOVERNANCE BNY Mellon maintains a risk governance structure designed to result in comprehensive risk oversight. The Board of Directors oversees risk management through two key Board committees: the Risk Committee and the Audit Committee. Additionally, the Corporate Governance, Nominating and Social Responsibility Committee (CGNSR) has Board-level oversight of ESG issues, including climate-related risks and opportunities, among other topics. CULTIVATING DIVERSE RISK TALENT We seek to advance diverse talent at all levels of the Risk & Compliance organization through innovative development programs, such as mentoring, cross- training and our Executive Development Program (EDP). Through the EDP specifically, rising high-potential Risk & Compliance leaders receive experiential learning, leadership education and exposure to the BNY Mellon Executive Committee and Board of Directors. In 2021, Risk & Compliance instituted a Diversity, Equity and Inclusion strategy to address the specialized needs of the function. Senior leaders sponsor each of the three strategy workstreams: Talent Attraction and Acquisition to implement inclusive hiring practices and expand recruiting channels; Talent Management and Development to ensure inclusivity across performance management, talent pipelines and succession planning; and Inclusive Culture to overcome barriers to belonging. FINANCIAL RESILIENCY BNY Mellon has a responsibility to demonstrate sound leadership in terms of capital strength, liquidity risk management, and payment, clearing and settlement activities. We are committed to maintaining a strong capital base to meet regulatory requirements, remaining a strong and trusted counterparty to our clients, and withstanding potentially adverse events. Our global resolution plan details how we would maintain critical operations in case of our failure or insolvency. Our 2021 stress test results demonstrated our financial strength and commitment to maintain robust levels of loss-absorbing capital. Compliance and Ethical Behavior BNY Mellon’s Code of Conduct applies to all employees. At the foundation of our Code are our Values: Passion for Excellence, Integrity, Strength in Diversity and Courage to Lead. This Code guides our behaviors in all business activities and helps shape our overall conduct and risk culture. The Code is a unifying document that sets forth the key principles that create a common set of expectations for all employees with regard to: respecting others, avoiding conflicts of interest, conducting business, working with governments, protecting company assets and supporting our communities. Our ongoing measures to reinforce these provisions and standards include annual employee training covering topics such as anti-corruption, protecting assets, business continuity, anti-money laundering and information risk. In 2021, we enhanced our ability to track certain violations of our Code related to employee behavior, such as adhering to our gifts and entertainment requirements, declaring outside activities for evaluation of conflicts of interest, and complying with the Firm’s Personal Securities Trading Policy. We use this to assist managers in addressing violations of company policies and apply disciplinary decisions based upon the company’s Human Resources procedures, as appropriate. These improvements strengthen the company’s oversight of employee compliance violations and consequences, the ability of management to identify violation trends that may need to be addressed, and our efforts to foster a strong risk culture. For all employees, training on topics such as ethics, safety and security in the workplace, unconscious bias, workplace bullying, and harassment are important to maintain an ethical and inclusive culture and are therefore mandatory to meet certain company and regulatory requirements. These trainings, in addition to ongoing risk management communications, help drive employee ownership of risk and compliance outcomes. ESCALATION AND SPEAKING UP We take any breach of rules, laws, regulations, policies or standards of business ethics very seriously. Our corporate culture of “Doing What’s Right” empowers all employees with the necessary knowledge and resources to identify, notify and report issues in a timely manner. We provide several ways to ask questions or make a
BNY MELLON ENTERPRISE ESG 45 RESPONSIBLE BUSINESS report, including an Ethics Helpline, operated by the BNY Mellon Ethics Office, and an Ethics Hotline, operated by an independent administrator. Anyone who reports a concern or reports misconduct in good faith, and with the reasonable belief that the information is true, is demonstrating a commitment to our values and following our Code. The company has zero tolerance for acts of retaliation. FINANCIAL CRIMES COMPLIANCE Money laundering and other financial crimes undermine confidence in the financial system and create other significant negative societal impacts. At BNY Mellon, we combat financial crime and work to prevent criminals from financing illegal activities through our network. Within our organization, we have a zero-tolerance policy on bribery and corruption. Our Codes of Conduct for employees and the Board detail our expectations regarding anti-corruption compliance. We monitor potential conflicts through our anti-corruption compliance program, which covers business dealings and relationships in countries where BNY Mellon and our subsidiaries and associates operate. The program is designed to comply with both U.S. and non-U.S. laws and regulations, including the U.S. Foreign Corrupt Practices Act and the UK Bribery Act. It covers business activities and regulatory requirements, including gifts and entertainment, charitable contributions, hiring practices and third-party intermediary due diligence. Enterprise Resiliency Enterprise resiliency, which is defined as the firm’s ability to prevent, respond to, recover and learn from operational disruptions, is a critical component of our overall business strategy. Our Enterprise Resiliency Office aligns, centralizes and integrates our resiliency disciplines and capabilities to deliver a coordinated approach toIncident and Crisis Management, Business Continuity and Disaster Recovery. As a global institution, BNY Mellon is exposed to unforeseeable and uncontrollable events that could cause varying degrees of disruption to normal business processes. Our Enterprise Resiliency Office maintains a Business Continuity Program (BCP) focused on designing and building response capabilities to navigate business disruptions. The BCP is implemented through an “all- hazards” planning approach with objectives including minimizing the impact of disruptions and facilitating service continuity within recovery time objectives and based on prioritization of business objectives and operations, regardless of the cause of the disruption. Learn more in Managing Climate Change . CONTINUITY DURING COVID-19 While the vast majority of our employees were operating in a fully remote work environment in 2021, we continued to deliver products and service clients effectively. Our approach to incident and crisis management, coupled with our technology capabilities, enabled the continuity of operations while remaining mindful of regulatory and compliance requirements and creating an environment that allowed us to attract, retain and cultivate talent. Our return-to-the-office strategy brought most of our employees back into the office in early March 2022 under a hybrid model where the majority of our employees will have a mix of remote and in-person work experiences. THIRD-PARTY GOVERNANCE The recent disruptions caused by the global pandemic, as well as natural disasters and other systemic shocks, emphasize the importance of a robust and resilient ecosystem of external vendors and BNY Mellon internal service provider entities. To help facilitate business continuity, BNY Mellon management consistently monitors and manages the ecosystem of third parties that deliver key products and services or perform activities on behalf of our businesses. BNY Mellon has an established Third-Party Governance program designed to: • Provide oversight and controls commensurate with the level of risk and complexity of third-party engagements, with heightened focus on critical activities • Incorporate the risk of material fourth-party exposure • Meet evolving legal and regulatory requirements as well as stakeholder expectations on ESG issues At the same time, we share with suppliers our expectations on the management of ESG issues, which now go beyond sustainability and transparency. We seek
BNY MELLON ENTERPRISE ESG 46 RESPONSIBLE BUSINESS to cultivate relationships with businesses that share our values, such as advancing diversity, respecting the environment and reducing carbon emissions. This is explained further in Supplier Responsibility . Cybersecurity As we accelerate our digital transformation and cyber threats become more sophisticated, maintaining the highest levels of cybersecurity is paramount to both protect our business and drive value to our clients. Our Cybersecurity Program. BNY Mellon’s Cybersecurity program is operated under the direction of the Chief Information Security Office (CISO). It is under continuous audit by internal auditors and subject to ongoing, formal challenge by the Technology Risk Management Team within the second line of defense. Senior oversight for the program is provided by executive-level committees composed of leadership from all three lines of defense, including the management-level Technology Risk Committee, Technology Oversight Committee, and Senior Risk and Controls Committee, and the Risk, Audit and Technology Subcommittees of the Board. Additionally, the CISO provides an annual update on the cybersecurity program to the full Board. External auditors also review our program, providing feedback on areas for further development. Our cybersecurity program is grounded in our Cybersecurity Services Model, which is composed of layered controls that align with internationally recognized standards, such as ISO 27001/2. The Bank of New York Mellon Corporation’s Information Security Management System is ISO/IEC 27001:2013 certified. Our certification was approved and recommended by the British Standards Institution (BSI) Group, the world’s largest management systems standards certification body. We monitor changing regulatory requirements, guidelines and technologies in all countries in which we operate, and our global program reflects industry and business best practices, including the National Institute of Standards and Technology Cybersecurity Framework. Learn more about our Information Security and Protection . An important component of our cybersecurity strategy is the protection of data across our operations and communications. We invest in advanced technology to protect data, including encryption techniques such as Transport Layer Security to protect communications between clients and internal systems. All of our techniques are based on industry best practices and standards, which are incorporated into internal policies. Threat Intelligence. Our Threat Intelligence team prepares for evolving security threats using information from diverse sources, including our peers and the broader financial services industry, as well as law enforcement, government, and a variety of public and private sources. We regularly evaluate our enterprise for vulnerabilities and risks, and watch for advanced adversaries, to increase situational and contextual awareness. 24/7/365. Our Security Monitoring global staff work shifts to provide coverage 24 hours a day, enabling the company to effectively manage business risks through the timely detection and escalation of data or technology incidents involving the violation of confidentiality, integrity or availability. SOC analysts perform “eyes on glass monitoring” of the Security Information & Event Management (SIEM) system. They triage suspicious technology activities identified by automated alerting and escalate to various incident-handling teams when activities are deemed a potential cyber threat. Employee Education . Employees in our technology departments and throughout the firm play a vital role in maintaining information systems security by identifying and mitigating risks. All employees complete information risk training upon hiring and annually, and participate in ongoing risk awareness campaigns. We track participation rates and survey results to evaluate effectiveness and identify areas for improvement. In addition, all employees are required to participate in and achieve a satisfactory level of proficiency in our ongoing cybersecurity risk awareness and education efforts. Client Privacy. We help our clients protect themselves from fraud, including cyberfraud and other fraudulent activity, by providing guidance on guarding against phishing, personal identity theft and other threats. Access our Terms of Use for more information.
BNY MELLON ENTERPRISE ESG 47 RESPONSIBLE BUSINESS Enterprise ESG 2025 Technology Goals Goal: Continually evolve business protocols to help ensure systems continuity in every jurisdiction in which we operate, and across borders KPI: Expand our information security management system based on an internationally recognized specification (i.e., ISO 27001) for all critical applications and business services Progress: BNY Mellon successfully recertified for a 3-year cycle the ISO 27001:2013 in 2021. We are conducting feasibility analysis of ISO27701:2019 Privacy Information Management System (PIMS) as an extension of ISO27001:2013 certification Goal: Evolve business protocols to provide technology knowledge, resilience and business continuity KPI: Cultivate a globally competitive level of workforce awareness concerning information systems security Progress: Increased the scope and cadence of experiential learning and threat simulations for staff (e.g., conducted tabletop exercise “wargames,” tested wargame audiences with individual spear-phishing emails before wargames, tested high-risk populations with in-inbox spear-phishing tests, including credential harvesting pages) Expanded written publications to reach new internal and external audiences (e.g., “Phish Catchers” series to reward best-practice staff hygiene behavior and spread security culture) Increased scope and cadence of live and recorded presentations for staff and clients (e.g., published first client-facing cyber threat and hygiene recorded presentation, trained all 18 executive assistants with 1:1 sessions) SPOTLIGHT A Catalyst for Inclusive Language Within Financial Services BNY Mellon is at the forefront of driving inclusive language throughout the field of cybersecurity and the broader realm of IT in the financial services industry. Our company served as the catalyst for raising industry awareness and driving change by initiating a recent paper on Use of Non-inclusive Language in Technology and Cybersecurity and Why It Matters . Released by UK Finance and produced jointly by EY and Microsoft, this paper encourages language neutrality by identifying and raising awareness of sensitive terms such as “repeat offenders” and “blacklisting” and replacing them with neutral terms. The concept for the paper originated with Hem Pant, Head of Information Security, BNY Mellon International and the Global Head of Cyber Third Party and Inter-Affiliates Assessments. Pant hopes that a new vocabulary will help make the field of cybersecurity more inclusive and expand the talent pipeline by removing the barrier of negative language based on race, gender or other attribute. Resiliency. Our resiliency management program focuses on: • Business continuity/technology recovery • Technology risk and control • IT service management (change/problem/incident management) • IT sourcing • Vendor risk management • Information security operations Our Cyber, Technology and Operations Center is the result of our commitment to resiliency. We have built a 360-degree watchtower with a clear view of what is happening in our systems and in the world around us. We have an optimized team representing every functional area we need to identify, and respond quickly to threats or incidents to perform better for our clients.
BNY MELLON ENTERPRISE ESG 48 RESPONSIBLE BUSINESS Climate Change-Driven and ESG Risks Because climate-related changes and events can directly impact the company’s operations, BNY Mellon is committed to understanding and addressing the risks to it posed by climate change. In 2021 we enhanced global risk frameworks to incorporate the identification and assessment of climate-related physical and transition risks as a risk driver. BNY Mellon is also acutely aware of the broader implications of ESG risks. We plan to expand our focus on climate risk to other aspects of environmental risks. In addition, BNY Mellon is further evaluating development opportunities in risk management approaches to social and governance considerations. Accordingly, we plan to further incorporate broader ESG risk considerations into our global Risk and Compliance frameworks as applicable. Learn more in Managing Climate Change Locate other climate change-related topics through our TCFD Index . STRONG GOVERNANCE We believe that the strength of BNY Mellon’s business reflects the high standards set by our governance structure. This structure, which provides guidance in managing the company from the Board down, is designed to benefit all of our stakeholders, including our stockholders, clients, employees and communities. Our corporate governance practices have enabled achievements in areas such as Board oversight of corporate culture, human capital management, and director recruitment efforts aimed, in part, at enhancing board ethnic and racial diversity. Effective internal governance and disclosures about the role of management and the Board in a variety of other areas, including technology resiliency and climate-related risk management, are significant for shaping expectations of investors, asset managers and the broader community. Our Opportunity and Approach Strong governance practices position BNY Mellon to provide quality services to clients in all market scenarios and conduct business with excellence and integrity. Our culture of integrity and accountability is underpinned by our practices, guidelines and policies. We are committed to operating with strong ethical business practices, fair and equitable compensation, a diversified board of directors, and transparency. We endeavor to provide regular and clear communication to our stakeholders on the topics that are important to them.
BNY MELLON ENTERPRISE ESG 49 RESPONSIBLE BUSINESS 2021 ACHIEVEMENTS Stockholder Engagement: Reached out to stockholders representing over 65% of the company’s outstanding shares. Diverse Board: One of the most diverse Boards on Wall Street, with 36.4% women and 36.4% from underrepresented ethnic/racial backgrounds, making our Board over 72% diverse on the basis of gender, race and ethnicity. * Focus on Board Refreshment: Seven of our current directors have been appointed to the Board within the last five years. * Notice of Annual Meeting and Proxy Statement 2022 . Corporate Governance Effective corporate governance is foundational to a prosperous, sustainable and responsible business, and it can profoundly impact how a company approaches its responsibilities to stockholders and other stakeholders. BNY Mellon is committed to a robust corporate governance framework consistent with best practices for public companies. Our Board of Directors, the Board’s Corporate Governance, Nominating and Social Responsibility (CGNSR) Committee, and management evaluate corporate governance developments on an ongoing basis, including through engagement with stakeholder groups, to identify and, where appropriate, implement changes to align with best practices as they evolve. As described below, the Board and the CGNSR Committee have been active in refining our governance framework. In 2021, the CGNSR Committee, which is composed entirely of independent directors, held seven meetings. As a signatory to the Commonsense Principles 2.0 , we embrace corporate governance principles for sound, long-term-oriented governance. Similarly, our endorsement of the Business Roundtable’s Statement on the Purpose of the Corporation signals our commitment to our stakeholders in our pursuit of improving our business performance. Enterprise ESG 2025 Governance Goals Goal: As part of the director recruitment and refreshment efforts for the parent Board of Directors, continue to ensure that candidate slates include individuals with diverse backgrounds and perspectives in order to maintain the Board’s diverse composition KPI: Review at least annually the diversity criteria applied by the Board in its process of evaluating the qualifications of potential candidates Progress: Completed for 2021 evaluation process KPI: Integrate into the evaluation of external search firms’ performance a review of such firms’ capabilities in developing diverse candidate pools New KPI initiated in 2021 Goal: Formalize proactive outreach program to engage stockholders on ESG performance KPI: Increase proactive engagement with top stockholders on ESG topics Progress: In 2021, BNY Mellon reached out to stockholders representing over 65% of the company’s outstanding shares and held discussions, including with respect to ESG topics, with those that accepted our invitation KPI: Enhance integration of ESG content in public reporting, including but not limited to BNY Mellon’s Proxy materials Progress: Please see Oversight of Environmental, Social and Governance Matters section of the 2022 Proxy Statement, pages 31-35
BNY MELLON ENTERPRISE ESG 50 RESPONSIBLE BUSINESS ESG and Climate Governance The CGNSR Committee and the full Board are composed of members who bring a diverse set of skills, backgrounds and experience to BNY Mellon, including in the energy and utilities spaces. These outside interests contribute to the directors’ exposure to, knowledge of and engagement with climate and other ESG matters. Director education courses relating to ESG are included in the regular roster of training opportunities made available to all directors, and the CGNSR Committee expects to continue to focus on ESG-specific director education topics to further enhance the directors’ understanding of and keep them up to date regarding ESG matters, including climate change. Members of BNY Mellon’s Executive Committee and senior-level Enterprise ESG and ESG Client Solutions team members meet with the CGNSR Committee on at least a semi-annual basis to present updates regarding enterprise environmental management, with a focus on environmental sustainability and climate- related goal setting, progress and strategy regarding our operational footprint, and may also provide other material information such as stakeholder input and peer comparison. Throughout 2021, senior management provided the CGNSR Committee with reports and updates regarding BNY Mellon's environmental and sustainability programs and updates on the Company’s ESG Client Solutions offerings. The Chair of the CGNSR Committee reports to the full Board of Directors regarding the topics covered by the CGNSR Committee at its previous meeting. In this way, the Board is kept apprised of material developments regarding our environmental goals and strategies, can monitor such developments, and can incorporate relevant information into its overall decision-making and strategizing processes as appropriate. KEY DATA: BOARD OF DIRECTORS* Average director attendance: 98% at Board and committee meetings held in 2021 Minimum required director attendance: 75% of Board and committee meetings Board independence: 91% Women directors: 36.4% Ethnic and racial diversity: 36.4% Directors who joined the Board in the last five years: 7 * T he figures provided with respect to director independence, diversity and tenure are based on Board membership following the 2022 Annual Meeting of Stockholders. CGNSR Committee ESG Oversight Environmental management strategy, goal setting and performance ESG reporting initiatives ESG Client Solutions and offerings Engagement between management and top investors
BNY MELLON ENTERPRISE ESG 51 RESPONSIBLE BUSINESS AN INDEPENDENT BOARD The Board of Directors governance framework features well-defined roles and authority with a leadership structure involving an independent Chair, separate from our CEO, Todd Gibbons, who serves as the only non-independent member of the Board. Independent directors meet in executive sessions, presided over by our independent Chair, at regularly scheduled Board meetings. Our CGNSR Committee and Board evaluate this structure annually, or more frequently as needed, to help ensure alignment with the needs of the company. STRENGTH IN DIVERSITY The strength of our Board is a product of the variety of our directors’ experience, diversity, differing perspectives and institutional knowledge. We are committed to fostering and maintaining diversity on our Board: diversity is an integral component of the process undertaken by the CGNSR Committee and the Board for recruiting director candidates and evaluating the composition of the Board. To capture the benefits inherent in differing perspectives, we seek to include directors with diverse backgrounds, including with respect to race, gender, ethnicity and sexual orientation. Following the election of directors at the 2022 Annual Meeting of Stockholders, 36.4% of our directors are women and an additional 36.4% of our directors are diverse on the basis of race or ethnicity. In addition, four of the six standing committees of the Board are chaired by a director who is diverse on the basis of race or gender. Our Board has a well-established focus on long-term business strategy and resiliency, leadership, and corporate culture and performance. This foundation positioned the Board to oversee and provide insight to management on the company’s response to the challenges, uncertainties and opportunities that occurred throughout 2021, including as it relates to our impact on our communities and society more broadly. In addition to the regular updates on the financial and operational impacts of the pandemic on our business, employees, clients and suppliers, the Board maintained a regular dialogue with management in 2021 regarding its direction and action on matters related to social justice, diversity and inclusion, and public policy and advocacy. More information about our Board of Directors is included in our 2022 Proxy Statement . EXECUTIVE COMPENSATION Our executive compensation program is structured to drive results over the long term. At target, 75% of our CEO’s incentive compensation and generally 70% of our other senior executives’ incentive compensation is delivered in equity awards, with the balance paid in cash. We pay bonuses and incentives based on performance against goals, including those on specified environmental, social and governance topics, such as diversity, equity and inclusion and risk management. See our 2022 Proxy Statement for our full compensation discussion and analysis. INVESTOR ENGAGEMENT Our Corporate Governance, Enterprise ESG and Investor Relations teams are committed to engaging regularly with our top investors. We offer meetings on governance issues between top investors and Board members and track the discussions and outcomes. In 2021, our analysts and executives met with broader investor audiences in our offices and virtually. Management and investor dialogue increased as we addressed topics such as executive compensation, company strategy and response to the COVID-19 pandemic, corporate governance, diversity and inclusion, and other issues relating to our Enterprise ESG strategy. Management reports regularly to the independent directors regarding investor discussions and feedback to keep them informed of stockholders’ perspectives on a variety of issues, including governance, strategy, climate and performance, and to enable them to consider and address those matters effectively. For example, stockholder feedback played a significant role in the design and implementation of a stockholder written consent right. It has also informed the CGNSR Committee’s oversight of climate-related and environmental sustainability matters, and helped shaped the focus of the Company’s initiatives and impact in a number of areas. Additionally, when BNY Mellon executed a resegmentation of our business and reclassification on the consolidated income statement during 2021, we kept investors informed of its impact on their ability to conduct year-over-year comparisons of our performance.
BNY MELLON ENTERPRISE ESG 52 RESPONSIBLE BUSINESS TAX TRANSPARENCY AND INTEGRITY Our firm’s culture of “Doing What’s Right,” as represented in our Code of Conduct, extends to paying taxes. BNY Mellon believes that taxes have an economic and social impact globally. As part of BNY Mellon’s overall ESG strategy, we are committed to acting with integrity in all tax matters and maintaining a transparent tax practice. BNY Mellon’s tax mission is to fully comply with all applicable laws and regulations in the jurisdictions where we operate and have an open dialogue with tax authorities during all authorized inquiries and audits. We seek to facilitate transactions that achieve a tax result that is consistent with the underlying economic consequences and are consistent with the letter of the law. We file all tax returns and make tax payments, in accordance with statutory requirements. More information related to taxes is in our 2021 Annual Report and in our Global Tax Strategy . ESG AND RESPONSIBLE INVESTMENT CLIENT SOLUTIONS Investors and organizations are grappling with increasing responsible investment (RI) and climate- focused regulation, the race to net zero, and growing volumes of ESG data. As institutional investors seek to better understand the impact of ESG factors on their portfolios, financial institutions are looking to further integrate responsible considerations throughout transactions and processes. All along the financial value chain, organizations are looking for secure, seamless, powerful solutions to advance sustainable finance and societal progress. Our Opportunity and Approach We are committed to using our reach, market influence and resources to address pressing global ESG issues. Across our enterprise, BNY Mellon products and services are increasingly being refined and enhanced to support client and investor needs to better manage ESG issues. Our servicing business helps to enable clients and investors to integrate ESG-related factors into their decision-making processes by equipping them with relevant data and tools. BNY Mellon Investment Management, our investment management arm, offers a diverse spectrum of RI strategies designed to help create a better future and seek better returns. This is intended to help both guide future ESG investments and improve the effectiveness of ESG metrics. Through these services and others, we strive to uncover and advance new ways of encouraging sustainable economic growth that protects healthy markets, safeguards environments and delivers value not only to our clients but also to communities, businesses, governments and people everywhere.
