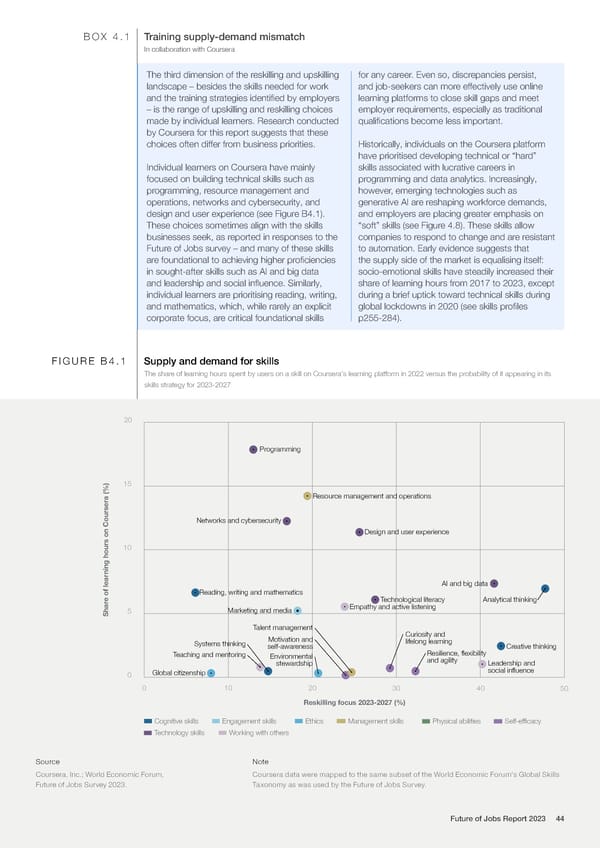
BOX 4.1 Training supply-demand mismatch In collaboration with Coursera The third dimension of the reskilling and upskilling for any career. Even so, discrepancies persist, landscape – besides the skills needed for work and job-seekers can more effectively use online and the training strategies identified by employers learning platforms to close skill gaps and meet – is the range of upskilling and reskilling choices employer requirements, especially as traditional made by individual learners. Research conducted qualifications become less important. by Coursera for this report suggests that these choices often differ from business priorities. Historically, individuals on the Coursera platform have prioritised developing technical or “hard” Individual learners on Coursera have mainly skills associated with lucrative careers in focused on building technical skills such as programming and data analytics. Increasingly, programming, resource management and however, emerging technologies such as operations, networks and cybersecurity, and generative AI are reshaping workforce demands, design and user experience (see Figure B4.1). and employers are placing greater emphasis on These choices sometimes align with the skills “soft” skills (see Figure 4.8). These skills allow businesses seek, as reported in responses to the companies to respond to change and are resistant Future of Jobs survey – and many of these skills to automation. Early evidence suggests that are foundational to achieving higher proficiencies the supply side of the market is equalising itself: in sought-after skills such as AI and big data socio-emotional skills have steadily increased their and leadership and social influence. Similarly, share of learning hours from 2017 to 2023, except individual learners are prioritising reading, writing, during a brief uptick toward technical skills during and mathematics, which, while rarely an explicit global lockdowns in 2020 (see skills profiles corporate focus, are critical foundational skills p255-284). FIGURE B4.1 Supply and demand for skills The share of learning hours spent by users on a skill on Coursera's learning platform in 2022 versus the probability of it appearing in its skills strategy for 2023-2027 20 Programming 15 Resource management and operations Networks and cybersecurity Design and user experience 10 ning hours on Coursera (%) AI and big data e of lear Reading, writing and mathematics Technological literacy Analytical thinking 5 Marketing and media Empathy and active listening Shar Talent management Motivation and Curiosity and Systems thinking self-awareness lifelong learning Creative thinking Teaching and mentoring Environmental Resilience, flexibility stewardship and agility Leadership and 0 Global citizenship social influence 0 10 20 30 40 50 Reskilling focus 2023-2027 (%) Cognitive skills Engagement skills Ethics Management skills Physical abilities Self-efficacy Technology skills Working with others Source Note Coursera, Inc.; World Economic Forum, Coursera data were mapped to the same subset of the World Economic Forum's Global Skills Future of Jobs Survey 2023. Taxonomy as was used by the Future of Jobs Survey. Future of Jobs Report 2023 44
 The Future of Jobs Report 2023 Page 43 Page 45
The Future of Jobs Report 2023 Page 43 Page 45