Deloitte The Metaverse Overview
This paper answers the key questions: What is the value of the Metaverse? What will it look like in the future? Is there an analysis framework to cover all of its components? What technologies do organizations need to shape their Metaverse? Where are the bottlenecks? How should companies respond to the rise of the Metaverse? What types of companies are in the Metaverse?
The Metaverse Overview: Vision, Technology, and Tactics
Preface 1. Vision and Values 1 . Vision and 4 meanings of the Metaverse 2. Six Characteristics of the Metaverse 3. The value of the Metaverse 4. Current bottlenecks in Metaverse development 2. Technology 1 . Technology clusters corresponding to Metaverse features 2. Key technologies'development stages and bottlenecks 3. Examples of Metaverse-related technology applications 30 3. lndustry 33 4 10 10 16 20 21 24 24 26 2. Metaverse industry framework 33 3. Types of participators, cooperation and competition34 35 4. Major platform players 5. The NFT industry chain 37 4. Metaverse tactics for enterprises 43 2. Metaverse development 43 3. Potential risks 44 4. China's attitude to the Metaverse44 5. Metaverse tactics 46
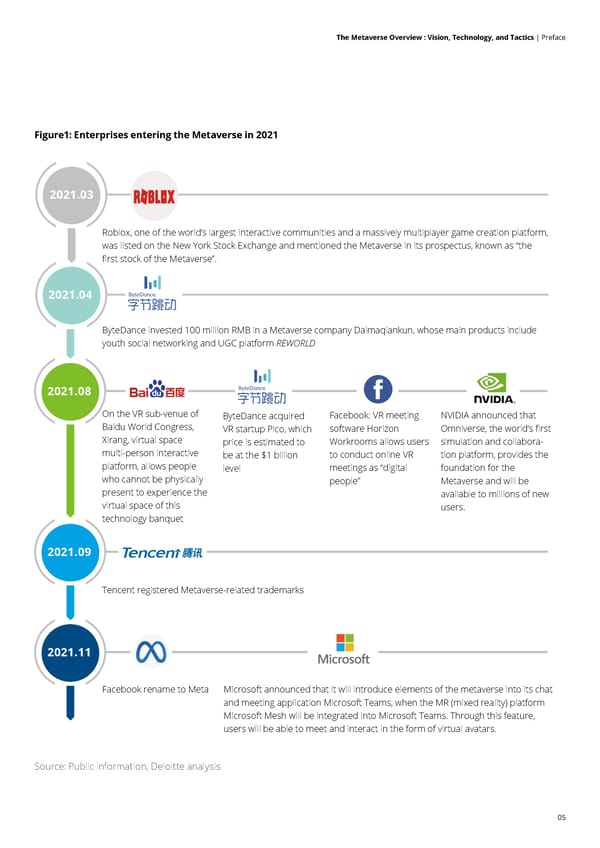
04 The Metaverse Overview : Vision, Technology, and Tactics | Preface Preface With the sharp drop in Meta's stock price in February 2022, the global Metaverse craze triggered by Facebook's rebrand reached a turning point. Excessive enthusiasm has since started to subside, and people now view the Metaverse opportunity more rationally. This paper answers the key questions: What is the value of the Metaverse? What will it look like in the future? Is there an analysis framework to cover all of its components? What technologies do organizations need to shape their Metaverse? Where are the bottlenecks? How should companies respond to the rise of the Metaverse? What types of companies are in the Metaverse? Facebook's renaming to Meta in October 2021 ignited global enthusiasm for the Metaverse. Capital market valuations of Metaverse-related stocks reached a peak one month later, but just three months after that, valuations of some Metaverse- related stocks had dropped by 20%-50%. People's attitudes towards the Metaverse have shifted from excitement and ambition to rationality and exploration. 1. 2021: Excitement & Ambition Looking back at 2021 – the first year of the Metaverse – its breakout was much more intense and the responses of market participants were much faster than they were when the internet entered global consciousness. From Roblox citing the concept in its prospectus and planting the first flag on the Metaverse landscape, to multiple companies entering the industry, and then to Facebook's changing its official name to Meta, the first Metaverse enterprises pushed its popularity to a climax (as shown in the figure). At the same time, many well-known institutions and individual participants demonstrated their willingness to try Metaverse applications. The University of California, Berkeley recreated its entire campus in Minecraft, where virtual avatars of graduates attended a ceremony and took group photos, virtual idol Liu Yexi became popular On TikTok, and US President Biden established Biden Island on Animal Crossing to attract voters. A glance at the global and Chinese markets reveals that the Metaverse is by no means just an experiment for small-scale players, but has become a landscape for all of humanity to jointly explore the next stages of development in society, technology, legal systems, and the arts.
05 The Metaverse Overview : Vision, Technology, and Tactics | Preface Source: Public information, Deloitte analysis 2021.04 2021.08 2021.09 2021.11 2021.03 ByteDance invested 100 million RMB in a Metaverse company Daimaqiankun, whose main products include youth social networking and UGC platform REWORLD Roblox, one of the world’s largest interactive communities and a massively multiplayer game creation platform, was listed on the New York Stock Exchange and mentioned the Metaverse in its prospectus, known as “the first stock of the Metaverse”. Tencent registered Metaverse-related trademarks Facebook rename to Meta On the VR sub-venue of Baidu World Congress, Xirang, virtual space multi-person interactive platform, allows people who cannot be physically present to experience the virtual space of this technology banquet ByteDance acquired VR startup Pico, which price is estimated to be at the $1 billion level Facebook: VR meeting software Horizon Workrooms allows users to conduct online VR meetings as “digital people” NVIDIA announced that Omniverse, the world’s first simulation and collabora- tion platform, provides the foundation for the Metaverse and will be available to millions of new users. Microsoft announced that it will introduce elements of the metaverse into its chat and meeting application Microsoft Teams, when the MR (mixed reality) platform Microsoft Mesh will be integrated into Microsoft Teams. Through this feature, users will be able to meet and interact in the form of virtual avatars. Figure1: Enterprises entering the Metaverse in 2021
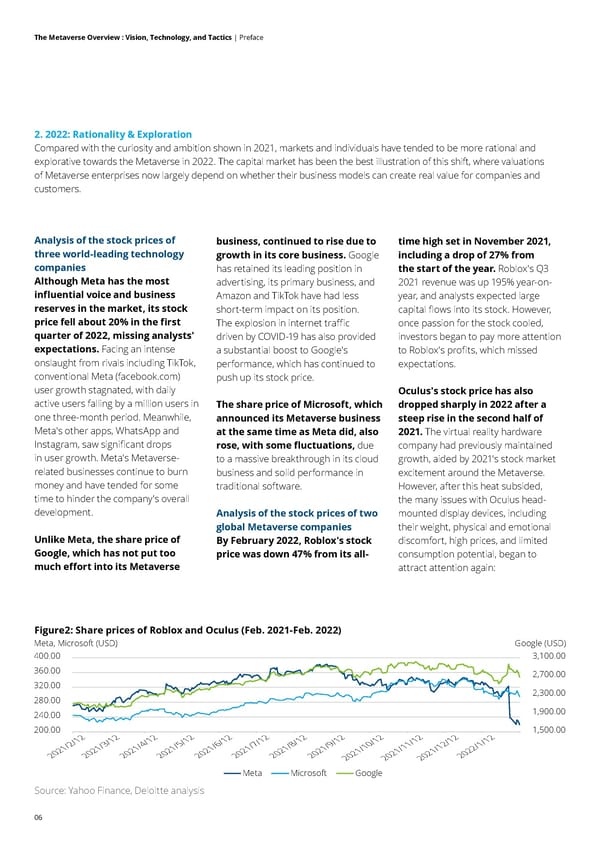
06 The Metaverse Overview : Vision, Technology, and Tactics | Preface 2. 2022: Rationality & Exploration Compared with the curiosity and ambition shown in 2021, markets and individuals have tended to be more rational and explorative towards the Metaverse in 2022. The capital market has been the best illustration of this shift, where valuations of Metaverse enterprises now largely depend on whether their business models can create real value for companies and customers. Analysis of the stock prices of three world-leading technology companies Although Meta has the most influential voice and business reserves in the market, its stock price fell about 20% in the first quarter of 2022, missing analysts' expectations. Facing an intense onslaught from rivals including TikTok, conventional Meta (facebook.com) user growth stagnated, with daily active users falling by a million users in one three-month period. Meanwhile, Meta's other apps, WhatsApp and Instagram, saw significant drops in user growth. Meta's Metaverse- related businesses continue to burn money and have tended for some time to hinder the company's overall development. Unlike Meta, the share price of Google, which has not put too much effort into its Metaverse business, continued to rise due to growth in its core business. Google has retained its leading position in advertising, its primary business, and Amazon and TikTok have had less short-term impact on its position. The explosion in internet traffic driven by COVID-19 has also provided a substantial boost to Google's performance, which has continued to push up its stock price. The share price of Microsoft, which announced its Metaverse business at the same time as Meta did, also rose, with some fluctuations, due to a massive breakthrough in its cloud business and solid performance in traditional software. Analysis of the stock prices of two global Metaverse companies By February 2022, Roblox's stock price was down 47% from its all- time high set in November 2021, including a drop of 27% from the start of the year. Roblox's Q3 2021 revenue was up 195% year-on- year, and analysts expected large capital flows into its stock. However, once passion for the stock cooled, investors began to pay more attention to Roblox's profits, which missed expectations. Oculus's stock price has also dropped sharply in 2022 after a steep rise in the second half of 2021. The virtual reality hardware company had previously maintained growth, aided by 2021's stock market excitement around the Metaverse. However, after this heat subsided, the many issues with Oculus head- mounted display devices, including their weight, physical and emotional discomfort, high prices, and limited consumption potential, began to attract attention again: Figure2: Share prices of Roblox and Oculus (Feb. 2021-Feb. 2022) Source: Yahoo Finance, Deloitte analysis 1,500.00 1,900.00 2,300.00 2,700.00 3,100.00 200.00 240.00 280.00 320.00 360.00 400.00 Meta, Microsoft (USD) Google (USD) 2021/2/12 2021/3/12 2021/4/12 2021/5/12 2021/6/12 2021/7/12 2021/8/12 2021/9/12 2021/10/12 2021/11/12 2021/12/12 2022/1/12 Meta Microsoft Google
07 The Metaverse Overview : Vision, Technology, and Tactics | Preface Figure3: Share prices of Roblox and Oculus (Feb. 2021-Feb. 2022) Source: Yahoo Finance, Deloitte analysis Roblox (USD) Oculus (USD) 0.00 0.20 0.40 0.60 0.08 1.00 1.20 0.00 20.00 40.00 60.00 80.00 100.00 120.00 140.00 160.00 2021/2/12 2021/3/12 2021/4/12 2021/5/12 2021/6/12 2021/7/12 2021/8/12 2021/9/12 2021/10/12 2021/11/12 2021/12/12 2022/1/12 Roblox Oculus Figure4: Share prices of Baidu, Alibaba, and Tencent (Feb. 2021-Feb. 2022) Source: Yahoo Finance, Deloitte analysis Baidu, Alibaba (USD) Tencent (USD) 0.00 20.00 40.00 60.00 80.00 0.00 50.00 100.00 150.00 200.00 250.00 2021/8/2 2021/9/2 2021/10/2 2021/11/2 2021/12/2 2022/1/2 2022/2/2 Baidu Alibaba Tencent Figure5: Share prices of AVIT, ZQGAME and COL (Feb. 2021-Feb. 2022) Source: Google Finance, Deloitte analysis AVIT COL ZQGAME 4 0 5 10 15 10 20 30 2021/10 2021/12 2022/1 2022/2 2021/10 2021/12 2022/1 2022/2 2021/10 2021/12 2022/1 2022/2 6 8 10 12 40 20 14
08 The Metaverse Overview : Vision, Technology, and Tactics | Preface Analysis of the stock prices of three leading Chinese technology companies Although Baidu, Alibaba, and Tencent have all deployed in the Metaverse, this has not influenced their stock prices much over the past six months, except during mild fluctuations during "Metaverse fever" in November 2021. However, Alibaba's stock price went into a volatile decline during the past quarter as its primary business revenue and gross merchandise value (GMV) growth disappointed. Analysis of the stock prices of three Chinese Metaverse companies China's Metaverse Index rose 30% in 2021, with most of that rise coming in the fourth quarter. ZQGAME was up 270%, AVIT rose 185%, and COL gained 69%. However, because they did not generate Metaverse-related income, all three companies' stock prices retreated 2022. As described above, capital market enthusiasm for the Metaverse has declined. There are three reasons for this. First, the development speed of Metaverse-enabling technologies and applications has not matched the continuous rise of consumer expectations for Metaverse applications. This year is expected to see a continuation of that trend, with Metaverse development throughout the year slower than the public expects. Second, most Metaverse practices, intending to cater to the Metaverse craze, remain at the conceptual stage. It is difficult to achieve far-reaching breakthroughs or returns on capital investment at speed. Third, technology, products, rules, and regulations continue to restrict the actualization of enterprises' and consumers' visions of the Metaverse. Technologies do not have the ability to create a true Metaverse experience yet, and related products including hardware and software have not matured. In our still centralized world, there has been no quick creation of decentralized rules to support the Metaverse, and it will not transform easily or quickly from a niche market into a universal consumer group. What kind of Metaverse will exist beyond its initial popularity and now that capital market excitement has cooled? The Metaverse will fundamentally reshape people's productivity, lives, and social relationships, in time creating a new world. This is the development direction of Metaverse. After the excitement subsides, companies that focus on accurate positioning, continuous development, and outstanding ability will produce a viable Metaverse that inspires renewed excitement.
