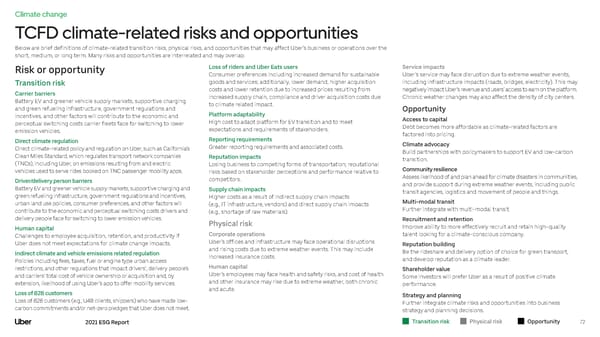
Climate change TCFD climate-related risks and opportunities Below are brief definitions of climate-related transition risks, physical risks, and opportunities that may affect Uber's business or operations over the short, medium, or long term. Many risks and opportunities are interrelated and may overlap. Risk or opportunity Loss of riders and Uber Eats users Service impacts Consumer preferences including increased demand for sustainable Uber’s service may face disruption due to extreme weather events, Transition risk goods and services; additionally, lower demand, higher acquisition including infrastructure impacts (roads, bridges, electricity). This may Carrier barriers costs and lower retention due to increased prices resulting from negatively impact Uber’s revenue and users’ access to earn on the platform. Battery EV and greener vehicle supply markets, supportive charging increased supply chain, compliance and driver acquisition costs due Chronic weather changes may also affect the density of city centers. and green refueling infrastructure, government regulations and to climate related impact. Opportunity incentives, and other factors will contribute to the economic and Platform adaptability Access to capital perceptual switching costs carrier fleets face for switching to lower High cost to adapt platform for EV transition and to meet Debt becomes more affordable as climate-related factors are emission vehicles. expectations and requirements of stakeholders. factored into pricing. Direct climate regulation Reporting requirements Climate advocacy Direct climate-related policy and regulation on Uber, such as California’s Greater reporting requirements and associated costs. Build partnerships with policymakers to support EV and low-carbon Clean Miles Standard, which regulates transport network companies Reputation impacts transition. (TNCs), including Uber, on emissions resulting from and electric Losing business to competing forms of transportation; reputational vehicles used to serve rides booked on TNC passenger mobility apps. risks based on stakeholder perceptions and performance relative to Community resilience Driver/delivery person barriers competitors. Assess likelihood of and plan ahead for climate disasters in communities, Battery EV and greener vehicle supply markets, supportive charging and Supply chain impacts and provide support during extreme weather events, including public green refueling infrastructure, government regulations and incentives, Higher costs as a result of indirect supply chain impacts transit agencies, logistics and movement of people and things. urban land use policies, consumer preferences, and other factors will (e.g., IT infrastructure, vendors) and direct supply chain impacts Multi-modal transit contribute to the economic and perceptual switching costs drivers and (e.g., shortage of raw materials). Further integrate with multi-modal transit. delivery people face for switching to lower emission vehicles. Physical risk Recruitment and retention Human capital Improve ability to more effectively recruit and retain high-quality Challenges to employee acquisition, retention, and productivity if Corporate operations talent looking for a climate-conscious company. Uber does not meet expectations for climate change impacts. Uber’s offices and infrastructure may face operational disruptions Reputation building Indirect climate and vehicle emissions related regulation and rising costs due to extreme weather events. This may include Be the rideshare and delivery option of choice for green transport, Policies including fees, taxes, fuel or engine type urban access increased insurance costs. and develop reputation as a climate leader. restrictions, and other regulations that impact drivers’ , delivery people’s Human capital Shareholder value and carriers’ total cost of vehicle ownership or acquisition and, by Uber’s employees may face health and safety risks, and cost of health Some investors will prefer Uber as a result of positive climate extension, likelihood of using Uber’s app to offer mobility services. and other insurance may rise due to extreme weather, both chronic performance. Loss of B2B customers and acute. Strategy and planning Loss of B2B customers (e.g., U4B clients, shippers) who have made low- Further integrate climate risks and opportunities into business carbon commitments and/or net-zero pledges that Uber does not meet. strategy and planning decisions. 2021 ESG Report Transition risk Physical risk Opportunity 72
 Uber ESG Report Page 71 Page 73
Uber ESG Report Page 71 Page 73