BNY MELLON ENTERPRISE ESG 53 RESPONSIBLE BUSINESS 2021 ACHIEVEMENTS ESG Data Management: Expanded the BNY Mellon ESG Data Analytics tool to support collateral management, securities lending and liquidity services. Responsible Investment: Increased number of RI funds to 27; grew assets managed by UN PRI signatories by 5.3% to $1.931 trillion * Inclusive Investment: Sponsored a global independent study, The Pathway to Inclusive Investment , calling for action to create a more inclusive investment world by encouraging more women to invest. Economic Opportunity: Contributed $3 million to South Carolina-based Optus Bank in support of investments in low- and moderate-income and minority communities as part of the U.S. Treasury Department’s Financial Agent Mentor-Protégé Program. * A UM represents the aggregate total of investment firm signatories’ assets under management at December 31, 2021. Includes Alcentra, ARX Investimentos, Insight Investment (including North America), Mellon Investments Corporation, Newton Investment Management (including North America) and Walter Scott & Partners. It does not include assets managed by investment firm personnel as dual officers of The Bank of New York Mellon and BNY Mellon Investment Adviser, Inc. Siguler Guff AUM is not included in this calculation, given the minority interest in the firm held by BNY Mellon. Insight’s AUM is represented by the market value of cash, securities and derivatives held in client accounts. Where a client mandate requires Insight to manage some or all of a client’s liabilities, and Insight is to be paid an investment management fee based upon the value of such liabilities, the AUM for the account will be based on the value of the liabilities plus the gross notional value of any derivatives used in the management thereof. ** D ata reflective of FY 2021; Dealogic and Refinitiv. Investment Management The world is undergoing a dramatic transformation that requires the responsible allocation of capital to address pressing environmental and social challenges. Tackling the climate crisis requires transformation of vital sectors of the world’s real economy — including energy generation, transportation, food production and infrastructure — and replacement of energy-intensive technology with low-emissions alternatives. The scale of the proposed investment is unprecedented by historical standards: research from BNY Mellon IM economists suggests the challenge will be enormous but achievable with the right incentives. Against the context of this transformation, we expect RI to expand significantly and become a key driver of investment returns in the coming years. We believe it is increasingly important to manage active portfolios with a comprehensive analysis of the risks and opportunities associated with the transition to a more sustainable future. In the long run, we believe discretionary investments will increasingly be expected to deliver a twin benefit of financial returns and a positive impact to society, which in turn will drive innovation in client solutions and even greater demand for RI products. SPECIALIST INVESTMENT SOLUTIONS As one of the largest asset managers globally, and with a parent company that touches the entire investment cycle, at BNY Mellon IM, we believe we have the influence and ability to provide more sustainable returns for all our stakeholders, through innovations in our RI product range, stewardship activities and working collaboratively to expand our expertise on the most material ESG issues. We seek to create long-term value by placing the collective prosperity and effective stewardship of our clients’ assets at the heart of our business. Our multi-boutique model creates deep diversity of thought, which enables us to develop innovative solutions and ultimately deliver shared prosperity. Our specialist investment firms are all investor driven, and the stewardship of our clients’ assets is at the heart of what they do. The approach to RI varies across these investment firms, as each is governed by its own management team and specializes in different market areas — from publicly-traded equities and bonds to cash, alternatives and privately traded markets. Each Sustainable Bonds: Administered 169 new sustainable, social and green bond issuances, totaling $ 89 billion, making us one of the leading trustees in green bonds by deal volume for the second consecutive year. **
BNY MELLON ENTERPRISE ESG 54 RESPONSIBLE BUSINESS firm has its own unique investment culture, philosophy, process and RI approach. BNY Mellon IM leverages the combined expertise of these firms to help our clients meet their own varied responsible investing goals. Enterprise ESG 2025 ESG Client Solutions Goal Goal: Provide best-in-class client solutions to the global ESG community by enabling ESG financing KPI: Increase assets managed by investment firms that are signatories to the PRI Progress: Increased to $1.931 trillion from $1.834 trillion as of 31 December 2020 * KPI: Increase number of clients who use our ESG Global Risk Solutions, and Data and Analytics solutions Progress: In 2021 the ESG Data Analytics solution was launched with a number of clients publicly announcing adoption, notably Florida State Board of Administration and BNY Mellon Collateral and Clearance KPI: Increase volume of new green bonds administered Progress: Increased to $62 billion in 2021 from $38.7 billion in 2020 ** KPI: Demonstrate ESG thought leadership and proof points as measured by industry recognition and client satisfaction metrics Progress: See publications at https://www.bnymellon.com/ us/en/about-us/esg-and- responsible-investment.html * A UM represents the aggregate total of investment firm signatories’ assets under management at December 31, 2021. Includes Alcentra, ARX Investimentos, Insight Investment (including North America), Mellon Investments Corporation, Newton Investment Management (including North America) and Walter Scott & Partners. It does not include assets managed by investment firm personnel as dual officers of The Bank of New York Mellon and The Dreyfus Corporation. Siguler Guff AUM is not included in this calculation, given the minority interest in the firm held by BNY Mellon. Insight’s AUM is represented by the market value of cash, securities and derivatives held in client accounts. Where a client mandate requires Insight to manage some or all of a client’s liabilities, and Insight is to be paid an investment management fee based upon the value of such liabilities, the AUM for the account will be based on the value of the liabilities plus the gross notional value of any derivatives used in the management thereof. ** Data reflective of FY 2021; Dealogic and Refinitiv. SPECIALIST INVESTMENT SOLUTIONS Global provider of credit solutions AUM: $40.6 billion (as of 12/31/21) 15 16 RI Approach: The PRI’s six Principles for Responsible Investment and analysis of ESG factors form an integral part of Alcentra’s investment process. A PRI signatory since 2018. Progress in 2021: • Established a dedicated Responsible Investment team • Developed a suite of proprietary tools to support the integration of ESG factors in the investment process • Became a member of the Institutional Investors Group on Climate Change (IIGCC) to work with peer investors toward a net zero and resilient future • Called for government action on climate change by signing on to the 2021 Global Investor Statement to Governments on the Climate Crisis Brazilian firm specializing in equity, long/short, macro, corporate bonds and fixed income strategies AUM: $7.2+ billion (as of 12/31/21) RI Approach: As several ESG factors have strong impact on Brazilian companies, in many cases significantly affecting their risk profile, investment experts at the firm focus on analysis and due diligence in this area. Progress in 2021: • Formalized several practices related to investment analysis, approving an RI policy • Became a signatory of the Principles for Responsible Investment • Developed RI training sessions for its professionals 15 On Ma y 31, 2022, The Bank of New York Mellon announced that Franklin Templeton had entered into a definitive agreement to acquire BNY Alcentra Group Holdings, Inc. (together with its subsidiaries, “Alcentra”) from BNY Mellon. The transaction is expected to be completed early in the first calendar quarter of 2023, subject to customary closing conditions, including certain regulatory approvals. 16 Asse ts under management (AUM) includes accounts managed by Alcentra NY, LLC, Alcentra Limited, and assets managed by Alcentra personnel for affiliates under dual officer arrangements.
BNY MELLON ENTERPRISE ESG 55 RESPONSIBLE BUSINESS Cash and liquidity manager offering a comprehensive platform of institutional liquidity solutions 17 AUM: $300+ billion (as of 12/31/21) RI Approach: Dreyfus has developed a RI strategy built on three core pillars: ESG integration, diversity and inclusion, and charitable giving. Progress in 2021: • Formally integrated ESG considerations into its credit analysis process • Filed BOLD SM (Black Opportunity for Learning and Development) shares with regulator in November 2021, a new share class of one of its flagship funds, which was launched in February 2022 • Continued trading the majority of purchases in a government securities cash management fund through minority brokers to augment diversity and inclusion efforts 17 Dr eyfus is a division of Mellon Investments Corporation (MIC) and BNY Mellon Investment Adviser, Inc. (BNYMIA). When managing Dreyfus money market mutual funds, Dreyfus personnel act in their capacity as dual employees of BNYMIA, the funds’ investment adviser, and members of its Dreyfus division. Global investment manager in the UK and U.S., specializing in fixed income solutions and liability-driven investments AUM: $1.1+ trillion 18 RI Approach: Insight’s approach to RI is underpinned by the belief that ESG issues are important drivers of investment value. Insight aims to systematically consider ESG issues within its research processes and, if it identifies material ESG risks, engages to understand and address issues to support its clients’ best interests. A PRI Signatory since 2006 and A+ rated in 2020. Progress in 2021: • Extended its Prime sovereign ESG ratings to include impact ratings of a country’s progress on ESG factors aligned with the UN Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) • Conducted engagements with debt issuers, the majority of which included some form of ESG dialogue • Launched two funds 19 in the Responsible Horizons range of fixed income portfolios using Insight’s own evidence-based approach to investment research and ESG analysis, supported by ESG ratings from its proprietary model Prime • Signed up to the Net Zero Asset Managers initiative and UN Global Compact • Awarded signatory status to the new voluntary UK Stewardship Code by the Financial Reporting Council 18 As o f December 31, 2021. Assets under management (AUM) are represented by the value of the client’s assets or liabilities Insight is asked to manage. These will primarily be the mark-to-market value of securities managed on behalf of clients, including collateral if applicable. Where a client mandate requires Insight to manage some or all of a client’s liabilities (e.g. LDI strategies), AUM will be equal to the value of the client specific liability benchmark and/or the notional value of other risk exposure through the use of derivatives. Insight North America (INA) is part of ‘Insight’ or ‘Insight Investment’, the corporate brand for certain asset management companies operated by Insight Investment Management Limited including, among others, Insight Investment Management (Global) Limited, Insight Investment International Limited and Insight Investment Management (Europe) Limited. Advisory services referenced herein are available in the US only through INA. INA’s AUM is $138.8bn as of December 31, 2021.Figures shown in USD. FX rates as per WM Reuters 4pm spot rates. Excludes previous parent introduced assets prior to 2009. Includes employees of Insight North America LLC (INA) and its affiliates, which provide asset management services as part of Insight, the corporate brand for certain companies operated by Insight Investment Management Limited (IIML). Insigh t North America LLC (INA) is a registered investment adviser under the Investment Advisers Act of 1940 and regulated by the US Securities and Exchange Commission. Insight North America (INA) is part of 'Insight' or 'Insight Investment', the corporate brand for certain asset management companies operated by Insight Investment Management Limited including, among others, Insight Investment Management (Global) Limited (IIMG) and Insight Investment International Limited (IIIL) and Insight Investment Management (Europe) Limited (IIMEL). 19 T wo additional Responsible Horizons funds were launched in early 2022.
BNY MELLON ENTERPRISE ESG 56 RESPONSIBLE BUSINESS Global specialist index investment manager delivering institutional-quality equity and fixed income index management AUM: $480+ billion 20 (as of 12/31/21) RI Approach: Mellon’s RI strategy and approach is built on three core pillars: stewardship, investment process and RI product. As a long-term shareholder and committed steward of its clients’ assets, Mellon recognizes the importance of exercising its fiduciary duty through proxy voting, shareholder governance, and engagement. A PRI Signatory since 2013 and A-rated in 2020. Progress in 2021: • Integrated third-party RI data and scores, where applicable, to assess relevance when building sampled portfolios • Remained committed to developing a suite of additional RI strategies to address its clients’ needs for ESG-specific outcomes Global investment manager in the UK and U.S., offering a variety of investment solutions across equity and multi- asset strategies AUM: $143 billion 21 RI Approach: Newton seeks to invest and behave responsibly; acting as active, engaged owners of financial assets in a manner that meets responsibilities and expectations to its clients and society as a whole. Using thematic frameworks, ESG analysis, active stewardship and RI data capabilities, its approach to RI helps it understand the mosaic of factors that may impact certain investment opportunities. A PRI Signatory since 2007 and rated A+ in 2021. 20 Mell on is a division of Mellon Investments Corporation (MIC) and Dreyfus is a division of MIC and BNY Mellon Investment Adviser, Inc. (BNYMIA). 21 As o f December 31, 2021. The Newton Investment Management Group describes a group of affiliated companies that provide investment advisory services under the brand name “Newton” or “Newton Investment Management.” Those companies are Newton Investment Management Ltd, registered in the UK, and Newton Investment Management North America LLC, registered in the U.S.. Progress in 2021: • Newton Investment Management Ltd awarded signatory status to the new voluntary UK Stewardship Code by the Financial Reporting Council • Began management of three new U.S.-domiciled Sustainable ETFs and converted four pooled investment funds with sustainable- or ethical- integrated considerations in EMEA, in conjunction with BNY Mellon IM • Signed up to the Net Zero Asset Managers initiative • Developed a technology-based solution to derive proprietary company-level ESG scores • Created new full-time RI roles across ESG research, stewardship and RI data integration • Expanded ESG data sources to enable more in-depth and efficient research and analysis Global multi-strategy private markets investment firm 22 AUM: $15+ billion 23 RI Approach: Siguler Guff integrates ESG factors into each stage of its investment process, including sourcing, due diligence, contractual negotiations, monitoring and, when warranted, remedial action. A PRI Signatory since 2013. Progress in 2021: • Evolved and refined its investment process in relation to its ESG & Responsible Investment Policy and established an ESG Committee, with responsibility for evaluating the effectiveness of internal ESG policies and reviewing wider ESG trends, aiming to meet or exceed industry best practices as well as uphold its internal values of integrity, stewardship and focus on long-term value 22 BNY Mellon owns a 20% interest in Siguler Guff & Company, LP and certain related entities (including Siguler Guff Advisers, LLC). 23 Sig uler Guff data is estimated as of September 30, 2021.
BNY MELLON ENTERPRISE ESG 57 RESPONSIBLE BUSINESS A UK-based global equity investment management firm AUM: $106 billion (as of 12/31/21) RI Approach: Walter Scott believes that the companies that make the best long-term investments typically adhere to the highest standards of integrity, sustainability and governance. Walter Scott integrates analysis of these factors into its investment process, while acting as trusted stewards of clients’ assets. Its approach to responsible investing and stewardship is focused on three key areas: Integrated Research & Analysis, Engagement, and Proxy Voting. A PRI Signatory since 2017. Progress in 2021 • Awarded signatory status to the new voluntary UK Stewardship Code by the Financial Reporting Council • Appointed a Head of Investment Operations and Sustainability • Established the role of Investment Manager - Responsible Investment, with responsibility for driving RI analysis and engagement • Established an Investment Stewardship Committee with responsibility for the governance and oversight of engagement and proxy voting • Deepened the integration of sustainability analysis into the investment process • Included discussion of sustainability issues in a majority of all owned company engagements DEFINING RESPONSIBLE INVESTMENT Despite acknowledgement of the importance of and interest in RI globally, there remains a lack of industry standardized terminology, with many terms used interchangeably. We define RI as investing for a better future and for better returns for all, regardless of the approach taken. To provide clarity on how we approach RI at BNY Mellon IM, we have laid out how we define certain RI-related terminology used by the investment management industry in a Glossary in this report. RESPONSIBLE INVESTMENT STYLES Responsible Investment covers a spectrum of investing styles, including ESG integration, exclusionary screening, best-in-class screening, sustainable investing, impact investing and philanthropy. For all investment styles, stewardship of clients’ assets is a key component, as is ongoing development of reporting ESG portfolio assessments to clients. While the majority of our RI products or solutions integrate ESG considerations, among a range of other factors, into the financial analysis and/or investment decisions, they do not have any objective or binding intent to be responsible. In addition, our firms offer a growing suite of funds and accounts that do have a binding and explicit intent to be responsible through either a rules-based approach to universe selection (negative and best-in-class screening) or an environmental and/or social objective or theme (sustainable/thematic investing and impact investing). In 2021 we expanded our range of offerings with a stated intent to be responsible through Newton, Insight and Alcentra. By the end of 2021, BNY Mellon IM firms offered 27 such funds and 20 separate accounts, including 10 in EMEA and seven in North America. We intend to continue this growth in 2022. Guided by a global head of Responsible Strategy hired in 2021, we are implementing a Responsible Investment program and creating a unified strategy even as each investment firm maintains autonomy over its individual approach. Our goal is to offer solutions across the spectrum of RI while anticipating both our clients’ needs and upcoming regulatory requirements globally. Recognizing that management and disclosure of ESG data is a key area of focus, we aim to develop enhanced reporting on environmental and social issues for our
BNY MELLON ENTERPRISE ESG 58 RESPONSIBLE BUSINESS clients during 2022. In developing RI products, BNY Mellon IM seeks to expand its investment solutions that provide a balance between creating long-term value for clients and beneficiaries and driving sustainable outcomes for the environment and society. RESPONSIBLE INVESTMENT EDUCATION As the field of responsible investing and related regulation evolves quickly, we provide training and education opportunities for both clients and market participants. For example, Insight conducted a Responsible Investment webinar , in which investment professionals addressed implementing a net zero strategy, incorporating ESG practices into liability- driven investment solutions and specialist fixed income strategies. In 2021, Walter Scott held its first virtual investment conference. The event, which focused on innovation, involved speakers from Walter Scott as well as a range of external speakers from academia, medicine, politics and business. A leading advocate of putting purpose at the heart of the business agenda discussed actions companies can take to deliver a “net positive” contribution to society and the environment. Throughout 2022 we intend to implement mandatory RI training for all client-facing staff within BNY Mellon IM globally to provide updates on regulatory changes and our clients’ responsible investing requirements. AMPLIFYING OUR IMPACT By joining with other businesses and investors aimed at advancing responsible investing, our firms amplify their impact and help accelerate the change needed to address global challenges. BNY Mellon IM firms participate in a variety of initiatives worldwide, including one or more of those shown below. Support for Responsible Investing Environmental Social Governance CDP Climate Disclosure Standards Board Climate Action 100+ Green Bond Principles Institutional Investors Group on Climate Change (IIGCC) Institute of Chartered Accountants of Scotland – Sustainability Panel Net Zero Asset Managers Initiative Task force on Climate-Related Financial Disclosures Transition Pathway Initiative 30% Club FAIRR (Farm Animal Investment Risk and Return) ShareAction Healthy Markets ShareAction Workforce Disclosure Initiative UK Sustainable Investment and Finance Association (UKSIF) Asian Corporate Governance Association GC100 & Investor Group International Corporate Governance Network (ICGN) and ICGN Global Stewardship Principles Investor Stewardship Group Principles for Responsible Investment UK Stewardship Code
BNY MELLON ENTERPRISE ESG 59 RESPONSIBLE BUSINESS SHARING OUR EXPERTISE BNY Mellon IM’s specialist investment firms also share their expertise in responsible and sustainable investment through reports and research on current trends and issues. Given their combined scope and scale, these firms have the ability to reach beyond our business and collaborate with our wider stakeholders (such as clients, invested entities and policymakers) to encourage broader impact. In 2021, our firms published regular insights on key trends and themes in the RI space, with many publishing annual RI reports and brochures explaining their individual RI approaches, proprietary ESG ratings systems and responses to climate risks. Reports from Newton , Insight and other firms are publicly available on the RI section of each investment firm’s website. In 2021, Walter Scott Partners released the findings of an 18-month in- depth research initiative on the long-term investment risks and opportunities of the global energy transition. Read the results in The Journey to a Carbon-Neutral Economy . Finally, our dedicated team of economists and strategists at BNY Mellon IM produced reports on RI issues, including a paper describing the investment costs and opportunities associated with the transition to net zero over the next few decades. SPOTLIGHT Advancing Sustainable Finance BNY Mellon is working with the Yale Initiative on Sustainable Finance to help the sustainable investing community chart a path forward. BNY Mellon CEO of Investment Management Hanneke Smits shared her perspectives at the initiative’s 2021 Annual Symposium, which spotlighted current insights on net zero, green bonds, growing regulatory pressures, and other emerging issues. Wealth Management BNY Mellon Wealth Management uses a goals-based approach to build portfolios that not only serve clients’ financial goals but also align with their sustainable, social and/or values-based goals. Our Wealth Management division guides clients including wealthy individuals and families, family offices, nonprofits and other institutional investors as they deploy capital across the social finance spectrum, from capital markets to philanthropy. With $321 billion in total client assets, 24 our Wealth Management Group invests across more than 50 responsible investing solutions. Investor Solutions LLC, a division of Wealth Management, provides multi-asset solutions to institutional investors. Its solutions include outsourced Chief Investment Officer (OCIO) services for retirement accounts, foundations and endowments, and family offices as well as model management, liquid alternatives and private equity. These services are increasingly focused on meeting clients’ responsible investing goals in addition to financial goals. In 2021, the Investor Solutions Manager Research team brought over 15 new RI active and passive strategies under coverage, 11 of which were added to Wealth Management’s core client investment platform. This includes the launch of its proprietary private markets impact fund, which will invest in a portfolio of underlying funds that seek both competitive private market financial returns and a measurable impact across environmental sustainability, financial inclusion and social equality. Through a newly created RI Advisory Board, Wealth Management brings together Investment team members and client-facing staff to share thought leadership and further Responsible Investment education for its employees. In 2021, Wealth Management produced thought leadership pieces on responsible investing on green investments , greenwashing , how to make an impact beyond philanthropy and impact investing . 24 Includes cus tody assets and assets under management as of December 31, 2021.
BNY MELLON ENTERPRISE ESG 60 RESPONSIBLE BUSINESS Asset Servicing and Digital As the “bank of banks,” we power the financial industry through our unique perspective, informed by one of the largest data sets in the world. Our consolidated Asset Servicing and Digital capabilities are transforming investment management with increased transparency and accelerated information delivery. We provide access to a vibrant data ecosystem powered by our proprietary application that both aligns future investments to clients’ ESG priorities and continually improves and optimizes the use of ESG data and metrics. With socially responsible and sustainable investing growing in importance, investors are becoming much more specific in communicating their ESG priorities — whether for portfolio management, managing climate- related risk or trying to create impact. Consequently, our consolidated Asset Servicing and Digital organization handled a growing demand for ESG integration and ESG- related data in 2021. Our powerful, artificial intelligence (AI)-informed ESG Data Analytics tool harmonizes data across many sources to support investment decision processes. Clients can use this tool to consolidate sustainability data from multiple sources into actionable portfolio monitoring, analysis and reporting. Our award-winning application 25 creates transparency and alignment between market participants, enabling them to build customized sustainable investment solutions. It draws on BNY Mellon’s data management expertise and wide network of clients. Selected ESG data can also be incorporated into customizable reporting solutions so that institutional investors can communicate the ESG exposures within investment portfolios, including financial impact, carbon metrics and other factors. 25 Best New Technology Introduced over the Last 12 Months (AI, machine learning and analytics), American Financial Technology Awards 2020; Technology Innovation of the Year, Global Investment Group Excellence Awards 2020 . EXPANDING OUR ESG DATA ANALYTICS TOOL We further enhanced the BNY Mellon ESG Data Analytics tool by integrating additional data sources, including proprietary ESG and climate intelligence from firms who have made their role in the ecosystem public. Through ESG Data Analytics, BNY Mellon clients will now be able to integrate these comprehensive ESG analytics into their asset allocation, portfolio management and reporting needs. This increases our ability to meet clients’ changing priorities and requirements, including their need for powerful tools to holistically manage their data at scale in the cloud, and to better align their ESG funds with regulatory or self-defined frameworks and standards. In addition, ESG Data Analytics functionality was incorporated into other BNY Mellon offerings as described below. • Investment boutiques are using ESG Data Analytics for research across data sets, clients' reporting and investor solutions for ESG/sustainable funds. • LiquidityDirect SM clients are now able to use ESG Data Analytics to quickly and easily analyze the ESG ratings of eligible investment options. This functionality helps them to align their cash investments in commercial paper (CP) and exchange- traded funds (ETFs) with their corporate social and ethical values. • RULE ® , our electronic collateral schedule manager, offers clients the ability to incorporate ESG factors into their collateral negotiations and decisions. • Our ESG Regulatory Reporting Service, powered by ESG Data Analytics, helps clients meet a range of reporting requirements, including those of the Sustainable Finance Disclosure Regulation (SFDR) and the TCFD. In an effort to create transparency on the state of the market, we published a number of thought leadership papers, including A Data-Driven Approach to Responsible Investment , which addresses investors’ ESG preferences and the data required to support these preferences. We also aimed at demystifying climate risk scenario analysis with Helping Investors Understand Climate Risk , a practical case study. Both papers reflect our ESG investor community focus where experimentation and sharing are encouraged.