09 The Metaverse Overview : Vision, Technology, and Tactics | Preface

10 The Metaverse Overview : Vision, Technology, and Tactics | Vision and Values 1. Vision and Values 1.1 Vision and 4 meanings of the Metaverse In this nascent phase of the Metaverse, the industry has not formed a unified standard for defining or understanding it. It is a garden in which 100 flowers are blooming and 100 schools of thought contend. David Bashuki, CEO of Roblox, has proposed eight elements of the Metaverse: identity, sociality, immersion, low latency, diversity, anywhere, economic system, and civilization. Renowned analyst Matthew Ball has identified six characteristics of the Metaverse: sustainability, real-time, no access restrictions, economic functions, connectivity, and creativity. Jon Radoff, founder of Beamable, has ideated seven levels of Metaverse construction: experience, discovery, creator economy, spatial computing, decentralization, human-computer interaction, and infrastructure. In China, some institutions have proposed that the Metaverse is a new internet application and social arena that integrates various new technologies, shaping a virtual space in an online world that mirrors the natural world in an increasingly realistic digital landscape. These different understandings and definitions of the Metaverse come from different perspectives, including experiential, technological, or regulatory interpretations. It is not easy to provide a concise, definitive, unified definition that covers all these dimensions. Starting from the original meaning of "Meta (Meta) + Verse (Universe)", Deloitte has defined and imagined the future of the Metaverse as "a converged world of the virtual and the real". This has four meanings: a virtual mirror world that simulates the real world, an innovative virtual world set apart from the real world, the real world as a facet of the Metaverse, and the convergence of the virtual and real worlds beyond either the virtual or the real world. In this chapter, we discuss the development vision of the Metaverse, its long-term value, its characteristics compared with current internet platforms, and development bottlenecks. Figure6: Definition and meanings in the Metaverse Source: Deloitte analysis 4 meanings Components of Metaverse “A virtual and real world converged universe” Real World Virtual Mirror World to simulate reality Virtual Native World A new virtual world Metaverse Virtual Mirror A virtual world simulating reality Real World The real world Convergence of Virtual and Real Worlds Surpasses Virtual or Real World Virtual Native Innovate virtual world

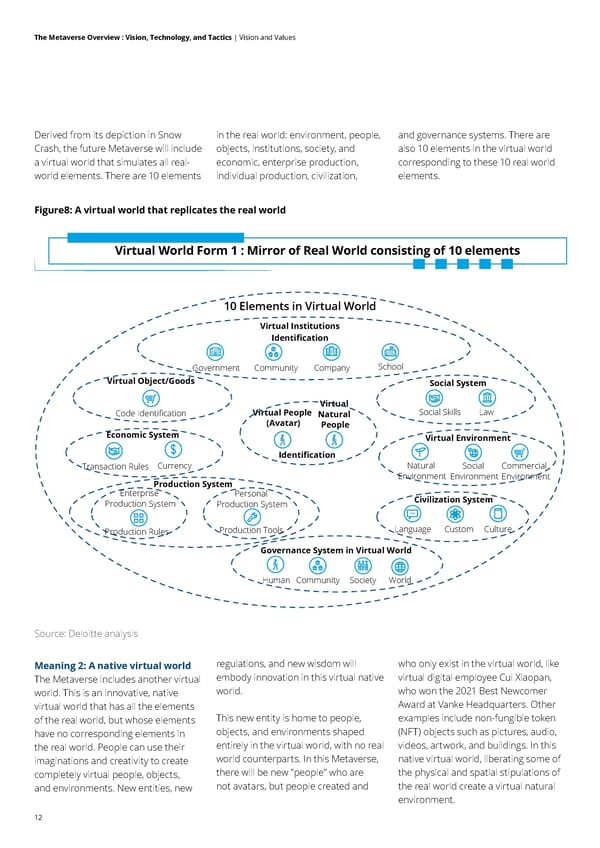
11 The Metaverse Overview : Vision, Technology, and Tactics | Vision and Values The Metaverse will include almost all elements of our real world. This is the key to understanding the long- term state of the Metaverse and how fundamentally and profoundly it will influence us. The four meanings above can described as follows: Meaning 1: A virtual mirror world that simulates reality The Metaverse includes a virtual world that simulates almost every element of the real world, including individual identity, enterprise identity, the business world, entertainment, social interaction, civilization, legal, tax, and governance structures, and one of the most critical features of our real world—feelings. This is an important starting point for understanding and envisioning the future direction of the Metaverse. The public's current perception of the Metaverse encompasses games, experiences, technologies, and social applications. These are parts of the Metaverse, but the future of the Metaverse is much more than the sum of those parts. The term Metaverse originated from a scene in Snow Crash. It is a conceptual extension of that scene to imagine a "real" virtual world that is a full simulation and complete mirror of the real world. Neil Stephenson's Snow Crash describes such a virtual world: the protagonist enters a commercial block, on the Champs-Élysées in the super-meta-domain (the Metaverse). The street is very long, traversing 65,536 kilometers. A vast number of people pass through the commercial block, where there are many shops. Opening a shop there requires third-party approval, buying land, obtaining the relevant licenses, and bribing Inspectors. Humans walk and interact with the neighborhood as digital avatars; populating a world the author calls the Metaverse. The picture below is a schematic diagram of the scene depicted in Snow Crash. There are many core elements of the real world in its described virtual world, including neighborhoods, social interaction, commercial real estate development, business activities, and even corruption. Figure7: The virtual world of Snow Crash Source: Public information, Deloitte analysis Headset Glasses Terminal Connect Connect Virtual identity Virtual Space Avalanche, 1992 The Virtual World Constructed by the Global Multimedia Protocol Group The public Authorize Companies Building façade to run business in $ $ $ Global Multimedia Protocol Group Champs Elysees in the Metaverse

12 The Metaverse Overview : Vision, Technology, and Tactics | Vision and Values Derived from its depiction in Snow Crash, the future Metaverse will include a virtual world that simulates all real- world elements. There are 10 elements in the real world: environment, people, objects, institutions, society, and economic, enterprise production, individual production, civilization, and governance systems. There are also 10 elements in the virtual world corresponding to these 10 real world elements. Figure8: A virtual world that replicates the real world Source: Deloitte analysis 10 Elements in Virtual World Virtual People (Avatar) Virtual Natural People Virtual Institutions Identification Identification School Community Company Government Virtual Object/Goods Economic System Social System Production System Enterprise Production System Personal Production System Virtual Environment Civilization System Governance System in Virtual World Currency Transaction Rules Social Skills Natural Environment Social Environment Commercial Environment Community Human Society World Language Custom Culture Production Tools Production Rules Code Identification Law Virtual World Form 1 : Mirror of Real World consisting of 10 elements Meaning 2: A native virtual world The Metaverse includes another virtual world. This is an innovative, native virtual world that has all the elements of the real world, but whose elements have no corresponding elements in the real world. People can use their imaginations and creativity to create completely virtual people, objects, and environments. New entities, new regulations, and new wisdom will embody innovation in this virtual native world. This new entity is home to people, objects, and environments shaped entirely in the virtual world, with no real world counterparts. In this Metaverse, there will be new "people" who are not avatars, but people created and who only exist in the virtual world, like virtual digital employee Cui Xiaopan, who won the 2021 Best Newcomer Award at Vanke Headquarters. Other examples include non-fungible token (NFT) objects such as pictures, audio, videos, artwork, and buildings. In this native virtual world, liberating some of the physical and spatial stipulations of the real world create a virtual natural environment.
13 The Metaverse Overview : Vision, Technology, and Tactics | Vision and Values Figure9: Three "new things" in the virtual native world Source: Deloitte analysis New Entities New Regulations New Wisdom Figure Object Environment Artificial Intelligence Human Intelligence (Creativity & Innovation) Decentralization & UGC Consensus Mechanism Mechanism Regulation has three aspects in this new native virtual world: governance by decentralized autonomous organizations (DAOs), which is completely different to the centralized model in the real world; user-created content (UGC) rather than the platform-generated content (PGC), which will completely liberate people to be creators and allow anything to be created; and the movement of people in the virtual world, unencumbered by real-world physical or spatial rules. New wisdom refers to artificial intelligence (AI). Virtual people, despite existing only in the Metaverse, will have the same or greater wisdom than human beings do in the real world. Currently, most AI seeks to simulate human beings by listening, speaking, reading, writing, smelling, touching, moving, and thinking. One day the wisdom of AI will go beyond human beings, and that day is not that far away given the acceleration of technology, with the computing power of Nvidia's CPUs now said to be 1 million times faster than it was 10 years ago. Current Metaverse platforms have already partially achieved the abovementioned three innovations in the native virtual world. When the virtual world frees us from the limitations of physical space, human beings can bring their thinking and creativity into full play, creating the potential for limitless innovation. Meaning 3: The real world The real world is an integral part of Metaverse. All elements in the virtual mirror world are facsimiles of elements in the real world. The value of the virtual world is generated by interactions between it and the real world. Meaning 4: Convergence and interaction of the virtual and real worlds In the end, the virtual world and the real world will form a closely converged and interacting world— from the virtual to the real, the real to the virtual, the virtual in the real, and the real in the virtual—like a "live action" version of the coexistence of robots in the real and virtual worlds seen in Terminator . This convergence and interaction mean the Metaverse will transcend both and each of the real and virtual worlds, calling back to the original meaning of the word "Meta" as above or beyond. The degree to which the virtual world is converging and interacting with the real world is a critical criterion in evaluating the value of the Metaverse. Among various definitions of the Metaverse, one posits that it will only
14 The Metaverse Overview : Vision, Technology, and Tactics | Vision and Values be when people rely on the virtual world more than they rely on the real world that the Metaverse will be fully formed. As mentioned earlier, the virtual and real world each have 10 elements. In this "4th Metaverse", these 10 elements (environment, people, objects, institutions, and society, and economic, enterprise production, individual production, civilization, and governance systems) will converge and interact. Integration (convergence and interaction) between the virtual and real worlds has four levels of varying difficulty, set out below from the easiest to most difficult: Level 1: The interaction of enterprise production systems. This sees the virtual world replicate and support the real world. For example, digital twin technology generates digital deconstructions and simulations of real machine equipment to support operational state prediction and Figure10: Convergence and Interaction of virtual-world and real-world elements Source: Deloitte analysis maintenance for physical machines. Many production and manufacturing scenarios have already explored and applied digital twin technology. Level 2: This level will see the integration of environment, people, objects, and institutions through unified coding rules and identification systems between the virtual and real world; the integration of the virtual and real economies through value exchange rules; and the integration of personal production systems through NFT-related copyright (virtual IP and real IP). Level 3: This level sees the integration of society and civilization, becoming even closer to the essence of the real world and thus much more difficult, encompassing social rules and systems of civilization that require long-term thinking, collision, and polishing. Level 4: The integration of governance rules is the most challenging Metaverse scenario, as it will involve disputes around and competition for governance rights. That is, who will govern this Metaverse, humans or AI in the virtual world, Metaverse companies or real-world government? Competition for control between government and the virtual world has already occurred in the clash for control of the data of billions of users between government and the internet giants. For the first time in human history, companies now own more of people's information than governments do, which has caused alarm in some government circles. The fight for governance of the Metaverse will intensify, with some pessimists positing that Metaverse governance rules will even affect and oppress the real world. In future, various virtual spaces, communities, and societies will emerge. Small, personal virtual spaces will combine to form a large virtual community spaces. Multiple virtual community spaces will combine and converge to form even larger and more diverse virtual social spaces. Different Virtual Economy Transaction Rules, Currency Virtual Civilization Language, Customs, Culture Virtual Society Social Media Low Difficulty of Merging High People Society Personal Production System Economic System Enterprise Production System Civilization System Governance System Elements in Real World Elements in Virtual World Virtual People Identification Natural People Virtual Institutions Institutions Virtual Environment Natural Environment Value Exchange Virtual Supports Reality NFT Copyright Civilization Rules Competition for Governance Virtual Object Code Identification Object Unified Coding Rules & Identification System Social Rules Virtual Enterprise Production System Production Rules Virtual Personal Production System Personal Creation Virtual Governance System
