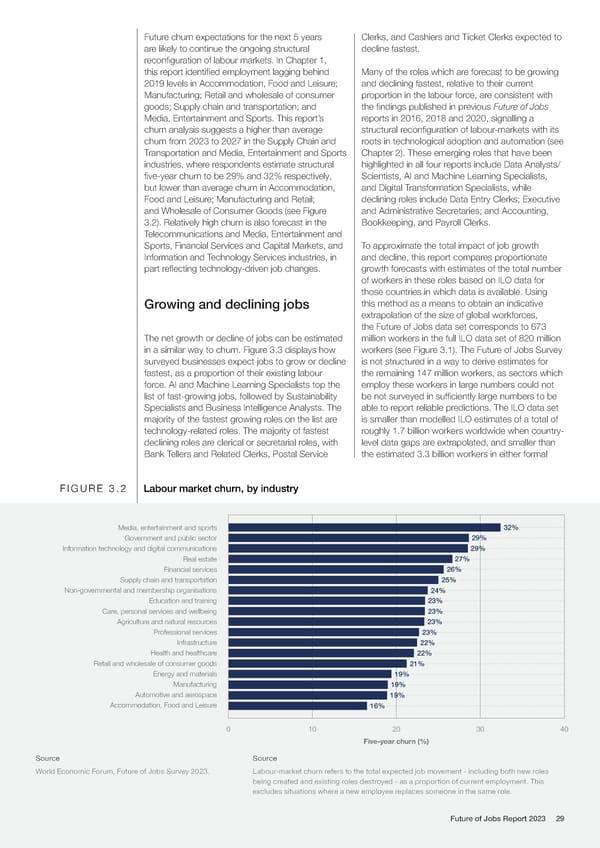
Future churn expectations for the next 5 years Clerks, and Cashiers and Ticket Clerks expected to are likely to continue the ongoing structural decline fastest. reconfiguration of labour markets. In Chapter 1, this report identified employment lagging behind Many of the roles which are forecast to be growing 2019 levels in Accommodation, Food and Leisure; and declining fastest, relative to their current Manufacturing; Retail and wholesale of consumer proportion in the labour force, are consistent with goods; Supply chain and transportation; and the findings published in previous Future of Jobs Media, Entertainment and Sports. This report’s reports in 2016, 2018 and 2020, signalling a churn analysis suggests a higher than average structural reconfiguration of labour-markets with its churn from 2023 to 2027 in the Supply Chain and roots in technological adoption and automation (see Transportation and Media, Entertainment and Sports Chapter 2). These emerging roles that have been industries, where respondents estimate structural highlighted in all four reports include Data Analysts/ five-year churn to be 29% and 32% respectively, Scientists, AI and Machine Learning Specialists, but lower than average churn in Accommodation, and Digital Transformation Specialists, while Food and Leisure; Manufacturing and Retail; declining roles include Data Entry Clerks; Executive and Wholesale of Consumer Goods (see Figure and Administrative Secretaries; and Accounting, 3.2). Relatively high churn is also forecast in the Bookkeeping, and Payroll Clerks. Telecommunications and Media, Entertainment and Sports, Financial Services and Capital Markets, and To approximate the total impact of job growth Information and Technology Services industries, in and decline, this report compares proportionate part reflecting technology-driven job changes. growth forecasts with estimates of the total number of workers in these roles based on ILO data for those countries in which data is available. Using Growing and declining jobs this method as a means to obtain an indicative extrapolation of the size of global workforces, the Future of Jobs data set corresponds to 673 The net growth or decline of jobs can be estimated million workers in the full ILO data set of 820 million in a similar way to churn. Figure 3.3 displays how workers (see Figure 3.1). The Future of Jobs Survey surveyed businesses expect jobs to grow or decline is not structured in a way to derive estimates for fastest, as a proportion of their existing labour the remaining 147 million workers, as sectors which force. AI and Machine Learning Specialists top the employ these workers in large numbers could not list of fast-growing jobs, followed by Sustainability be not surveyed in sufficiently large numbers to be Specialists and Business Intelligence Analysts. The able to report reliable predictions. The ILO data set majority of the fastest growing roles on the list are is smaller than modelled ILO estimates of a total of technology-related roles. The majority of fastest roughly 1.7 billion workers worldwide when country- declining roles are clerical or secretarial roles, with level data gaps are extrapolated, and smaller than Bank Tellers and Related Clerks, Postal Service the estimated 3.3 billion workers in either formal FIGURE 3.2 Labour market churn, by industry Media, entertainment and sports 32% Government and public sector 29% Information technology and digital communications 29% Real estate 27% Financial services 26% Supply chain and transportation 25% Non-governmental and membership organisations 24% Education and training 23% Care, personal services and wellbeing 23% Agriculture and natural resources 23% Professional services 23% Infrastructure 22% Health and healthcare 22% Retail and wholesale of consumer goods 21% Energy and materials 19% Manufacturing 19% Automotive and aerospace 19% Accommodation, Food and Leisure 16% 0 10 20 30 40 Five-year churn (%) Source Source World Economic Forum, Future of Jobs Survey 2023. Labour-market churn refers to the total expected job movement - including both new roles being created and existing roles destroyed - as a proportion of current employment. This excludes situations where a new employee replaces someone in the same role. Future of Jobs Report 2023 29
 The Future of Jobs Report 2023 Page 28 Page 30
The Future of Jobs Report 2023 Page 28 Page 30