BNY MELLON ENTERPRISE ESG 61 RESPONSIBLE BUSINESS SERVING CLIENTS ACROSS THE INVESTMENT LIFE CYCLE With our clients integrating ESG considerations across various stages of the investment life cycle, we recognize the importance of developing solutions with this in mind. We have offered our institutional client base investment compliance monitoring capabilities with ESG and norms- based screening for more than a decade. SPOTLIGHT Using Artificial Intelligence Responsibly As BNY Mellon adopts innovative technology through our digital transformation, the use of artificial intelligence and data analytics (AIDA) is becoming embedded across our enterprise. We recognize that our use of AI and data requires active oversight of ethical issues, such as the amount of energy required to power AI applications, potential algorithmic bias and data collection. We are committed to doing the right thing for clients, the industry and our employees. We acknowledge our responsibilities to the wider financial system and look to ensure the ethical use of this technology. As a member of the Veritas consortium led by the Monetary Authority of Singapore (MAS), BNY Mellon is collaborating with 25 banks and technology firms to develop a framework around the responsible adoption of AIDA. MAS members seek to assess their AIDA solutions against the principles of fairness, ethics, accountability and transparency. In 2021, Hans Brown, BNY Mellon Head of Enterprise Innovation and Chief Information Officer for Corporate Technology, served on the judging panel of the APIX inaugural Global Veritas Challenge, validating entries from fintechs developing capabilities to assess for the fairness of AI applications in banking. In addition to judging this industry competition, BNY Mellon was a leading participant in the Singapore FinTech Festival, a five-day virtual event that attracted more than 60,000 participants from over 160 countries in November 2021. Issuer Services CORPORATE TRUST Corporate Trust offers the infrastructure, technology and administrative services to help financial institutions, corporations, insurers, governments and sovereigns navigate the debt capital markets. Sustainable investments are a large part of BNY Mellon’s strategy and long-term vision, and Corporate Trust supports our clients’ ESG needs with a traditional range of products and solutions. ESG Bonds As one of the leading global trustees for ESG and sustainable bonds, BNY Mellon is advancing society’s transition to a more sustainable future. We support debt issuances in various capacities, acting as trustee, principal registrar, and paying, transfer, calculation, authentication and issuing agent. Our role is expanding as we continue to support the increasing investments and the diversity of these bonds, which now encompass green, social and impact bonds. In 2021, more than $530 billion was issued in sustainability-linked loans and bonds, which includes instruments for which repayment is tied to the achievement of institutional ESG targets, such as greenhouse gas emissions reductions. 26 26 Sustainable Debt Issuance Breezed Past $1.6 Trillion in 2021 , Bloomberg NEF, Jan. 12, 2022 27 Social and green bond data reflective of FY 2021; Dealogic and Refinitiv. While green bonds fund projects with environmental benefits, such as clean transportation or renewable energy projects, we are also on the forefront of social and other types of impact bonds. Social bonds are entirely dedicated to projects or activities that promote improved social welfare or positive societal impact, often targeting essential services such as healthcare, education, affordable education and basic infrastructure. The issuance of this asset class continued as the pandemic entered its second year, allowing our Corporate Trust team to serve as trustee and paying agent on social bonds in 2021. BNY Mellon also administered 138 new green bond issuances totaling $62 billion in 2021. With a global market share of 21% in deal count origination, we are one of the leading trustees in green bonds by deal volume. 27 By working with clients whose investments are intended to deliver environmental and social benefits, we use our global reach to drive positive change.
BNY MELLON ENTERPRISE ESG 62 RESPONSIBLE BUSINESS We act as a listing agent for issuers listing securities on the Luxembourg Green Exchange, a platform exclusively for 100% ESG-focused securities. We also continue to maintain “Observer” status to the International Capital Market Association’s Green Bond Principles, which are voluntary process guidelines to promote integrity and transparency in the market. Infrastructure and Public-Private Partnerships As urban population growth continues, so does the need for substantial investment in infrastructure. Public- private partnership investments have the potential to mobilize needed capital toward green and sustainable projects. Corporate Trust administers bonds and loans that help finance a wide range of infrastructure projects. Catastrophe Bonds and Insurance-Linked Securities While green bonds focus on actions designed to mitigate the long-term effects of climate change, catastrophe bonds and insurance-linked securities help address its immediate impacts. Catastrophe (CAT) bonds help reduce the cost of insuring risk from natural disasters by transferring the exposure from insurers to financial investors. Corporate Trust is an active administrator of these structures, contributing to BNY Mellon’s position as the leading CAT bond trustee globally, with 79% 28 of the global CAT bond market share in 2021. ESG ADVISORY SOLUTIONS As ESG investing grows, BNY Mellon helps our clients that issue depositary receipts understand and navigate the increasing complexities and evolving regulations on sustainable investing and disclosure. Our services range from providing roadmaps to help issuer clients manage investor concerns to assisting issuer clients in developing ESG strategies that are integrated with their capital markets and investor relations activities. Specifically, we support issuer clients in four major areas: Education and Benchmarking: Identify material themes within peer groups and industries, including company- specific ESG ratings, peer benchmarking reports, sector trends and regional trends. 28 Catastrophe Bond & Insurance-Linked Securities Deal Directory , Artemis Engagement Policy and Strategy: Develop roadmaps to assist in understanding investors’ specific ESG concerns, reviewing internal ESG practices, and enhancing communications efforts with investors and other relevant stakeholders. Intermediary Engagement: Help issuer clients understand and engage with key players, including ESG ratings providers, sustainability index providers, specialized firms and associations, and proxy advisers. Investor Engagement: Identify institutional investors that have embedded active ESG criteria into their investment processes and facilitate engagement with them; facilitate understanding of top shareholders’ ESG priorities and engagement with the right people at these firms. Through our advisory services, we guide issuer clients’ growing focus on key emerging issues, such as managing climate change concern and implementing the TCFD recommendations. Following our inaugural Future First Forum in 2021, we plan to issue a selection of Future First Insights white papers, including Tackling the TCFD Challenge , published in March 2022. This paper highlights views from investors and issuers as well as a broad outline of ways to approach climate reporting. Managing Investor Relations Team Carbon Impact As more companies make net zero commitments and aim for greater transparency around their sustainability performance, visibly curbing travel-related carbon emissions can positively impact both carbon footprint and public perception. Research conducted by BNY Mellon Depositary Receipts on The Carbon Impact of Investor Relations Activity evaluated potential costs and benefits investor relations teams could realize by reducing carbon emissions through virtual meetings and using carbon offsets to lessen the impact of in-person events. Another BNY Mellon study, Corporate Access Through COVID-19 and Beyond , shows that a significant number of investors are receptive to virtual meetings. Engaging Issuers and Investors In 2021, we deepened conversations between our Depositary Receipt issuer clients and institutional investors across the U.S. by hosting our inaugural Future First Forum ESG Investor Conference. At this conference, BNY Mellon Capital Markets hosted issuer- to-investor one-on-one meetings for our issuers in the
BNY MELLON ENTERPRISE ESG 63 RESPONSIBLE BUSINESS financial services sector. With the facilitation of the Depositary Receipts team, these meetings focused on the sustainability profile of those issuers and included ESG teams from both investors and issuers. Following the event, we conducted a perception study with the participants so that we can publish actionable advice to our full client base with our learnings on what works and what is lacking in ESG investor engagement from the point of view of all participants. Treasury Services BNY Mellon Treasury Services provides global payment, trade and liquidity services, enabling our clients to move money around the world quickly, safely and reliably. Our digital strategy is a leading force in reshaping the treasury industry, with an emphasis on enabling clients to leverage the latest digital solutions and technologies available. The investment BNY Mellon has made in digital Treasury solutions has proven to be both necessary and timely. Adaptations to COVID-19 highlight the ability of digital solutions to mitigate the disruption of traditional paper-based processes, in addition to the movement already underway as customers look for safer, faster ways to make and receive payments. As such, our use of the latest digital technologies helps safeguard customers, minimize risks and build trust. We harness the growing volume, velocity and variety of data entrusted to our Treasury business with a clear data strategy to assist organizations in their goals toward improved cash management. And we maintain effective data controls to meet regulatory requirements and client expectations. Through advanced data analytics and information management, BNY Mellon is building transparency, risk mitigation and market intelligence to help power our clients’ success. SPOTLIGHT Closing the Economic Opportunity Gap Across the United States, there are over 5,000 financial institutions, but only 149 of those are minority owned or controlled. 29 These institutions play a vital role in promoting economic viability, particularly in low- and moderate-income communities. BNY Mellon has made a $3 million deposit to supplement South Carolina-based Optus Bank’s investments and support its mission of investing in underserved communities. Our investment is part of BNY Mellon’s expanded relationship with Optus Bank through our participation in the U.S. Treasury Department’s Financial Agent Mentor-Protégé Program. This program facilitates voluntary relationships between the largest U.S. commercial banks as mentors and small and/or minority depositary institutions as protégés. The investment is directed to closing economic opportunity gaps by supporting investments in low- and moderate- income and minority communities. BNY Mellon’s new investment is part of our broader initiatives to support underrepresented communities through philanthropic engagement, workforce development activities and support of minority depositary institutions. Our relationship with Optus is seeding our enterprise-wide Community Banking approach to work with more such banks that are integral to community financial health, growth and resiliency. This growing initiative will enable us to play a more direct role in helping to reduce inequity in access to capital and close the racial wealth gap. It aligns with our vision of DEI as a Business Imperative, one of our DEI strategic pillars, and illustrates how we integrate it across our operating model. Learn more about our Treasury Services . 29 U.S. Bureau of Fiscal Service
BNY MELLON ENTERPRISE ESG 64 RESPONSIBLE BUSINESS PAPER-TO-DIGITAL JOURNEY In 2021, businesses and consumers expressed greater interest in migrating along the paper-to-digital continuum by transitioning to innovative solutions for sending and receiving funds and associated payment- related details between counterparties. These low- carbon solutions yield more efficient processing through automation, facilitate fraud prevention through account and identity-validation tools, and limit the potential for exceptions. Through active industry leadership and engagement with network operators and solution providers, we continue to advocate on our clients’ behalf for an optimal experience with Faster Payments solutions and to help them achieve their goals. BNY Mellon is making it possible for our bank, corporate and fintech clients to transact safely and securely in an increasingly digital environment by enabling clients to take full advantage of the following systems and applications. REAL-TIME PAYMENTS BNY Mellon’s Real-Time Payments 30 (RTP ® ) solution promotes immediacy and transparency in the global financial payments market. We enhance the payment experience by providing an affordable, scalable platform for electronic payments and receivables, help create economic opportunity, and advance financial inclusion. In 2021, we continued to support the growth of the Real- Time Payments Network operated by The Clearing House (TCH), which increased from 94 to 190 participating banks in 2021, expanding network reach to 61% of U.S. demand deposit accounts eligible to receive real-time payments. A pioneer in electronic billing, BNY Mellon facilitated the origination of the first end-to-end Request for Payment e-bill for business-to-consumer billing. We were also the first bank in the U.S. to launch and initiate 24/7/365 transactions through the RTP service in conjunction with TCH in 2017. We share our knowledge, collaborate through industry work groups and committees, and seek to introduce new use cases, such as Real-Time E-Bills and Payments. 30 R TP and the RTP Network are a registered service mark of The Clearing House Payments Company L.L.C. SPOTLIGHT Real-Time E-Bills and Payments In our ongoing efforts to make the global payments system more secure, efficient and equitable for all customers, BNY Mellon introduced Real-Time E-Bills and Payments functionality, with Verizon becoming the first company to adopt and send request-for-payment messages to its customers, marking the start of a new era in North American payments. These customers can now pay their bills immediately, at any time of day, 365 days a year, and enjoy enhanced security over other prevailing bill payment options. Gaining greater control of personal finances is especially valuable for the growing number of workers living with weekly paychecks or irregular income streams. For example, Verizon customers receiving a Real-Time E-Bill through their online or mobile experience can schedule a payment to be made at specific time in the future, such as a recurring payday or as an on-demand payout from a platform supporting a supplementary income stream, such as from ride-hailing or food delivery apps. This secure, convenient service empowers these customers to preserve income by better avoiding insufficient fund balances and resulting overdraft fees and other expenses. ACCOUNT VALIDATION SERVICES Recognizing that trust and integrity are essential to an effective global financial payments system and societal stability, BNY Mellon deploys resources and innovation to develop capabilities that combat rising electronic payments fraud. Now in its third year, BNY Mellon’s Account Validation Services (AVS) solution allows clients to validate account status and ownership before making a payment. 31 Businesses can confidently verify account status and ownership with bank-consortium data in real time through AVS, which leverages Early Warning Services’ National Shared Database SM . This service is compliant with the new Nacha Web Debit 31 Payment Chek is a trademark of Early Warning Services, LLC.
BNY MELLON ENTERPRISE ESG 65 RESPONSIBLE BUSINESS Pre-Validation Rule that went into effect in March 2021. This rule requires Originators of web debits to perform account validations in certain circumstances while also augmenting Automated Clearing House (ACH), wire and RTP with recipient verification. In parallel, we continue to address fraud prevention and improve the disbursement experience with our BNY Mellon Tokenized Payments ® with Zelle ®32 solution, which eliminates the need for clients to store or process payees’ bank account information and provides a fast, secure, convenient digital experience benefiting our clients and their payment recipients, both consumers and small businesses. Through these various services, we help our clients to stay on the forefront of fraud prevention and contribute to a more secure and stable financial system. CARBON FOOTPRINT REDUCTION As our clients increasingly use digital services such our Real-Time Payments and BNY Mellon Tokenized Payments with Zelle solutions, we call their attention to the environmental benefits of digital versus paper-based transactions. For the second year, Treasury clients are using our Carbon Footprint analytics tool to quantify and track the carbon footprint generated by the paper consumption of their treasury practice. This tool informs environmentally conscious clients of the potential benefits of transitioning away from paper-based payments and aligns with the widening array of digital alternatives that BNY Mellon provides. Our analytics for 2021 indicated that a 10% reduction of clients’ paper payment transactions would equate to removing approximately 125,000 pounds of carbon dioxide (CO2) from the environment. 32 Z elle and the Zelle related marks are wholly owned by Early Warning Services, LLC and are used herein under license. Markets BNY Mellon recognizes the vital role of market infrastructure as a catalyst for scaling sustainable finance. We support clients’ ESG strategies that seek to direct liquidity and flows toward sustainable outcomes, as well as support increasing market transparency on ESG data points and improving broader market integrity. SECURITIES FINANCE AND ESG INVESTING BNY Mellon’s securities lending program is inherently flexible and hence compatible with our clients’ ESG strategies, as it empowers clients to exercise discretion, applying a wide range of parameters to decide the scope of securities to be lent and which securities to recall for the exercise of voting rights, as well as setting acceptable collateral and cash reinvestment guidelines. At an industry level, BNY Mellon is actively engaged with trade associations, ESG labelling bodies, policymakers and regulators with regard to the development of globally relevant best practices for ESG compatible securities lending. LIQUIDITYDIRECT The BNY Mellon LiquidityDirect SM platform provides clients with investment options and ESG screening tools that enable them to align investments with their core values. Via LiquidityDirect, investors have access to a broad range of money market funds and other short- term investments, including funds 33 that: • Advance diversity and inclusion by executing trades through diverse broker/dealers • Conduct securities screening based on a range of ESG criteria for portfolio construction • Direct a portion of revenues or management fees to an organization where the fund and client’s ESG values align LiquidityDirect also helps clients assess eligible investment options to determine their impact by using our Focused Investing Application. Through relationships with ESG data providers and development of a questionnaire for fund companies focused on ESG, diversity and inclusion, the Focused Investing Application enables clients to compare investment options across a standard and normalized set of data. 33 De tails on each of the funds are set out in the funds’ prospectuses and SEC filings.
BNY MELLON ENTERPRISE ESG 66 RESPONSIBLE BUSINESS We help clients address ESG investment challenges, from non-standardization to securing meaningful insights on the environmental and social impact of their investments. By adding capabilities to embed clients’ ESG investing criteria in their short-term cash management, we are helping them to connect the dots between their values and investments. Capital Markets BNY Mellon Capital Markets, LLC (Capital Markets) is a full-service securities broker/dealer and a wholly owned subsidiary of The Bank of New York Mellon Corporation. Capital Markets provides underwriting services in debt and equity capital across public and private markets for a wide variety of issuers that are seeking to finance green, sustainable or impact projects. Over the past decade, impact investing has been widely embraced both as an investment strategy and an approach to addressing pressing social and environmental challenges. In June 2021, the Global Impact Investing Network estimated the size of the global impact investing market to be $715 billion. 34 Investors pursue impact investments as a way to generate financial returns with positive social and environmental impacts. THE FUTURE OF CAPITAL MARKETS In the wake of the pandemic and an unequal economic recovery, global capital markets participants recognize the need for reforms to build resilience, remain competitive in the face of innovation, and retain their customers’ trust. Through a new collaboration with the World Economic Forum’s Financial and Monetary Systems Platform, BNY Mellon has launched a series of multi-stakeholder conversations on creating a more inclusive and resilient financial system. In the first installment, BNY Mellon’s Chief Growth Officer Akash Shah outlined six issues that will define the future of capital markets . 34 Annual Impact Investor Survey 2020 , GIIN Clearance and Collateral Management BNY Mellon provides securities clearing and collateral management services in 35 countries and is the leading provider of U.S. government securities clearance and settlement services. In 2021, we introduced a number of ESG indices and ESG ratings for our online collateral schedule program, RULE ® . With these new capabilities, collateral receivers and providers can agree that only securities with a specified index, or that have a certain ESG rating, are acceptable as collateral. The functionality for the ESG ratings capabilities is drawn from a leading ESG data provider through BNY Mellon’s ESG Data Analytics platform, which assigns securities with environmental, social and governance scores, and then aggregates them into a final ESG letter rating, from AAA to CCC. iFlow ® Green Analysis As a leading global custodian, BNY Mellon is in the unique position of monitoring custody flows in foreign exchange and country level equities. Through our iFlow Green platform, we gain insights into the extent to which investors are accounting for sustainability factors. We share our findings in Introducing iFlow Green .
BNY MELLON ENTERPRISE ESG 67 RESPONSIBLE BUSINESS Investing in Communities In the United States, two BNY Mellon banking entities — BNY Mellon, N.A. and The Bank of New York Mellon — are evaluated in accordance with the Community Reinvestment Act (CRA) of 1977, the federal law intended to encourage banks to help meet the credit needs of the communities in which they operate. BNY Mellon’s banking subsidiaries in the U.S. meet their obligations under the CRA through investing, lending and performing community service in low- and moderate- income communities. Regulators have rated BNY Mellon, N.A. as “Outstanding” and The Bank of New York Mellon as “Satisfactory” during their most recent CRA performance evaluations. Each year, BNY Mellon helps build stronger, more resilient communities by providing financing for affordable housing and investing in small businesses. These efforts are complemented by our corporate giving and community impact activities . These monetary donations, in-kind services and employee involvement in certain qualified activities and organizations are tracked through our internal Community Impact Online portal. In 2021, CRA-qualified giving represented a $13.9 million commitment. FINANCING AFFORDABLE HOUSING One of the most significant ways BNY Mellon’s banking subsidiaries meet their CRA obligations is by providing financing to expand quality, affordable, and where possible, energy-efficient housing. Each year, BNY Mellon provides construction loans, letters of credit and equity in the form of low-income housing tax credits (LIHTC) to clients. By financing affordable housing developments, BNY Mellon helps clients provide quality affordable housing while simultaneously improving the quality of life in low- and moderate-income communities. 2021 K E Y DATA: AFFORDABLE HOUSING INVESTMENTS New LIHTC equity investments: 6 investments totaling $130.5 million Construction, line and letter of credit financing: $371.5 million Units produced (LIHTC investments only): 486 units SMALL BUSINESS INVESTMENT CORPORATION PORTFOLIO Small Business Investment Corporations (SBICs) are CRA-eligible investment vehicles authorized and regulated by the U.S. Small Business Administration. BNY Mellon’s SBIC portfolio consists of investments totaling $150.9 million in 20 funds. Responsible Financing and the Equator Principles The Equator Principles are an internationally recognized framework used by financial institutions to assess the social and environmental risks of their project financing 35 activities. Although BNY Mellon is not and does not plan to become active in project financing and is therefore not an Equator Principles signatory, we adhere to guidelines consistent with the Equator Principles for other lending activities, such as large- scale infrastructure projects. Our periodic lending portfolio evaluations against these guidelines show minimal exposure to environmental and social risk. 35 The E quator Principles uses the Basel Committee on Banking Supervision’s definition of project finance, which is “a method of financing in which the lender looks primarily to the revenues generated by a single Project, both as the source of repayment and as security for the exposure. This type of financing is usually for large, complex and expensive installations that might include, for example, power plants, chemical processing plants, mines, transportation infrastructure, environment, and telecommunications infrastructure.” Basel Committee on Banking Supervision, International Convergence of Capital Measurement and Capital Standards (“Basel II”), November 2005.
GLOBAL CITIZENSHIP With renewed resolve, BNY Mellon is embracing our opportunity to steward the world’s natural and financial capital. With a Future First SM focus, we’re examining the impact of climate change on our business, and the impact of our business on the planet. W e continue to work towards using natural resources efficiently, implementing thoughtful energy solutions, and addressing our role in climate change. We seek to help individuals and communities reach their full potential by cultivating a diverse, ethical supply chain, advocating on relevant issues, and protecting human rights. By advancing the welfare of our planet and people, w e contribute to the following SDGs:
BNY MELLON ENTERPRISE ESG 69 GLOBAL CITIZENSHIP MANAGING CLIMATE CHANGE As its physical, policy and financial implications reverberate with growing intensity, climate change is a key ESG topic of significant relevance to corporations. Regulatory agencies continue to closely monitor climate- related systemic risks and assess their current and potential impacts on overall global financial stability. Many financial institutions are moving to address climate-related risks and opportunities in a rapidly evolving environment. Many institutions are developing and offering climate products and solutions to support transitions. In a variety of ways, societal players are preparing for a reimagined future. Opportunity and Approach Our Climate Vision: To steward the world’s natural and financial capital by embedding climate considerations across our operations and by providing clients with a spectrum of climate-aligned solutions. We have built a Future First enterprise-wide climate change strategy that is aligned with broader organizational objectives such as our Enterprise ESG Goals and leading external frameworks such as the TCFD recommendations. Our strategy also expands on our Purpose-Driven Growth Agenda , as it helps advance our corporate objectives, values and behaviors, on a number of levels. The careful consideration of climate risk complements our risk management approach that has served us and our clients well. As a leader in the global capital markets, we are mapping a thoughtful approach to managing risks and seeking opportunities. Climate Strategy The enterprise-wide climate change strategy we developed includes five pillars, is aligned with broader organizational goals, and is underpinned by a governance structure and operating model with defined roles and responsibilities, access to data, employee training, and client engagement. The focus on climate strategy within our Future First ESG approach communicates the tone at the top, helps drive innovation and change throughout the organization, and supports cross-functional collaboration. It additionally creates a more coordinated, central management structure to support the achievement of our climate change-related ambitions.
BNY MELLON ENTERPRISE ESG 70 GLOBAL CITIZENSHIP Strategic Focus Areas PILLARS Enterprise Integration Climate Risk Management Net Zero Exploration Supporting Client Transitions External Leadership Enablers—Governance, Data and Training 1 2 3 4 5 ENTERPRISE INTEGRATION We are considering climate change as a part of our business strategy and as a culture builder rather than solely a social responsibility. Thus, we have begun to embed a climate lens into the way in which we operate. We have begun and plan to continue formally applying this lens across key areas of the business, including in various due diligence processes, client service, risk management and employee professional development. CLIMATE RISK MANAGEMENT We are supporting the identification and assessment of climate-related physical and transition risks as a driver across all six enterprise risk categories through enhanced global risk frameworks, the Three Lines of Defense risk approach, and risk management policies and processes. NET ZERO EXPLORATION We are planning to engage select business functions and lines of business to understand the impacts of a global corporate net zero commitment across our operations and consider potential pathways that may align with our business model and specific types of banking and financial services. SUPPORTING CLIENTS IN THEIR TRANSITION We are developing new products and services that can help customers transition to a low-carbon economy by addressing changes in technology, markets and regulation, and facilitating their journey. EXTERNAL CLIMATE LEADERSHIP We are working to establish climate leadership as a custodian through thought leadership, digital enablement and stakeholder engagement to better prepare the industry for the effects climate change will have on business. Our strategy utilizes the TCFD recommendations and other frameworks to formalize the integration and communication of climate change-related matters both within our organization and externally to stakeholders. The TCFD recommendations have also shaped the initial framework of our multiyear project to identify and disclose impacts on our business. Incorporating TCFD and supervisory frameworks has enhanced our understanding and management of climate risk exposure, and helped us prepare for live and pending regulations. As we continue along our journey to embed ESG and climate considerations across our business, we may adjust our reporting trajectory if necessary. Learn more . As both a business and values-driven ambition, our enterprise-wide climate strategy delivers other significant organizational benefits. We believe inspiring employees toward climate innovation helps cultivate a sense of belonging and purpose. Unlocking our people’s passion for the environment builds excellence and courage to lead in developing climate change solutions. Given the global concern surrounding climate change, the opportunity to help tackle complex climate challenges as part of a shared effort holds wide appeal to the current and next generation of clients and employees. Our people welcome the opportunity to make bold moves by developing climate-focused products and solutions such as our ESG Data Analytics that are focused on creating new value for clients by helping them grow and become more efficient.