15 The Metaverse Overview : Vision, Technology, and Tactics | Vision and Values Figure11: The entrance to virtual reality Figure12: Six characteristics of the Metaverse Source: Deloitte analysis Source: Deloitte analysis world elements, people, avatars, currencies, and activities will flow freely between these different spaces and worlds, realizing information flows and a virtual space-time shuttle. People will participate freely in the Metaverse with a specific digital identity they use to interact with the real world. The entrance to virtual reality There are two entrances to the Metaverse through virtual-real interaction: the first is to apply digital tools, including portable and wearable AR/VR devices, and the second is to apply brain-computer interface technology, which transmits electrical and biogenic signals directly to the human brain, achieving real-time, barrier-free information exchange. In terms of business models, there are two occasions to enter the Metaverse. One is a personal occasion, in which people at home, in the office, or the natural environment can enter the virtual world through virtual-real interaction tools, various XR devices. The second is a public occasion, where a third party provides an entrance to the Metaverse, akin to personal KTV huts in shopping malls or Script Kill roleplaying. We illustrate these occasions below. The Metaverse is evolving in two dimensions: from the real to the virtual and virtual to the real. From real to virtual involves real scenes superimposed on immersive digital experience, including virtual education, virtual training, and virtual malls. In virtual to real, the virtual world extends into reality. For example, virtual game Niantic Lightship promotes social interactions by designing scenarios including real-world map positioning, environment and object recognition and judgment, and real-time interactive sharing. Real World Virtual Mirror To simulate reality Eye, Nose, Mouth, Tongue, Body Natural & Social Environment, Civilization & Governance System UGC Real Estate Economics, Digital Artwork Decentralization Virtual Native A complete virtual world Metaverse Six Characteristics vs Internet Immersive Experience Complete World System User-Generated Content Huge Economic Value New Regulation Competition for Governance Big Uncertainty Device Connection Metaverse Wireless Brain -computer VR Glasses VR Gloves VR Helmet VR Armor Voice Interaction Eye Tracking Motion Capture Haptic Interaction … Signal Transition Signal Hearing Seeing Touching Tasting Smelling Coding Signal Transition Occasions to Enter the Metaverse Personal Digital Tools BCI Home, Private Workplace Public Equipment provided by 3rd parties
16 The Metaverse Overview : Vision, Technology, and Tactics | Vision and Values Figure13: The Production Metaverse Source: Deloitte analysis 1.2 Six characteristics of the Metaverse Based on the descriptions above, and compared with current internet platforms, the Metaverse has six characteristics: realistic immersive experiences, a complete real world structure, UGC, huge economic value, new regulations and rules, and large potential uncertainty. Characteristics 1: Realistic immersive experience Realistic immersive experiences provide verisimilitude of the senses, objects, and environment, and have driven Metaverse excitement. The Metaverse creates sensory verisimilitude by upgrading 2D internet experiences to 3D, sensory ones. The senses here are mainly visual and auditory. For example, most video games have 2D pictures and sound effects. A small number of games have added senses including pressure and shock, but these sensory experiences are far from actual physical and tactile experiences. With the development of technologies including somatosensory devices, digital smell, digital taste, and brain-computer interfaces, the ideal Metaverse integrates vision, hearing, touch, smell, taste and ideas to bring players infinitely closer to real sensory experiences. Object verisimilitude is the use of digital twin technology to create digital virtual objects, forming a mapping relationship that is very similar to real objects in shape, texture, and use. In environmental verisimilitude, a virtual world runs like the real world. Like the real world, this virtual world is always online, real time, and includes an infinite number of people who can connect and communicate with each other. In other words, it is sustainable, real-time, has no access restrictions and possesses connectivity and creativity, as described by Matthew Ball. In this way, the virtual world gives users a feeling that the surrounding environment, people, and things are real. Immersive experiences geared toward personal sensory experiences are easier to understand. The following describes the immersive experience of the Metaverse that simulates the production process. The Production Metaverse use digital twins as its core technology to simulate the production environment, processes, and objects (see figure below). R&D Stage Network and Computing Technology 5G/6G Cloud Computing Edge Computing AI Technology Computer vision Machine Learning Natural language processing Intelligent Voice Blockchain Technology Consensus Mechanism Distributed Storage Intelligent Contract Distributed Ledger IoT Application Layer Network Layer Perception Layer Interactive technologies Hologram Sensing Technology Random Interaction Video game technology 3D Engine Real-time rendering Space rendering Consumption End Manufacturing Stage Inside the Enterprise Economic System Inside the Enterprise Enterprise and Supplier Enterprise and Downstream Enterprise and Collaboration Virtual Plan Virtual Identity Full Life Cycle Symbiosis of Virtualize-tion and Reality Underlying Structure Backend Infrastructure Virtual Design Virtual Model Open Office Virtual Identity Employee- visit before buying Employee maintenance Monitor & Command Real Factory Virtual Factory Manufacturing Monitor & Command Customer-visit before buying Product training Virtual Meeting Virtual Identity Virtual Office Manufacturing Monitor & Command
17 The Metaverse Overview : Vision, Technology, and Tactics | Vision and Values The first aspect of the production Metaverse is integrated virtual-real symbiosis at the R&D stage. R&D personnel from different places can enter the virtual world together for product planning, design, and testing in 3D form, solving problems including long test periods and unstable manufacturing processes. The second aspect of the production Metaverse real-virtual symbiosis in manufacturing. Highly immersive, real- time data simulation manufacturing management is realized through Internet-of-Things and digital twin systems. Employees wear AR devices for manufacturing and production monitoring in a real or virtual factory, which greatly improves the operational efficiency of field personnel and overall efficiency of remote managers. The third aspect of the production Metaverse is real-virtual symbiosis during sales, split into three scenarios: during sales, in use, and after- sales maintenance. This supports interactions between employees and customers in the virtual world looking at the same digital twins products. The last production Metaverse element is real-virtual symbiosis in the internal operations and management of enterprises. This enables employees to create and customize virtual offices, and have a friendly avatar that can freely communicate and solve management problems in the virtual realm. There is a great degree of overlap in the underlying technical architecture of the immersive experiences of the production-oriented Metaverse and human sensory experience. Characteristics 2: A complete world structure Unlike the internet world, the virtual world of the Metaverse will have all 10 elements of the real world. The existing internet world represented by media, social networking, e-commerce, and industrial internet is a world in narrow-sense, simulating only part of whole social, business, and production systems in the real world. The existing internet world does not clearly reflect elements such as real estate development, government and governance, and social civilization. The Metaverse, meanwhile, will be a complete replica of the real world, simulating all of its 10 elements. The 10 virtual elements of the Metaverse will correspond to those in the real world: the natural environment, people (identity recognition), institutions (government, community, schools, enterprises) , objects, social systems (social interaction, social rules), the economy (transaction rules, virtual currency), enterprise production (production rules), personal production (personal creations including NFT artwork), civilization (language, customs, culture), and governance (decentralized governance). Characteristics 3: UGC UGC is a new creative arena in which Metaverse residents create content and applications in their own virtual worlds. Unlike internet platforms, where owners create most of the content and establish the rules, users will create their own content and rules in the Metaverse, with platforms providing the technical tools they need. For example, in Roblox, people can use some simple tools embedded in the Figure14: The complete world structure of the virtual world Source: Deloitte analysis Elements in Real World Elements in Virtual World Virtual Governance System Governance System Virtual Civilization Language, Customs, Culture Civilization System Virtual Personal Production System Personal Creation Personal Production System Virtual Enterprise Production System Production Rules Enterprise Production System Virtual Economy Transaction Rules, Currency Economic System Virtual Society Social Media People Society Virtual People Identification Natural People Virtual institutions Institutions Virtual Environment Natural Environment Virtual Object Code Identification Object
18 The Metaverse Overview : Vision, Technology, and Tactics | Vision and Values Figure15: Centralization vs decentralization Source: Deloitte analysis platform to design a game, and launch this game for other users to play. In the context of the virtual world mirroring the real world, UGC is closer to how the real world works, with people finding new land, building homes, and developing their own rules. Characteristics 4: Huge potential economic value Based on what the Metaverse can provide for people, its value arises from five elements: • Social economy: The Metaverse provides various social scenarios with immersive experiences and people pay for these • Land economy: As in the real-world property industry, there is "land" in the Metaverse, and people need to pay real money to buy it before building virtual companies, homes, or communities. Virtual land is not cheap, despite it being just a piece of coding. Metaverse platforms will create limited space to simulate the natural scarcity of space in the real world, and charge people based on that scarcity rather than length of code • Identity economy: This experience revolves around avatars. Everyone will have their own avatar in the virtual world and will pay for this personalized version of themselves. This realm of the Metaverse will attract attention from capital • Digital art economy: this is based on the value of various forms of NFT digital artworks, including audio, video, pictures, and even virtual shoes • Finance economy: The value of financial investments or speculation opportunities In essence, the value of the Metaverse comes from its equivalent sources of value in the real world, that is, exclusivity, competition, and the spatial and temporal scarcity of things. Many people think that the Metaverse, as a digital virtual space like the internet, will be inexhaustible and easily copied, pasted, and used for their own use, but the Metaverse does not work like this. The creators of Metaverse platforms will endow the Metaverse with scarcity through technologies including information anti-proliferation, homomorphic encryption, code and chain non-homogenization certificates, and manage digital asset rights through these technologies so data becomes tamper-proof. At the same time, the Metaverse has less scarcity than the real world, making it possible for it to surpass the real world's economic value. It will achieve this through powerful digital productivity, allowing everyone to create diverse forms, all of which Centralized Structure Definition Features Cases Consensus Mechanism Centre The center is associated with nodes. Nodes must depend on the center and are not directly associated with one another. Bank, Traditional Internet, Social & Game Platforms Poor data privacy, vulnerable to attack, slow response speed, nodes lack information control Traditional Regulation Decentralized Structure Nodes are interconnected. Under a consensus mechanism, each node can become a phased center, and the platform is maintained by all nodes. Bitcoin, DeFi Strong data privacy, anti-attack, fast response, open & transparent, traceable New Regulation Definition Features Cases
19 The Metaverse Overview : Vision, Technology, and Tactics | Vision and Values will have value to someone, and overcoming the natural elements and limitations of current political and legal systems. In the Metaverse, these limitations can be broken and more value generated. Furthermore, creation and trading is more flexible in the Metaverse, supporting smooth and free transactions within a single virtual world, between two virtual worlds, or between the virtual and real world. Characteristics 5: New regulations Although the virtual world is a complete simulation of the real world, Metaverse creators hope that the operating rules of the virtual world can be different to the centralized structures of the real world. They want the virtual world to operate based on decentralization. The original intention of human beings in creating virtual worlds was to avoid certain limitations in the real world. For example, online virtual social networking after the emergence of the internet avoids the limitation of having to travel long distances to meet friends. The Metaverse will mitigate this and other limitations while weakening personal identity and wealth restrictions in society. There are many problems in the real world, including the uneven distribution of resources and the disparity between rich and poor. If the Metaverse is unable to avoid centralization, then this will not only hinder our ability to address real- world problems in, but also make these problems more prominent. For example, powerful people in the real world could use their resources or prestige to quickly accumulate great wealth in the virtual realm, and even establish power-biased operating rules to absorb more wealth, and then feed this back into the real world. In this way, the Metaverse would execute an even more unequal distribution of resources and widen the gap between the rich and the poor. The concept of the Metaverse as a parallel world means weakening "central privilege" in the real world. Creators in the Metaverse have developed regulations and rules through DAOs. No country, company, or individual controls these, and new members who want to join a virtual world can automatically do so by following the DAO's rules. DAOs allow people in the Metaverse who create more value to attain more in the virtual world. DAOs record the relationship between a creator and their creations, and others need to pay to obtain the Figure16: Governance structure of the Metaverse Source: Deloitte analysis Who are the rule makers of the Metaverse? Who is the ultimate manager of the Metaverse? To whom do the economic dividends of the virtual world belong? The game of unilateral power The game of trilateral power The game of many forces AI robot Intervention Government Private capital Metaverse Developers Metaverse Virtual Human Non-human Virtual Human Private Capital Metaverse Developers Government Private Capital Metaverse Developers Metaverse Virtual Natural Human Government Intervention Fusion Co-cons- ruction Autonomy & consciousness transcend human control The expansion of the metaverse capital economy & gradual formation of virtual society Staggered Governance Structure Real World Virtual World Virtual world managers manage people in real world Real People Virtual Natural People – Ordinary Users Virtual Natural People - Managers Real world manages some ordinary users in virtual world Fusion Co-cons- ruction
