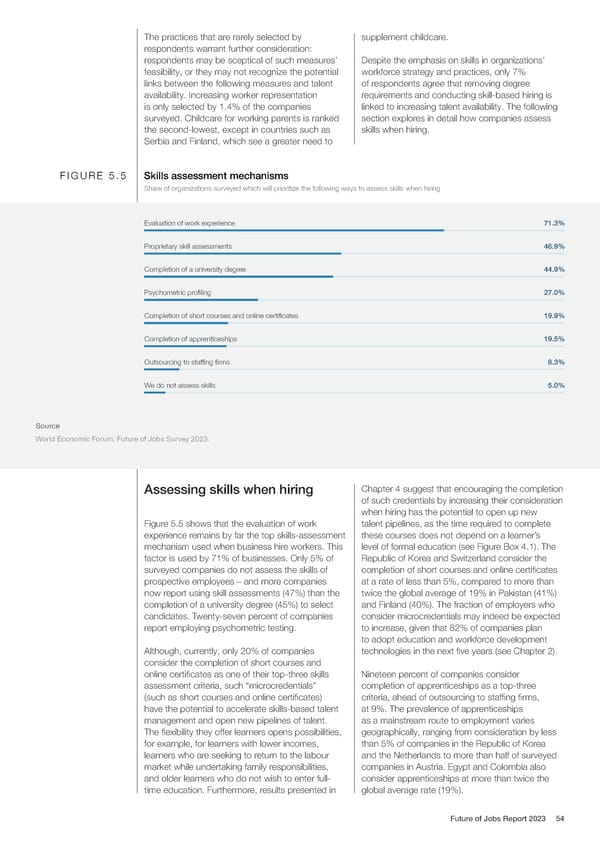
The practices that are rarely selected by supplement childcare. respondents warrant further consideration: respondents may be sceptical of such measures’ Despite the emphasis on skills in organizations’ feasibility, or they may not recognize the potential workforce strategy and practices, only 7% links between the following measures and talent of respondents agree that removing degree availability. Increasing worker representation requirements and conducting skill-based hiring is is only selected by 1.4% of the companies linked to increasing talent availability. The following surveyed. Childcare for working parents is ranked section explores in detail how companies assess the second-lowest, except in countries such as skills when hiring. Serbia and Finland, which see a greater need to FIGURE 5.5 Skills assessment mechanisms Share of organizations surveyed which will prioritize the following ways to assess skills when hiring Evaluation of work experience 71.3% Proprietary skill assessments 46.9% Completion of a university degree 44.9% Psychometric profiling 27.0% Completion of short courses and online certificates 19.9% Completion of apprenticeships 19.5% Outsourcing to staffing firms 8.3% We do not assess skills 5.0% Source World Economic Forum, Future of Jobs Survey 2023. Assessing skills when hiring Chapter 4 suggest that encouraging the completion of such credentials by increasing their consideration when hiring has the potential to open up new Figure 5.5 shows that the evaluation of work talent pipelines, as the time required to complete experience remains by far the top skills-assessment these courses does not depend on a learner’s mechanism used when business hire workers. This level of formal education (see Figure Box 4.1). The factor is used by 71% of businesses. Only 5% of Republic of Korea and Switzerland consider the surveyed companies do not assess the skills of completion of short courses and online certificates prospective employees – and more companies at a rate of less than 5%, compared to more than now report using skill assessments (47%) than the twice the global average of 19% in Pakistan (41%) completion of a university degree (45%) to select and Finland (40%). The fraction of employers who candidates. Twenty-seven percent of companies consider microcredentials may indeed be expected report employing psychometric testing. to increase, given that 82% of companies plan to adopt education and workforce development Although, currently, only 20% of companies technologies in the next five years (see Chapter 2). consider the completion of short courses and online certificates as one of their top-three skills Nineteen percent of companies consider assessment criteria, such “microcredentials” completion of apprenticeships as a top-three (such as short courses and online certificates) criteria, ahead of outsourcing to staffing firms, have the potential to accelerate skills-based talent at 9%. The prevalence of apprenticeships management and open new pipelines of talent. as a mainstream route to employment varies The flexibility they offer learners opens possibilities, geographically, ranging from consideration by less for example, for learners with lower incomes, than 5% of companies in the Republic of Korea learners who are seeking to return to the labour and the Netherlands to more than half of surveyed market while undertaking family responsibilities, companies in Austria. Egypt and Colombia also and older learners who do not wish to enter full- consider apprenticeships at more than twice the time education. Furthermore, results presented in global average rate (19%). Future of Jobs Report 2023 54
 The Future of Jobs Report 2023 Page 53 Page 55
The Future of Jobs Report 2023 Page 53 Page 55