BNY MELLON ENTERPRISE ESG 71 GLOBAL CITIZENSHIP NEW IN 2021 CONTRIBUTING TO COP26 To contribute to and learn from the global dialogue on climate readiness and response, a team of BNY Mellon leaders joined the COP26 summit in Scotland. There they gathered with representatives from governments, nongovernmental organizations and the private sector, acting together to accelerate action toward the goals of the Paris Agreement and the UN Framework Convention on Climate Change. BNY Mellon Senior Executive VP and Head - International Hani Kablawi joined a panel on OS- Climate, announcing BNY Mellon’s commitment to using its reach, market influence and resources to advance its open-source ESG data platform. Climate-Related Issue Governance Formal governance and oversight responsibilities for climate-related issues sit ultimately with our Board. Operational management responsibilities related to climate risk are delegated to the management body through the Executive Committee and via our Three Lines of Defense approach. Local management for subsidiary legal entities replicate these responsibilities for specific consideration aligned to their respective business and risk profiles. The work to integrate climate considerations across our business is a part of our larger efforts to embed an ESG lens into the way we operate. In 2021, our internal TCFD Working Group participated in the reporting of this work as a component of the public ESG reporting processes driven by the Enterprise ESG team. The Executive Committee received reports on the work of the TCFD Working Group and reviewed that information prior to its presentation to the CGNSR Committee of the Board, which is the highest-level body with purview over climate considerations. In addition, the boards of directors of the various legal entities within the broader BNY Mellon organization are consulted for strategic input and presented with updates on a regular basis. NEW IN 2021 COMMITTEE MANDATES Committees with oversight responsibilities for certain of BNY Mellon’s legal entities have taken on specific allocated responsibilities with respect to climate change risk, with further committee mandates to be reviewed and updated in 2022. We are developing ongoing reporting on climate change-related risks to support the Board and its delegated committees across the first and second lines of defense. Escalation routes are now in place to consider reporting at an aggregate level and to address identified climate change risks through various internal processes and frameworks. These include the assessment of new clients, third-party vendors and inter-affiliates, as well as new product development and business process changes, to ensure that potential climate change risks are identified and managed at the point of origination. Each of these assessments are being embedded in business-as-usual processes used to assess all potential sources of risk. Climate Risk Management Since BNY Mellon plays a vital role in global financial markets, effective risk management is critical to our success. Risk management begins with a strong risk culture, our system of values and behaviors that influence the risk decisions made by managers and employees. We reinforce our culture through policies and procedures, along with our Code of Conduct. Our risk culture is grounded in BNY Mellon’s values: • Passion for Excellence • Integrity • Strength in Diversity • Courage to Lead Our business model requires taking on risk intelligently in a responsible and measured manner, and balancing risk relative to return to achieve our strategic objectives and business plans. Because climate-related changes and events can directly impact the company’s operations, BNY Mellon is committed to understanding and addressing the risks posed by climate change by employing a comprehensive risk management approach as part of our existing Risk Management Framework. Our Framework has always considered certain impacts of climate change through processes such as Operational Risk and Business Continuity/Operational Resilience; see the Enterprise Resiliency section in this report. As we evolve our approach, we now explicitly consider the impacts of climate change-related financial, physical and transition risks across our corporate-wide portfolio.
BNY MELLON ENTERPRISE ESG 72 GLOBAL CITIZENSHIP NEW IN 2021: EXPANDED RISK MANAGEMENT FRAMEWORK With the goal of considering climate change risks in a structured and robust manner, BNY Mellon has expanded our Risk Management Framework to provide an objective basis to identify and consider climate change-related risks within decision-making. This Climate Risk Framework is being integrated into existing global risk processes and addresses all risk categories (Strategic, Credit, Market, Liquidity, Operational and Model risks). Based on these foundational changes, the impact of climate change risks is increasingly incorporated into business-as-usual considerations in risk appetite, the impact on financial and nonfinancial risk categories, scenario analysis and stress testing, operational resilience, and potential implications for capital and liquidity requirements. Enhancements have included embedding climate risk assessments in applicable policies, each enterprise risk category framework, risk identification, quantification and mitigation, assessment of new products and services, client selection, credit analysis, third-party vendor review, governance forums and reporting, capital, stress testing and scenario analysis, and resiliency considerations. The understanding, identification, measurement and mitigation of risk are essential elements of our global risk frameworks. The framework is founded upon a strong risk culture that incorporates both effective governance and key risk management elements. A number of risk management activities are prescribed through this framework. These activities include, but are not limited to: • Establishing Risk Appetite Statements at corporate, business line and legal entity levels • Considering all six principal risk categories that form the enterprise risk taxonomy (Strategic, Credit, Market, Liquidity, Operational and Model risks) • Employing enterprise- and business line-level risk assessments • Identifying and measuring risk • Utilizing stress testing and scenario analysis PHYSICAL AND TRANSITION RISKS As an extension of our driving philosophy to Consider Everything SM , we are committed to understanding and addressing potential internal and external sources of risk. Within our approach to holistic risk management, we recognize climate change-driven risk, both physical and transition, as a potential material risk driver. A risk driver is an event that leads to a consequential impact on BNY Mellon. For instance, climate change leads to an increase in physical risks that could then have an impact across a range of different risk types in various ways. Climate change-driven risk is therefore an overarching driver of risk that may impact all risk categories to which we are exposed through the ongoing execution of our business strategy. Climate risk includes both physical risks of more extreme and frequent weather events caused by climate change and transition risks as the world converts to a lower-carbon economy, as committed to through the 2015 Paris Agreement. BNY Mellon is exposed to climate-related physical and transition risks, both directly and indirectly, through our client base and business activities. Managing BNY Mellon’s operations appropriately to address climate risk is vital to operational and financial resiliency and stability. Physical Risk. This involves risk from weather-related events such as storms, flooding, wildfires and droughts where the likelihood and intensity of such events is increasing due to anthropogenic global warming. Physical risks may result in the following: damage to physical premises and infrastructure of BNY Mellon, our clients and other stakeholders; impact on operations; disruption to service providers; availability of resources; and supply chain disruptions. Both acute and chronic physical effects are considered as part of the risk framework and are defined as follows: • Acute Physical Risk. Refers to event-driven extreme weather impacts; disruptions to operations, transportation, supply chains, etc.; damage to physical assets; and impacts on insurance liabilities • Chronic Physical Risk. Encompasses longer- term shifts in climate patterns, e.g., rising mean temperature; water stress; degradation or limitations on resource availability, e.g., labor, natural resources, etc.
BNY MELLON ENTERPRISE ESG 73 GLOBAL CITIZENSHIP Transition Risk. This refers to risks associated with the transition to a low-carbon economy. These risks will include changes to fiscal and environmental policy, regulation, legislation and technology, as well as investor and consumer sentiment changes that may impact the financial, legal, strategic and reputational risks of our organization. As a result, climate change risk management within BNY Mellon begins by assessing how climate change-driven risk may impact either our organization or our clients. The risk management framework in place requires and supports the identification, reporting, escalation and mitigation of all material risk drivers, including climate change risk. THREE LINES OF DEFENSE Management of climate change-driven risk is implemented in line with our organizational structure and follows the Three Lines of Defense model of our Risk Management Framework. The first line of defense is the business. Each of our businesses takes and owns the risk associated with its activities, and manages the risks and related control processes and procedures. The Risk Management and Compliance functions are the second line of defense, and the third line of defense is Internal Audit. The first line of defense is responsible for identifying and mitigating all risks, including climate risks. As the second line of defense, the Risk and Compliance function is responsible for supporting, reviewing and challenging the first line and has responsibility for the design and implementation of the global risk framework. The third line of defense, our Audit function, provides independent review of any aspect of implementation. NEW IN 2021 CLIMATE RISK TRAINING To support the implementation of the Climate Risk Framework and embed governance oversight responsibilities, we conducted training sessions and provided materials to boards, relevant committees and select teams across all three lines of defense with specific climate risk management obligations. The program outlined the risk management requirements and explained the importance of climate risk within business-as-usual activities. Participants were introduced to risk management tools available for identifying, assessing and managing climate risks. The training encourages participants to lead by example and set the tone to support a culture that institutionalizes appropriate risk management behavior with respect to climate risk. Risk Taxonomy. To ensure risks are consistently identified and categorized across the company, BNY Mellon uses an enterprise-wide risk taxonomy that considers risk across our six enterprise risk categories: Strategic, Credit, Market, Liquidity, Operational and Model risks. This Risk Management Framework enables consistent risk identification across the company. Through this existing framework, climate change-driven financial, physical and transition risks are assessed as risk drivers impacting across all risk types. Risk Appetite. Our Corporate Risk Appetite Statement expresses the aggregate level of risk we are willing to assume, within risk capacity constraints, in order to meet strategic and business objectives. We determine risk appetite by balancing risk and return, considering regulatory, capital and liquidity needs and maintaining a balance sheet that remains resilient throughout market cycles. Our Risk Appetite Statement currently allows for the monitoring and measurement of the potential impact of climate change as a risk driver across all six enterprise risk categories. The Corporate Risk Appetite Statement includes requirements that reinforce the need to ensure climate risk is incorporated into risk assessments and risk-based decision-making. These requirements are cascaded to all lines of business, including Investment Management, Market and Wealth Services, and Securities Services business segments, and all material legal entities. The Board approves the Corporate Risk Appetite Statement, including risk appetite limits for major risk categories. Although limits are not set with specific consideration of climate change (or other risk drivers), the limits in place do provide constraints on any buildup of climate risk. Risk Materiality. The Risk Management Framework employs a risk materiality matrix, which is a corporate- wide, risk-specific benchmark that provides a consistent measurement mechanism for assessing risk likelihood, significance and impact. Risks associated with climate change are assessed using this common benchmark along with all other risk drivers.
BNY MELLON ENTERPRISE ESG 74 GLOBAL CITIZENSHIP RISK IDENTIFICATION As a driver of risk, climate change may have an impact on all financial and nonfinancial risks to which BNY Mellon is subject. The effects of climate change may occur independently, or as part of a broader risk event. BNY Mellon uses several risk identification processes, which are embedded within the management of each major risk type as identified through our risk taxonomy. The potential financial impacts of climate change risk are currently identified through qualitative subject matter expert assessment within the first and second lines of defense. Risk identification forms the foundation for setting our risk appetite and determines Key Risk Indicators (KRIs) for ongoing monitoring and management. Time Horizons. Given the nature of our business model, the majority of assets and liabilities are short-dated in nature and we have limited exposure to risks occurring over longer time horizons. Nevertheless, assessment of risk materiality is considered across short to long time horizons depending on the risk type. Stress testing and business model risk analyses conducted at the European Bank 36 and the London Branch of the Institutional Bank, 37 explicitly consider the full time horizon provided for under The Network for Greening the Financial System (NGFS) scenarios up to 2050. Although assessments of potential financial impacts or in identifying mitigating actions may be over a shorter time horizon as described, elements of the business potentially subject to higher risk are time independent. We recognize that both transition and physical risks may manifest in the short term. Therefore, KRIs are specifically considered without reference to the time horizon. The KRIs either: • Explicitly include a long-term time horizon (such as stress testing) • Are time independent (such as assessment of higher risk sectors or geographies) • Consider an event that may occur at any point in the future but applied to the portfolio as it stands at the point of assessment (such as point-in-time fair-value stress loss assessments) 36 The Bank o f New York Mellon SA/NV 37 The Bank o f New York Mellon MATERIALITY ASSESSMENT FINDINGS BNY Mellon’s initial materiality assessment of climate change-driven risks indicates that the corporate-wide risk profile is low, given the nature of business offerings, operating model, strategy, balance sheet and revenue model. Nevertheless, our initial assessment identified the following as the most material potential sources of climate change-driven risk over both the near and longer term: • Revenue concentrations to clients in high-risk sectors and geographies, which may impact future revenue generation 38 • Reputational impacts through market, customer or societal reaction to our strategy, business model, the clients we do business with or the third parties we rely on for service provision, among others • Credit and investment portfolio on balance sheet exposures to high-risk sectors and geographies, which may generate higher credit risk losses or increased provisions 38 • Strategic risks relating to strategic direction, revenue reliance, cost of transition, and client and staff retention, which may impact the viability of the business model in future • Operational risks covering a range of operational risk types, which cover both physical and transition risks as well as potential service and market disruption that may lead to either direct operational losses or indirect effects on service provision • Fair-value adjustments relating to potential market risk impacts on investment portfolio holdings and the trading book While both physical and transition risks as considered in these assessments cover a range of potential events and market, policy or other changes, reputational risk related to climate change is also specifically identified as a key potential risk to BNY Mellon. 38 High risk sec tors, as used to segment both revenue and on balance sheet asset risks, are derived from publicly available industry segmentations. These segmentations consider a range of factors relating to both physical and transitional risks, including GHG emissions. Due to the nature of BNY Mellon’s business model and balance sheet, which incorporates high asset credit quality and well diversified income flows, aggregate measures of climate risk are currently more informative for internal, risk-based decision-making. As such, specific climate risk indicators such as counterparty-specific GHG emission levels are not currently used in isolation to measure risk but will be given more prominence over time as companies and third-party data providers provide more consistent and decision-useful GHG emissions data.
BNY MELLON ENTERPRISE ESG 75 GLOBAL CITIZENSHIP RISK MEASUREMENT AND REPORTING Based on an initial assessment of potentially material climate change impacts on those risks defined in the risk taxonomy, we defined a measurement approach using KRIs, covering both physical and transition risks in most cases. Ongoing assessments, as they may lead to the refinement of BNY Mellon’s material risks, will inform the development of further or more refined indicators over time. We will use these KRIs to provide insight on the magnitude of potential climate change risk drivers as they may impact on risk profile. Our KRIs include: • Measures of credit risk through monitoring of exposure to sectors or geographies that are particularly exposed to both physical and transition climate change risks • Measures of the impact of climate-related market or macroeconomic events, through aggregate stress testing and tailored sensitivities used to assess market risk in the trading and banking book • Scenarios used to assess potential operational risk tail events, including monitoring of observed climate-related events • Assessments of the concentration of revenue to clients in higher-risk sectors or geographies • Assessments of operational locations or third- party service providers potentially exposed to more vulnerable locations • Regular benchmarking of peers and employee attitudes to identify strategic climate trends NEW IN 2021 INTERNAL REPORTING We have developed an internal climate-related KRI reporting process and began reporting based on available data in 2021. This is initially focused on the most potentially material risks to BNY Mellon and includes the identification of on-balance-sheet exposures to clients at potentially higher risk of both physical and transition climate change effects. Initial quantification demonstrates that BNY Mellon has limited exposure to these risk areas at present. Ongoing measurement and reporting will be used to support management discussion and the development of risk strategy with respect to climate change-driven risks. In 2022, we plan to provide aggregate reporting across all KRIs to senior management and governance forums that hold broad risk management responsibilities. In addition, we plan to further embed climate change risk into existing risk assessment processes. Key processes that will directly and explicitly incorporate climate risk assessment include: • Client due diligence and underwriting processes • New product approvals • Business process changes • Location strategy • Third-party vendor assessment • Sub-custodian onboarding The impact of climate change-driven risk on business strategy is therefore predominantly focused on changes to strategy at the micro level, i.e., understanding how climate change-driven risks affect individual decision- making as part of the development of clients, products and services. Scenario Analysis and Stress Testing BNY Mellon continues to consider the impacts of climate change across different BNY Mellon stress testing processes, including the Internal Capital Adequacy Assessment Process (ICAAP) at the European regional level and Comprehensive Capital Analysis and Review (CCAR) war gaming process at the corporate level. NEW IN 2021 EXPANDED ANALYSES BNY MELLON EUROPEAN BANK AND UK BANK 39 While many of the effects of climate change are expected to manifest over a multi-decade time horizon, including global, regional and local implications of rising temperatures, some impacts such as natural disasters are expected to manifest over a shorter time horizon. As part of the 2021 ICAAPs, BNY Mellon considered two factors as drivers of energy transition risk: (1) the abrupt implementation of stringent policy measures that aim to mitigate the adverse impact of climate change and 39 The Bank of New York Mellon (International) Limited
BNY MELLON ENTERPRISE ESG 76 GLOBAL CITIZENSHIP 1. Confidence Shock - Uncertainty regarding government policies to combat climate change triggers a drop in the confidence of consumers, producers and investors. 2. Technology Shock - Investment in the research and development of renewable energy generation and storage is higher than ever, boosting the share of renewable energy in the energy mix and creating the potential for technological breakthroughs. 3. Policy Shock - Policymakers are pressured into taking abrupt, stringent measures against climate change, triggered by, for example, (i) a natural disaster, (ii) legal action holding policymakers accountable for climate change, or (iii) a strong reaction by policymakers in response to the realization that the time to act is running out. 4. Double Shock - Climate change mitigation policies and progress in renewable energy technology turn out to be mutually reinforcing. Within each scenario, transition paths included macroeconomic impacts with specific industry sector financial impacts (haircuts). Consistent with the 2020 analysis, the 2021 European and UK ICAAP processes were used to analyze the financial impacts from climate change (both physical and transition risks) by assuming static strategic and client behaviors. Additional climate change impacts were considered through the materialization of operational risks, such as system outages caused by natural disasters in various locations. The 2021 assessments continue to indicate our European and UK banks have sufficient capital to withstand the four scenarios analyzed, over the given time horizons. These assessments are now being further enhanced for the 2022 ICAAP to reflect the NGFS scenarios and assumptions to better understand the impacts of climate change with industry standard scenarios. (2) technological breakthroughs that lower CO2 emissions but also disrupt parts of the economic system through a process of creative destruction. As part of our stress testing exercise, the European Bank and the UK Bank enhanced their analysis over the 2020 exercise by using four different academically defined climate change scenarios for the impact analysis. These scenarios are described below: Passive Yes No Active Technological breakthroughs Policy stance Technology shock The share of renewable energy in the energy mix doubles, due to a technological breakthrough Confidence shock Corporations and households postpone investments and consumption, due to uncertainty about policy measures and technology Double shock The carbon price rises globally by USD 100 per ton, due to additional policy measures The share of renewable energy in the energy mix doubles, due to a technological breakthrough Policy shock The carbon price rises globally by USD 100 per ton, due to additional policy measures Source: An energy transition risk stress test for the financial system of the Netherlands; Robert Vermeulen, Edo Schets, Melanie Lohuis, Barbara Kölbl, David-Jan Jansen and Willem Heeringa, 2018 De Nederlandsche Bank N.V.
BNY MELLON ENTERPRISE ESG 77 GLOBAL CITIZENSHIP CORPORATE-LEVEL CLIMATE HEAT MAPPING During the second half of 2021, our Capital Adequacy team conducted an initial climate change heat-mapping exercise to provide insights into areas of climate vulnerabilities to help inform initial scoping for stress testing activities. This team, in conjunction with a third party, assessed the potential impact of physical risk on samples from the following portfolios: Residential Mortgage, Commercial Real Estate, Select Non-agency MBS; and BNY Mellon’s Facilities and Data Centers. Capital Adequacy also assessed the potential impact of transition risk on samples of the following portfolios: Commercial Real Estate; Corporate Loans; Investment Portfolio; and Select Investment Management funds. We relied upon climate change scenarios provided by industry standard third parties such as NGFS, the International Energy Agency (IEA) and the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC). Climate change scenarios helped explain macroeconomic and market outlooks under three potential warming pathways: orderly transitions, disorderly transitions and hothouse world. Using the results of these analyses, we developed Climate Risk Heat Maps based on potential outcomes of multiple climate transition pathways. The resulting heat maps provided “spot checks” of our current vulnerabilities. The heat maps were used to develop an initial vulnerability assessment ranking five asset types against incremental climate risk impact. Climate-Related Enterprise Resiliency BNY Mellon recognizes that climate change increases inherent risk, requiring additional compensating controls and solutions to counter the increasing frequency and severity of climate-related events that challenge the resiliency of our business. Given our global footprint, we are committed to managing and monitoring potential climate-related impacts as part of our resiliency plans, which help prepare us to maintain business continuity in the face of disruptions. As part of our resiliency planning, we take the following climate-related risks and challenges into consideration: • Rising sea levels in areas where BNY Mellon has a significant number of employees, such as New York City, London, Houston, Chennai, Hong Kong and Singapore • Increased frequency and severity of natural disasters, for example, storms, wildfires and droughts, and the subsequent political, economic and government instability associated with these challenges • Increased stress on public utilities, which is often exacerbated by growing demands, combined with the impacts from storms and natural disasters BNY Mellon mitigates these additional risks and challenges by implementing various solutions that aim to maintain continuity, such as: • Exercising cross-regional work shift strategies, in the event of wide-area disruptions, as part of our Business Continuity Planning • Geographically diversifying our physical locations, including office facilities and data centers • Hardening our physical locations to better endure physical damage caused by natural disasters • Maintaining appropriate engagement with government agencies in jurisdictions where we have a physical presence to facilitate timely exchange of relevant notification and other emergency management information BNY Mellon’s Incident and Crisis Management team, working together with others in our Enterprise Resiliency Office and throughout the organization, regularly monitors for incidents that could result in a disruption, including the climate-related natural disasters highlighted above. This monitoring aims to limit potential impact and disruption by supporting a timely response to, and effective management of, these types of incidents.
BNY MELLON ENTERPRISE ESG 78 GLOBAL CITIZENSHIP FACILITIES MANAGEMENT OPERATIONAL RESPONSE TO CLIMATE CHANGE RISKS BNY Mellon recognizes that climate change is amplifying operational risk exposure due to disruptive weather patterns and events. Additionally, precipitation and temperature extremes including floods, fires and storms prompt companies to ensure that strong management and resiliency plans are in place. Responses to these events have implications for operational stability and, more broadly, the reputation of the industry. Our enterprise resiliency program addresses physical infrastructure risks through investments in emergency power generation, flood planning, geographically distributed workforce balancing, and backup systems in technology and data centers. We evaluate potential climate-related impacts such as chronic sea level rise, stress on public utilities, weather events, shifting government regulations, and social and economic instability in locations where we operate. Acute physical dimensions including seismic properties, exposure to storms, and 500-year floodplain evaluations (zones that have a one in 500, or 0.2% chance of experiencing a flood occurrence in a given year) are assessed as potential risks that should be mitigated and are addressed as necessary. BNY Mellon incorporates climate risk management strategies into our operational controls. For example: • At BNY Mellon’s Corporate Headquarters in New York City, a flood resiliency project included hydro barrier installation planning, the elevation and relocation of electrical systems, and the installation of additional pumping equipment • Backup power generation is considered and installed at various locations • Our data centers are sited to minimize climate- related risks and proximity to other potential physical risks Because the implications of climate change are evolving, we continuously evaluate potential emerging impacts and develop corresponding appropriate actions. In 2021, BNY Mellon took two key steps in support of this. BNY Mellon has conducted a detailed climate risk and resiliency assessment of our real estate portfolio in both its current and future states. This study has identified potential vulnerabilities within our physical real estate portfolio that could impact business continuity and impose costs on BNY Mellon. Vulnerabilities to extreme weather events have been recently observed, such as the 2021 Texas winter storm and subsequent power crisis, and 2021 Luxembourg flood. As a result of this assessment, we have initiated steps to increase resiliency and address vulnerabilities at the identified locations. Additionally, we will continue to review and update relevant internal policies as necessary to address potential risk assessment findings, for example, those related to the construction of new spaces, specific geographic analysis approaches, backup power generation systems, flood hardening and existing equipment maintenance procedures. Climate-Related Solutions to Serve Clients Guided by our corporate purpose, we are committed to helping clients manage their ESG-related risks and opportunities, including those related to climate. We continue to develop and offer ESG solutions that: • Help clients invest responsibly • Provide them with the global reach, data and analytics to make better-informed Responsible Investment decisions • Facilitate sustainable debt and equity financing • Provide innovative investment solutions and help clients understand the effects of climate change on their portfolios ASSET SERVICING AND DIGITAL Our asset servicing clients are increasingly focused on how to invest or create products that help to mitigate climate-related risk or align to new opportunities associated with green or climate-positive impact investment. We offer a powerful solution: our ESG Data Analytics tool, which offers the ability to drill down into specific climate-related metrics.