20 The Metaverse Overview : Vision, Technology, and Tactics | Vision and Values Metaverse Experience Promote Real World Efficiency Enter the Metaverse with Entertainment Education Shopping Trade Virtual Community game Creative Collaboration Platform A 2nd Life New Influence & Social Status New Income right to use or own all or part of these virtual creations. In contrast, the real, centralized world allows any game prop to be copied at almost zero cost. Characteristics 6: Big uncertainty Governance structure is the core issue in the Metaverse, that is, who will be on top of its future governance structure. The governance structure in the Metaverse is interlaced. One scenario is virtual worlds managed by real people. Most of the early Metaverse worlds had this governance structure. Real people write code to create virtual worlds and manage avatars in them. In another scenario, real people are constrained and managed by the virtual world, with groups of virtual world managers who manage people in the real world. This small group establishes the rules, controls the virtual world and its citizens, with virtual individuals managing a large group of real people. Who will top the Metaverse governance structure in future? AI is at the root of this problem—will human beings rule robots or will we eventually create robots that surpass human beings? It is probably not the original intention, but AI self-learning could make robots eventually surpass human intelligence, giving them the ability to rule the world. This governance issue is so critical because the virtual world of the Metaverse carries has enormous economic and political power. Some prototypes of the Metaverse, such as online game purchases of virtual props, community purchases of real estate, and virtual currency transactions, have already shown the economic power of the virtual world, and this power will only grow. At the same time, the number of users of the products of the global internet giants has already exceeded the number of residents of any single country. When designing the Metaverse, all creators will need to decide who has the final say in the virtual world and who owns its economic benefits. 1.3 The value of the Metaverse The Metaverse can bring tangible value to people and the real world. This is the fundamental driver of the Metaverse wave. In the end, the value the Metaverse will bring to people is multifaceted, spiritual and material, including five main elements: • Entertainment: games and social activities, where players enter the Metaverse to enjoy immersive and realistic interactions, resulting in a pleasant experience of games and socializing • A second Life: collaboration platforms where creators build their own personal worlds in a virtual space, giving individuals the opportunity to experience a life that is different from the real world Figure17: User value in the Metaverse Source: Deloitte analysis
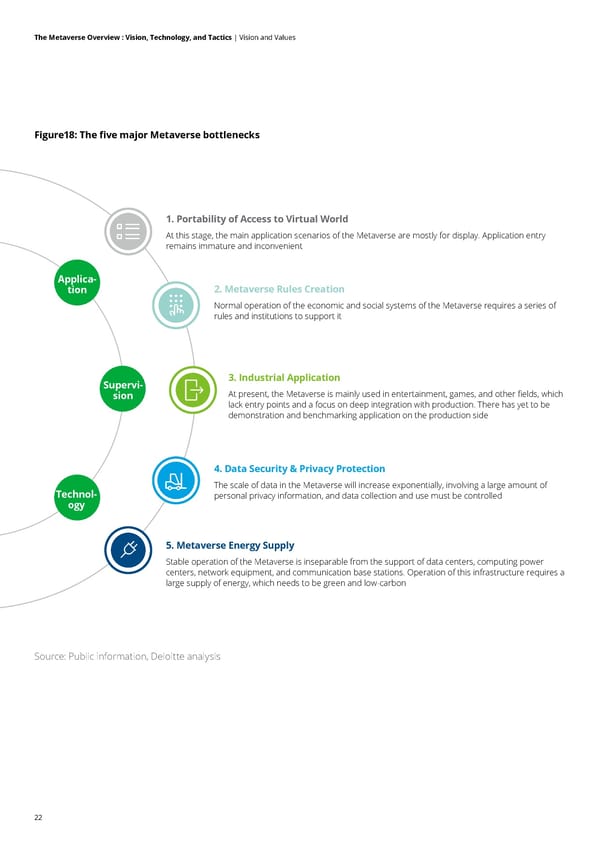
21 The Metaverse Overview : Vision, Technology, and Tactics | Vision and Values • Efficiency in the real world: Technologies such as digital twins, XR, and AI can improve the efficiency of many industries, including education, manufacturing, and retail. Activity in these industries will be unconstrained by time and space, experiences will be upgraded, and quality will improve • New wealth: virtual currencies and trading in virtual objects provide an opportunity to reshuffle wealth • New influence and social status: in virtual communities, creating a different avatar for oneself and partaking in social activities provide opportunities to achieve a new social status These five values mean that although the rise of the Metaverse has slowed temporarily, it retains huge potential for growth and increased value. 1.4 Current bottlenecks in Metaverse development Development of the Metaverse is in its infancy, although the market has high expectations. The ideal form of the Metaverse will eventually arrive, including elements of what we have described in the previous content. However, as the Metaverse matures, it will inevitably encounter bottlenecks that need to be broken through. The most prominent bottlenecks at this stage are: • Portability of access to the virtual world. At present, wearable devices including AR/VR sets continue to dominate people's entry into the Metaverse. In the future, entering and interacting in the Metaverse will be more flexible and convenient. Just like the League of Legends meeting in The Avengers, there will be no need to wear cumbersome equipment. After connecting to a line, the avatar of the other party will appear in front of you and your avatar will appear in the other party's space, enabling simulated interaction. VR/ AR kit is becoming more lightweight and convenient, and in 10 years, AR contact lenses should mature. Generally, major technical constraints remain and there needs to be more innovative thinking. • Rules of governance in the virtual world. This requires long- term research, exploration, and testing to design social, economic, cultural, tax, legal, and governance rules in the virtual world. If this is too conservative, construction of the Metaverse will not meet expectations. If it is too radical, it will intensify contradictions and even threaten the real world. • Industrial Metaverse applications. At present, the Metaverse is used mainly on the consumer side, including entertainment, social networking, games, and NFT art. It is not integrated closely enough with industry and manufacturing. The real-time sustainability, digital twins, and integrated reality in the Metaverse have deep application prospects for manufacturing, but technological limitations mean this potential is a long way from realization. • Information security and privacy. Network security and data privacy have become increasingly serious issues in recent years. The characteristics of the Metaverse, such as sustainability, real-time, connectivity, and creativity, indicate that the amount of data it hosts will increase exponentially, and the retrieval and use of data will become more frequent. How to balance information security with development of the Metaverse needs forward-looking consideration. • Energy supply. The complex mechanisms of the Metaverse consume vast network, storage, and computing power resources. Its stable operation will inevitably require the construction of new infrastructure. Current 5G networks, IDC centers, high performance computing, and AI are far from meeting the conditions required for a smooth Metaverse experience. In addition, amid a trend towards global carbon neutrality, the issue of how to build and operate infrastructure in a green way also needs consideration.
22 The Metaverse Overview : Vision, Technology, and Tactics | Vision and Values Figure18: The five major Metaverse bottlenecks Source: Public information, Deloitte analysis 1. Portability of Access to Virtual World At this stage, the main application scenarios of the Metaverse are mostly for display. Application entry remains immature and inconvenient 5. Metaverse Energy Supply Stable operation of the Metaverse is inseparable from the support of data centers, computing power centers, network equipment, and communication base stations. Operation of this infrastructure requires a large supply of energy, which needs to be green and low-carbon 2. Metaverse Rules Creation Normal operation of the economic and social systems of the Metaverse requires a series of rules and institutions to support it 4. Data Security & Privacy Protection The scale of data in the Metaverse will increase exponentially, involving a large amount of personal privacy information, and data collection and use must be controlled 3. Industrial Application At present, the Metaverse is mainly used in entertainment, games, and other fields, which lack entry points and a focus on deep integration with production. There has yet to be demonstration and benchmarking application on the production side Applica- tion Supervi- sion Technol- ogy
23 The Metaverse Overview : Vision, Technology, and Tactics | Technology
24 The Metaverse Overview : Vision, Technology, and Tactics | Technology 2. Technology 2.1 Technology clusters corresponding to Metaverse features The sequence of user access to the Metaverse and its corresponding technologies have the following clusters: • Access, which emphasizes immersive experiences driven by XR. • Interaction, which focuses on high simulation interactions between different users or objects, driven mainly by AI and supported by game engines. • Digital content, the creation of virtual objects or spaces using digital twins, real-time rendering, and 3D engines. • Rules and identity, which support mutual recognition and interactions between different users and entities in the virtual world, typically based on blockchain. • Large-scale, continuous online availability to ensure continuous operation and real-time feedback of the virtual world as if it were the real world. This requires a large number of high-speed computing and information transmission capabilities that use cloud computing, high performance computing, wireless communication (5G and 6G). In addition to enabling interactions, AI algorithms will underpin most other technologies. Access – Immersive experiences Convenient access and a realistic immersive experience are one of the core features of the Metaverse. The technologies that support this in consumer scenarios are XR-based, including access and somatosensory devices, holographic imaging technology, and brain-computer interaction. There are also other more advanced forms of access equipment technology, such as computer vision, speech recognition, NLP and other algorithms behind these. In manufacturing scenarios, digital twins and sensing technologies that simulate and perceive the physical world are the main supporting technologies. The immersive experience of the physical world mainly relies on sensors and digital twin technology to realize perception and simulation. Sensors include physical and biological perception of the environment (air, temperature, and humidity), physical equipment (machine malfunctions, energy consumption), biometric identification (plant growth, animal signs). Interaction – high simulation interaction This covers interactions between people and people or people and the physical world, including blooming flowers, a change in the shape of a palm when shaking hands, and damage to vehicles when they collide. 3D engines, real-time rendering, digital twins, spatial computing, and other technologies drive these interactions. There is also language-, text-, and image-based interaction and feedback between people in the Metaverse, which typically requires AI of varying degrees of sophistication. Content – creating virtual objects and spatial content Metaverse content creation technologies include game engines (providing important technical support for digital content), 3D modelling (for building high-speed and high- quality materials), real-time rendering Technology is the core element underpinning realization of the Metaverse, enabling the creation of all of the components and experiences of the virtual world. Many clusters of enabling technologies support the Metaverse, each cluster has several subcategories, and each subcategory can support multiple Metaverse functions. For the convenience of this discussion, we use the sequence of key user scenarios in the Metaverse as the spine of the following summary of technical categories. These key scenarios correspond to the key features of the Metaverse. After identifying the main supporting technologies, we describe the current stage of each major category.
25 The Metaverse Overview : Vision, Technology, and Tactics | Technology Ensure Large-scale Users Stay Online 5G/6G Technology Cloud Computing Edge Computing IoT Technology Immersive Experience, High Simulation XR BCI Hologram Technology Sensing Technology Real-time Operation, Multi-dimensional Interaction Machine Learning Smart Voice Computer Vision NLP Digital Twin Efficient Content Production Game Engine Real-Time Rendering 3D Engine Network & Computing Technology Simulation Interactive Technology Artificial Intelligence Creation & Interaction Platform Blockchain Technology (including NFTs) Identity & Rules Distributed Storage Distributed Ledger Consensus Mechanism Timestamp Technology Data Transmission & Authentication Mechanism Digital Twin Tech Cluster Role Tech Category Metaverse Characteristic Path to the Metaverse Virtual-Real Interface Algorithm Support Content Production The Most Intuitive Way to Present Virtual-Real interface The Core Code of the Metaverse Identity and Authen- tication Mechanisms Basic Support Network Environ- ment & Data Processing Figure19: Required technologies for Metaverse scenarios and characteristics Source: Deloitte analysis (simulating physical effects when different Metaverse objects interact), timestamps (for the traceability and confidentiality of underlying data), and other technologies. NFTs underpin the ability to identify unique created items and artworks to ensure their scarcity and non- replicability. Rules and identity – uniqueness and decentralization The virtual world is a "universe" because it brings things closer to the essence of human society, including status and systems for economy, society, and civilization, necessitating a decentralized model. Blockchain technology, which includes distributed storage and ledgers, mechanisms for consensus and data transmission and verification, and timestamps, typically drive these rules and identities. Continuous online use – large-scale information computing and real- time transmission Any interaction in the virtual world requires the processing of a vast amount of data and transmission of multiple signals. At the same time, to stimulate real life, interactive responses in the virtual world require extremely low latency. When we are socializing in the Metaverse and set out to shake hands with another person, if they take three seconds to respond, this will not be an immersive, lifelike experience. These needs require extremely fast background calculations. Continuous large-scale, real-time online availability requires technologies including network communication and computing, mainly 5G/6G (to ensure wireless communications in the Metaverse); cloud computing (sufficient background computing power to ensure more powerful, lightweight terminals at the front end), edge computing (to solve problems of cost, responsiveness, and network congestion), and Internet of Things (IoT). These supporting technologies are still far from creating a fully formed Metaverse experience, but some specific, "pre-Metaverse" scenarios have applied key technologies.
