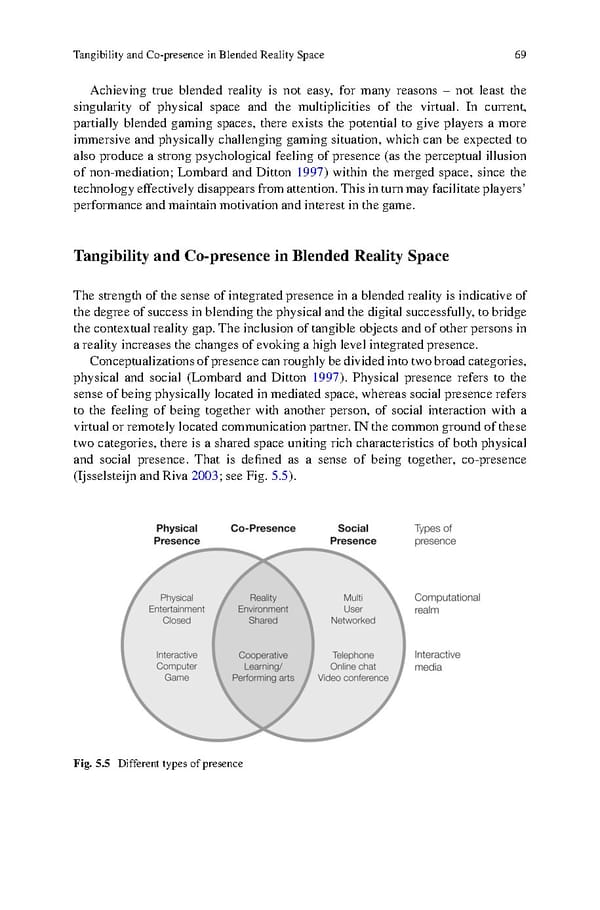
Tangibility and Co-presence in Blended Reality Space 69 Achieving true blended reality is not easy, for many reasons – not least the singularity of physical space and the multiplicities of the virtual. In current, partially blended gaming spaces, there exists the potential to give players a more immersive and physically challenging gaming situation, which can be expected to also produce a strong psychological feeling of presence (as the perceptual illusion of non-mediation; Lombard and Ditton 1997) within the merged space, since the technologyeffectivelydisappearsfromattention.Thisinturnmayfacilitateplayers’ performanceand maintain motivation and interest in the game. Tangibility and Co-presence in Blended Reality Space Thestrength of the sense of integrated presence in a blended reality is indicative of the degree of success in blending the physical and the digital successfully, to bridge the contextual reality gap. The inclusion of tangible objects and of other persons in a reality increases the changes of evoking a high level integrated presence. Conceptualizationsofpresencecanroughlybedividedintotwobroadcategories, physical and social (Lombard and Ditton 1997). Physical presence refers to the sense of being physically located in mediated space, whereas social presence refers to the feeling of being together with another person, of social interaction with a virtual or remotely located communicationpartner. IN the common groundof these two categories, there is a shared space uniting rich characteristics of both physical and social presence. That is defined as a sense of being together, co-presence (Ijsselsteijn and Riva 2003;seeFig.5.5). Fig. 5.5 Different types of presence
 Human Experiential Design of Presence in Everyday Page 76 Page 78
Human Experiential Design of Presence in Everyday Page 76 Page 78