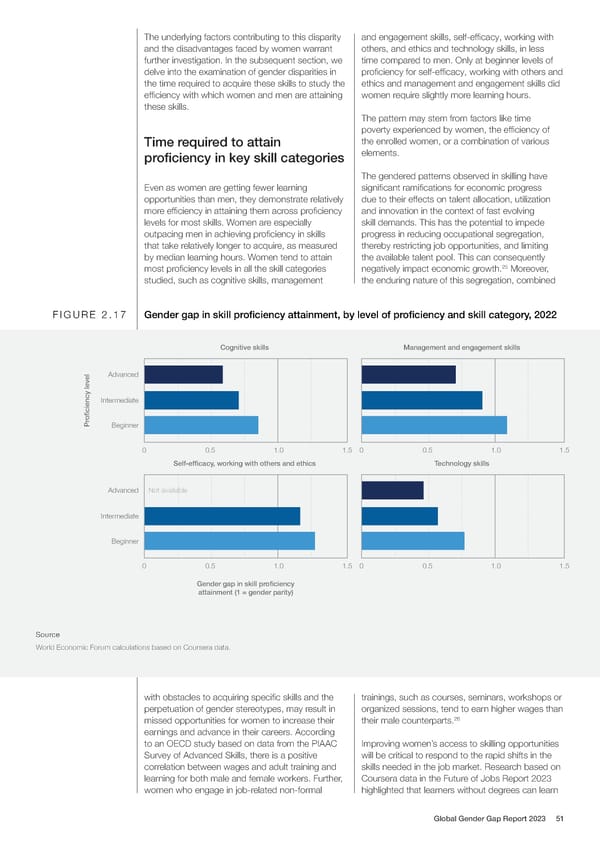
The underlying factors contributing to this disparity and engagement skills, self-ef昀椀cacy, working with and the disadvantages faced by women warrant others, and ethics and technology skills, in less further investigation. In the subsequent section, we time compared to men. Only at beginner levels of delve into the examination of gender disparities in pro昀椀ciency for self-ef昀椀cacy, working with others and the time required to acquire these skills to study the ethics and management and engagement skills did ef昀椀ciency with which women and men are attaining women require slightly more learning hours. these skills. The pattern may stem from factors like time poverty experienced by women, the ef昀椀ciency of Time required to attain the enrolled women, or a combination of various pro昀椀ciency in key skill categories elements. The gendered patterns observed in skilling have Even as women are getting fewer learning signi昀椀cant rami昀椀cations for economic progress opportunities than men, they demonstrate relatively due to their effects on talent allocation, utilization more ef昀椀ciency in attaining them across pro昀椀ciency and innovation in the context of fast evolving levels for most skills. Women are especially skill demands. This has the potential to impede outpacing men in achieving pro昀椀ciency in skills progress in reducing occupational segregation, that take relatively longer to acquire, as measured thereby restricting job opportunities, and limiting by median learning hours. Women tend to attain the available talent pool. This can consequently 25 most pro昀椀ciency levels in all the skill categories negatively impact economic growth. Moreover, studied, such as cognitive skills, management the enduring nature of this segregation, combined FIGURE 2.17 Gender gap in skill proficiency attainment, by level of proficiency and skill category, 2022 Cognitive skills Management and engagement skills Advanced Intermediate oficiency level Pr Beginner 0 0.5 1.0 1.5 0 0.5 1.0 1.5 Self-efficacy, working with others and ethics Technology skills Advanced Not available Intermediate Beginner 0 0.5 1.0 1.5 0 0.5 1.0 1.5 Gender gap in skill proficiency attainment (1 = gender parity) Source World Economic Forum calculations based on Coursera data. with obstacles to acquiring speci昀椀c skills and the trainings, such as courses, seminars, workshops or perpetuation of gender stereotypes, may result in organized sessions, tend to earn higher wages than 26 missed opportunities for women to increase their their male counterparts. earnings and advance in their careers. According to an OECD study based on data from the PIAAC Improving women’s access to skilling opportunities Survey of Advanced Skills, there is a positive will be critical to respond to the rapid shifts in the correlation between wages and adult training and skills needed in the job market. Research based on learning for both male and female workers. Further, Coursera data in the Future of Jobs Report 2023 women who engage in job-related non-formal highlighted that learners without degrees can learn Global Gender Gap Report 2023 51
 Global Gender Gap Report 2023 Page 50 Page 52
Global Gender Gap Report 2023 Page 50 Page 52