26 The Metaverse Overview : Vision, Technology, and Tactics | Technology 2.2 Key technologies' development stages and bottlenecks There is a barrel effect around Metaverse technologies, in which the "shortest board" technology determines the realizable extent of the Metaverse. At present, various technologies only meet the development needs of the initial Metaverse, with 5G having achieved large-scale, low-latency coverage that can accommodate the current scale of Metaverse users, and support for UGC content, 3D engines, and computing power. Current technology and content can meet the primary requirements of the Metaverse, and will continue to evolve. VR, AR and other virtual reality technologies have also reached the basic requirements of the Metaverse and now need to be optimized. Whether XR will become the main entrance to the virtual realm is still unknown. The blockchain is developing steadily, and downstream application scenarios are constantly expanding. Regional policies and laws regulate blockchain-based virtual currency technology. XR XR provides an immersive experience, with the goal of taking over human Figure20: XR experience development Figure21: XR development Source: Public information, Deloitte analysis No Immersion Partial Immersion Deep Immersion Primary Immersion Full Immersion Experience Somatosensory Realization Basic Implementation Initial Realization Not Yet Started Visual 2D Screen Visual 3D Hearing Seeing Hearing Touching Seeing Hearing Touching Smelling Odor Digitization Seeing, Hearing Touching, Smelling Ideas Tasting Brain-Computer Interface Taste? ? Taste is a combination of multiple senses: flavor comes from smell and texture relies on touch, which is very difficult to make virtual Seeing - Glasses, Screen Hearing - Headphones, Speakers Smelling - Smell Movie Touching - Somatosensory Devices Idea - Brain-Computer Interface Tasting Technology VR/AR , Spatial Audio Technology & Acoustic Simula- tion Technology Sensor, AI, Somatosensory Device Source: Deloitte analysis • Home demand catalyzes VR/AR industry penetration • 5G commercial officially announced • Oculus, Microsoft, HTC, Huawei, iQiyi, OPPO, 3Glasses,Pico, Value and other companies intensively launched related products 1968 2012 2014 2015 2016 2017 2018 2019 2021 2020 2011 • Facebook bought Oculus VR for USD2 billion and launched VR headset • Sony announced Project Morpheus VR headset • Google released CardBoard to blend content into VR headsets via smart phone • Samsung released Samsung Gear VR • Microsoft announced development of AR glasses Hololens • AR game phenomenon Pokemon Go launched Numerous companies started to launch new projects: • BBC released 360° documentary We Wait • Six Flags America launched VR roller coaster • Media company RYOT produced VR series Investment Fever Climaxes Constrained by business models and technical bottlenecks, growth was sluggish • Apple releasesd Arkit • Google released Arcore • Baidu, Alibaba and Tencent AR platforms issued • Concept stock Roblox listed • Facebook , Tencent, ByteDance, NetEase, Nvidia, and Epicgames, etc. have successively implemented strategies 1.0 Experiment Germination • Oculus VR developer VR headset Oculus Rift raises USD2.4 million • Google releases AR Google Glass VR/AR Enters the Public Eye 2.0 Development Boom • Ivan Sutherland , the "father of computer graphics" in the United States, developed the first computer graphics- driven helmet- mounted 3D display • The founder of Oculus VR invented prototype VR device 3.0 Trough 4.0 High Speed Develoment 5G + Epidemic + Metaverse • Oculus Go VR headset released • VR game Beat Saber sold 1 million copies • Huawei launched AR engine platform
27 The Metaverse Overview : Vision, Technology, and Tactics | Technology Blockchain Blockchain has developed steadily. After an early stage of exploration, market preparation, and recognition, it has entered industrial deployment, most commonly in the financial sector. In the Metaverse, blockchain and NFTs will resolve problems around ownership and identification of production and assets in the Metaverse. Blockchain technology has entered the NFT stage, heralding an era of digital content capitalization. The main difficulties in blockchain development are technical bottlenecks and regulatory compliance challenges. Technology Finance and e-government have adopted blockchain technology. In other business scenarios with relatively high requirements, blockchain struggles to meet demand. Most notably, given blockchains are distributed systems, bottlenecks in throughput, confirmation delay, and storage costs have restricted their application. These bottlenecks contradict one another, making them difficult to overcome simultaneously. For application scenarios like the Metaverse, there are higher requirements for speed, throughput, Figure22: XR bottlenecks Source: Deloitte analysis vision, hearing, and touch, and realizing the input and output of information in the Metaverse through motion capture. In somatosensory realization, visual and auditory simulation interaction is currently the most advanced technology in the virtual space. Simulations of smell, touch, and ideas (human thinking) have started. Simulated taste, a synthesis of multiple senses, has not yet been achieved. Overall development of XR technology, having bottomed out over the past three or four years, is entering another period of high-speed growth. Content and technology are the two current bottlenecks in XR. Many manufacturers have invested heavily in VR/AR hardware, but for large-scale consumer application, equipment remains expensive and beset by a poor sense of use, environmental restrictions, poor portability, compatibility restrictions, and short battery life. High-quality content, the endogenous way to attract users, will drive the development of hardware and the overall Metaverse industry. At present, VR content is not mature, and remains dominated by application scenarios such as games, social networking, and film and television. Application scenarios including virtual offices and fitness have begun to deepen, but the coverage, quantity, and quality of other application scenarios still need to be improved. On the world's most mainstream VR content platform, Steam, for example, VR games are its most popular products but only account for 8% of total content. In addition, content developing slowly and the number of VR users has not yet attained scale, which exacerbated this slow development and led to content falling to keep pace with hardware advances. Content Less content low amount of content poor quality slow content development Terminals user physical discomfort high price Poor portability short battery life low device compatibility Space restrictions
28 The Metaverse Overview : Vision, Technology, and Tactics | Technology Private Network of IoT Emerged, Giants Entered IoT Pulled by the supply side, some industries have initially achieved scale and local interconnection The supply side and the demand side have basically achieved a balance, industry boundaries have begun to blur, and the scope of horizontal data circulation has increased Demand-side pull, ubiquitous, definable, and creation of unified infrastructure 5G Network Deployment Accelerates, Vertical Application Business Breakthroughs IoT Penetrates All Walks of Life Pre-Outbreak Outbreak Full-Outbreak 2016 2020 2030 2050 Standardization of Terminals, Networks, Equipment, etc. Realizes True IoT Bitcoin's first genesis block mined 2008 2009 2010 2013 2014 2015 2016 2017 2018 2019 2020 2021 2012 Bitcoin concept is proposed The concept of blockchain was first proposed Germany recognized Bitcoin as legal; Canaan Yunzhi released 1st commercial mining machine Ethereum raised Bitcoins worth $18.3 million VISA Europe uses blockchain to send money Bitcoin Lightning Network launch IPFS project team announced establishment of the Filecoin project Launch of OpenSea, now the world's largest NFT trading Beeple’s NFT encrypted digital artwork purchased for USD million; Wyoming passes DAO bill Estonian government began incorporating blockchain into digital IDs Ethereum white paper released Tether issues USD-based stablecoin The first zero-knowledge proof zk-Snarks released; ERC-20 token standard proposed Decentralized Ledger Decentralized Computing Platform Defi Decentralized Finance NFT (Non-fungible Token) DAO (Decentral- ized Autono- mous Organization) receives more than $ USD100m in crowdfunding Release of the first version of DAI, opening the era of decentral- ized finance Payment giant PayPal announced support for cryptocur- rency payments Launch of Yunb, the first NFT digital asset trading platform in China Facebook released Libra white paper Ethereum proposed a complete programming language, users can develop decentralized APPs through their own smart contracts, and realize a decentralized database through a consensus mechanism, making Ethereum a truly decentralized computing platform DAI is the first fully decentralized stable currency on Ethereum and the cornerstone of decentralized finance Figure23: Blockchain development Source: Public information, Deloitte analysis and storage costs, so decentralization or security sometimes have to be sacrificed for efficiency. In addition, "information barriers" and challenges to creating "on-chain" physical assets are affecting the implementation of blockchain technology in the Metaverse. Regulatory compliance There are also policy risks in the continuous development of the blockchain. Bad actors can easily use the anonymity and anti-tamper characteristics of the blockchain to spread misleading information, threaten network security, and damage user privacy. In addition, there have been frequent cases of illegal financial activity under the banner of "blockchain", disrupting the normal market order. IoT The development of IoT has three stages: pre-outbreak, outbreak, and full-scale outbreak. At present, the core technology of the global IoT continues to develop, with the creation of unified standards, an improving industrial ecosystem, and a rapidly developing global IoT industry. However, it will take a few more years before the IoT outbreak. Three challenges need to be solved for IoT to achieve scale and accelerate its evolution: First, high cost. IoT is costly because there are so many types of sensors, including camera, weather, and pollution sensors. This makes it difficult to create scale effect, and Figure24: IoT development Source: Public information, Deloitte analysis
29 The Metaverse Overview : Vision, Technology, and Tactics | Technology Figure25: Development of mobile communication networks Figure26: Computing power development Source: Public information, Deloitte analysis Source: Public information, Deloitte analysis Download Speed: 2 Kbps Download Time: 6 days Download Speed: 100 Kbps Download Time: 2.5 hours Download Speed: 150 Mbps Download Time: 20 seconds Download Speed: 100 Gbps Download Time: 1Tb (300 movies) - 1 second Download Speed: 8 Mbps Download Time: 2 minutes Download Speed: 10 Gbps Download Time: 3 movies - 1 second 1G 1979 1991 1998 2008 2018 2030 3G 5G 2G 4G 6G pushes up marginal cost, making IoT construction expensive. Second, the technology is not yet mature. Big data analysis is still required after sensors collect data from the edge. It is not yet possible to integrate and connect data collection and analysis across different industries and fields. The high-value of data will only be released once analysis is integrated deeply with industry applications. Third, security issues. Compared with the hard secure protection of mobile phones, IoT sensor structure is relatively simple, making it easily used as a springboard for distributed technology attacks. IoT must solve these development problems of cost, technology, and security before it can become widely used in the industry. Mobile communication networks The transition from 5G to 6G is still in its early stages. The ideal Metaverse requires at least 6G or even more powerful networks. 6G network communication should be fully implemented by 2030. 6G can go far beyond the powers of 5G to support microsecond or even sub- microsecond delay communication, positioning accuracy of 10 centimeters indoors and 1 meter indoors, and the "Internet of Everything" on a global scale. Intuitively, in the 6G era, when downloading 300 movies will take just the blink of an eye, then it will also be possible to achieve almost zero-latency shuttle interactions in the Metaverse. The development of 6G networks is hugely reliant on breakthroughs in its four main technologies: terahertz technology, air-space-sea-terrestrial integration, deterministic networks, and AI-based air interfaces. Because the frequency band of terahertz technology is 1-4 orders of magnitude greater than existing microwave communication, it can carry more data, easily overcome bandwidth limitations, and meet the communication requirements of large data transmission rates. A globally connected 6G communication network that integrates satellite, deep-sea ocean and terrestrial communication 2000 2005 2010 2015 2020 2025 Simulation, Oil & Gas, Meteorology Industry Application Intelligent & Diversified Applications Business applications are gradually enriched Animation Rendering, Life Sciences, Aerospace, Unmanned Driving, Financial Economy, Smart Cities, etc. Shenzhen Jinan Tianjin Lenovo DEEPCOMP 6800 Dawning 5000A Changsha Guangzhou Wuxi Zhengzhou Kunshan Xi’an Chengdu Taiyuan Hefei Xiamen Wuzhen Lanzhou Qingdao Wuhan Sensetime Tencent Alibaba Scientific Research Application 2003: Lenovo DEEPCOMP 6800. Top500 14 2004: Dawning 4000A. Top500 10 2008: Dawning 5000A. Top500 10 2008: Lenovo DEEPCOMP 7000. Top 500 19 The construc- tion of computing centers has accelerated
30 The Metaverse Overview : Vision, Technology, and Tactics | Technology networks is an important direction of development. Deterministic network technology with high reliability and low latency will accelerate the 6G era and shape a wide range of applications. The combination of wireless transmission and AI at the physical layer of communication is also a key trend in the 6G era. Computing power In the past 20 years in China, the application of computing power made advances and the construction of computing centers has accelerated. With high-performance computing (HPC) focused on scientific research applications and key fields such as simulation, oil & gas, and meteorology, the use of computing power has become more diverse through deployment in intelligent applications fields like animation rendering, life sciences, aerospace, unmanned driving, the financial economy, and smart cities. Business applications have been enriched and growth in industry applications is accelerating. Current computing, storage, and networking infrastructure cannot realize a true Metaverse vision. To achieve this true Metaverse, computing power needs to be increased by another 1,000-fold. AI, edge, and quantum computing will be the main infrastructure technologies for development of the Metaverse. At present, AI chips are still in a period of rapid development. Chips need to achieve close parallel processing to support more diverse AI calculations in the Metaverse. This will require a series of technological breakthroughs. Edge computing can reduce latency and improve computing efficiency. In an overall architecture, a central cloud implements global scheduling, the edge cloud focuses on local large-scale data processing, and the terminal transforms vast amounts of physical inputs into massive caches of data. Quantum computing, meanwhile, has the ability to support exponentially growing data operations, has the potential to break through into the "post-Moore" era, and can solve the Metaverse's computing power bottleneck. But quantum computing is still at the of prototype development stage. Despite barriers to achieving massive increases in computing power, the time for further breakthroughs is not far away. After all, as we mentioned previously, Nvidia's CPU speed has increased 1 million-fold in the past 10 years. 2.3 Examples of Metaverse-related technology applications Although far from creating a true Metaverse, various applications have deployed the above-mentioned technologies. We call these pre- Metaverse applications and detail representative examples below. Simulation – interactive games, commerce, education and culture • Games: Game-based social networking is being transformed and Figure27: Examples of Metaverse-related technology applications Source: Deloitte analysis Game VR games become the entrance of metaverse Business Shopping software introduces VR product try-on interface Manufacture AI empowers smart manufac- turing Medical AI improves medical efficiency Social Everyone builds a virtual community Film and television Support real-time audio and video interactive creation Smart City Blockchain strengthens smart city construction Pay Blockchain makes virtual currency transactions possible Education VR/AR innovative teaching methods Simulation Interactive Technology Artificial Intelligence and Digital Twins Create an Interactive Platform IDENTIFICATION AND PAYMENT Culture Forbidden City AR Cultural Tourism Exhibition integrates face, gesture recognition and somatosensoryinter- action
31 The Metaverse Overview : Vision, Technology, and Tactics | Technology expanded to encompass VR game- based social networking, VR movie social networking (e.g. Douban) and VR travel social networking (e.g. Mafengwo). • Commerce and trade: VR/AR technology is now used for virtual product displays, for example in Alliance Studio's 3D VR mall, where people use virtual navigation to move between and browse stores and products and access payment gateway support. This convergence of online and physical shopping is a highly competitive new shopping model. • Education and training: Users enter a virtual education space through VR/AR head-mounted display equipment, enjoying a more attractive, interactive and intelligent learning environment. For example, STRIVR products used in employee training, which increases the participation of employees, reduces the amount of training required, and helps people master content faster. • Culture: Using interactive simulation technology to digitize the cultural heritage of ancient buildings, breaking the constraints of time and space and improving the display effect and efficiency of cultural landmarks. For example, the Forbidden City AR Cultural Tourism Exhibition integrates face and gesture recognition with somatosensory interaction, enabling exhibitors to freely and easily obtain information that is pivotal to the long- term protection, renewal, promotion, and continuation of historical and cultural sites. Digital twins and AI – manufacturing and medicine • Manufacturing: Product design, process optimization, quality management, supply chain management, predictive maintenance, and customer experience analysis can use digital twins. For example, in automobile manufacturing, Siemens uses digital twins to simulate and verify each stage of development, avoiding possible failures in actual production. • Healthcare: Digital twins used in drug clinical trials, medical care, and surgical rehearsals help provide patients with more efficient, and effective services. AI can create pre-life simulations to build digital prediction models for patients, providing prediction record analysis and decision support throughout their lives. Creative, interactive platforms – social networking, film, and television • Social: Content creators are encouraged to build virtual worlds and create content and interactions in the Metaverse. For example, Horizon Worlds allows users to enter virtual spaces as creators, have real collaboration and sharing experiences, and explore constantly created and evolving virtual worlds. • Film and television: Creative interactive platforms provide innovative impetus for content forms including film and television, variety shows, and short videos. For example, Tencent Video is an online interactive creation platform that encourages original creators to participate. Blockchain – smart city and finance • Smart city: A city's information, energy, transportation, and other infrastructure is combined on a blockchain to give full play to the huge value of data. At the beginning of the construction of Xiongan New Area, it began to use blockchain technology to empower smart city construction. • Finance: Blockchain technology connects the global financial system to make transactions more efficient and cheaper. The Metaverse has more advanced means of payment, because its economic activity supports the transaction of virtual goods. Pure digital currency made possible by blockchain can be used to buy goods. Technologies will eventually converge to empower various application scenarios, liberate productivity, advance insights, improve decision- making, and upgrade business.
