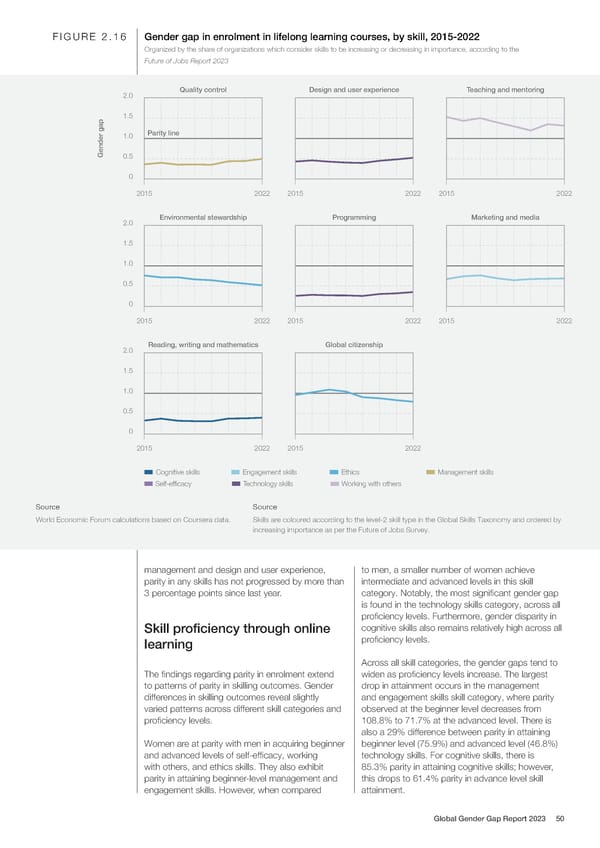
FIGURE 2.16 Gender gap in enrolment in lifelong learning courses, by skill, 2015-2022 Organized by the share of organizations which consider skills to be increasing or decreasing in importance, according to the Future of Jobs Report 2023 2.0 Quality control Design and user experience Teaching and mentoring 1.5 1.0 Parity line Gender gap0.5 0 2015 2022 2015 2022 2015 2022 2.0 Environmental stewardship Programming Marketing and media 1.5 1.0 0.5 0 2015 2022 2015 2022 2015 2022 2.0 Reading, writing and mathematics Global citizenship 1.5 1.0 0.5 0 2015 2022 2015 2022 Cognitive skills Engagement skills Ethics Management skills Self-efficacy Technology skills Working with others Source Source World Economic Forum calculations based on Coursera data. Skills are coloured according to the level-2 skill type in the Global Skills Taxonomy and ordered by increasing importance as per the Future of Jobs Survey. management and design and user experience, to men, a smaller number of women achieve parity in any skills has not progressed by more than intermediate and advanced levels in this skill 3 percentage points since last year. category. Notably, the most signi昀椀cant gender gap is found in the technology skills category, across all pro昀椀ciency levels. Furthermore, gender disparity in Skill pro昀椀ciency through online cognitive skills also remains relatively high across all learning pro昀椀ciency levels. Across all skill categories, the gender gaps tend to The 昀椀ndings regarding parity in enrolment extend widen as pro昀椀ciency levels increase. The largest to patterns of parity in skilling outcomes. Gender drop in attainment occurs in the management differences in skilling outcomes reveal slightly and engagement skills skill category, where parity varied patterns across different skill categories and observed at the beginner level decreases from pro昀椀ciency levels. 108.8% to 71.7% at the advanced level. There is also a 29% difference between parity in attaining Women are at parity with men in acquiring beginner beginner level (75.9%) and advanced level (46.8%) and advanced levels of self-ef昀椀cacy, working technology skills. For cognitive skills, there is with others, and ethics skills. They also exhibit 85.3% parity in attaining cognitive skills; however, parity in attaining beginner-level management and this drops to 61.4% parity in advance level skill engagement skills. However, when compared attainment. Global Gender Gap Report 2023 50
 Global Gender Gap Report 2023 Page 49 Page 51
Global Gender Gap Report 2023 Page 49 Page 51