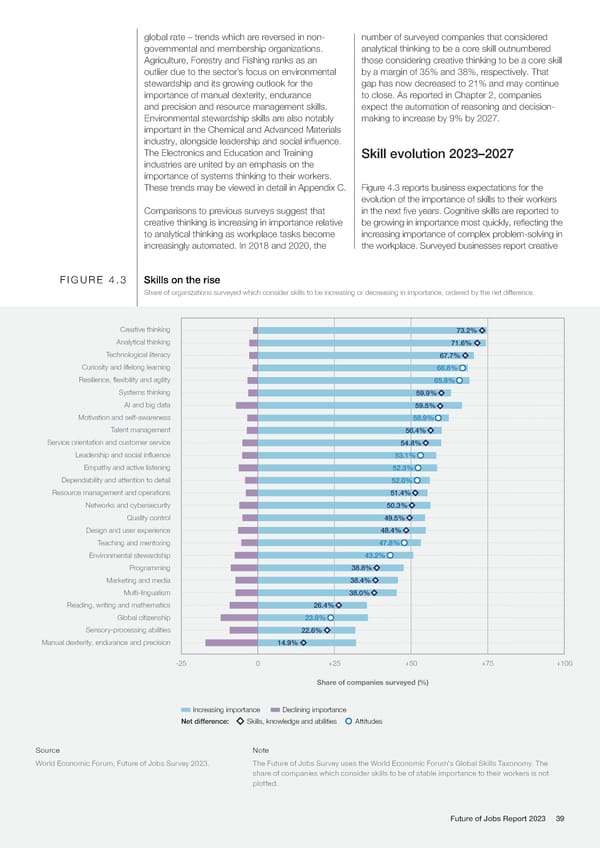
global rate – trends which are reversed in non- number of surveyed companies that considered governmental and membership organizations. analytical thinking to be a core skill outnumbered Agriculture, Forestry and Fishing ranks as an those considering creative thinking to be a core skill outlier due to the sector’s focus on environmental by a margin of 35% and 38%, respectively. That stewardship and its growing outlook for the gap has now decreased to 21% and may continue importance of manual dexterity, endurance to close. As reported in Chapter 2, companies and precision and resource management skills. expect the automation of reasoning and decision- Environmental stewardship skills are also notably making to increase by 9% by 2027. important in the Chemical and Advanced Materials industry, alongside leadership and social influence. The Electronics and Education and Training Skill evolution 2023–2027 industries are united by an emphasis on the importance of systems thinking to their workers. These trends may be viewed in detail in Appendix C. Figure 4.3 reports business expectations for the evolution of the importance of skills to their workers Comparisons to previous surveys suggest that in the next five years. Cognitive skills are reported to creative thinking is increasing in importance relative be growing in importance most quickly, reflecting the to analytical thinking as workplace tasks become increasing importance of complex problem-solving in increasingly automated. In 2018 and 2020, the the workplace. Surveyed businesses report creative FIGURE 4.3 Skills on the rise Share of organizations surveyed which consider skills to be increasing or decreasing in importance, ordered by the net difference. Creative thinking 73.2% Analytical thinking 71.6% Technological literacy 67.7% Curiosity and lifelong learning 66.8% Resilience, flexibility and agility 65.8% Systems thinking 59.9% AI and big data 59.5% Motivation and self-awareness 58.9% Talent management 56.4% Service orientation and customer service 54.8% Leadership and social influence 53.1% Empathy and active listening 52.3% Dependability and attention to detail 52.0% Resource management and operations 51.4% Networks and cybersecurity 50.3% Quality control 49.5% Design and user experience 48.4% Teaching and mentoring 47.8% Environmental stewardship 43.2% Programming 38.8% Marketing and media 38.4% Multi-lingualism 38.0% Reading, writing and mathematics 26.4% Global citizenship 23.8% Sensory-processing abilities 22.6% Manual dexterity, endurance and precision 14.9% -25 0 +25 +50 +75 +100 Share of companies surveyed (%) Increasing importance Declining importance Net difference: Skills, knowledge and abilities Attitudes Source Note World Economic Forum, Future of Jobs Survey 2023. The Future of Jobs Survey uses the World Economic Forum's Global Skills Taxonomy. The share of companies which consider skills to be of stable importance to their workers is not plotted. Future of Jobs Report 2023 39
 The Future of Jobs Report 2023 Page 38 Page 40
The Future of Jobs Report 2023 Page 38 Page 40