32 The Metaverse Overview : Vision, Technology, and Tactics | Industry
33 The Metaverse Overview : Vision, Technology, and Tactics | Industry Access Mobile PC BCI Somatose- nsory Devices Speech Recognition VA/AR Camera Tech Infrastructure IoT Internet Cloud Computing Wires and Wireless Communications Networks Tech Platform (Engine) Digital Twins Game Engine Blockchain AI Spatial Computing NFT Application Industrial Scenarios Industrial Scenarios Consumer Scenarios Governance Scenarios Environment 3. Industry 3.1 Metaverse industry framework Given the broad contents in and different understandings of the Metaverse, a unified industry framework is critical for analyzing the industry, developing solutions, and other Metaverse-related work in a structured way. We view the Metaverse as a large enterprise application with four layers: Access layer: VR/AR, somatosensory devices, brain-computer interfaces, and other technologies that connect users to the Metaverse. There are numerous enterprises already involved in Metaverse. Our framework for the Metaverse industry below facilitates analysis of the sector, related companies, and different business applications. Application layer: Generates all digital contents and applications, including environment building, industrial manufacturing applications, games, social activities, digital artworks, economic activity, and virtual offices. Technology platform layer: Contains technologies that support virtual community building, community rules and application development, including the generation and import of virtual infrastructures such as blocks and architectures; supporting technologies such as game engines and content distribution platforms; and AI algorithms that support intelligent applications and interaction. Technology infrastructure layer: The underlying technologies of the Metaverse including internet, IoT, 5G/6G, and cloud computing. We use this industry framework to compare different participants in the Metaverse. People wanting to enter the Metaverse or investors and companies can use this to identify specific opportunities in the Metaverse industry. Figure28: Industry Framework Source: Deloitte analysis
34 The Metaverse Overview : Vision, Technology, and Tactics | Industry 3.2 Types of participators, cooperation and competition There are four main classes of Metaverse solution providers: internet companies, hardware companies, software development companies, and new entrepreneurs. In the future Metaverse landscape, these four classes of company will be involved in stronger cooperation inside, and stronger competition outside, each class. The leading internet companies include Meta, Google, and Amazon in the US, and Baidu, Alibaba, Tencent, and Bytedance in China. Most of them own the multiple technologies needed to create the Metaverse, have massive user bases, abundant application scenarios, and have brought the Metaverse into their long-term strategies. They are expected to take the main roles of Metaverse platform constructors and community owners. The second group, software companies, is represented by Microsoft, which has business plans for all four layers of the Metaverse and is emphasizing enterprise applications. The future Metaverse will see fierce competition between Microsoft and internet companies, especially in the access layer, technology platform layer, and infrastructure network layer (including cloud) where both groups have a footprint. In the application layer, Microsoft's strength is the enterprise Metaverse, whereas most internet companies attach greater importance to consumer Metaverse. However, we also expect stronger competition in this layer as most internet companies are also serving and enlarging their enterprise market. The third group (hardware companies) is represented by NVIDIA. NVIDIA maintains strong leadership in AI, high- performance computing (HPC), and chips, establishing solid foundations in the Metaverse infrastructure and technology platform layers. In the second half of 2021, NVIDIA announced Omniverse—the first simulation and cooperation platform to support Metaverse construction. Omniverse is now open to millions of users and because it has high efficiency and low cost is expanding rapidly in multiple fields, including architecture, media, product design, and autonomous- driving. Moreover, Omniverse has formed its own ecosystem based on micro-services and a third-party digital content creator. The fourth group are the new entrepreneurial Metaverse companies, with each focusing on a specific segment. Many of them have been around longer and acquired first- mover advantage in their specific markets, such as Roblox (gaming and community), Decentraland (community and gaming), OpenSea (NFTs), and Sandbox (gaming and community). Although the market values of Roblox and OpenSea have each exceeded USD10 billion, most entrepreneurial Metaverse companies have a small market size and have are dedicated to niche technologies or applications, including Lingo3D, Attrsense, Cyzone, and Deemos. For internet giants, these innovative enterprises can become solutions providers for specific Metaverse scenarios via collaboration or M&A. For example, Tencent has invested heavily in Roblox, Bytedance has acquired VR provider Pico, and Meta acquired Oculus several years ago. Figure29: Participants in the Metaverse Source: Deloitte analysis 小鸟看看 Internet Vendors Hardware Technology Manufactur- ers Software Technology Vendors Entrepreneur (Small Particles of Technical Flow)
35 The Metaverse Overview : Vision, Technology, and Tactics | Industry 3.3 Major platform players Platform-based players (mainly large internet and technology companies), rely on their mature technologies, broad user bases, and existing application scenarios to quickly deploy Metaverse applications. Benefiting from capital advantages, they can expand their Metaverse reach through investment or M&A in areas not yet covered by their own businesses. This section analyzes these industry giants and provides an overview of their Metaverse layouts. Meta Meta has one of the most comprehensive layouts in Metaverse. It has dabbled in hardware, software, content, digital currency and other segments of the Metaverse through strategy and transformation. Meta has launched several programming tools including Spark AR, Presence Platform, and Pytorch to build and develop the Metaverse community. In the access layer, Meta's Oculus leads the global market for XR devices, with its latest product, Oculus Quest 2, taking up to 75% of the market. In content, Meta has acquired several VR game and cloud game developers and launched virtual social and office platforms like Horizon Worlds and Horizon Workrooms. In digital currency, it has Libra and is now marketing the Diem token. In the platform layer, Meta has released the Presence Platform covering a series of machine cognition and AI functions that include Insight SDK, Interaction SDK, Voice SDK, Tracked Keyboard SDK, and other components, and plans to build an ecosystem that supports Metaverse learning. In the network layer, Meta has launched open infrastructure and data center network hardware that supports cloud services and is growing in areas like AI. Microsoft Microsoft is devoted to all four layers and helps enterprise customers with digital transformation through a series of products including HoloLens, Mesh, Cloud, and Azure Digital Twins. Unlike Meta, which emphasizes the consumer end (household applications, office, social apps, and UGC content); Figure30: American internet and technology enterprises in the Metaverse Source: Open source data, Deloitte analysis Perception & Display Layer Meta Google Microsoft Amazon Network Layer Platform Layer Application Layer Cloud Computing AR Shopping Development Platform Sumerian Speech Recognition Transcribe Medical Social Contact Horizon Worlds VA/AR oculus Open Computing Data Center AI Internet Gaming Beat Saber Fitness Les Mills Bodycombat Development Platform Presence Platform Android OS AI Cloud Computing TPU AI Chip Gaming STADIA Google Daydream VR Platform Speech Recognition wayii Video YouTube VR VA/AR HOLOLENS Somatosensory Device Kinect Cloud Computing Content Delivery Network Edge Computing AI Games (Activision Blizzard, MINECRAFT) Operating System Tool Software Meeting + MR (Microsoft Teams)
36 The Metaverse Overview : Vision, Technology, and Tactics | Industry Microsoft puts more efforts into the enterprise Metaverse. In August 2021, Microsoft announced its enterprise Metaverse solution, with two core features: Dynamics 365 Connected Spaces and Mesh for Teams. Dynamics 365 Connected Spaces helps company administrators analyze the movements and interactions of consumers in grocery stores or employees on factory floors. Mesh for Microsoft Teams integrates Microsoft Mesh (an MR meeting platform) into Microsoft Teams, allowing people in different locations to collaborate on Teams using 3D avatars. In the hardware layer, Microsoft has VR/AR visualization (the Hololens series) and somatosensory technology (Kinect). In terms of applications, apart from enterprise software mentioned above, Microsoft has acquired Minecraft and Activision Blizzard in gaming. As the second-largest public cloud server in the world, Microsoft is experienced in edge computing and AI. Google Google has solid foundation in the infrastructure layer of the Metaverse through its AI and cloud service. In 2017, Google's strategy changed from Mobile First to AI First, and it now leads the AI industry in R&D and applications. Tensor Flow, Google's open-source software for AI, is widely used worldwide, and Google has launched TPU chips specifically for Tensor Flow. In cloud computing, Google Cloud is among the world's top four public cloud service providers. With its combined efforts in cloud computing and AI, Google can play an important role in Metaverse infrastructure. In the access layer, it does not yet have a top product but the release of Google Glass in 2012 should not be ignored. Google has only a few deployments in the application layer, and mainly combines existing businesses with the Metaverse concept, including Stadia in cloud games and YouTube VR in software services. Amazon Amazon's Metaverse strategy of is mainly based on its current cloud computing AWS and e-commerce business. It has provided cloud-computing services to help Meta accelerate R&D on its AI projects. The two companies will also cooperate to help customers improve the performance of PyTorch (a deep learning computing framework) on AWS, and accelerate the modelling, training, and deployment in AI and machine learning. Amazon also cooperates with Epic games and provides it with cloud- computing services. Epic Games' ace product, Fortnite, has 350 million users worldwide. As a Metaverse game, it requires massive computing resources. Almost all of its workload is currently on AWS. In addition, Amazon is using its advantages in retail to develop AR shopping applications. Chinese internet companies in the Metaverse Chinese internet companies are developing applications for multiple layers of the Metaverse by utilizing their own strengths. Baidu Baidu's Metaverse advantage is in AI and hardware, as an internet giant with an early strategy and in-depth development of AI. Its business ranges from search engines to AI applications including chips, AI open-source algorithms, and intelligent driving, with AI running through every aspect of its business. In hardware, Baidu has been involved in VR for many years with a full-scale product line that includes consumer- oriented (iQIYI Qiyu series) and enterprise-oriented VR (Baidu VR). In applications, Baidu has launched Xirang alongside its VR lines. This is a mixed enterprise-consumer virtual community that aims to create a virtual world supporting multiplayer interactions. Baidu also has autonomous-driving technology and could make this one of its Metaverse applications. Alibaba In the Metaverse, Alibaba focuses on two core advantages: Metaverse solutions based on cloud computing and combining e-commerce user experience optimization with the Metaverse. It has extensive experience in cloud computing, with a public cloud that ranks third in the global market, only behind Amazon and Microsoft. In 2021, Alibaba put more effort into the Metaverse, creating cloud game Yuanjing, building an XR laboratory, and launching NFT platform Jingtan. In e-commerce, Taobao supported VR shopping since 2016. Tencent Tencent's Metaverse strengths are backed by its huge user base and rich application scenarios in social interaction, lifestyle services, and entertainment content. Starting with the popular games Roblox and Fortnite, Tencent has assembled a development team for Metaverse games and invested in
37 The Metaverse Overview : Vision, Technology, and Tactics | Industry Perception & Display Layer Network Layer Platform Layer Application Layer AI Cloud Computing (Volcano Engine) Social, Gaming (Reboot World) NFT Products ( TikTok Top Moments) Game Engine (Restart the World) VR/AR(pico) VR/AR ( Baidu VR) VA/AR AI AI Chips Internet Social, Gaming (Hyryang) NFT Platform (Whale Scout) Cloud Computing (Alibaba Cloud) AI Blockchain (Ant Chain) VR Shopping ( Buy+) Cloud Game (Yuanjing) VA/AR (TenVR) Cloud Computing (Tencent Cloud) IoT AI Blockchain (Confidence Chain) Social Contact Game Engine (Unreal) NFT Platform (Magic Core) Cloud Gaming ( START) Epic, the American game development and marketplace platform. In cloud computing, Tencent launched cloud game START, and with the Metaverse gaining more attention in 2021 registered a series of trademarks including QQ Metaverse, Tencent Music Metaverse, Game for Peace Metaverse, Honor of Kings Metaverse, and Oasis Metaverse. In NFTs, Tencent has developed the Huanhe marketplace built on top of its proprietary Zxin Chain. 3.4 The NFT industry chain NFTs are one of the fastest-growing arenas of the Metaverse, catering to people's curiosity, pursuit of artistic creativity, and investment demand for digital art collections. The NFT industry chain has four layers: infrastructure, production, circulation, and derivatives. The infrastructure technology layer is mainly composed of ByteDance ByteDance focuses on hardware entrance, content and applications, and its current product matrix including Douyin, Xigua Video, Toutiao, and TikTok support networks in its Metaverse strategy. In the access layer, ByteDance acquired Pico, a leading Chinese VR manufacturer in September 2021. In the application layer, in April 2021 ByteDance invested RMB100 million in Code Qiankun, which developed and blockchain (public chains, side chains, developer tools, token standards, wallets, and payments) and network- attached storage. The infrastructure layer creates and captures the value of the NFT value chain through NFT minting. For example, the gas fee during minting goes to the blockchain, and the more NFTs minted, the higher the value captured by the blockchain. owns Reworld, a game creation and interactive content platform for teens. It has also launched Pixsoul, a social app featuring face art creation. ByteDance's launch of its Metaverse social game app Party Island, which is currently in beta testing, is expected soon. In October 2021 TikTok launched its first NFT series, TikTok Top Moments. In the network layer, ByteDance is entering the market with Volcengine as an independent business unit for the public cloud market. Public chains are independent, community-oriented blockchains like Ethereum and Flow Blockchain. Ethereum, with its long history, is the leading blockchain in the NFT market. Sidechains are new blockchains created to alleviate high traffic, improve public chain performance, and realize certain functions that some public chains cannot fulfill. Protocol standards create an underlying logic Figure31: Chinese internet and technology enterprises in the Metaverse Source: Open source data, Deloitte analysis
