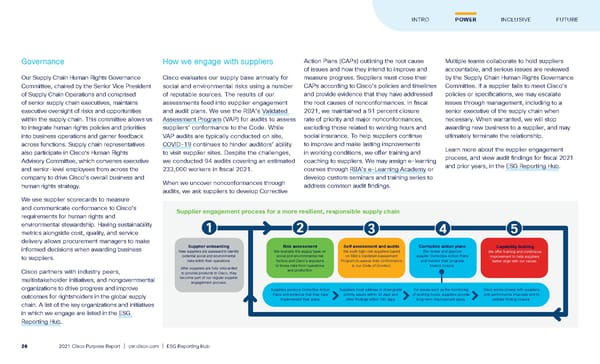
Governance Our Supply Chain Human Rights Governance Committee, chaired by the Senior Vice President of Supply Chain Operations and comprised of senior supply chain executives, maintains executive oversight of risks and opportunities within the supply chain. This committee allows us to integrate human rights policies and priorities into business operations and garner feedback across functions. Supply chain representatives also participate in Cisco’s Human Rights Advisory Committee, which convenes executive and senior-level employees from across the company to drive Cisco’s overall business and human rights strategy. We use supplier scorecards to measure and communicate conformance to Cisco’s requirements for human rights and environmental stewardship. Having sustainability metrics alongside cost, quality, and service delivery allows procurement managers to make informed decisions when awarding business to suppliers. Cisco partners with industry peers, multistakeholder initiatives, and nongovernmental organizations to drive progress and improve outcomes for rightsholders in the global supply chain. A list of the key organizations and initiatives in which we engage are listed in the ESG Reporting Hub . How we engage with suppliers Cisco evaluates our supply base annually for social and environmental risks using a number of reputable sources. The results of our assessments feed into supplier engagement and audit plans. We use the RBA’s Validated Assessment Program (VAP) for audits to assess suppliers’ conformance to the Code. While VAP audits are typically conducted on site, COVID-19 continues to hinder auditors’ ability to visit supplier sites. Despite the challenges, we conducted 94 audits covering an estimated 233,000 workers in fiscal 2021. When we uncover nonconformances through audits, we ask suppliers to develop Corrective Action Plans (CAPs) outlining the root cause of issues and how they intend to improve and measure progress. Suppliers must close their CAPs according to Cisco’s policies and timelines and provide evidence that they have addressed the root causes of nonconformances. In fiscal 2021, we maintained a 91 percent closure rate of priority and major nonconformances, excluding those related to working hours and social insurance. To help suppliers continue to improve and make lasting improvements in working conditions, we offer training and coaching to suppliers. We may assign e-learning courses through RBA’s e-Learning Academy or develop custom seminars and training series to address common audit findings. Multiple teams collaborate to hold suppliers accountable, and serious issues are reviewed by the Supply Chain Human Rights Governance Committee. If a supplier fails to meet Cisco’s policies or specifications, we may escalate issues through management, including to a senior executive of the supply chain when necessary. When warranted, we will stop awarding new business to a supplier, and may ultimately terminate the relationship. Learn more about the supplier engagement process, and view audit findings for fiscal 2021 and prior years, in the ESG Reporting Hub . Supplier engagement process for a more resilient, responsible supply chain 1 Supplier onboarding New suppliers are assessed to identify potential social and environmental risks within their operations. After suppliers are fully onboarded to provide products to Cisco, they become part of our regular supplier engagement process. 2 Risk assessment We evaluate the supply base on social and environmental risk factors and Cisco’s exposure to those risks from operations and production. 3 Self assessment and audits We audit high-risk suppliers based on RBA’s Validated Assessment Program to assess their conformance to our Code of Conduct. 4 Corrective action plans We review and approve supplier Corrective Action Plans and monitor their progress toward closure. Suppliers produce Corrective Action Plans and evidence that they have implemented their plans. Suppliers must address or downgrade priority issues within 30 days and other findings within 180 days. For issues such as the monitoring of working hours, suppliers provide long-term improvement plans. Cisco works closely with suppliers until performance improves and to validate finding closure. 5 Capability building We offer training and continuous improvement to help suppliers better align with our values. FUTURE INTRO POWER INCLUSIVE 2021 Cisco Purpose Report | csr.cisco.com | ESG Reporting Hub 26
 Cisco Purpose Report Page 26 Page 28
Cisco Purpose Report Page 26 Page 28