BNY MELLON ENTERPRISE ESG 79 GLOBAL CITIZENSHIP DEPOSITARY RECEIPTS ESG professionals within our Advisory team facilitate communication between issuers, investors and key ESG intermediaries of depositary receipts, engaging directly with investors in order to ascertain how they incorporate climate and ESG factors into their investment approach and feed that back to clients. Learn more . CORPORATE TRUST We support issuers in raising capital through sustainable bonds, including green, social and impact bonds, that fund projects with social and environmental benefits, such as combating climate change. Learn more . INVESTMENT MANAGEMENT Our Responsible Investment approach varies by our eight independently governed specialist investment firm, but the effective stewardship of our client assets is common to all. Two of our firms are signatories to the Net Zero Asset Managers initiative. Learn more about Investment Management . ENVIRONMENTAL SUSTAINABILITY Investors, clients and employees expect the business community to exhibit stronger leadership on environmental and climate action. These expectations present numerous opportunities, because taking action on climate change can help businesses grow, innovate, create new jobs, encourage investment and adapt to the challenges of a changing planet. Reducing emissions, conserving resources and operating more responsibly can lower businesses’ operating costs and attract new customers — ultimately helping maintain a competitive advantage locally and globally. 40 Our Opportunity and Approach From landmark EU climate change legislation to the U.S. rejoining the Paris Agreement, movement toward decarbonization gained momentum during 2021. We strive to improve our environmental impact and addressing climate-related risks and opportunities through an approach to sustainability that spans our business, including a focus on the management of global operations and our commercial real estate portfolio. BNY Mellon’s Environmental Sustainability Policy Statement , which was updated in 2021, sets forth the scope of our efforts, guiding principles and commitments. 40 COP26 sees UK businesses lead the world in climate change commitments , www.gov.uk
BNY MELLON ENTERPRISE ESG 80 GLOBAL CITIZENSHIP 2021 ACHIEVEMENTS Carbon Neutral: Achieved carbon neutrality in our operations for the seventh consecutive year * Global Paper Neutrality: Achieved paper neutrality in our operations globally in 2021, building on four years of paper neutrality in the U.S. and India, via PrintReleaf, a certified offset program Climate Leader : Recognized on CDP’s Climate Change “A” List for the ninth consecutive year ** Renewable Energy: Commissioned solar installations at two owned sites within our property portfolio * F or Scope 1 and Scope 2 GHG emissions, including our data centers, as well as Scope 3 business travel emissions. ** T he A List 2021, CDP 2025 Environmental Sustainability Goals We continue to work toward our Enterprise ESG 2025 goals and have made substantial progress in the past year. The COVID-19 pandemic and resulting remote work environment again drove material reductions in our emissions, waste and water consumption, although some normalization is expected in 2022. Enterprise ESG 2025 Environmental Sustainability Goals Maintain commitment to environmental sustainability, including effectively managing natural resource use KPI: Reduce Scope 1 and Scope 2 GHG emissions by 20% from a 2018 base year, including data centers, in line with Science-Based Targets (SBTi) methodology Progress: Reduced Scope 1 and 2 emissions by an incremental 12% in 2021 and 36% cumulatively * KPI: Maintain carbon neutrality commitment ** Progress: Achieved carbon neutrality ** KPI: Divert 80% of office waste from landfills Progress: Achieved a 75% diversion rate KPI: Target zero waste to landfills for technology equipment Progress: Zero technology waste sent to landfills KPI: Achieve paper neutrality in the U.S. and India Progress: Expanded the scope of our paper neutrality commitment from U.S. and India to a global commitment. Achieved paper neutrality and adopted a paper-free office concept * KPI: Drive water use reduction in building operations Progress: Reduced water use by 60% relative to 2015 baseline * * T he COVID-19 pandemic and resulting remote work environment helped drive material reductions. ** F or Scope 1 and Scope 2 GHG emissions, including our data centers, as well as Scope 3 business travel emissions.
BNY MELLON ENTERPRISE ESG 81 GLOBAL CITIZENSHIP Emissions Reduction In 2019, BNY Mellon set a Scope 1 and Scope 2 GHG emissions reduction target of 20% by 2025, including data centers, relative to a 2018 base year. This Scope 1 and 2 target aligns with the SBTi methodology aimed at limiting increases in global warming to well below 2ºC. We remain committed to meeting or exceeding this target. In 2021, we reduced such emissions by 12%, including data centers, contributing to a 36% cumulative abatement since 2018. Reductions in our 2021 Scope 1 and 2 emissions were the result of COVID-19 impacts on our workplace, a decrease in our office space, continued investment in energy efficiency initiatives such as improvements in building controls and data center cooling systems, and improvements in the carbon intensity of the electricity grid around the world. We are making targeted investments in LED lighting in many of our offices and are progressing solar panel installations at two owned sites within our property portfolio to further reduce our emissions in future years. Carbon Neutral Since 2015 We have been carbon neutral for our global direct Scope 1, indirect Scope 2 and Scope 3 business travel emissions since 2015. Our three-part approach for achieving carbon neutrality includes: (1) reducing our energy use and related GHG emissions, as described above; (2) procuring renewable electricity through Renewable Energy Certificates (RECs); and (3) purchasing carbon offsets to compensate for any remaining emissions in our footprint. In 2021, we sourced 99% of electricity used to power all global locations, including data centers, from renewable sources, generally in the form of RECs – accepted market-based legal instruments that convey the environmental attributes of renewable energy generation and use. To compensate for operational emissions that cannot be eliminated through energy efficiency and renewable electricity, we purchase carbon offsets through clean energy financing and carbon sequestration initiatives. In 2021, 50% of our carbon offsets were directed to the funding of renewable energy projects globally, 25% funded grassland conservation and reforestation projects in the U.S, and 25% funded solar water heating in India. Data Center Emissions As BNY Mellon undergoes a digital transformation, our usage of data has grown, which requires additional data center support and increases our energy use. In 2021, our enterprise data centers accounted for approximately 46% of the electricity used in our global properties, equivalent to 42% of our total Scope 1 and Scope 2 carbon emissions, making them a critical component of our strategy to meet emissions targets. In our daily management of the enterprise data centers, the power usage effectiveness (PUE) is continuously monitored to confirm that each facility is operating efficiently. To achieve our five-year goal to reduce GHG emissions, we offset our increased energy use by replacing legacy mechanical and electrical equipment with newer and more energy-efficient systems. Independent Verification BNY Mellon engages an independent, third-party organization to verify our Scope 1, Scope 2 and Scope 3 business travel emissions, renewable energy purchases and carbon neutrality status at a limited assurance level (see the full verification statement ). The verification of o ur emissions lends transparency and confidence in our methodology, and enhances our ability to track energy- efficiency opportunities. A CDP Climate Change Leader In 2021, BNY Mellon was again named to the Climate Change “A List” for our actions to reduce emissions, mitigate climate risks and develop thoughtful initiatives. Over 13,000 companies responded to CDP’s 2021 climate change questionnaire, and only 200 achieved the Climate “A List.” BNY Mellon is one of two U.S.-based financial services companies to earn Climate “A List” and is the only U.S.-based financial institution to earn this ranking from CDP for nine consecutive years. 41 WATER CONSERVATION We decreased water consumption by 60% in 2021 relative to a 2015 baseline, though a large portion of this reduction was related to lower office occupancy due to the COVID-19 pandemic. We achieved sustained reductions in water consumption through upgrades to high-efficiency fixtures during renovations, updates to irrigation systems, leak detection and monitoring of mechanical equipment. 41 The A List 2021 , CDP
BNY MELLON ENTERPRISE ESG 82 GLOBAL CITIZENSHIP Waste Management In light of the growing environmental impacts related to waste in general and the accumulation of waste in landfills and corresponding release of methane, we look for ways to continually improve our waste diversion. Our approach includes recycling, composting, incineration at waste-to-energy plants, employee education, and thoughtful receptacle layout designs and signage. Beyond managing office waste, we prioritize reusing and recycling used furniture and non-technology equipment where possible. Recognizing the negative environmental impacts and potential health hazards associated with improper disposal, we maintain a no-landfill philosophy for end-user technology waste. In 2021, we recycled or properly disposed of over 220 tons of technology equipment. Through these combined efforts, we recycled 74% of our waste in 2021, which contributed to our landfill diversion rate of 75%. MANAGING PRINTING AND PAPER USE Due to the pandemic-related drop in office occupancy and remote working, BNY Mellon’s use of paper has decreased sharply. In line with our Purpose-Driven Growth Agenda and 2025 environmental sustainability goals, our new Managed Print initiative will help maintain that trend by encouraging a culture of “conscious printing.” As employees have become more accustomed to using collaboration tools and devices to communicate without paper, we are adopting a no-print philosophy under which materials would be printed on an exception- only basis. This campaign aligns with a concurrent global vendor and printer review, which will result in the reduction in multifunctional devices. We anticipate a host of environmental benefits from the utilization of fewer machines and corresponding reduction in energy use, ink cartridges and paper. This Managed Print initiative builds on our track record of five years of paper neutrality in the U.S. and India through conservation and a partnership with PrintReleaf, a certified offset program that plants a number of trees equivalent to the pages printed. In addition, we recycled 2.8 million pounds of paper in 2021 through our program to recycle confidential paper after destruction. PROTECTING BIODIVERSITY BNY Mellon plays a vital role in protecting a small, but very impactful part of our ecosystem by hosting beehives at several U.S. locations. By hosting these hives and urging our employees to protect and preserve honeybee populations, we are supporting pollinators that play a vital role in agriculture, food production and overall biodiversity. These efforts are especially critical given that the U.S. loses nearly one-half of all beehives every year. 42 SUSTAINABILITY AMBASSADORS During a period when substantial numbers of our employees continued to work remotely, we reimagined the role of our global internal employee network of over 400 Environmental Sustainability Ambassador members. As a new approach to engaging employees in environmental issues, we are introducing an online ESG data portal through which employees can access real- time, location-specific environmental performance data for BNY Mellon facilities globally. Our goal is to increase awareness and understanding that can lead to behavior change and positive environmental actions, such as the examples highlighted below. • Our Hong Kong Ambassador chapter conceived a program, in collaboration with the building landlord, to convert food waste into energy and compost • EMEA Ambassadors collaborated with employees around the world to produce a video, from the perspective of their children, on why sustainability is important • Our Pittsburgh chapter hosted a webcast to promote the many ways employees can act in a more sustainable manner in their daily lives REAL ESTATE AND WORKSPACES In 2020 and 2021, we developed a climate risk and scenario-based resiliency assessment of our real estate portfolio, which also reflects our support of the TCFD recommendations. This study identified emerging climate risks, in particular related to physical infrastructure, which helps to guide relevant investments and internal policies. In 2021, we advanced significant renovations at two prominent BNY Mellon locations in the UK and India and anticipate achieving 42 US beekeepers continue to report high colony loss rates, no clear progression toward improvement , Auburn University.
BNY MELLON ENTERPRISE ESG 83 GLOBAL CITIZENSHIP Leadership in Energy and Environmental Design (LEED) environmental certifications at both sites. We also progressed relocation of our offices in Brussels and are seeking an Excellent rating from the BREEAM sustainability assessment certification program for that facility, to be occupied in 2022. The design of our workspaces contributes to the wellbeing and productivity of our employees, and affects our energy use and GHG emissions. In light of the global pandemic, we are committed to providing work environments that are environmentally and economically sustainable for the long term. Throughout our real estate portfolio, we implemented various measures to provide our employees with a productive and safe working environment, including improved indoor air quality and new cleaning protocols, among others. Changes in this evolving space will have implications for the future of the way we work and the environmental footprint of the company. We utilize third-party green building certification frameworks, including the U.S. Green Building Council’s LEED certification, the U.S. EPA’s ENERGY STAR program and international standards such as ISO 14001, to guide our office designs and environmental programs. 2021 KEY DATA: REAL ESTATE AND WORKSPACES Occupied real estate by square foot with third- party sustainability certification: 48% ISO 14001-certified facilities: 92% in EMEA region SUPPLY CHAIN Our Opportunity and Approach As a major global financial services leader operating in 35 countries, BNY Mellon touches much of the world’s asset movements every day. We rely on a broad network of suppliers for a variety of products and services to support our company and successfully deliver products and services to our clients globally. Through the development of sound supplier relationships, BNY Mellon can continue to improve our performance and market position, and uphold our responsibilities to the market and our clients. By harnessing the power of our purchasing influence, we also seek to cultivate a diverse, responsible supply chain that helps people and communities reach their full potential. We strive to conduct our business with the highest ethical standards, manage social and environmental issues responsibly, manage risks and safeguard human rights. We expect our suppliers to do the same.
BNY MELLON ENTERPRISE ESG 84 GLOBAL CITIZENSHIP Enterprise ESG 2025 Supplier Diversity Goal Build a Supplier Diversity program that has longevity, consistent with BNY Mellon’s value proposition and diversity initiatives KPI: Refine program resources to improve program processes and increase efficiencies Progress: • Identified and contracted with new software tool company to aid management of diverse suppliers • Working with sourcing group to integrate Supplier Diversity data into accounts payable and source-to-pay tools KPI: Implement a company- wide sustainable training program on supplier diversity Progress: • Developed training for client-facing colleagues to assist with RFP responses KPI: Increase outreach with diverse suppliers through supplier development and education experiences Progress: • Made meaningful connections with diverse suppliers by participating in various events during 2021 • Launched first Supplier Diversity Mentoring program • Launched FAC program (Facilitate, Advocate, and Contract) Supplier Responsibility In 2021, we updated and expanded our Supplier Code of Conduct to more clearly articulate our expectations related to worker health and safety, labor and human rights, environmental sustainability, diversity and inclusion, ethics, community commitment, conflicts of interest and other responsible business practices. We set high standards for ourselves in these areas and expect our suppliers to meet similar standards of excellence. We expect our suppliers to understand and act in accordance with this Code, including by aligning their corresponding guidelines, policies and practices, and by communicating and enforcing applicable Code requirements throughout their organization and across their own supply chains. Any violations of our Supplier Code of Conduct can be reported through our confidential Ethics Help Line . Supplier Diversity Developing a supply chain that encompasses small and diverse suppliers not only brings valuable perspectives to our company, but it is also an important part of our corporate strategy and helps advance our Enterprise ESG goals. We seek to do business with best-in-class, cost-competitive and innovative diverse suppliers and small businesses. Our Supplier Diversity program is designed to provide opportunities for businesses owned and operated by minorities, women, veterans, individuals with disabilities and LGBTQ+ individuals as well as small businesses. Our updated Supplier Code of Conduct outlines our approach and expectations that our direct suppliers will include small and diverse-owned business in their own supply chain, and we may ask them to report their second-tier spend with these suppliers. Our Executive leadership fully supports our efforts to promote the economic growth and development of small and diverse businesses. We created the Facilitate, Advocate, and Contract (FAC) program to drive spending with a targeted diverse group to bring to parity with other diverse groups. We have also been collaborating closely with our lines of business and corporate functions to increase spend in nontraditional professional services, such as broker/dealers, asset management firms and legal firms. As part of our commitment to diverse supplier development, we launched our Supplier Diversity Mentoring program in 2021 with an initial cohort of four mentor-mentee pairs. This program is aimed at increasing diverse and small business capabilities through guidance and feedback from BNY Mellon colleagues.
BNY MELLON ENTERPRISE ESG 85 GLOBAL CITIZENSHIP OUTREACH AND EXTERNAL ADVOCACY RELATIONSHIPS We are members of many advocacy organizations, including the Financial Services Roundtable for Supplier Diversity, National Gay & Lesbian Chamber of Commerce, National Minority Supplier Development Council, New York & New Jersey Minority Supplier Development Council, National Veteran-Owned Business Association, WEConnect International, Women’s Business Enterprise National Council and Women’s Business Enterprise Council – Metro New York. Our participation magnifies our outreach and demonstrates our commitment to working with diverse vendors. Engagement with local and diverse suppliers can benefit our business as well as local communities through job creation, and revenue and income generation. We regularly host events to advise current and potential diverse vendors on how to do business with BNY Mellon. ADVOCACY AND POLITICAL ENGAGEMENT Our Opportunity and Approach BNY Mellon has a unique voice and perspective to bring to the policy and political process and is committed to working constructively with policymakers and market participants to move the financial services industry forward. Certain employees engage through our Political Action Committee (PAC) program, trade associations and other voluntary activities in accordance with applicable laws, regulations, and internal policies and procedures. Enterprise ESG 2025 Public Policy Goal Continue to engage with stakeholders on key regulatory and legislative issues important to BNY Mellon KPI: Expand internal awareness of regulatory and legislative impacts and trends Progress: Expanded internal awareness of regulatory and political trends/impacts through elections webinars, regular public policy and government affairs updates, and updates and outlooks for internal working groups and clients KPI: Strategically advocate on priority legislative and regulatory issues affecting BNY Mellon Progress: Worked with leadership to determine policy priorities and engage with policymakers through trade associations, bilateral meetings and comment letters. Topics included capital markets reform, money market fund reform, Treasury market reform and digital assets BNY Mellon’s Public Policy and Government Affairs team is responsible for all political activity by or on behalf of BNY Mellon, including administration of the PACs. The Public Policy and Government Affairs team reports to the General Counsel and provides updates at least annually to the CGNSR Committee of the Board of Directors. These activities are conducted in accordance
BNY MELLON ENTERPRISE ESG 86 GLOBAL CITIZENSHIP with BNY Mellon’s Code of Conduct, internal policies and procedures, applicable laws and regulations, and in consultation with the Compliance and Legal Departments. EMPLOYEE-FUNDED POLITICAL ACTION COMMITTEES AND POLITICAL CONTRIBUTIONS BNY Mellon has two PACs funded entirely by voluntary contributions from eligible employees. Employees are not reimbursed or compensated in any way for political activities or contributions. BNY Mellon did not make any corporate contributions 43 in 2021. We do not use corporate funds for independent political expenditures to support or oppose any candidate for office. FEDERAL POLITICAL ACTION COMMITTEE CONTRIBUTIONS IN 2021 (USD)* Republican Democratic To t a l U.S. House $ 31,50 0 $91,000 $122,500 U.S. Senate $35,500 $54,000 $89,500 To t a l $67,000 $145,000 $212,000 * A dditional contributions include $5,000 made to Pennsylvania candidates, resulting in $217,000 in total PAC disbursements. In 2021, our federal lobbying expenses were $1,110,000. Further information on our public policy engagement and lobbying and industry participation in trade associations is available here . 43 A corpor ate contribution is defined to include a state candidate committee, a 501(c) 4, 527 or ballot initiatives. PROTECTING HUMAN RIGHTS Our Opportunity and Approach We consider human dignity paramount, and we work to preserve and champion human rights throughout our company, our supply chain and broader society. We require that all employees be treated with fairness, dignity and respect at work. We are committed to preserving human rights by instituting policies that help prevent modern slavery and human trafficking in our operations and supply chain. These values help define our company, and we reinforce them through policies governing our supply chain and employment practices: Drug- and Alcohol-free Workplace policy Equal Employment Opportunity/Affirmative Action (EEO/AA) policy Gender Equality Statement Health and Safety Statement Human Rights Statement Notice of Affirmative Action Programs and Notice to Veterans and Individuals with Disabilities Modern Slavery Act Statement Sexual and Other Discriminatory Harassment policy WHAT GUIDES US When determining our approach to respecting human rights, we look to leading international standards, such as the UN Universal Declaration of Human Rights, International Labor Organization (ILO) Core Conventions and UN Guiding Principles on Business and Human Rights. We are further guided by our participation as a signatory to the UN Global Compact. Informed by these global principles, the BNY Mellon Human Rights Statement demonstrates a commitment to human rights that is embedded in the culture and values that define our company and is reflected in our policies and actions toward our employees, suppliers, clients and the communities and countries where we do business and throughout our value chain. This statement was updated and approved in February 2022. Our expanded statement clarifies its scope with direct links to the UK and Australia Modern Slavery Acts,
BNY MELLON ENTERPRISE ESG 87 GLOBAL CITIZENSHIP includes a dedicated governance structure section, and acknowledges the influence of international standards. This updated statement, the company’s employee and supplier codes of conduct, governance framework, core values and other related corporate policies encompass the foundational principles that drive our commitment and efforts to safeguard human rights. Together, these tools empower our employees and contractors to report and escalate concerns of unethical conduct, such as corruption, discrimination, harassment, child labor, prison labor, forced labor or slavery in any form. Enterprise ESG 2025 Human Rights Goal Continue the commitment to preventing modern slavery and human trafficking in our operations, supply chain and communities KPI: Conduct due diligence and training practices to promote understanding of Modern Slavery principles Progress: Instituted training on modern slavery and human trafficking to procurement employees and select stakeholders within Legal, Risk and Compliance MODERN SLAVERY We are committed to preventing acts of modern slavery and human trafficking both in our own business activities and throughout our supply chain. Our Supplier Code of Conduct evidences this commitment. We expect our suppliers to be committed to act ethically and with integrity in all their business dealings and relationships and to implement and enforce effective systems and controls that prevent modern slavery from taking place in their businesses and supply chains. We reaffirm our commitment and actions each year through our UK Modern Slavery Act Annual Transparency Statement and Australia Modern Slavery Act Annual Transparency Statement, which reflect our awareness of modern slavery and steps we take to prevent it. We also continue our review of governance, due diligence and training practices to promote an understanding of Modern Slavery Act principles. We set out our expectations and commitments in a number of policies, including those above. In addition to preserving human rights in our own workplace and supply chain, we also look for ways to contribute to solutions throughout the world, serving as a positive influence for the protection of human rights. TAKING ACTION AGAINST INEQUITIES BNY Mellon’s Signature Pro Bono program and Legal Department Pro Bono program enable employees of all professional backgrounds to lend their talents to assist nonprofits and marginalized individuals confronting social injustice and inequities. Across the organization, our people take action to champion equity, diversity and human rights, often working with stakeholders in the public and charitable sectors. In 2021, our professionals around the globe provided pro bono services to those in need, both individually and through partnerships with other financial institutions, law firms and nonprofit organizations, to promote racial justice and combat social inequity. These volunteers addressed a variety of issues, as described in these examples below. Unlocking Opportunity • Assisted 27 pre-screened lawful permanent residents on their path to U.S. citizenship through a virtual Naturalization Clinic in partnership with DLA Piper and the Immigration Institute of the Bay Area in San Francisco • Provided advice and assistance to domestic workers in Hong Kong to understand their rights under the law and gain access to justice through the HELP for Domestic Workers organization • Staffed the biweekly Toynbee Hall Virtual Clinic, providing employment law advice to low-income clients in London • Provided technology advising on cybersecurity to Education Partnership, a nonprofit that distributes supplies to under-resourced classrooms in Greater Pittsburgh, helping the organization safeguard its client and donor information
BNY MELLON ENTERPRISE ESG 88 GLOBAL CITIZENSHIP Racial Justice • Partnered with Morgan Lewis and BNY Mellon grantee Human Rights First to provide screening for Afghan refugees to potentially apply for asylum in the U.S., with several BNY Mellon lawyers taking on full representation of refugees in asylum proceedings in partnership with Morgan Lewis • Provided research assistance on several projects, including on state laws concerning criminal record expungement, access to technology in education, child labor practices and unintentional forms of discrimination, through our involvement as a Leadership Partner in Lawyers for Good Government’s Lawyers for Racial Justice Initiative • Assisted with drafting a multilingual practice guide on rights under Brazilian and international law of those arrested, detained or subjected to abuse, in partnership with Instituto Pro Bono • Advised United to Change and Inspire (UK) on development of a corporate structure to support its racial justice work • Assisted Sponsors for Educational Opportunity (SEO), a nonprofit devoted to closing the achievement gap for underserved youth, in the design of an HR development plan Supporting the LGBTQ+ Community • Collaborated with The Ali Forney Center, a BNY Mellon grantee that serves homeless LGBTQ+ youth in New York on the management of its client and donor data • Assist LGBTQ+ asylum-seekers in obtaining legal status in the U.S. through our partnership with Legal Services NYC, also a grantee of BNY Mellon • Assist clients in Pittsburgh and New York in obtaining name changes so that their legal identities can match their gender identities in an ongoing partnership with the Transgender Legal Defense and Education Fund SOCIAL JUSTICE GRANTS As part of our strategic grant-making in 2021 , BNY Mellon directed approximately $1.4 million in grants championing justice, advocacy, reform and equal protection under the law. Recipients included organizations addressing racial and economic disparities, such as the National Network for Safe Communities at John Jay College, NAACP Legal Defense and Educational Fund (LDF), Southern Poverty Law Center, and Vera Institute of Justice. In addition, we funded organizations supporting the Asian American Pacific Islander community following the racially motivated attacks on Asian Americans and organizations supporting the LGBTQ+ communities, including: • The Ali Forney Center shelter, which provides services for homeless LGBTQ+ youth in New York City • Hudson Pride Center LGBTQ+ community advocacy center in Jersey City, New Jersey • Start Small Think Big and StartOut, two nonprofit organizations that provide comprehensive support and services to empower marginalized and low- and moderate-income and LGBTQ+ entrepreneurs, respectively.
