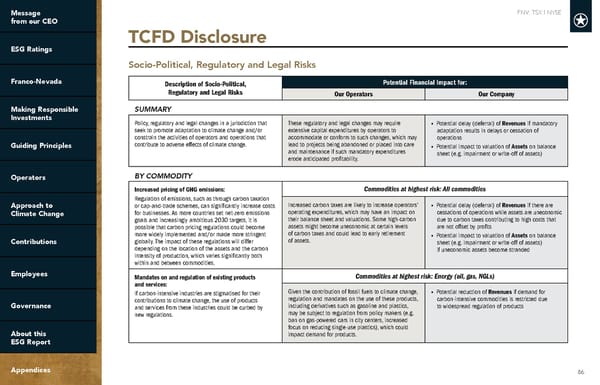
FNV: TSX | NYSE 86 TCFD Disclosure Socio-Political, Regulatory and Legal Risks Description of Socio-Political, Regulatory and Legal Risks Potential Financial Impact for: Our Operators Our Company SUMMARY Policy, regulatory and legal changes in a jurisdiction that seek to promote adaptation to climate change and/or constrain the activities of operators and operations that contribute to adverse effects of climate change. These regulatory and legal changes may require extensive capital expenditures by operators to accommodate or conform to such changes, which may lead to projects being abandoned or placed into care and maintenance if such mandatory expenditures erode anticipated profitability. • Potential delay (deferral) of Revenues if mandatory adaptation results in delays or cessation of operations • Potential impact to valuation of Assets on balance sheet (e.g. impairment or write-off of assets) BY COMMODITY Increased pricing of GHG emissions: Regulation of emissions, such as through carbon taxation or cap-and-trade schemes, can significantly increase costs for businesses. As more countries set net-zero emissions goals and increasingly ambitious 2030 targets, it is possible that carbon pricing regulations could become more widely implemented and/or made more stringent globally. The impact of these regulations will differ depending on the location of the assets and the carbon intensity of production, which varies significantly both within and between commodities. Commodities at highest risk: All commodities Increased carbon taxes are likely to increase operators’ operating expenditures, which may have an impact on their balance sheet and valuations. Some high-carbon assets might become uneconomic at certain levels of carbon taxes and could lead to early retirement of assets. • Potential delay (deferral) of Revenues if there are cessations of operations while assets are uneconomic due to carbon taxes contributing to high costs that are not offset by profits • Potential impact to valuation of Assets on balance sheet (e.g. impairment or write-off of assets) if uneconomic assets become stranded Mandates on and regulation of existing products and services: If carbon-intensive industries are stigmatised for their contributions to climate change, the use of products and services from these industries could be curbed by new regulations. Commodities at highest risk: Energy (oil, gas, NGLs) Given the contribution of fossil fuels to climate change, regulation and mandates on the use of these products, including derivatives such as gasoline and plastics, may be subject to regulation from policy makers (e.g. ban on gas-powered cars in city centers, increased focus on reducing single-use plastics), which could impact demand for products. • Potential reduction of Revenues if demand for carbon-intensive commodities is restricted due to widespread regulation of products
 2022 ESG Report | Franco-Nevada Page 85 Page 87
2022 ESG Report | Franco-Nevada Page 85 Page 87