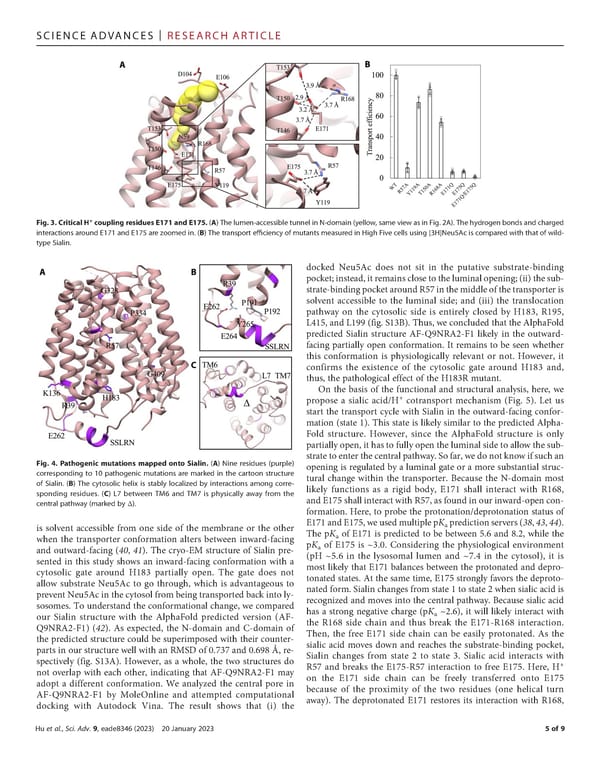
SCIENCEADVANCES | RESEARCHARTICLE + Fig. 3. Critical H coupling residues E171 and E175. (A) The lumen-accessible tunnel in N-domain (yellow, same viewasin Fig. 2A). The hydrogen bonds and charged interactions around E171 and E175 are zoomed in. (B) The transport e昀케ciency of mutants measured in High Five cells using [3H]Neu5Ac is compared with that of wild- type Sialin. docked Neu5Ac does not sit in the putative substrate-binding pocket;instead,itremainsclosetotheluminalopening;(ii)thesub- strate-bindingpocketaroundR57inthemiddleofthetransporteris solvent accessible to the luminal side; and (iii) the translocation pathway on the cytosolic side is entirely closed by H183, R195, L415, and L199 (fig. S13B). Thus, we concluded that the AlphaFold predicted Sialin structure AF-Q9NRA2-F1 likely in the outward- facing partially open conformation. It remains to be seen whether this conformation is physiologically relevant or not. However, it confirms the existence of the cytosolic gate around H183 and, thus, the pathological effect of the H183R mutant. Onthe basis of the functional and structural analysis, here, we propose a sialic acid/H+ cotransport mechanism (Fig. 5). Let us start the transport cycle with Sialin in the outward-facing confor- mation (state 1). This state is likely similar to the predicted Alpha- Fold structure. However, since the AlphaFold structure is only partially open, it has to fully open the luminal side to allow the sub- Fig. 4. Pathogenic mutations mapped onto Sialin. (A) Nine residues (purple) strate to enter the central pathway. So far, we do not know if such an corresponding to 10 pathogenic mutations are marked in the cartoon structure opening is regulated by a luminal gate or a more substantial struc- of Sialin. (B) The cytosolic helix is stably localized by interactions among corre- tural change within the transporter. Because the N-domain most sponding residues. (C) L7 between TM6 and TM7 is physically away from the likely functions as a rigid body, E171 shall interact with R168, central pathway (marked by Δ). andE175shallinteractwithR57,asfoundinourinward-opencon- formation. Here, to probe the protonation/deprotonation status of E171andE175,weusedmultiplepK predictionservers(38,43,44). is solvent accessible from one side of the membrane or the other a when the transporter conformation alters between inward-facing The pKa of E171 is predicted to be between 5.6 and 8.2, while the pK of E175 is ~3.0. Considering the physiological environment and outward-facing (40, 41). The cryo-EM structure of Sialin pre- a sented in this study shows an inward-facing conformation with a (pH ~5.6 in the lysosomal lumen and ~7.4 in the cytosol), it is cytosolic gate around H183 partially open. The gate does not most likely that E171 balances between the protonated and depro- allow substrate Neu5Ac to go through, which is advantageous to tonated states. At the same time, E175 strongly favors the deproto- prevent Neu5Acinthecytosolfrombeingtransportedbackintoly- nated form. Sialin changes from state 1 to state 2 when sialic acid is sosomes. To understand the conformational change, we compared recognized and moves into the central pathway. Because sialic acid our Sialin structure with the AlphaFold predicted version (AF- has a strong negative charge (pKa ~2.6), it will likely interact with Q9NRA2-F1) (42). As expected, the N-domain and C-domain of the R168 side chain and thus break the E171-R168 interaction. the predicted structure could be superimposed with their counter- Then, the free E171 side chain can be easily protonated. As the parts in our structure well with an RMSD of 0.737 and 0.698 Å, re- sialic acid moves down and reaches the substrate-binding pocket, spectively (fig. S13A). However, as a whole, the two structures do Sialin changes from state 2 to state 3. Sialic acid interacts with + not overlap with each other, indicating that AF-Q9NRA2-F1 may R57 and breaks the E175-R57 interaction to free E175. Here, H adopt a different conformation. We analyzed the central pore in on the E171 side chain can be freely transferred onto E175 AF-Q9NRA2-F1 by MoleOnline and attempted computational because of the proximity of the two residues (one helical turn docking with Autodock Vina. The result shows that (i) the away). The deprotonated E171 restores its interaction with R168, Huetal., Sci. Adv. 9, eade8346 (2023) 20 January 2023 5of9
 The molecular mechanism of sialic acid transport mediated by Sialin Page 4 Page 6
The molecular mechanism of sialic acid transport mediated by Sialin Page 4 Page 6