BNY MELLON ENTERPRISE ESG 89 GLOBAL CITIZENSHIP SPOTLIGHT Afghan Response and Supporting Refugees As a humanitarian crisis unfolded in Afghanistan, BNY Mellon acted on our commitment to protect human rights with a multifaceted response to aid Afghan citizens and refugees and others affected by this catastrophe. We contributed a $100,000 grant to the American Red Cross working in partnership with the International Committee of the Red Cross to meet the urgent medical needs of displaced Afghan adults and children who have fled the ongoing violence as well as an additional $100,000 to Human Rights First to support refugee protection and resettlement. We mobilized and matched employee contributions through our BNY Mellon Community Impact program, encouraging employee donations to the humanitarian organizations BNY Mellon supported, including those serving military veterans and journalists. BNY Mellon employees also assisted Afghan allies seeking asylum and strengthened the capacity of refugee-serving organizations through our Legal Pro Bono and Signature Pro Bono programs. We directed an additional $50,000 to the UK-based nonprofit Breaking Barriers to expand its services for recent Afghan refugees in the two most widely spoken Afghan languages. We also serve as a founding member of the Breaking Barriers’ Business Behind Refugees initiative, which calls on businesses to hire or support refugees in the UK. For businesses, hiring refugees can bring value, address skills gaps, nurture a diverse and inclusive workplace, and enhance social impact by solving real barriers to employment faced by these individuals. A SHARED COMMITMENT We expect the recipients of our philanthropic funding to share our commitment to protect human rights. We require nonprofit organizations, such as charities and nongovernmental organizations, applying for financial sponsorship or donations to certify compliance with our Non-Discrimination Policy Certification for Non-Profits and to complete a thorough vetting process.
APPENDIX The following is supplemental information to BNY Mellon’s 2021 Enterprise ESG Report. It is arranged according to the Global Reporting Initiative (GRI) Standards indicator list. All data is reported as of December 31, 2021, unless otherwise noted. This index provides responses for individual GRI indicators in the following ways: (1) section and page references to our 2021 Enterprise ESG Report; (2) direct responses within the index; (3) references to other company reports (e.g., Annual Report or Proxy Statement); or (4) materials located on our website.
BNY MELLON ENTERPRISE ESG 91 APPENDIX GLOBAL REPORTING INITIATIVE (GRI) INDEX CATEGORY: STANDARD DISCLOSURES Aspect: Organizational Profile Standard Disclosure Our Response GRI 102: General Disclosures 2016 102-1 Name of the organization BNY Mellon Annual Report 202 1, General, p.3 102-2 Activities, brands, products, and services BNY Mellon Annual Report 2021 , Results of Operations, p.3 BNY Mellon Annual Report 2021 , Results of Operations, p.14-24 102-3 Location of headquarters BNY Mellon Annual Report 2021 , Corporate Information, inside back cover 102-4 Location of operations BNY Mellon Annual Report 2021 , International operations, p.22-24 BNY Mellon Location Directory 102-5 Ownership and legal form BNY Mellon Annual Report 2021 , General, p.3 102-6 Markets Served BNY Mellon Annual Report 2021 , Review of business, p.14-22 BNY Mellon Annual Report 2021 , International operations, p.22-24 10 2-7 Scale of the Organization BNY Mellon Annual Report 2021 , Review of business, p.14-21 BNY Mellon Annual Report 2021 , International operations, p. 22-24 102-8 Information on employees and other workers EE01 Document, see end of GRI Index BNY Mellon Annual Report 2021 , Human capital, p.3-5 102-9 Supply chain BNY Mellon Enterprise ESG Report 2021, Supply Chain, p.83-85 102-10 Significant changes to the organization and its supply chain BNY Mellon Annual Report 2021 , A Winning Strategy, II-XIII 10 2-11 Precautionary Principle or approach BNY Mellon Enterprise ESG Report 2021, Environmental Sustainability, p.79-83 BNY Mellon Enterprise ESG Report 2021, Responsible Financing and the Equator Principles, p.67 102-12 External initiatives BNY Mellon Enterprise ESG Report 2021, Support for Responsible Investing, p.58 Trade Association Memberships 102-13 Membership of associations BNY Mellon Enterprise ESG Report 2021, Support for Responsible Investing Initiatives, p.58 Trade Association Memberships BNY Mellon 2022 Proxy Statement Item 1 Election of Directors, p.12–17
BNY MELLON ENTERPRISE ESG 92 APPENDIX Aspect: Strategy Standard Disclosure Our Response GRI 102: General Disclosures 102-14 Statement from senior decision makers BNY Mellon Annual Report 2021 , CEO Letter, p.I BNY Mellon Enterprise ESG Report 2021, Message From Our CEO, p.6 102-15 Key impacts, risks, and opportunities BNY Mellon Enterprise ESG Report 2021, Our Approach, p . 8 -17 BNY Mellon Annual Report 2021 , Impact of coronavirus pandemic on our business, p.5 BNY Mellon Annual Report 2021 , Risk Management, p.50-57 Aspect: Ethics and Integrity Standard Disclosure Our Response GRI 102: General Disclosures 102-16 Values, principles, standards, and norms of behavior BNY Mellon Employee Code of Conduct The Bank Of New York Mellon Corporation Directors’ Code of Conduct 102-17 Mechanisms for advice and concerns about ethics BNY Mellon Employee Code of Conduct The Bank Of New York Mellon Corporation Directors’ Code of Conduct
BNY MELLON ENTERPRISE ESG 93 APPENDIX Aspect: Governance Standard Disclosure Our Response GRI 102: General Disclosures 2016 102-18 Governance structure BNY Mellon 2022 Proxy Statement , Our Corporate Governance Practices, p.22-27 102-19 Delegating authority BNY Mellon Enterprise ESG Report 2021, Enterprise ESG Governance, p .16 102-20 Executive-level responsibility for economic, environmental, and social topics BNY Mellon Enterprise ESG Report 2021, Enterprise ESG Governance, p .16 102-21 Consulting stakeholders on economic, environmental, and social topics BNY Mellon 2022 Proxy Statement , Committees and Committee Charters, p.3 8– 41 102-22 Composition of the highest governance body and its committees BNY Mellon 2022 Proxy Statement , Committees and Committee Charters, p.39 102-23 Chair of the highest governance body BNY Mellon 2022 Proxy Statement , Board Leadership Structure, p.27 102-24 Nominating and selecting the highest governance body BNY Mellon 2022 Proxy Statement , Director Qualifications, p.18 102-25 Conflicts of interest BNY Mellon 2022 Proxy Statement , Director Qualifications, p.18 The Bank Of New York Mellon Corporation Directors’ Code of Conduct , p .1 102-26 Roles of highest governance body in setting purpose, values, and strategy BNY Mellon Enterprise ESG Report 2021, Enterprise ESG Governance, p .16 BNY Mellon 2022 Proxy Statement , Committees and Committee Charters, p.8- 41 102-27 Collective knowledge of highest governance body BNY Mellon Enterprise ESG Report 2021, Enterprise ESG Governance, p .16 BNY Mellon 2022 Proxy Statement , Committees and Committee Charters, p.8- 41 102-28 Evaluating the highest governance body’s performance BNY Mellon 2022 Proxy Statement , Evaluation of Board and Committee Effectiveness, p.25 102-29 Identifying and managing economic, environmental, and social impacts BNY Mellon Enterprise ESG Report 2021, Enterprise ESG Governance, p .16 BNY Mellon 2022 Proxy Statement , Committees and Committee Charters, p.8- 41 BNY Mellon Enterprise ESG Report 2021, Our Approach, p . 8 -17 102-30 Effectiveness of risk management processes BNY Mellon 2022 Proxy Statement , Committees and Committee Charters, p.3 8- 41 Risk Committee Charter
BNY MELLON ENTERPRISE ESG 94 APPENDIX 102-31 Review of economic, environmental, and social topics BNY Mellon Enterprise ESG Report 2021, Enterprise ESG Governance, p .16 BNY Mellon 2022 Proxy Statement , Committees and Committee Charters, p.3 8- 41 BNY Mellon Enterprise ESG Report 2021, Our Approach, p . 8 -17 102-32 Highest governance body’s role in sustainability report BNY Mellon Enterprise ESG Report 2021, Enterprise ESG Governance, p .16 BNY Mellon 2022 Proxy Statement , Committees and Committee Charters, p.3 8- 41 BNY Mellon Enterprise ESG Report 2021, Our Approach, p . 8 -17 102-33 Communicating critical concerns BNY Mellon 2022 Proxy Statement , Our Corporate Governance Practices, p.20 -27 Corporate Governance Guidelines Communications with Independent Chairman 102-34 Nature and total number of critical concerns BNY Mellon Annual Report 2021 , Risk Factors, p.75-102 102-35 Remuneration policies BNY Mellon 2022 Proxy Statement , Director Compensation, p.43-45 BNY Mellon 2022 Proxy Statement , Item 2. Advisory Vote On Compensation, p.6-47 BNY Mellon 2022 Proxy Statement , Equity Compensation Plans, p.91 102-36 Process for determining remuneration BNY Mellon 2022 Proxy Statement , Director Compensation, p.43-45 BNY Mellon 2022 Proxy Statement , Item 2. Advisory Vote On Compensation, p.46-47 BNY Mellon 2022 Proxy Statement , Equity Compensation Plans, p.91 102-37 Stakeholders’ involvement in remuneration BNY Mellon 2022 Proxy Statement , Director Compensation, p.43-45 BNY Mellon 2022 Proxy Statement , Item 2. Advisory Vote On Compensation, p.6-47 BNY Mellon 2022 Proxy Statement , Equity Compensation Plans, p.91 102-38 Annual total compensation ratio BNY Mellon 2022 Proxy Statement , Pay Ratio, p.81 102-39 Percentage increase in annual total compensation ratio BNY Mellon 2022 Proxy Statement , Pay Ratio, p.81
BNY MELLON ENTERPRISE ESG 95 APPENDIX Aspect: Stakeholder Engagement Standard Disclosure Our Response GRI 102: General Disclosures 2016 102-40 List of stakeholder groups BNY Mellon Enterprise ESG Report 2021, Enterprise ESG Governance, p .16 BNY Mellon Enterprise ESG Report 2021, Stakeholder Engagement, p .12 102- 41 Collective bargaining agreements BNY Mellon fully complies with local laws regarding employee rights and collective bargaining. In certain locations outside of the U.S. we have works councils, engage with trade unions and adhere to applicable national collective bargaining agreements. We also have client and vendor relationships with trade unions. Our Code of Conduct applies to our employees globally and emphasizes the company’s commitment to foster a culture where all employees feel valued, engaged and are able to bring their whole selves to the workplace. Employees are encouraged to raise any concerns through multiple channels identified in the Code of Conduct. 102-42 Identifying and selecting stakeholders BNY Mellon Enterprise ESG Report 2021, Enterprise ESG Governance, p .16 BNY Mellon Enterprise ESG Report 2021, Stakeholder Engagement, p .12 102-43 Approach to stakeholder engagement BNY Mellon Enterprise ESG Report 2021, Enterprise ESG Governance, p .16 BNY Mellon Enterprise ESG Report 2021, Stakeholder Engagement, p .12 102-4 4 Key topics and concerns raised BNY Mellon Enterprise ESG Report 2021, Stakeholder Engagement, p .12 BNY Mellon 2022 Proxy Statement, Corporate Governance Highlights, p.7
BNY MELLON ENTERPRISE ESG 96 APPENDIX Aspect: Reporting Practice Standard Disclosure Our Response GRI 102: General Disclosures 2016 102-45 Entities included in the consolidated financial statements BNY Mellon Annual Report 2021 , Review of busines segments, p.4-24 BNY Mellon Enterprise ESG Report 2021, About this Report, p.2 102-46 Defining report content and topic Boundaries BNY Mellon Enterprise ESG Report 2021, About this Report, p.2 BNY Mellon Enterprise ESG Report 2021, Our Approach p . 8 -14 102-47 List of material topics BNY Mellon Enterprise ESG Report 2021, Our Approach, p . 8 -14 102-48 Restatements of information None 102-49 Changes in reporting BNY Mellon Enterprise ESG Report 2021, New in This Report, p.2 102-50 Reporting period BNY Mellon Enterprise ESG Report 2021, About This Report, p.2 102-51 Date of most recent report BNY Mellon Enterprise ESG Report 2020 was published in June 2021 102-52 Reporting Cycle BNY Mellon Enterprise ESG Report 2021, About This Report, p.2 102-53 Contact point for questions regarding the report futurefirst@bnymellon.com 102-54 Claims of reporting in accordance with the GRI Standards BNY Mellon Enterprise ESG Report 2021, About this Report, p.2 102-56 External assurance We do not currently seek external assurance over our Enterprise ESG Report but we do have limited assurance over our Scope 1, 2 & 3 emissions. See Verification Opinion Declaration Greenhouse Gas Emissions, Enterprise ESG Report 2021, p .1 22 CATEGORY: MANAGEMENT APPROACH Aspect: Management Approach Standard Disclosure Our Response GRI 103: Management Approach 2016 10 3-1 Explanation of the material topic and its Boundary BNY Mellon Enterprise ESG Report 2021, Our Approach, p . 8 -17 103-2 The management approach and its components BNY Mellon Enterprise ESG Report 2021, Our Approach, p . 8 -17 103-3 Evaluation of the management approach BNY Mellon Enterprise ESG Report 2021, Our Approach, p . 8 -17
BNY MELLON ENTERPRISE ESG 97 APPENDIX CATEGORY: ECONOMIC Aspect: Economic Performance Standard Disclosure Our Response GRI 201: Economic Performance 2016 201-1 Direct economic value generated and distributed BNY Mellon Annual Report 2021 , Financial Summary, p.2 BNY Mellon Annual Report 2021 , Noninterest expense, p.3 BNY Mellon Enterprise ESG Report 2021, Our Community Impact, p.35-40 BNY Mellon Enterprise ESG Report 2021, Investing in Communities, p.67 201-2 Financial implicated and other risks and opportunities due to climate change See CDP Response 201-3 Defined benefit plan obligations and other retirement plans BNY Mellon Annual Report 2021 , Note 18–Employee benefit plans, p.162 201-4 Financial assistance received from government BNY Mellon Annual Report 2021 , Note 12–Income taxes, p.153 Aspect: Indirect Economic Impacts Standard Disclosure Our Response GRI 203: Indirect Economic Impacts 2016 20 3-1 Infrastructure investments and services supported BNY Mellon Enterprise ESG Report 2021, Issuer Services, p.61–63 BNY Mellon Enterprise ESG Report 2021, Markets, p.65-66 BNY Mellon Enterprise ESG Report 2021, Investing in Communities, p.67 BNY Mellon Enterprise ESG Report 2021, Asset Servicing and Digital, p.60-61 203-2 Significant indirect economic impacts BNY Mellon Enterprise ESG Report 2021, Issuer Services, p.61–63 BNY Mellon Enterprise ESG Report 2021, Markets, p.65-66 BNY Mellon Enterprise ESG Report 2021, Technology in Financial Services, p. 61 BNY Mellon Enterprise ESG Report 2021, Asset Servicing and Digital, p.60-61 BNY Mellon Enterprise ESG Report 2021, Treasury Services, p.63-65 Aspect: Procurement Practices Standard Disclosure Our Response GRI 204: Indirect Economic Impacts 2016 20 4 -1 Proportion of spending on local suppliers BNY Mellon Enterprise ESG Report 2021, Supply Chain, p.83–85
BNY MELLON ENTERPRISE ESG 98 APPENDIX Aspect: Anti-corruption Standard Disclosure Our Response GRI 205: Anti- corruption 2016 20 5 -1 Operations assessed for risks related to corruption BNY Mellon Enterprise ESG Report 2021, Compliance and Ethical Behavior, p.44-45 BNY Mellon Employee Code of Conduct 205-2 Communications and training about anti-corruption policies and procedures BNY Mellon Enterprise ESG Report 2021, Compliance and Ethical Behavior, p.44-45 BNY Mellon’s anti-corruption policies and procedures have been communicated to the general public via BNY Mellon’s website, and communicated to all employees and the Board of Directors. BNY Mellon Employee Code of Conduct 205-3 Confirmed incidents of corruption and actions taken BNY Mellon Annual Report 2021 , Legal Proceedings, p.183-186 Aspect: Anti-competitive behavior Standard Disclosure Our Response GRI 206: Anti- competitive behavior 2016 20 6 -1 Legal actions for anti- competitive behavior, anti-trust, and monopoly practices BNY Mellon Annual Report 2021 , Legal Proceedings, p.183-186
BNY MELLON ENTERPRISE ESG 99 APPENDIX CATEGORY: ENVIRONMENTAL Aspect: Energy Standard Disclosure Our Response GRI 302: Energy 2016 Management approach disclosure BNY Mellon Enterprise ESG Report 2021, Environmental Sustainability, p.79-83 See CDP Response 302-1 Energy consumption within the organization a. Total fuel consumption within the organization from non-renewable sources, in joules or multiples, and including fuel types used: 99,669 gigajoules (includes natural gas, fuel oil, car gasoline, and jet fuel) b. Total fuel consumption within the organization from renewable sources, in joules or multiples, and including fuel types used: While BNY Mellon does not purchase fuel from renewable sources directly; we do purchase carbon offsets and renewable electricity products to offset all of our emissions generated from Scope 1, Scope 2 and Scope 3 business travel. c. Report in joules, watt-hours or multiples, the total: Electricity consumption, Heating consumption, Cooling consumption, Steam consumption Electricity consumption: 874,640 gigajoules (BNY Mellon purchases renewable electricity products to offset our entire electricity use). BNY Mellon does not have any heating or cooling consumption. Steam consumption: 26,782 gigajoules d. In joules, watt-hours or multiples, the total: Electricity sold, Heating sold, Cooling sold, and Steam sold: BNY Mellon does not sell any electricity, heating, cooling or steam. e. Total energy consumption within the organization in joules or multiples: 1,001,090 gigajoules f. Standards, methodologies, and assumptions used: BNY Mellon follows The Corporate Standard Greenhouse Gas Protocol for calculating emissions and energy use. An Operational Control boundary is used. g. Source of the conversion factors used: Conversions for Fuel and Electricity were done with the U.S. Energy Information Administration’s Energy Conversion Calculator. Steam was converted from BTU to joules using the factor: 1 BTU=1055.05585 joules as defined by the International Energy Agency’s Unit Converter
BNY MELLON ENTERPRISE ESG 100 APPENDIX 302-2 Energy consumption outside of the organization BNY Mellon follows The Corporate Standard Greenhouse Gas Protocol for calculating emissions and energy use. An Operational Control boundary is used. BNY Mellon considers energy consumed from purchased goods and services, capital goods, fuel-and-energy-related activities, upstream transportation and distribution, business travel, employee commuting, downstream leased assets, and investments relevant to our operations. For more detail on methodologies and assumptions used, please see CDP response 2020. Conversions for Fuel and Electricity were done with the U.S. Energy Information Administration’s Energy Conversion Calculator. 302-3 Energy intensity a. Energy intensity ratio: 62.84 gigajoules per million dollars; 0.90 gigajoules per square foot. b. Denominators: 2021 revenue (15,931 million dollars); 2021 average rentable square feet of real estate portfolio (11,180,541 sq. ft.). c. Fuel, electricity and steam are included; BNY Mellon does not consume additional sources of heating or cooling. d. The ratio uses energy consumed within the organization within BNY Mellon’s operational control scope 1 and 2. 302-4 Reduction of energy consumption 625,309 gigajoules. Fuel, electricity and steam are included; BNY Mellon does not consume additional sources of heating and cooling. BNY Mellon’s base year is 2010 for energy tracking. 2010 was chosen as the base year because this was this first year we were able to effectively measure energy consumption. Energy consumption in 2010 was rebaselined due to increase in accuracy of activity data. BNY Mellon’s energy reduction was calculated by subtracting 2021 energy consumption from the base year’s energy consumption. This reduction is the result of ongoing real estate portfolio optimization initiatives and specific energy reduction projects. BNY Mellon sets its energy reduction targets in the form of emission reduction targets as these are a surrogate for energy targets. BNY Mellon calculates its total energy consumption in conjunction with calculating its greenhouse gas inventory. Therefore, The Greenhouse Gas Protocol: A Corporate Accounting and Reporting A Corporate Accounting and Reporting Standard (Revised Edition) is the published methodology and standard used in energy and emission calculation.