38 The Metaverse Overview : Vision, Technology, and Tactics | Industry and consensus during NFT minting and include ERC20, ERC721, and ERC1155. Developer tools help develop blockchain applications. Network storage is data storage on a blockchain, represented by InterPlanetary File System IPFS distributed storage. A wallet, e.g. Tokenall, is a tool for private key storage without holding tokens. The production and circulation layers host platforms that produce and trade NFT works. Production platforms have two usual models, UGC and PGC, to create NFT artworks, games, virtual worlds, and marketplaces. For example, Decentraland is a decentralized virtual world based on Ethereum. Users of Decentraland can create, explore, and trade NFT works in this virtual world. Sandbox launched its blockchain-based Play-to-Earn game in 2018, which has no storyline or settled ending but allows players to experience the game and acquire digital assets that are tradable in the blockchain. The Huanhe NFT marketplace in China belongs to Tencent, which is devoted to developing digital collection business that confirms with compliance requirements. Cryptopunks was one of the earliest NFT collections on Ethereum, where the most expensive trade reached USD7.5 million. OpenSea is the world's largest comprehensive NFT marketplace, where users can mint, display, trade, and auction NFTs. The derivative layer includes exhibition platforms and combinations of NFT applications with other industries. This layer includes NFT fund Metapurse, a cryptocurrency fund created and funded by Metakovan and operated with Twobadour. It focuses on identifying early-stage projects across blockchain infrastructure, finance, artwork, collectibles, and virtual real estate, and creates virtual museums, art exhibitions, music, and technology events. Decentralized finance or DeFi is one example of a combination of NFTs and finance. It empowers traders to save, borrow, transact, and buy insurance without a centralized entity (bank or financial institution) and overhaul the traditional banking system. Liquidity has often limited the financialization and popularization of digital art. NFT20 is a decentralized NFT derivatives trading market and protocol that addresses this issue by allowing NFT producers to create liquidity pools for their projects and traders to benefit from those pools' greater liquidity and fair prices. Its trading volume and liquidity ensure fair prices for all. NFT20 tokens can also be bought as an investment. Figure32: NFT industry chain and companies Source: Public information data, Deloitte analysis Infrastructure Technology Layer Production Layer Circulation Layer Derivative Layer NFT + Defi Exhibition Platform Integrated Trading Platform Digital Art Platform NFT Artwork NFT Games Virtual World Network Storage Blockchain Platform NFT Industry Chain Representative Companies & Business Introduction The NFT ecology of the Ethereum public chain was developed earlier, and it is the absolute overlord of the current NFT infrastructure Ant Chain is the external brand of Ant Group's intelligent technology business, dedicated to linking trust with technology IPFS is a global, peer-to-peer distributed file storage system Any NFT work holder can deposit works to the fund pool in exchange for NFT20 tokens for liquidity Decentraland is an Ethereum-based decentralized virtual reality platform that allows users to create, explore, and trade in virtual worlds Cryptopunks, one of the earliest NFTs on Ethereum, currently has the most expensive transaction at USD7.5 million Magic Core is Tencent's NFT trading software, committed to the implementation of digital collectibles business under a compliant framework Currently the world's largest comprehensive NFT trading platform, users can mint, display, trade, and auction NFTs Metapurse hosts NFT art, music and tech events where anyone can participate remotely
39 The Metaverse Overview : Vision, Technology, and Tactics | Industry NFT business and circulation models Participants in NFT circulation are either upstream-creators, midstream-platforms, or downstream-bidders. Figure34: NFT value distribution Figure33: NFT circulation Source: Public information, Deloitte analysis Source: Public information, Deloitte analysis NFTs generate value at every link, including gas fees charged by blockchains, sales and trading fees charged by platforms, and copyright payments to content creators. Typically, upstream creators pay gas fees to a blockchain when creating an NFT. They then pay gas fees to the blockchain and commission to a platform when the NFT is published. Creators also collect transaction fees from buyers, and buyers pay gas and platform fees. If the NFT is traded again, the creator receives a copyright fee and the platform charges a resale service fee. The seller collects the NFT payment and pays resale service, royalty income, and gas fees. The buyer pays for the NFT and pays gas fees too. NFT Platforms Creators Mainly Individual Creators: 90% Individuals; 10% Teams Deals / Bidders • Global: OpenSea, SuperRare, Nifty Gateway, Rarible • China: Ali Auction, AntChain, Tencent Magic Core Young People: 58% Millennials, 33% Gen X Upstream Midstream Downstream Gas: a Gas fee is needed for recording creation and transaction information on the blockchain Sales/Resale Services Fee: NFT transactions through the platform need to pay the platform certain service fees Sales Revenue, Royalties: creator’s income comes from the sales income in the primary market and the circulation royalties income in the secondary market Value Distribution Value Attribution Blockch ain Creation Platform Creator 1 2 3 NFT Market Value Distribution Creation Issue & sell Transfer Infrastructure layer Gas fee Gas fee Gas fee creation layer (creator) not in the chain: 0 within the chain: Gas fee without platform: sales revenue-Gas fee with platform: first sales revenue-Gas fee Royalties creation layer (primary transfer platform) first sales revenue creation layer (secondary transfer platform) resale service fee collector (seller) resale revenue-resale service fee-royalties-Gas fee collector (buyer) issue revenue-Gas fee resale revenue-Gas fee Established Time Entry Forms of Creators First Sales Service Fee Resale Service Fee Royalties of Creators OpenSea 2017 Not Set 2.5% 2.5% 10% SuperRare 2018 Application 15% 3% 10% Nifty Gateway 2018 Targeted Invitation and Application - 5%+0.3USD Self Design Rarible 2019 Application 2.5% (in the price) 2.5% (out of the price) Up to 50% Examples of Main NFT Market
40 The Metaverse Overview : Vision, Technology, and Tactics | Industry The three roles in circulation Upstream NFT developers include individuals and organizations using the UGC of PGC model. Individual creators represent 90% of NFT developers worldwide, but in China, professional teams dominate NFT creation. Most downstream buyers and bidders are young. According to the auction data from Everyday: The First 5,000 Days, millennials (1981-1996) and Gen X (1965-1980) bought more than 90% of the NFTs, showing the current NFT market belongs to young people with buying power, at least for now. Globally, the midstream NFT trading platforms include OpenSea, SuperRare, Nifty Gateway, and Rarible. In China they include Alibaba Auction, Ant Chain, Tencent Huanhe, and NFT China. Internet and technology companies dominate China's NFT market because NFTs cannot be traded freely there. There are major differences in the technology, types of artworks, and oversight on Chinese and global platforms. Figure35: NFT creation Figure36: NFT markets globally and in China Source: Deloitte analysis Source: Deloitte analysis PGC UGC Creators Professional teams generate content users generate content platform releases NFT with its own artist team or external artists users can create NFT works and upload, currently support audio, video, pictures, etc. Model of creation Cases Global: Nifty China: Ali Auction, AntChain, Tencent MagicCore, JD lingxi Global: OpenSea, SuperRare, Rarible, etc. Profit model- platform Sales sharing: the platform cooperates with well-known IP, and the sales are divided according to the agreed proportion service fee: users pay Gas fees to upload their work to the chain through the platform, and the platform can earn Gas fees as a middleman Gas spread: the platform charges users a fee when they sell NFT, about 5%~15% Profit model- creators sales sharing, contract fee sales revenue-chain fee-service fee Global Market China’s Market Blockchai focus on public chain focus on private chain Currency Ethereum, RARI and other cryptocurrencies legal currencies, e.g. RMB, digital RMB Restrictions Lax regulation And flexible trading some can be donated, not open for resale Restrictions more relaxed rise and fall restricted rise and fall Type of Artwork wealthy less Threshold of Creators including high and low thresholds focus on high thresholds China vs. global platforms
41 The Metaverse Overview : Vision, Technology, and Tactics | Industry Demographically, NFT market is more mature overseas, especially in Europe and the US. Among the biggest NFT buyers, 55% are in the Americas, 27% in Europe, and only 18% in Asia, mainly due to the greater flexibility of overseas markets. Current problems Four major problems currently beset the NFT market, the most prominent being security and market supervision. There is a long way to go before the massive adoption of NFTs and it will require cooperation and joint efforts from multiple counterparts. The four major problems are a lack of liquidity, with high price thresholds and no fair pricing mechanism; the security and uncertainty of blockchain storage, with occasional NFT losses; NFTs being a niche market limited to digital art, collections, and games, with a long way to go before mass adoption; and as-yet-unsettled market rules, with regulatory development far slower than NFT market growth, and the lack of a gateway for NFT supervision. Figure37: Profile of NFT bidders and buyers Figure38: Problems in the NFT market Source: leadleo.com, Deloitte analysis Source: Deloitte analysis 发展面临 的问题 流动性匮乏 储存安全不确定 应用领域小众 市场规则不完善 58% 33% 6% 3% Millennials (1981-1996) X age (1965-1980) Z age (1997-2012) baby boomers (1946-1964) 55% 33% 6% America Europe Asia NFT dealers/Bidders, Users Portfolio: Take Everyday: The first 5000 Days the Bidding of as an Example Problems Lack of Liquidity Uncertain Storage Security Niche Application Field Market Rules Are Not Perfect
42 The Metaverse Overview : Vision, Technology, and Tactics | Metaverse tactics for enterprises
43 The Metaverse Overview : Vision, Technology, and Tactics | Metaverse tactics for enterprises 4. Metaverse tactics for enterprises 4.1 Metaverse development Defining Metaverse development depends on how immersive the experience is, user scale, the smartness of AI technology, and how much humans rely on the virtual world. Our predictions for Metaverse development are based on the key factor of "ownership of governance". There will be five stages in the Metaverse development: We are currently in the agrarian age when primary applications spread rapidly. A huge amount of new enterprises and services are emerging, and most of them can find their niche because the Metaverse remains a This chapter explores the future stages of the Metaverse, major potential risks, the attitude to NFTs in China, and how companies should respond to Metaverse opportunity. "blue ocean" market. Big companies are accumulating experience across the Metaverse, while startups thrive on segmented portions of the Metaverse, similar to how people fed themselves in the agricultural age. This stage will only last around 10 years) as the public is already forming a consensus on how much value the Metaverse brings. The next stage will be oligopoly after the biggest companies achieve their strategies and stop accumulating, having gained the largest slice of the market. This stage will last for around 20 years as these giants build high barriers to competition. The Metaverse will then enter a symbiosis of virtualization and reality. People will shuttle back and forth between the virtual and real worlds. Virtual humans and AI will enter many scenarios, interacting and coexisting with humans. The length of this period depends on technical breakthroughs in AI. Finally, the virtual and the real will compete with each other. This will happen after around 50 years when virtual humans are intelligent enough and even surpass the average intelligence of human beings, being able to compete with humans for control. Figure39: Development stages of the Metaverse Source: Deloitte analysis Primitive Society ~2020 Oligopoly 2031- 2050 Symbiosis of Virtual and Real 2050 - 2070 Farming Stage 2020~2030 Game of Virtual Reality ~ 2071 The technologi- cal rudiments of the Metaverse emerge The primary Metaverse form lands. The Metaverse is a blue ocean A few Metaverse giants appear, creating an oligopoly Humans use the virtual world to the same extent as they use the real world The game of the Wisdom of Virtual Humans vs Human Control of the Metaverse
