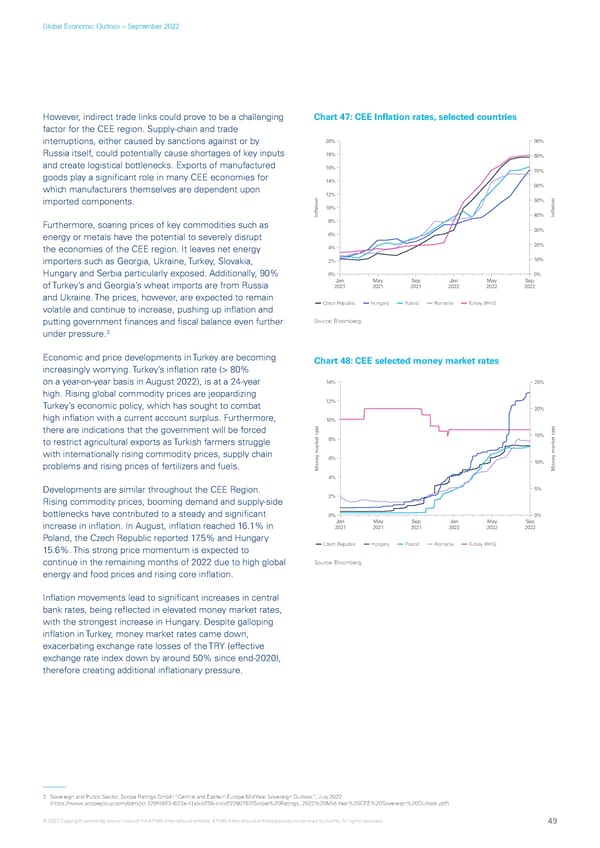
Global Economic Outlook – September 2022 However, indirect trade links could prove to be a challenging Chart 47: CEE Inflation rates, selected countries factor for the CEE region. Supply-chain and trade interruptions, either caused by sanctions against or by 20% 90% Russia itself, could potentially cause shortages of key inputs 18% 80% and create logistical bottlenecks. Exports of manufactured 16% 70% goods play a significant role in many CEE economies for 14% which manufacturers themselves are dependent upon 60% 12% imported components. 50% 10% Inflation 40% Inflation Furthermore, soaring prices of key commodities such as 8% energy or metals have the potential to severely disrupt 6% 30% the economies of the CEE region. It leaves net energy 4% 20% importers such as Georgia, Ukraine, Turkey, Slovakia, 2% 10% Hungary and Serbia particularly exposed. Additionally, 90% 0% 0% Jan May Sep Jan May Sep of Turkey’s and Georgia’s wheat imports are from Russia 2021 2021 2021 2022 2022 2022 and Ukraine. The prices, however, are expected to remain Czech Republic Hungary Poland Romania Turkey (RHS) volatile and continue to increase, pushing up inflation and putting government finances and fiscal balance even further Source: Bloomberg. 3 under pressure. Economic and price developments in Turkey are becoming Chart 48: CEE selected money market rates increasingly worrying. Turkey’s inflation rate (> 80% CEE3 on a year-on-year basis in August 2022), is at a 24-year 14% 25% high. Rising global commodity prices are jeopardizing Turkey’s economic policy, which has sought to combat 12% 20% high inflation with a current account surplus. Furthermore, 10% there are indications that the government will be forced to restrict agricultural exports as Turkish farmers struggle et rate8% 15% et rate with internationally rising commodity prices, supply chain 6% problems and rising prices of fertilizers and fuels. 10% Money mark Money mark 4% Developments are similar throughout the CEE Region. 5% Rising commodity prices, booming demand and supply-side 2% bottlenecks have contributed to a steady and significant 0% 0% increase in inflation. In August, inflation reached 16.1% in Jan May Sep Jan May Sep 2021 2021 2021 2022 2022 2022 Poland, the Czech Republic reported 17.5% and Hungary 15.6%. This strong price momentum is expected to Czech Republic Hungary Poland Romania Turkey (RHS) continue in the remaining months of 2022 due to high global Source: Bloomberg. energy and food prices and rising core inflation. Inflation movements lead to significant increases in central bank rates, being reflected in elevated money market rates, with the strongest increase in Hungary. Despite galloping inflation in Turkey, money market rates came down, exacerbating exchange rate losses of the TRY (effective exchange rate index down by around 50% since end-2020), therefore creating additional inflationary pressure. 3 Sovereign and Public Sector, Scope Ratings GmbH “Central and Eastern Europe MidYear Sovereign Outlook”, July 2022 (https://www.scopegroup.com/dam/jcr:129f4653-633a-41ab-b756-c4cdf2260787/Scope%20Ratings_2022%20Mid-Year%20CEE%20Sovereign%20Outlook.pdf) © 2022 Copyright owned by one or more of the KPMG International entities. KPMG International entities provide no services to clients. All rights reserved. 49
 KPMG Global Economic Outlook - H2 2022 report Page 48 Page 50
KPMG Global Economic Outlook - H2 2022 report Page 48 Page 50