BNY MELLON ENTERPRISE ESG 101 APPENDIX Aspect: Water and Effluents Standard Disclosure Our Response GRI 303: Water and Ef fluents 2016 GRI 103: Management approach disclosure BNY Mellon Enterprise ESG Report 2021, Environmental Sustainability, p.79-83 30 3-1 Interactions with water as a shared resource BNY Mellon withdraws all of its water from municipal sources. Water is consumed in our office and data center facilities. Water is discharged through municipal sewer sources. Water-related impacts are assessed and addressed on a local site basis and from a corporate-wide basis. 303-2 Management of water discharge-related impacts All wastewater is discharged through municipal sewer sources. 303-3 Water withdrawal BNY Mellon withdraws all of its water from municipal sources. BNY Mellon withdrew a total of 179.93 megaliters of water in 2021 (123.12 megaliters in the U.S. and 56.41 megaliters in international locations). All water withdrawals are freshwater. Facility Managers account for all water withdrawn from sources based upon water bills and report to Sustainability team for data collection. 303-4 Water discharged BNY Mellon does not actively track water discharge volumes, category or area. All water is discharged through third-party municipal sewer sources. 303-5 Water consumption BNY Mellon uses water in our office facilities for our cafeterias, cooling and heating needs, restrooms, and irrigation. BNY Mellon Enterprise ESG Report 2021, Environmental Sustainability, p.79-83 Aspect: Emissions Standard Disclosure Our Response GRI 305: Emissions 2016 GRI 103: Management approach disclosure BNY Mellon Enterprise ESG Report 2021, Environmental Sustainability, p.79-83 See CDP Response 30 5 -1 Direct (Scope 1) GHG emissions 6,214 Metric Tonnes of CO 2 e 305 -2 Energy indirect (Scope 2) GHG emissions 89,671 Metric Tonnes of CO 2 e 305-3 Other indirect (Scope 3) GHG emissions 1,219 Metric Tonnes of CO 2 e (business travel only) 305-4 GHG emissions intensity See CDP Response 305-5 Reduction of GHG emissions BNY Mellon Enterprise ESG Report 2021, Environmental Sustainability, p.79-83 See CDP Response
BNY MELLON ENTERPRISE ESG 102 APPENDIX Aspect: Effluents and Waste Standard Disclosure Our Response GRI 306: Effluents and Waste 2016 GRI 103: Management approach disclosure BNY Mellon Enterprise ESG Report 2021, Environmental Sustainability, p.79-83 30 6 -1 Water discharge by quality and destination BNY Mellon does not actively track water discharge volumes. All water is discharged through third-party municipal sewer sources. 30 6 -2 Waste by type and disposal method BNY Mellon does not produce hazardous waste. Recycling = 4,551,129 pounds Composting = 10,630 pounds Incineration (mass burn) = 312,300 pounds Landfill = 1,766,859 pounds Waste was disposed of by the waste hauler contractor. Waste data is provided to facility manager regarding frequency of pickup, quantity of pickup, and fate of waste. 306-3 Significant spills There were no significant spills that occurred at BNY Mellon in 2021. 306-4 Transport of hazardous waste BNY Mellon does not transport hazardous waste. 306-5 Water bodies affected by water discharges and/or runoff BNY Mellon discharges all water withdrawals through third-party municipal sewer sources. Aspect: Environmental Compliance Standard Disclosure Our Response GRI 307: Environmental Compliance 2016 GRI 103: Management approach disclosure BNY Mellon Enterprise ESG Report 2021, Risk Management, p.42–48 307-1 Non-compliance with environmental laws and regulations No environmental fines or sanctions were imposed on BNY Mellon in 2021. Aspect: Supplier Environmental Assessment Standard Disclosure Our Response GRI 308: Environmental Compliance 2016 GRI 103: Management approach disclosure Environmental section of the Supplier Code of Conduct 30 8-1 New suppliers screened using environmental criteria Contributing to the World Around Us section of the Supplier Code of Conduct 308-2 Negative environmental impacts in the supply chain and actions taken Contributing to the World Around Us section of the Supplier Code of Conduct
BNY MELLON ENTERPRISE ESG 103 APPENDIX CATEGORY: SOCIAL Aspect: Employment Standard Disclosure Our Response GRI 401: Employment 2016 GRI 103: Management approach disclosure BNY Mellon Enterprise ESG Report 2021, Culture & Purpose, p .18 - 4 0 4 01-1 New employee hires and employee turnover BNY Mellon Enterprise ESG Report 2021, Diversity, Equity and Inclusion, p .19 –2 6 BNY Mellon Enterprise ESG Report 2021, Employee Engagement and Wellbeing, p.30–35 4 01-2 Benefits provided to full-time employees that are not provided to temporary or part-time employees BNY Mellon Enterprise ESG Report 2021, Employee Engagement and Wellbeing, p.30-35 4 01-3 Parental leave 16 weeks parental leave in the U.S., and 16 weeks company-paid maternity leave all other countries Aspect: Training and Education Standard Disclosure Our Response GRI 404: Training and Education 2016 GRI 103: Management approach disclosure BNY Mellon Enterprise ESG Report 2021, Leadership And Development, p.26–30 4 0 4 -1 Average hours of training for employees BNY Mellon Enterprise ESG Report 2021, Leadership and Development, p.26-30 4 0 4 -2 Programs for upgrading employee skills and transition assistance programs BNY Mellon Enterprise ESG Report 2021, Leadership and Development, p.26-30 404-3 Percentage of employees receiving regular performance and career development reviews BNY Mellon Enterprise ESG Report 2021, Leadership and Development , p.26-30
BNY MELLON ENTERPRISE ESG 104 APPENDIX Aspect: Diversity and Equal Opportunity Standard Disclosure Our Response GRI 405: Diversity and Equal Opportunity 2016 GRI 103: Management approach disclosure BNY Mellon Enterprise ESG Report 2021, Diversity, Equity and Inclusion, p .19 -2 6 2021 Proxy Statement Pay Equity at BNY Mellon BNY Mellon EEO/AA Policy 4 0 5 -1 Diversity of governance bodies and employees BNY Mellon Enterprise ESG Report 2021, Diversity, Equity and Inclusion, p .19 -2 6 2021 Proxy Statement 4 05 -2 Ratio of basic salary and remuneration of women to men BNY Mellon Gender Pay Gap Report 202 1 Aspect: Human Rights Assessment Standard Disclosure Our Response GRI 412: Human Rights Assessment 2016 GRI 103: Management approach disclosure BNY Mellon Enterprise ESG Report 2021, Protecting Human Rights, p.86-89 412-1 Operations that have been subject to human rights reviews or impact assessments BNY Mellon Enterprise ESG Report 2021, Protecting Human Rights, p.86-89 BNY Mellon Human Rights Statement BNY Mellon Supplier Code of Conduct BNY Mellon Modern Slavery Act 412-2 Employee training on human rights policies or procedures In order to respond to the UK Modern Slavery Act, we have conducted due diligence in partnership with our legal counsel, procurement team and Human Resources, and our CGNSR Committee of the Board of Directors has signed our statement and disclosure. We will report annually on our policies, training, due diligence processes and the effectiveness of our measures to combat modern slavery and trafficking. These efforts build on our Supplier Code of Conduct and Master Agreement templates, which include human rights provisions for all potential new suppliers. 412-3 Significant investment agreements and contracts that include human rights clauses or that underwent human rights screening BNY Mellon Human Rights Statement
BNY MELLON ENTERPRISE ESG 105 APPENDIX Aspect: Local Communities Standard Disclosure Our Response GRI 413: Local Communities 2016 GRI 103: Management approach disclosure BNY Mellon Enterprise ESG Report 2021, Protecting Human Rights, p.86-89 BNY Mellon Human Rights Statement BNY Mellon Supplier Code of Conduct BNY Mellon Modern Slavery Act 413-1 Operations with local community engagement, impact assessments, and development programs BNY Mellon Enterprise ESG Report 2021, Our Community Impact, p.35-40 BNY Mellon Enterprise ESG Report 2021, Investing in Communities, p.67 413-2 Operations with significant actual and potential negative impacts on local communities Aspect: Supplier Social Assessment Standard Disclosure Our Response GRI 414: Supplier Social Assessment 2016 GRI 103: Management approach disclosure BNY Mellon Modern Slavery Act BNY Mellon Human Rights Statement 414 -1 New suppliers that were screened using social criteria BNY Mellon Modern Slavery Act BNY Mellon Human Rights Statement 414 -2 Negative social impacts in the supply chain and actions taken BNY Mellon Supplier Code of Conduct Aspect: Public Policy Standard Disclosure Our Response GRI 415: Public Policy 2016 GRI 103: Management approach disclosure BNY Mellon Enterprise ESG Report 2021, Advocacy and Political Engagement, p.85–86 415 -1 Political contributions BNY Mellon Enterprise ESG Report 2021, Advocacy and Political Engagement, p.85–86
BNY MELLON ENTERPRISE ESG 106 APPENDIX Aspect: Customer Privacy Standard Disclosure Our Response GRI 418: Customer Privacy 2016 GRI 103: Management approach disclosure BNY Mellon Enterprise ESG Report 2021, Risk Management, p.42–48 418-1 Substantiated complaints concerning breaches of customer privacy and losses of customer data BNY Mellon Annual Report 2021 , Legal Proceedings, p.183–186 Data Privacy Aspect: Socioeconomic Compliance Standard Disclosure Our Response GRI 419: Socioeconomic Compliance 2016 GRI 103 : Management approach disclosure BNY Mellon Enterprise ESG Report 2021, Risk Management, p.42–48 419 -1 Non-compliance with laws and regulations in the social and economic area BNY Mellon Annual Report 2021 , Legal Proceedings, p.183–186 * CDP Response Footnote: CDP formerly the Carbon Disclosure Project www.cdp.net
BNY MELLON ENTERPRISE ESG 107 APPENDIX UN GLOBAL COMPACT COMMUNICATION ON PROGRESS (COP) COMMITMENT STATEMENT FROM CEO CEO LETTER Principle 1: Human Rights Businesses should support and respect the protection of internationally proclaimed human rights. 1) BNY Mellon Enterprise ESG Report 2021, Protecting Human Rights, p.86-89 2) BNY Mellon Human Rights Statement Principle 2: Human Rights Businesses should make sure they are not complicit in human rights abuses. 1) BNY Mellon Enterprise ESG Report 2021, Protecting Human Rights, p.86-89 2) BNY Mellon Human Rights Statement 3) BNY Mellon Supplier Code of Conduct Principle 3: Labor Businesses should uphold the freedom of association and the effective recognition of the right to collective bargaining. 1) BNY Mellon Employee Code of Conduct BNY Mellon fully complies with local laws regarding employee rights and collective bargaining. In certain locations outside of the U.S., we have works councils, engage with trade unions and adhere to applicable national collective bargaining agreements. We also have client and vendor relationships with trade unions. Our Code of Conduct applies to our employees globally and emphasizes the company’s commitment to foster a culture where all employees feel valued, engaged and are able to bring their whole selves to the workplace. Employees are encouraged to raise any concerns through multiple channels identified in the Code of Conduct. Principle 4: Labor Businesses should uphold the elimination of all forms of forced and compulsory labor. 1) BNY Mellon Enterprise ESG Report 2021, Protecting Human Rights, p.86-89 2) BNY Mellon Human Rights Statement 3) BNY Mellon Supplier Code of Conduct & Ethics Help Line 4) BNY Mellon Modern Slavery Act In order to respond to the UK Modern Slavery Act, we have conducted due diligence in partnership with our legal counsel, procurement team and Human Resources, and our CGNSR Committee of the Board of Directors has signed our statement and disclosure. We will report annually on our policies, training, due diligence processes and the effectiveness of our measures to combat modern slavery and trafficking. These efforts build on our Supplier Code of Conduct and Master Agreement templates, which include human rights provisions for all potential new suppliers.
BNY MELLON ENTERPRISE ESG 108 APPENDIX Principle 5: Labor Businesses should uphold the effective abolition of child l ab or. 1) BNY Mellon Enterprise ESG Report 2021, Protecting Human Rights, p.86–89 2) BNY Mellon Human Rights Statement 3) BNY Mellon Supplier Code of Conduct 4) BNY Mellon Modern Slavery Act Principle 6: Labor Businesses should uphold the elimination of discrimination in respect to employment and occupation. 1) BNY Mellon Enterprise ESG Report 2021, Diversity, Equity and Inclusion, p .19 –2 6 2) BNY Mellon Enterprise ESG Report, Supply Chain, p.83–85 3) BNY Mellon Human Rights Statement 4) BNY Mellon Supplier Code of Conduct 5) Pay Equity at BNY Mellon 6) BNY Mellon EEO/AA Policy 7) BNY Mellon Gender Pay Gap Report 8) Sexual and Other Discriminatory Harassment Policy 9) Employee Code of Conduct Principle 7: Environment Businesses should support a precautionary approach to environmental challenges. 1) BNY Mellon Environmental Sustainability Policy Statement 2021 2) Considering Climate at BNY Mellon Report 2021 3) BNY Mellon Enterprise ESG Report 2021, Responsible Financing and the Equator Principles, p.67 4) BNY Mellon Enterprise ESG Report 2021, Risk Management, p.42–48 5) BNY Mellon Enterprise ESG Report 2021, Environmental Sustainability p.79-83 Principle 8: Environment Businesses should undertake initiatives to promote greater environmental responsibility. 1) BNY Mellon Environmental Sustainability Policy Statement 2021 2) Considering Climate at BNY Mellon Report 2021 3) BNY Mellon Enterprise ESG Report 2021, Environmental Sustainability, p.79–8 3 4) Environmental section of the Supplier Code of Conduct 5) Contributing to the World Around Us section of the Supplier Code of Conduct Principle 9: Environment Businesses should encourage the development and diffusion of environmentally friendly technologies. 1) Considering Climate at BNY Mellon Report 2021 2) BNY Mellon Enterprise ESG Report 2021, ESG and Responsible Investment Client Solutions, p.52–67 3) ESG and Responsible Investment at BNY Mellon Principle 10: Anti-corruption Businesses should work against corruption in all its forms, including extortion and briber y. 1) BNY Mellon Enterprise ESG Report 2021, Risk Management, p.42–48 2) BNY Mellon Employee Code of Conduct 3) BNY Ethics Hotline by EthicsPoint 4) BNY Mellon Annual Report 2021 , Legal Proceedings, p.183–186 BNY Mellon’s anti-corruption policies and procedures have been communicated to the general public via BNY Mellon’s website, and communicated to all employees and the Board of Directors.
BNY MELLON ENTERPRISE ESG 109 APPENDIX TASK FORCE ON CLIMATE-RELATED FINANCIAL DISCLOSURES RECOMMENDATIONS INDEX We publicly stated our support for the TCFD recommendations in 2019. For background on our journey and how we consider climate, please see page 17 . For information about how we consider each of the guidelines, the table below references the specific Report page. DISCLOSURE RESPONSE Governance Disclose the organization’s governance around climate-related risks and opportunities a) Describe the board’s oversight of climate-related risks and opportunities. BNY Mellon Enterprise ESG Report 2021, ESG and Climate Governance p.50 BNY Mellon Enterprise ESG Report 2021, Climate-Related Issue Governance p.71 b) Describe management’s role in assessing and managing climate- related risks and opportunities. BNY Mellon Enterprise ESG Report 2021, Enterprise ESG Governance p .16 BNY Mellon’s Environmental Sustainability Policy Statement . BNY Mellon Enterprise ESG Report 2021, Managing Climate Change p . 6 9 -7 9 Strategy Disclose the actual and potential impacts of climate-related risks and opportunities on the organization’s businesses, strategy and financial planning where such information is material. a) Describe the climate-related risks and opportunities the organization has identified over the short, medium and long term. BNY Mellon Enterprise ESG Report 2021, Climate Risk Management p.71-7 5 BNY Mellon Enterprise ESG Report 2021, Climate-Related Solutions to Serve Clients p .7 8 –7 9 BNY Mellon Enterprise ESG Report 2021, ESG and Responsible Investment Client Solutions p.52-62 b) Describe the impact of climate- related risks and opportunities on the organization’s business, strategy and financial planning. BNY Mellon Enterprise ESG Report 2021, Climate Risk Management p.71-7 5 BNY Mellon Enterprise ESG Report 2021, Climate-Related Solutions to Serve Clients p .7 8 –7 9 c) Describe the resilience of the organization’s strategy, taking into consideration different climate- related scenarios, including a 2°C or lower scenario. BNY Mellon Enterprise ESG Report 2021, Scenario Analysis and Stress Testing p. 7 5 -7 7 See Considering Climate at BNY Mellon Report 2021 p .17–2 0
BNY MELLON ENTERPRISE ESG 110 APPENDIX Risk Management Disclose how the organization identifies, assesses and manages climate-related risks. a) Describe the organization’s processes for identifying and assessing climate-related risks. BNY Mellon Enterprise ESG Report 2021, Climate Change-Driven and ESG Risks p.48 BNY Mellon Enterprise ESG Report 2021, Climate Risk Management p.71-79 b) Describe the organization’s processes for managing climate- related risks. BNY Mellon Enterprise ESG Report 2021, Climate Change-Driven and ESG Risks p.48 BNY Mellon Enterprise ESG Report 2021, Climate Risk Management p.71-7 5 c) Describe how processes for identifying, assessing and managing climate-related risks are integrated into the organization’s overall risk management. BNY Mellon Enterprise ESG Report 2021, Risk Management p.42-43 BNY Mellon Enterprise ESG Report 2021, Climate Risk Management p .7 2-74 Metrics and Targets Disclose the metrics and targets used to assess and manage relevant climate-related risks and opportunities where such information is material. a) Disclose the metrics used by the organization to assess climate- related risks and opportunities in line with its strategy and risk management process. BNY Mellon Enterprise ESG Report 2021, Climate Risk Management p.75 B NY Mellon Enterprise ESG Report 2021, Environmental Sustainability p.79-83 b) Disclose Scope 1, Scope 2, and if appropriate, Scope 3 Greenhouse Gas (GHG) emissions, and the related risks. BNY Mellon Enterprise ESG Report 2021, GHG Emissions table p .111 c) Describe the targets used by the organization to manage climate- related risks and opportunities and performance against targets. BNY Mellon Enterprise ESG Report 2021, Environmental Sustainability, p.80–81
BNY MELLON ENTERPRISE ESG 111 APPENDIX 2021 GHG Emissions values (Metric Tons CO 2 e): Scope 2018 (Baseline) 2019 2020 2021 Reduction from 2018 baseline Scope 1 8,005 8,102 5,919 6,214 -22.4% Scope 2 14 2 ,15 2 130,205 10 7, 9 7 1 89,671 -36.9% Scope 1&2 To t al 150,157 138,307 113 , 8 9 0 95,885 - 3 6 .1% Scope 3 business travel 17,19 4 14,605 2,259 1,219 -92.9% Scope 1, 2, 3 business travel total 167,351 152,912 116 ,14 9 9 7,10 4 -42.0%
BNY MELLON ENTERPRISE ESG 112 APPENDIX GLOSSARY This year, we added a glossary to promote awareness of ESG concepts and facilitate an understanding of the stories and performance we describe in this report. We recognize that ESG terms continue to evolve and the glossary below is our interpretation of current terminology. To create this glossary, we referred to several standards, organizations and alliances including: the Global Reporting Initiative (GRI), the Global Sustainable Investment Alliance (GSIA), the Greenhouse Gas (GHG) Protocol, the Impact Investing Institute, Principles for Responsible Investing (PRI), Science Based Targets Initiative (SBTi), the Task Force for Climate-related Disclosure (TCFD), and the United Nations Global Compact (UNGC). Bloomberg Gender Equality Index (GEI): The GEI is the world’s only comprehensive investment-quality data source on gender equality. It tracks the performance of public companies committed to disclosing their efforts to support gender equality through policy development, representation and transparency. Carbon neutral: This is a state achieved when unabated carbon emissions are compensated or balanced by another means, often through purchasing carbon offsets and/or renewable energy credits. Climate-related physical risk: This refers to the risk climate change poses to physical assets or operations, such as direct damage to assets and indirect impacts from supply chain disruption. Organizations’ financial performance may also be affected by changes in water availability, sourcing and quality; food security; and extreme temperature changes affecting organizations’ premises, operations, supply chain, transport needs and employee safety. Physical risks resulting from climate change can be event driven (acute) or longer-term shifts (chronic) in climate patterns. Acute risk: Acute physical risks refer to those that are event-driven, including increased severity of extreme weather events, such as cyclones, hurricanes, floods or wildfires. Chronic risk: Chronic physical risks refer to longer- term, ongoing shifts in climate patterns (e.g., sustained higher temperatures) that may cause sea level rise, long-lasting droughts or chronic heat waves. Climate-related transition risk: This refers to the risks associated with the transition to a low-carbon economy. The most common transition risks relate to extensive policy, legal, technology and market changes to address mitigation and adaptation requirements related to climate change. Depending on the nature, speed and focus of these changes, transition risks may pose varying levels of financial and reputational risk to organizations if they do not comply or adapt. Custodian bank: A custodian bank is a specialized financial institution responsible for holding and safeguarding assets of its clients, for instance: banks, insurance companies, mutual funds, hedge funds and pension funds. Diversity, Equity and Inclusion (DEI): DEI is an ethos that recognizes the value of diverse voices and considers inclusivity and employee wellbeing as central facets of success. To bring those values to life, companies implement programs and initiatives that actively make their offices more diverse, equitable and inclusive spaces. Dow Jones Sustainability Indices (DJSI): One of the most highly regarded global sustainability indices, issued jointly by S&P Dow Jones Indices and SAM. Enterprise ESG: This is an approach that incorporates an ESG lens into all aspects of how a corporation is managed. Enterprise ESG ensures that environmental, social and governance factors are considered and performance is measured and reported. At BNY Mellon, Enterprise ESG refers to our approach to integrating ESG into the business functions. We firmly believe the strength of our client solutions is underpinned by our own actions and behavior as an enterprise. Environmental, social and governance (ESG): ESG is both a business strategic approach and a tool to help identify key opportunities and manage risks deriving from environmental, social and governance factors. Also see entry for {Sustainability} below. ESG integration: This describes the systematic and explicit incorporation of environmental, social and governance factors into financial analysis and investment decisions to better manage risks and improve returns.
BNY MELLON ENTERPRISE ESG 113 APPENDIX ESG Materiality: When used in relation to ESG, this term is used to describe the quality of being relevant or significant. In the context of this report, material ESG factors are factors that are relevant or significant to the key internal and external stakeholders of a company. FTSE4Good: The FTSE4Good Index Series is a collection of socially responsible, or ESG, stock indices administered by the Financial Times Stock Exchange- Russell Group (FTSE). The purpose of these indices is to identify companies that score highly in ESG measures. Global Reporting Initiative (GRI): The GRI is an international, independent standards organization that helps businesses, governments and other organizations understand, measure and communicate their social and environmental impacts to all stakeholders. The GRI Standards are some of the oldest and most widely used ESG standards in the world. The Network for Greening the Financial System (NGFS): This is a group of central banks and supervisors committed to sharing best practices, contributing to the development of climate- and environment-related risk management in the financial sector, and mobilizing mainstream finance to support the transition toward a sustainable economy. Net zero: This describes the state when a corporation reduces its relevant Scope 1, 2 and 3 category GHG emissions following science-based, below-1.5-degree pathways as much as possible, with any remaining GHG emissions being fully neutralized by like-for-like removals (e.g., permanent removals for fossil carbon emissions). Principles for Responsible Investment (PRI): PRI is an international network of investors working together to implement its six aspirational principles, often referenced as “the Principles.” Its goal is to understand the implications of sustainability for investors and support signatories to facilitate incorporating these issues into their investment decision-making and ownership practices. In implementing these principles, signatories contribute to the development of a more sustainable global financial system. Proxy voting: This refers to ballot casting by a person or firm on behalf of a shareholder of a corporation. Responsible Investment (RI): We define RI as enabling positive change through investment, regardless of the approach taken. RI covers a spectrum of investing styles, including ESG integration; exclusionary screening; best-in-class screening; sustainable investing; impact investing; and philanthropy. Stewardship of clients’ assets is a key component of RI, as is the assessment of the ESG profile of client portfolios (RI reporting). Best-in-class/positive screening: This is a rules- based approach to preferentially tilt a portfolio toward investment in sectors, companies or projects selected for positive or best-in-class ESG characteristics relative to industry peers. Exclusionary/negative screening: This is a rules- based approach to remove investments from the investable universe based on a particular set of values. It could involve the exclusion of certain sectors, companies, countries or other issuers based on activities considered not investable. Exclusion criteria (based on norms and values) can refer, for example, to product categories (e.g., weapons, tobacco), company practices (e.g., animal testing, violation of human rights, corruption) or controversies. Impact investing: This is the practice of investing with the dual objectives of generating a positive, measurable and intended social and/or environmental impact alongside generating a financial return. Philanthropy/Charitable giving: Philanthropy involves charitable giving to a worthy cause on a large scale. Philanthropy can include donating money to a worthy cause or volunteering time, effort, or other forms of altruism. Philanthropic investing is the practice of investing based not on profit but on an altruistic desire to help others or society as a whole. RI Reporting: This describes the assessment of the ESG profile of client portfolios. Stewardship: This is the practice of the responsible allocation, management and oversight of capital to create long-term value for clients and beneficiaries, which also provides sustainable benefits for the economy, the environment and society. Stewardship activities include, but are not limited to, engagement with issuers; voting at shareholder meetings; filing of shareholder resolutions/proposals; direct roles on investee boards and board committees; negotiation with and monitoring of the stewardship actions of suppliers in the investment chain; engagement with policymakers; engagement with standard setters; contributions to public goods (such as research); and public discourse (such as media) that support stewardship.
BNY MELLON ENTERPRISE ESG 114 APPENDIX Sustainable investing: This describes investing in companies that are managing long-term outcomes for society and/or the environment. It encompasses stakeholder responsibility, or investing with consideration of a “Triple Bottom Line” — people, planet and profit. Thematic investing: In order to align investments to areas of superior long-term growth dynamics, thematic investing seeks to identify the areas of major structural change in the world and drive capital accordingly. Thematic investing allows investors to address key environmental and social issues by investing in specific themes such as climate, healthcare and sustainable agriculture. Science-Based Targets (SBTs): Greenhouse gas emission reduction targets are considered science-based if they are in line with what the latest climate science deems necessary to meet the goals of the Paris Agreement. T his is limiting global warming to well below 2°C above pre-industrial levels and pursuing efforts to limit warming to 1.5°C. Science, Technology, Engineering and Math (STEM): S TEM is an interdisciplinary approach to learning in which rigorous academic concepts are coupled with real- world lessons as students apply science, technology, engineering and mathematics in contexts that make connections between school, community, work and the global enterprise, enabling the development of STEM literacy and, with it, the ability to compete in the new economy. Socially Responsible Investing (SRI): This is the exclusionary practice of not investing money in companies and funds that do not have desired social or environmental impacts. Sustainability: In 1987, the United Nations Brundtland Commission defined sustainability as “meeting the needs of the present without compromising the ability of future generations to meet their own needs.” Sustainability is the overarching concept of jointly considering people, planet and profit in the management of a corporation. Sustainable Finance Disclosure Regulation (SFDR): I ntroduced by the European Commission, the SFDR imposes mandatory ESG disclosure obligations for asset managers and other financial markets participants. The SFDR aims to bring a level playing field for financial market participants and financial advisers on transparency in relation to sustainability risk. Task Force for Climate-related Financial Disclosures (TCFD): The Financial Stability Board established the TCFD to develop recommendations for more effective climate-related disclosures that could promote more informed investment, credit and insurance underwriting decisions. The recommended TCFD Financial Disclosures are organized into four categories: Governance, Strategy, Risk Management, and Metrics and Targets. The TCFD is unique in that it focuses on assessing the ability of a company to mitigate risks and maximize opportunities related to climate change. United Nations Global Compact (UNGC): The UNGC is the world’s largest corporate sustainability initiative, encouraging companies to align strategies and operations with universal principles on human rights, labor, environment and anti-corruption.
