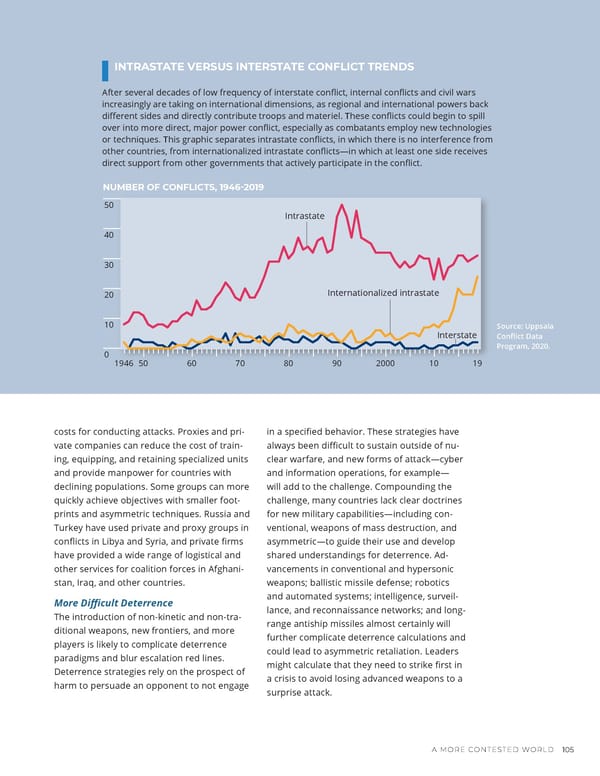
INTRASTATE VERSUS INTERSTATE CONFLICT TRENDS After several decades of low frequency of interstate conflict, internal conflicts and civil wars increasingly are taking on international dimensions, as regional and international powers back different sides and directly contribute troops and materiel. These conflicts could begin to spill over into more direct, major power conflict, especially as combatants employ new technologies or techniques. This graphic separates intrastate conflicts, in which there is no interference from other countries, from internationalized intrastate conflicts—in which at least one side receives direct support from other governments that actively participate in the conflict. NUMBER OF CONFLICTS, 1946-2019 50 Intrastate 40 30 20 Internationalized intrastate 10 Source: Uppsala Interstate Conflict Data Program, 2020. 0 1946 50 60 70 80 90 2000 10 19 costs for conducting attacks. Proxies and pri- in a speci昀椀ed behavior. These strategies have vate companies can reduce the cost of train- always been di昀케cult to sustain outside of nu- ing, equipping, and retaining specialized units clear warfare, and new forms of attack—cyber and provide manpower for countries with and information operations, for example— declining populations. Some groups can more will add to the challenge. Compounding the quickly achieve objectives with smaller foot- challenge, many countries lack clear doctrines prints and asymmetric techniques. Russia and for new military capabilities—including con- Turkey have used private and proxy groups in ventional, weapons of mass destruction, and con昀氀icts in Libya and Syria, and private 昀椀rms asymmetric—to guide their use and develop have provided a wide range of logistical and shared understandings for deterrence. Ad- other services for coalition forces in Afghani- vancements in conventional and hypersonic stan, Iraq, and other countries. weapons; ballistic missile defense; robotics and automated systems; intelligence, surveil- More Di昀케cult Deterrence lance, and reconnaissance networks; and long- The introduction of non-kinetic and non-tra- range antiship missiles almost certainly will ditional weapons, new frontiers, and more further complicate deterrence calculations and players is likely to complicate deterrence could lead to asymmetric retaliation. Leaders paradigms and blur escalation red lines. Deterrence strategies rely on the prospect of might calculate that they need to strike 昀椀rst in harm to persuade an opponent to not engage a crisis to avoid losing advanced weapons to a surprise attack. A MORE CONTESTED WORLD 105
 GlobalTrends 2040 Page 112 Page 114
GlobalTrends 2040 Page 112 Page 114