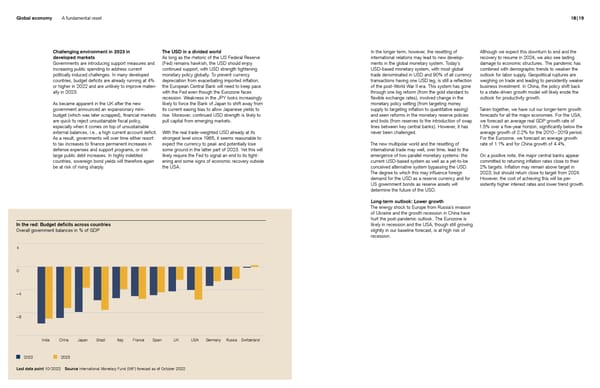
Global economy A fundamental reset 18 | 19 Challenging environment in 2023 in The USD in a divided world In the longer term, however, the resetting of Although we expect this downturn to end and the developed markets As long as the rhetoric of the US Federal Reserve international relations may lead to new develop- recovery to resume in 2024, we also see lasting Governments are introducing support measures and (Fed) remains hawkish, the USD should enjoy ments in the global monetary system. Today’s damage to economic structures. The pandemic has increasing public spending to address current continued support, with USD strength tightening USD-based monetary system, with most global combined with demographic trends to weaken the politically induced challenges. In many developed monetary policy globally. To prevent currency trade denominated in USD and 90% of all currency outlook for labor supply. Geopolitical ruptures are countries, budget deficits are already running at 4% depreciation from exacerbating imported inflation, transactions having one USD leg, is still a reflection weighing on trade and leading to persistently weaker or higher in 2022 and are unlikely to improve materi- the European Central Bank will need to keep pace of the post-World War II era. This system has gone business investment. In China, the policy shift back ally in 2023. with the Fed even though the Eurozone faces through one big reform (from the gold standard to to a state-driven growth model will likely erode the recession. Weakness in the JPY looks increasingly flexible exchange rates), involved change in the outlook for productivity growth. As became apparent in the UK after the new likely to force the Bank of Japan to shift away from monetary policy setting (from targeting money government announced an expansionary mini- its current easing bias to allow Japanese yields to supply to targeting inflation to quantitative easing) Taken together, we have cut our longer-term growth budget (which was later scrapped), financial markets rise. Moreover, continued USD strength is likely to and seen reforms in the monetary reserve policies forecasts for all the major economies. For the USA, are quick to reject unsustainable fiscal policy, pull capital from emerging markets. and tools (from reserves to the introduction of swap we forecast an average real GDP growth rate of especially when it comes on top of unsustainable lines between key central banks). However, it has 1.5% over a five-year horizon, significantly below the external balances, i.e., a high current account deficit. With the real trade-weighted USD already at its never been challenged. average growth of 2.2% for the 2010 – 2019 period. As a result, governments will over time either resort strongest level since 1985, it seems reasonable to For the Eurozone, we forecast an average growth to tax increases to finance permanent increases in expect the currency to peak and potentially lose The new multi polar world and the resetting of rate of 1.1% and for China growth of 4.4%. defense expenses and support programs, or risk some ground in the latter part of 2023. Yet this will international trade may well, over time, lead to the large public debt increases. In highly indebted likely require the Fed to signal an end to its tight- emergence of two parallel monetary systems: the On a positive note, the major central banks appear countries, sovereign bond yields will therefore again ening and some signs of economic recovery outside current USD-based system as well as a yet-to-be committed to returning inflation rates close to their be at risk of rising sharply. the USA. conceived alternative system bypassing the USD. 2% targets. Inflation may remain above target in The degree to which this may influence foreign 2023, but should return close to target from 2024. demand for the USD as a reserve currency and for However, the cost of achieving this will be per- US government bonds as reserve assets will sistently higher interest rates and lower trend growth. determine the future of the USD. Long-term outlook: Lower growth The energy shock to Europe from Russia’s invasion of Ukraine and the growth recession in China have hurt the post-pandemic outlook. The Eurozone is In the red: Budget deficits across countries likely in recession and the USA, though still growing Overall government balances in % of GDP slightly in our baseline forecast, is at high risk of recession. 4 0 – 4 – 8 India China Japan Brazil Italy France Spain UK USA Germany Russia Switzerland 2022 2023 Last data point 10/2022 Source International Monetary Fund (IMF) forecast as of October 2022
 Credit Suisse Investment Outlook 2023 Page 9 Page 11
Credit Suisse Investment Outlook 2023 Page 9 Page 11