BNY MELLON ENTERPRISE ESG 115 APPENDIX EQUAL EMPLOYMENT OPPORTUNIT Y 2021 Employer Information Report EEO-1 Male Workforce Job categories Hispanic or Latino White Black or African American Native Hawaiian or Pacific Islander Asian American Indian or Alaskan Native Tw o o r More Races Overall total Executive/ SR Officials & MGRS 0 11 0 0 2 0 0 13 First/Mid Officials & MGRS 110 2043 112 1 426 0 42 2,734 Professionals 372 4775 387 9 1592 9 127 7, 2 71 Technicians 6 44 13 0 12 0 2 77 Sales Workers 5 81 1 0 7 0 0 94 Administrative Support 272 2119 427 7 324 2 99 3,250 Craft Workers 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 Operatives 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 1 Laborers & Helpers 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 Service Workers 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 1 To t a l 765 9,074 9 41 17 2,363 11 270 13, 4 41 Previous Report Total 767 9,565 960 19 2,328 12 315 13,966
BNY MELLON ENTERPRISE ESG 116 APPENDIX Female Workforce Job categories Hispanic or Latino White Black or African American Native Hawaiian or Pacific Islander Asian American Indian or Alaskan Native Tw o o r More Races Overall total Executive/ SR Officials & MGRS 0 3 1 0 0 0 0 4 First/Mid Officials & MGRS 93 1027 15 4 1 188 0 32 1,495 Professionals 325 2868 4 41 4 972 7 98 4,715 Technicians 1 32 4 0 6 0 0 43 Sales Workers 2 19 0 0 1 0 1 23 Administrative Support 452 2074 858 10 504 7 101 4,006 Craft Workers 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 Operatives 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 Laborers & Helpers 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 Service Workers 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 To t a l 873 6,023 1,458 15 1,671 14 232 10,286 Previous Report Total 908 6,503 1,576 9 1,700 13 249 10,958 Male and Female Combined Totals Hispanic or Latino White Black or African American Native Hawaiian or Pacific Islander Asian American Indian or Alaskan Native Tw o o r More Races Overall total To t a l 1,638 15,097 2,399 32 4,034 25 502 23,727 Previous Report Total 1,675 16,068 2,536 28 4,028 25 564 24,924
BNY MELLON ENTERPRISE ESG 117 APPENDIX FORWARD-LOOKING STATEMENTS We have included in this report statements that may constitute “forward-looking statements.” Forward- looking statements are not historical facts or statements of current conditions, but instead represent only our beliefs regarding future events, many of which, by their nature, are inherently uncertain and outside our control. These statements are not guarantees of future results or performance and involve certain known and unknown risks, uncertainties and assumptions that are difficult to predict and are often beyond our control. These statements relate to, among other things, our goals, targets, aspirations, strategy, plans, intentions and objectives, and actual outcomes and results may differ materially from those expressed in, or implied by, any of these forward-looking statements. Factors that could cause our outcomes and results to differ from the forward-looking statements include global socio-demographic and economic trends, energy prices, technological innovations, climate-related conditions and weather events, our ability to gather and verify data regarding environmental impacts, our ability to successfully implement various initiatives throughout the company under expected timeframes, the compliance of various third parties with our policies and procedures, legislative and regulatory changes, and other unforeseen events or conditions. In addition, important factors that generally affect our business and operations can be found under “Risk Factors” in Part I, Item 1A of our Annual Report on Form 10-K for the year ended December 31, 2021, and in subsequent reports filed with the Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC). Certain disclosures included in this report are being provided in connection with our application of guidelines and recommendations of the Global Reporting Initiative, the UN Global Compact, the Task Force on Climate- related Financial Disclosures and others. Our approach to the disclosures included in this report differs from our approach to the disclosures we include in our mandatory regulatory reports, including our filings with the SEC. While certain matters discussed in this report may be significant, any significance should not be read as necessarily rising to the level of materiality used for the purposes of complying with the U.S. federal securities laws and regulations, even if we use the word “material” or “materiality” in this report. This report is intended to provide information from a different perspective and in more detail than that required to be included in other regulatory reports, including our filings with the SEC. All forward-looking statements speak only as of the date on which such statements are made, and BNY Mellon undertakes no obligation to update any statement to reflect events or circumstances after the date on which such forward-looking statement is made or to reflect the occurrence of unanticipated events. LEGAL NOTICES AND DISCLOSURES BNY Mellon is the corporate brand of The Bank of New York Mellon Corporation and may be used to reference the corporation as a whole and/or its various subsidiaries generally. This material and any products and services may be issued or provided under various brand names of BNY Mellon in various countries by duly authorized and regulated subsidiaries, affiliates, and joint ventures of BNY Mellon, which may include any of those listed below: The Bank of New York Mellon, a banking corporation organized pursuant to the laws of the State of New York, whose registered office is at 240 Greenwich St, NY, NY 10286, USA. The Bank of New York Mellon is supervised and regulated by the New York State Department of Financial Services and the US Federal Reserve and is authorized by the Prudential Regulation Authority (PRA) (Firm Reference Number: 122467). The Bank of New York Mellon also operates in the UK through its London branch (UK companies house numbers FC005522 and BR000818) at One Canada Square, London E14 5AL, UK and is subject to regulation by the Financial Conduct Authority (FCA) at 12 Endeavour Square, London, E20 1JN, UK and limited regulation by the PRA at The Bank of England, Threadneedle St, London, EC2R 8AH, UK. Details about the extent of our regulation by the PRA are available from us on request. In the U.K., a number of services associated with BNY Mellon Wealth Management’s Family Office Services – International are provided through The Bank of New York Mellon, London Branch. LEGAL NOTICES
BNY MELLON ENTERPRISE ESG 118 APPENDIX Investment management services are offered through BNY Mellon Investment Management EMEA Limited, BNY Mellon Centre, One Canada Square, London E14 5AL, which is registered in England No. 1118580 and is authorised and regulated by the Financial Conduct Authority. Offshore trust and administration services are through BNY Mellon Trust Company (Cayman) Ltd. BNY Mellon Fund Services (Ireland) Designated Activity Company is registered with Company No 218007, having its registered office at One Dockland Central, Guild Street, IFSC, Dublin 1, Ireland. It is regulated by the Central Bank of Ireland. The Bank of New York Mellon SA/NV, a Belgian public limited liability company, with company number 0806.743.159, whose registered office is at 46 Rue Montoyerstraat, B-1000 Brussels, Belgium, authorised and regulated as a significant credit institution by the European Central Bank (ECB), under the prudential supervision of the National Bank of Belgium (NBB) and under the supervision of the Belgian Financial Services and Markets Authority (FSMA) for conduct of business rules, a subsidiary of The Bank of New York Mellon. The Bank of New York Mellon SA/NV operates in Ireland through its Dublin branch at Riverside II, Sir John Rogerson’s Quay Grand Canal Dock, Dublin 2, D02KV60, Ireland and is registered with the Companies Registration Office in Ireland No. 907126 & with VAT No. IE 9578054E. The Bank of New York Mellon SA/NV, Dublin Branch is subject to limited additional regulation by the Central Bank of Ireland at New Wapping Street, North Wall Quay, Dublin 1, D01 F7X3, Ireland for conduct of business rules and registered with the Companies Registration Office in Ireland No. 907126 & with VAT No. IE 9578054E. The Bank of New York Mellon SA/NV operates in Germany as The Bank of New York Mellon SA/NV, Asset Servicing, Niederlassung Frankfurt am Main, and has its registered office at MesseTurm, Friedrich-Ebert- Anlage 49, 60327 Frankfurt am Main, Germany. It is subject to limited additional regulation by the Federal Financial Supervisory Authority (Bundesanstalt für Finanzdienstleistungsaufsicht, Marie-Curie-Str. 24-28, 60439 Frankfurt, Germany) under registration number 122721. The Bank of New York Mellon SA/NV operates in the Netherlands through its Amsterdam branch at Strawinskylaan 337, WTC Building, Amsterdam, 1077 XX, the Netherlands. The Bank of New York Mellon SA/NV, Amsterdam Branch is subject to limited additional supervision by the Dutch Central Bank (“De Nederlandsche Bank” or “DNB”) on integrity issues only (registration number 34363596). DNB holds office at Westeinde 1, 1017 ZN Amsterdam, the Netherlands. The Bank of New York Mellon SA/NV operates in Luxembourg through its Luxembourg branch at 2-4 rue Eugene Ruppert, Vertigo Building – Polaris, L- 2453, Luxembourg. The Bank of New York Mellon SA/NV, Luxembourg Branch is subject to limited additional regulation by the Commission de Surveillance du Secteur Financier at 283, route d’Arlon, L-1150 Luxembourg for conduct of business rules, and in its role as UCITS/AIF depositary and central administration agent. The Bank of New York Mellon SA/NV operates in France through its Paris branch at 7 Rue Scribe, Paris, Paris 75009, France. The Bank of New York Mellon SA/NV, Paris Branch is subject to limited additional regulation by Secrétariat Général de l’Autorité de Contrôle Prudentiel at Première Direction du Contrôle de Banques (DCB 1), Service 2, 61, Rue Taitbout, 75436 Paris Cedex 09, France (registration number (SIREN) Nr. 538 228 420 RCS Paris - CIB 13733). The Bank of New York Mellon SA/NV operates in Italy through its Milan branch at Via Mike Bongiorno no. 13, Diamantino building, 5th floor, Milan, 20124, Italy. The Bank of New York Mellon SA/NV, Milan Branch is subject to limited additional regulation by Banca d’Italia - Sede di Milano at Divisione Supervisione Banche, Via Cordusio no. 5, 20123 Milano, Italy (registration number 03351). The Bank of New York Mellon SA/NV operates in Denmark as The Bank of New York Mellon SA/NV, Copenhagen Branch, filial af The Bank of New York Mellon SA/NV, Belgien, and has its registered office at Tuborg Boulevard 12, 3. DK-2900 Hellerup, Denmark. It is subject to limited additional regulation by the Danish Financial Supervisory Authority (Finanstilsynet, Århusgade 110, 2100 København Ø). The Bank of New York Mellon SA/NV operates in Spain through its Madrid branch with registered office at Calle José Abascal 45, Planta 4ª, 28003, Madrid, and enrolled on the Reg. Mercantil de Madrid, Tomo 41019, folio 185 (M-727448). The Bank of New York Mellon, Sucursal en España is registered with Banco de España (registration number 1573).
BNY MELLON ENTERPRISE ESG 119 APPENDIX The Bank of New York Mellon SA/NV operates in England through its London branch at 160 Queen Victoria Street, London EC4V 4LA, UK, registered in England and Wales with numbers FC029379 and BR014361. The Bank of New York Mellon SA/NV, London branch is authorized by the ECB (address above) and is deemed authorised by the Prudential Regulation Authority. Subject to regulation by the Financial Conduct Authority and limited regulation by the Prudential Regulation Authority. Details of the Temporary Permissions Regime, which allows EEA-based firms to operate in the UK for a limited period while seeking full authorisation, are available on the Financial Conduct Authority’s website. The Bank of New York Mellon (International) Limited is registered in England & Wales with Company No. 03236121 with its Registered Office at One Canada Square, London E14 5AL. The Bank of New York Mellon (International) Limited is authorised by the Prudential Regulation Authority and regulated by the Financial Conduct Authority and the Prudential Regulation Authority. Regulatory information in relation to the above BN Y Mellon entities operating out of Europe can be accessed at the following website: ht tps://www.bnymellon.com/RID . For clients located in Switzerland The information provided herein does not constitute an offer of a financial instrument or an offer to provide financial service in Switzerland pursuant to or within the meaning of the Swiss Financial Services Act (“FinSA”) and its implementing ordinance. This is solely an advertisement pursuant to or within the meaning of FinSA and its implementing ordinance. Please be informed that The Bank of New York Mellon and The Bank of New York Mellon SA/NV are entering into any OTC derivative transactions as a counterparty, i.e. each is acting for its own account or for the account of one of its affiliates. As a result, where you enter into any OTC derivative transactions with us, you will not be considered a “client” (within the meaning of the FinSA) and you will not benefit from the protections otherwise afforded to clients under FinSA. The Bank of New York Mellon, Singapore Branch, is subject to regulation by the Monetary Authority of Singapore. For recipients of this information located in Singapore: This material has not been reviewed by the Monetary Authority of Singapore. The Bank of New York Mellon, Hong Kong Branch (a branch of a banking corporation organized and existing under the laws of the State of New York with limited liability), is subject to regulation by the Hong Kong Monetary Authority and the Securities & Futures Commission of Hong Kong. For clients located in Australia, The Bank of New York Mellon is regulated by the Australian Prudential Regulation Authority and also holds an Australian Financial Services Licence No. 527917 issued by the Australian Securities and Investments Commission to provide financial services to wholesale clients in Australia. For clients located in Malaysia, none of The Bank of New York Mellon group entities, including The Bank of New York Mellon, Kuala Lumpur, Representative Office, are registered or licensed to provide, nor does it purport to provide, financial or capital markets services of any kind in Malaysia under the Capital Markets and Services Act 2007 of Malaysia or Financial Services Act 2013 of Malaysia. The Bank of New York Mellon has various other branches in the Asia-Pacific Region which are subject to regulation by the relevant local regulator in that jurisdiction. The Bank of New York Mellon Securities Company Japan Ltd, as intermediary for The Bank of New York Mellon. The Bank of New York Mellon, DIFC Branch, regulated by the Dubai Financial Services Authority (DFSA) and located at DIFC, The Exchange Building 5 North, Level 6, Room 601, P.O. Box 506723, Dubai, UAE, on behalf of The Bank of New York Mellon, which is a wholly-owned subsidiary of The Bank of New York Mellon Corporation. Pershing is the umbrella name for Pershing LLC (member FINRA, SIPC and NYSE), Pershing Advisor Solutions (member FINRA and SIPC), Pershing Limited (UK), Pershing Securities Limited (UK), Pershing Securities International Limited (Ireland), Pershing (Channel Islands) Limited, Pershing Securities Canada Limited, Pershing Securities Singapore Private Limited, and Pershing India Operational Services Pvt Ltd. Pershing businesses also include Albridge Solutions, Inc., a technology provider, and Lockwood Advisors, Inc., an investment adviser registered in the United States under the Investment Advisers Act of 1940. Pershing LLC is a member of SIPC, which protects securities customers of its members up to $500,000 (including $250,000 for
BNY MELLON ENTERPRISE ESG 120 APPENDIX claims for cash). Explanatory brochure available upon request or at sipc.org. SIPC does not protect against loss due to market fluctuation. SIPC protection is not the same as, and should not be confused with, FDIC insurance. BNY Mellon Investment Management is one of the world’s leading investment management organizations and one of the top U.S. wealth managers, encompassing BNY Mellon’s affiliated investment management firms and global distribution companies. Products and services may be provided under various brand names and in various countries by subsidiaries, affiliates and joint ventures of The Bank of New York Mellon Corporation where authorized and regulated as required within each jurisdiction. The investment products and services mentioned in this material are not insured by the FDIC (or any other state or federal agency), are not deposits of or guaranteed by any bank, and may lose value. Alcentra Limited, Insight Investment International Limited, Newton Investment Management Limited and Walter Scott & Partners Limited are authorized and regulated by the Financial Conduct Authority. Alcentra NY, LLC, BNY Mellon Investment Advisers, Inc., Insight Investment International Limited, Insight North America LLC, Mellon Investments Corporation, Newton Investment Management Limited, Newton Investment Management North America LLC and Walter Scott & Partners Limited are SEC registered investment advisers. The Alcentra Group refers to the affiliated companies Alcentra, Ltd and Alcentra NY, LLC. AUM includes assets managed by both companies. Assets under management reflect assets of all accounts and portions of accounts managed by Alcentra for Alcentra and its affiliates. ARX is the brand used to describe the Brazilian investment capabilities of BNY Mellon ARX Investimentos Ltda. Dreyfus is a division of Mellon Investments Corporation (MIC) and BNY Mellon Investment Adviser, Inc. (BNYMIA). When managing Dreyfus money market mutual funds, Dreyfus personnel act in their capacity as dual employees of BNYMIA, the funds’ investment adviser, and members of its Dreyfus division. Insight Investment’s investment advisory services in North America are provided through two different investment advisers registered with the SEC, using the brand Insight Investment: Insight North America LLC and Insight Investment International Limited. The North American investment advisers are associated with other global investment managers that also (individually and collectively) use the corporate brand Insight Investment and may be referred to as ‘Insight’ or ‘Insight Inves tment ’. The Newton Investment Management Group describes a group of affiliated companies that provide investment advisory services under the brand name “Newton” or “Newton Investment Management.” Those companies include Newton Investment Management Ltd. and Newton Investment Management North America LLC. BNY Mellon owns a 20% interest in Siguler Guff & Company, LP and certain related entities (including Siguler Guff Advisers, LLC). All investments involve risk including loss of principal. Certain investments involve greater or unique risks that should be considered along with the objectives, fees, and expenses before investing. Past performance is not a guide to future performance of any instrument, transaction, strategy, or financial structure and a loss of original capital may occur. Calls and communications with BNY Mellon may be recorded, for regulatory and other reasons. Disclosures in relation to certain other BNY Mellon group entities can be accessed at the following website: http://disclaimer.bnymellon.com/eu.htm . This material is intended for wholesale/professional clients (or the equivalent only), is not intended for use by retail clients and no other person should act upon it. Persons who do not have professional experience in matters relating to investments should not rely on this material. BNY Mellon will only provide the relevant investment services to investment professionals. Not all products and services are offered in all countries. If distributed in the UK, this material is a financial promotion. If distributed in the EU, this material is a marketing communication. This material, which may be considered advertising, (but shall not be considered advertising under the laws and regulations of Brunei, Malaysia or Singapore), is for general information purposes only and is not intended to provide legal, tax, accounting, investment, financial or other professional advice on any matter. This material
BNY MELLON ENTERPRISE ESG 121 APPENDIX does not constitute a recommendation or advice by BNY Mellon of any kind. Use of our products and services is subject to various regulations and regulatory oversight. You should discuss this material with appropriate advisors in the context of your circumstances before acting in any manner on this material or agreeing to use any of the referenced products or services and make your own independent assessment (based on such advice) as to whether the referenced products or services are appropriate or suitable for you. This material may not be comprehensive or up to date and there is no undertaking as to the accuracy, timeliness, completeness or fitness for a particular purpose of information given. BNY Mellon will not be responsible for updating any information contained within this material and opinions and information contained herein are subject to change without notice. BNY Mellon assumes no direct or consequential liability for any errors in or reliance upon this material. This material may not be distributed or used for the purpose of providing any referenced products or services or making any offers or solicitations in any jurisdiction or in any circumstances in which such products, services, offers or solicitations are unlawful or not authorized, or where there would be, by virtue of such distribution, new or additional registration requirements. BNY Mellon Wealth Management conducts business through various operating subsidiaries of The Bank of New York Mellon Corporation. Any references to dollars are to US dollars unless specified otherwise. This material may not be reproduced or disseminated in any form without the prior written permission of BNY Mellon. Trademarks, logos and other intellectual property marks belong to their respective owners. The Bank of New York Mellon, member of the Federal Deposit Insurance Corporation (FDIC). bnymellon.com P lease click here for additional information regarding disclaimers and disclosures . © 2022 The Bank of New York Mellon. All rights reserved.
VERIFICATION OPINION D ECLARATION GREENHOUSE GAS EMISSIONS To: Stakeholders of BNY Mellon APEX Companies LLC, (Apex ) was engaged to conduct an independent verification of the greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions reported by BNY Mellon for the per iod s tated b e l ow. Th is Verifi c at i o n Opinio n Declaration applies t o the related information included within the scope of work described below. The determination of the GHG emissions is the sole responsibility of BNY Mellon . BNY Mellon is respon sible for the prep aration and f air pr e se n t at i o n of t he GHG emissio ns statement in accord ance with the criteria . Apex’ s sole responsibility was to provide independent verification opi ni on on the accuracy of the GHG e missions reported, and on the underlying systems and processes use d to coll ect, an a ly ze and rev iew the i n fo r m at ion. Apex is responsible for expressing an opinion on the GHG emissions statement based on the verification. Verification activi ties applied in a limited level of assurance verification are less extensive in natu re, tim in g and e xt ent than i n a re as on able leve l o f as surance verification. Boundaries of the reporting company GHG emissions covered by the verification: • Operational Control • Worldwide for Scope 1 and 2 Emissions • USA and UK only for Scope 3 Emissions T y p es of GHGs : CO 2 , N 2 O, CH 4 , HFCs GHG Emiss ions St at e men t : Electricity Consumption Megawatt Hours (MWH) for 20 2 1 Electricity Consumption MWH 242,956 Purchased Renewable Energy Certificates (RECs) , Guarantees of Origin (GOs) and other renewable electricity instruments i n MWH applied to Scope 2 Emissions from Purchased Electricity 250,781 BNY Mellon Entity - Wide GHG Emissions for 20 2 1 Scope 1 E missions - Metric Tonnes (mt) of CO 2 equivalent (CO 2 e ) 6,214 Scope 2 Emissions – Location Based mt CO 2 e 89,671 S c ope 2 Emissions – Market Based mt CO 2 e (purchased steam emissions and electricity emissions not covered by renewable electricity instrumen ts ) 1,974 Scope 3 Emissions – Category 6 Business Travel mt CO 2 e 1,219 Total S cope 1 + Scope 2 Market Based + Scop e 3 Business Trave l mt CO 2 e 9,407 GHG Emission Offsets and Net Emissions for 20 2 1 Purchased GHG Emission Offsets mt CO 2 e 10,000 Net Emissions CO 2 e (Scope 1 + Scope 2 Market Based + Scope 3) - Purchased GHG Emission O ffsets 0
P age 2 Data and information supp or tin g the Scope 1 an d Scope 2 GHG emissions assertion w ere in most cases historical in nature , but in some cases estimated . Data and information supporting the Scope 3 GHG emissions assertion were in some cases estimated , rather than historical in nature . Per iod covered by G HG emissions verif icatio n : • Calendar Year 20 2 1 : January 1 , 2 0 2 1 to December 31, 20 2 1 Criter ia against which verification c onducted: • World Resources Institute (WRI)/World Busin es s C ouncil for Sustainable Develop ment (WBCSD) Greenhouse G as Pr otocol , Corporat e Accounting and Reporting Standard , Revised Edition (Scope 1 and 2) and the GHG Protocol Scope 2 Guidance, an amendment to the GHG Protocol Corporate Standard • WR I/WBCS D Corporate Value Cha in (Sc ope 3) Accounting and Reporting Standard R efe rence Standard : • ISO 14064 - 3 Second Editi on 2019 - 04 : Greenhouse gases -- Part 3: S pe ci f ication wi t h gu i dance for the ve rification a nd valid a tion of greenhouse g as state ment s Le vel of Assurance and Qual ificat ions : • Limited • This verifica tion used a mate ri ali ty threshold of +/ - 5% for aggregate errors in sampled data for each of the abo ve indic at or s . • Q ualificat ions: None GHG Verification M e thodology: Evidence - ga thering procedures included , but were not limited to: • Interviews with r elevan t personnel of BN Y M ellon ; • Review of documentary evid ence prod uc ed by BNY Mellon ; • Revie w o f BNY Mellon data and information sy s t em s and methodology fo r collectio n, aggregation, analysis and review of inform ation used to determ ine GHG em ission s ; • Review of data and meth od olo gy for tracking purchases, certification an d retirement of RECs, GOs, and GHG Offsets; and, • A u dit of sample of d ata used by BNY Mellon to determine GHG emissions. Verification Opinion: Based on the verification process and procedu r es conducted to a li mi t ed assurance level of the GHG emissions state me nt shown above, Apex found no evi dence that the GHG emissions statement : • is n ot mate rially correc t and is not a fair r e presentation of the GHG em ission s d a ta and information; and • has no t been prepared in a c co r d ance with the WRI/WBCSD G HG Protocol Corporat e Acco un ti n g and Reporting Standar d ( Scop e 1 and 2 ), and W RI/WBCSD Green house Gas Protocol Corpora te Value Chain Accoun ting and Reporting Standar d (Sco pe 3) .
P age 3 It is our opinion that BNY Mellon has establish e d ap prop riate systems for the collection, aggrega tion and an al ys i s of qu antitative data for det ermination of the se GHG emissions for t he stated period and bound a rie s. St at ement of independence, imp artiality and competence Apex is an indepen d ent profession a l se rvic es company that speci alizes in Health, Sa fety, Socia l an d Enviro nmental man agement s erv ices including as surance with over 3 0 y ears history in providing t hes e ser vi ces. No member of the ver ification team has a business relationship w ith BNY Mellon , i ts Director s or Managers be yond that required o f this assignment . W e conducted t his ver ification i ndependen tly and to our knowled ge there ha s been no confl i ct of in terest. Apex has implemented a Co de of Ethics across the business to maintain h igh ethic a l st andards a mong staff in th eir d ay - to - day busin ess activities. T he v e rification t eam has extensive experienc e in conducting assura nce over environmental, so c ial, eth ical an d health and safety inform ation, systems and processes, has over 20 yea r s combine d e xp erience i n this field and an excellent unders tanding of Apex’s s ta n dard methodo logy fo r the verif ication o f greenhouse gas emiss ions data. Attestation: Mary E. Armstrong - Friberg , Lea d Verifier David Re illy , Technical Revi ewer Senior Project Man ager Senior Project Manager APEX Companies, LLC A PEX Com pa nies, LLC Cleveland, Ohio Santa Ana , California May 10 , 2022 T his verification opinion declaration , including th e opinion expressed he rein, is provided to BNY Mellon a n d is solely f or t he benefit of BNY M ellon i n acco rdance wi th the terms of our a greement. W e consent to the release o f this opinion by you to CDP in order to satisfy the terms of CDP dis closure r equirements but withou t accepting or assuming an y re s p ons ibili ty or liabi l i t y on our part to CDP or to any ot her par ty who may have access to this opinion .
BNY MELLON ENTERPRISE ESG 125 APPROACH bnymellon.com/futurefirst