44 The Metaverse Overview : Vision, Technology, and Tactics | Metaverse tactics for enterprises 4.2 Potential risks The advance of the Metaverse will present potentially significant risks related to addiction, privacy, intellectual property, economics, oligopoly, and governance. • Addiction: With continuous development of the Metaverse, addiction risk is becoming more significant. The Metaverse breaks the physical rules of the real world, redefines production and lifestyles in the digital world, and transforms social productivity. However, brand- new visual stimulus and interactive experiences could make people addicted to the virtual world and unable to extricate themselves from it. It is therefore critical to find a way to balance the relationship between the real world and the Metaverse, letting the latter play a more positive role. • Privacy: The Metaverse will become a massive, extremely complex, open, and dynamically optimized system that is more deeply integrated than the "old" internet has been in people's daily work and lives. Any malicious use of the data recorded by every interaction of people with the Metaverse will bring huge risks to people's privacy. • Intellectual Property: With the integration of the digital and real worlds, the ownership and distribution of intellectual property in the virtual world and the problem of virtual item embezzlement will challenge intellectual property management. • Economics: Economic risk includes the possibility that the contradiction between huge economic value in the virtual world and the virtual nature of this value leads to speculative behavior, or that the Metaverse is attacked, invaded, disrupted, and destroyed, damaging real-world economic and social development. • Oligopoly: Construction of the Metaverse requires a huge amount of investment to realize mass user interaction and form unified standards, and needs stable service providers, which creates potential oligopoly risk. Avoiding this risk is crucial to Metaverse development. • Governance: The most desirable relationship between virtual and human humans; whether decentralization of the digital world is realized or it merely becomes the embodiment of a group of developers' personal will; the influence of the digital world on the real world; and the division of governance across the virtual and real worlds are key problems and complex to solve. 4.3 China's attitude to the Metaverse Generally, China's attitude towards the Metaverse has been to embrace it actively but move forward cautiously. China welcomes Metaverse technology innovation and industrial cultivation, but is strict with digital currency and NFT trading. Embrace actively Source: Deloitte analysis Figure40: Potential risks Capital Manipulation There are still many uncertainties in the embryonic Metaverse, and industries and markets need to return to rationality Opinion Bubble Irrational public opinion bubbles echo irrational stock market volatility Hashrate Pressure How to ensure the stability of cloud computing, low-cost computing power resources, and many other problems, remain to be solved Economic Risk Economic risk can spill over from the virtual to the real world Ethical Constraints How to construct the ethical framework consensus of the Metaverse in a decentral- ized framework needs to be explored from multiple perspectives Monopoly Tension Competition among the giants determines the relatively closed nature of their ecology, and it is difficult to achieve complete openness and decentralization. Privacy Risk As the base resource supporting the continuous operation of the Metaverse, individuals’ data needs to be updated and expanded constantly, and the compliant collection, storage and management of data resources remains to be discussed Addicted to Risk Excessive immersion in virtual worlds can exacerbate psychological problems such as social anxiety and alienation Industry Evolution Conceptual breakthroughs have not fundamentally changed the status quo of industrial evolution Intellectual Property Multi-agent collaboration and adaptation applications across the virtual-real boundary are likely to lead to disputes over production rights
45 The Metaverse Overview : Vision, Technology, and Tactics | Metaverse tactics for enterprises The Ministry of Industrial and Information Technology (MIIT) recently mentioned the Metaverse for the first time and local governments are making plans for the Metaverse. MIIT: cultivate a group of innovative SMEs in the Metaverse and other emerging industries. The MIIT has said it will support SMEs with digital transmission, seize the opportunity to push forward new infrastructure and develop the digital economy, and cultivate innovative SMEs specializing in the digital industry and innovative SMEs in emerging industries such as the Metaverse, blockchain, and AI. Beijing Municipal Administrative Center (Beijing MC) the first mover At the Beijing MC Industry Development Promotion Conference in Tongzhou District, Beijing issued a series policies including "Metaverse- related policies" focusing on content design, industrial spaces, application scenarios, and partnership in the Metaverse. Shanghai includes Metaverse in 14th Five-Year Plan According to the 14th Five-Year Plan for Shanghai Electronic Information Manufacturing Industry, Shanghai plans to develop quantum computing, 3rd-generation semiconductors, 6G technology, the Metaverse and other industries, and create image engine and blockchain technology to meet the development needs of the Metaverse. Shanghai is encouraging application of the Metaverse to public services, business, social entertainment, industrial manufacturing, production security, and video games. Jiangsu to build Metaverse Ecological Industry Demonstration Zone Binhu District of Wuxi City launched the Metaverse Ecological Industry Development Plan of Taihu Bay Science and Technology Innovation Leading Zone, aiming to build a paragon of international innovation and a domestic Metaverse ecological industry demonstration zone. Zhejiang accelerates Metaverse development Zhejiang's Guidance on The Construction of Future Industry Pilot Zones in Zhejiang Province states that the Metaverse, alongside AI, blockchain, and 3rd-generation semiconductors, is one of the most important strategies for Zhejiang's industry pilot zone due to launch by 2023. Zhejiang will accelerate the development of an open innovation platform in brain-machine cooperation, VR, and blockchain, and boost industrial technology and integrated innovations. Wuhan writes Metaverse into government work report The government work report of the 15th People's Congress of Wuhan in Hubei Province talks about accelerating


46 The Metaverse Overview : Vision, Technology, and Tactics | Metaverse tactics for enterprises development of the digital industry and pushing the integration of the Metaverse, big data, cloud computing, blockchain, geospatial information, and quantum technology with the real economy. Hefei and Hainan bring Metaverse into future strategy Within the next five years, Hefei plans to put more effort into future industry, aiming to develop a group of pilot companies, leading-edge technologies, and high end products in areas including the Metaverse, superconducting materials, and precision medicine. In Hainan, meanwhile, the Sanya Municipal People's Government and NetEase have signed a strategic cooperation agreement in which NetEase base its Hainan headquarters in Sanya. From this new base, it will develop the NetEase Metaverse Industrial Base project to promote high-quality development of Hainan's digital culture and creative industries, and create an international digital innovation center that integrates internet technology with digital content production, copyright operations, and products. Move forward cautiously China's policies on digital currencies and digital art transactions are the main reflection of its cautious attitude towards the Metaverse China has strict supervision on digital assets. Back in 2013 and 2017, the People's Bank of China and other government departments issued notices clarifying that Bitcoin does not have the same legal status as fiat currencies and financial institutions should not use it to price products or services, or directly or indirectly provide Bitcoin-related services. The notices clarify that token issuance is essentially an unapproved, illegal public financing, with suspected illegal sales of tokens and securities, illegal fundraising, fraud, pyramid schemes, and other illicit activities. In 2021, China adopted stricter digital currency policies, with mining designated as an eliminated industry and clarification that digital currencies such as Bitcoin and Ethereum do not have the same legal rights as fiat currencies. Related financial activities and overseas digital currency exchanges providing services to residents in China have been declared illegal. In the NFT space, platforms needs to finish a very strict approval process before conducting business. This requires them to have licenses for value-added telecommunications and the dissemination of audio-visual programs via information networks, a permit for cyber culture business operations, one recordation for blockchain information services and another for artwork business record. It is difficult for enterprises to acquire all of these. Furthermore, it is difficult to operate an NFT marketplace. According to the Implementation Opinions of the General Office of the State Council on Straightening out and Rectifying Various Types of Trading Venues, standardized contract transactions cannot be conducted by centralized trading methods including call or continuous auctions, electronic matching, anonymous trading. The Opinions also prohibit acting as a market maker and other trading methods. In addition, as NFTs are considered to have financial attributes, marketplace must obtain approvals from the State Council and its financial authorities. 4.4 Metaverse tactics The Metaverse presents a huge opportunity but also major risks. Enterprises aiming to embrace the Metaverse should take the following approaches: • Active learning. The Metaverse is essentially a new technology-driven revolution in society with deep influence. To embrace this change, enterprises should understand its full scope before seeking opportunities in the Metaverse. • Gain first-mover advantage. Enterprises hoping to enter the Metaverse and provide services to companies or individuals must move fast, provide targeted solutions, and enter customers' consciousness to amplify results. The capital market, enterprises, and individuals accepted the concept of the Metaverse rapidly. Despite recent drops in market valuations of Metaverse-related companies, it gained acceptance much faster than the internet did when it emerged. This means each window of opportunity will not be open for long and first-mover advantage is key. • Treat the Metaverse as an advanced digital transformation. Businesses that want to empower themselves with Metaverse technologies and models can consider these part of their overall digital transformation and intelligent
47 The Metaverse Overview : Vision, Technology, and Tactics | Metaverse tactics for enterprises upgrading. When the concept of the Metaverse was proposed, all of the relevant technologies already existed and had varying extents of application. All of the same technologies are also required in digital transformation. The immersive experience of the Metaverse suits marketing and consumer interactions, R&D and manufacturing use digital twins and 3D simulation, and AI algorithms are already widely used. • Focus on business model innovation based on core competitiveness. Companies that want to enter the Metaverse market to develop innovative businesses should explore the Metaverse value chain to find a link in that chain that fits their existing capabilities. For example, the four layers of the NFT market have corresponding core capabilities, NFT infrastructure requires blockchain and NFT expertise, NFT production requires creative resources, NFT trading requires a platform, and NFT derivatives require industry applications. The entry points for a Metaverse business are similar to those in the NFT market, and enterprises should use their own capabilities and characteristics to choose their positioning. • Build an ecosystem. Metaverse technology is becoming increasingly precise, and demand for application scenarios is expanding. Enterprises must build ecosystems around their core competitive advantages to provide customers with integrated application scenarios and solutions. • Avoid risk. Act according to national polities, protect data and network security to prevent data breaches, and avoid speculation in the Metaverse to prevent economic risks. Conclusion The Metaverse is guided and driven by human imagination and contains a vast amount of complex content. Its application also varies from country-to-country. Enterprises should embrace the Metaverse, clarify their positioning and layout in the Metaverse, and continuously strengthen their core capabilities and ecosystem construction to maximize the benefit of this new universe. Most of all, they should look forward to exploring and discussing the Metaverse together. References 1. 于佳宁、何超《元宇宙》 2. 清华大学《元宇宙发展研究报告2.0版》https://finance.sina.com.cn/tech/2022-02-14/doc-ikyamrna0602028.shtml 3. 北京大学&安信证券《2022年元宇宙全球年度报告》https://finance.sina.com.cn/tech/2022-01-09/doc-ikyakumx9177489.shtml 4. 头豹研究院《2021年中国NFT平台研究报告》https://www.leadleo.com/report/details?id=61df87cc7cc3970455097803 5. 国海证券《元宇宙专题深度——未来的未来》https://dfscdn.dfcfw.com/download/A2_cms_f_20211124112942284944&direct=1& abc8501.pdf 6. 《中央部委首提元宇宙,多地政府超前布局》https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/q73EskbA0Jtc65c8HlKOXQ
48 The Metaverse Overview : Vision, Technology, and Tactics | Deloitte Contacts Deloitte Contacts Taylor Lam Vice Chairman/ TMT Industry Leader Deloitte China Tel: +86 10 8520 7126 Email: talam@deloitte.com.cn Hanson Wang Lead Partner, Deloitte Consulting Metaverse CoE Consulting Partner, TMT Industry Deloitte China Tel: +86 10 8534 2558 Email: Hansonwang@deloitte.com.cn Sunny Chen Consulting Consultant Deloitte China Tel: +86 21 6141 2151 Email: sunnyychen@deloitte.com.cn Mark Lian Technology Sector Leader Deloitte China Tel: +86 755 3353 8668 Email: mlian@deloitte.com.cn Eric Ma Consulting Senior Manager Deloitte China Tel: +86 10 8524 8708 Email: eircma@deloitte.com.cn
49

50 Office locations Hefei Room 1506 Tower A China Resource Building No.111 Qian Shan Road Shu Shan District Hefei 230022, PRC Tel: +86 551 6585 5927 Fax: +86 551 6585 5687 Hong Kong 35/F One Pacific Place 88 Queensway Hong Kong Tel: +852 2852 1600 Fax: +852 2541 1911 Jinan Units 2802-2804, 28/F China Overseas Plaza Office No. 6636, 2nd Ring South Road Shizhong District Jinan 250000, PRC Tel: +86 531 8973 5800 Fax: +86 531 8973 5811 Macau 19/F The Macau Square Apartment H-L 43-53A Av. do Infante D. Henrique Macau Tel: +853 2871 2998 Fax: +853 2871 3033 Nanchang Unit 08-09, 41/F Lianfa Plaza No.129 Lv Yin Road Honggutang District Nanchang 330038, PRC Tel: +86 791 8387 1177 Nanjing 40/F Nanjing One IFC 347 Jiangdong Middle Road Jianye District Nanjing 210019, PRC Tel: +86 25 5790 8880 Fax: +86 25 8691 8776 Ningbo Room 1702 Marriott Center No.168 Heyi Road Haishu District Ningbo 315000, PRC Tel: +86 574 8768 3928 Fax: +86 574 8707 4131 Sanya Floor 16, Lanhaihuating Plaza (Sanya Huaxia Insurance Center) No. 279, Xinfeng street Jiyang District Sanya 572099, PRC Tel: +86 898 8861 5558 Fax: +86 898 8861 0723 Shanghai 30/F Bund Center 222 Yan An Road East Shanghai 200002, PRC Tel: +86 21 6141 8888 Fax: +86 21 6335 0003 Shenyang Unit 3605-3606, Forum 66 Office Tower 1 No. 1-1 Qingnian Avenue Shenhe District Shenyang 110063, PRC Tel: +86 24 6785 4068 Fax: +86 24 6785 4067 Shenzhen 9/F China Resources Building 5001 Shennan Road East Shenzhen 518010, PRC Tel: +86 755 8246 3255 Fax: +86 755 8246 3186 Suzhou 24/F Office Tower A, Building 58 Suzhou Center 58 Su Xiu Road, Industrial Park Suzhou 215021, PRC Tel: +86 512 6289 1238 Fax: +86 512 6762 3338 / 3318 Tianjin 45/F Metropolitan Tower 183 Nanjing Road Heping District Tianjin 300051, PRC Tel: +86 22 2320 6688 Fax: +86 22 8312 6099 Wuhan Unit 1, 49/F New World International Trade Tower 568 Jianshe Avenue Wuhan 430000, PRC Tel: +86 27 8538 2222 Fax: +86 27 8526 7032 Xiamen Unit E, 26/F International Plaza 8 Lujiang Road, Siming District Xiamen 361001, PRC Tel: +86 592 2107 298 Fax: +86 592 2107 259 Xi'an Room 5104A, 51F Block A Greenland Center 9 Jinye Road, High-tech Zone Xi'an 710065, PRC Tel: +86 29 8114 0201 Fax: +86 29 8114 0205 Zhengzhou Unit 5A10, Block 8, Kineer Center No.51 Jinshui East Road Zhengdong New District Zhengzhou 450018, PRC Tel: +86 371 8897 3700 Fax: +86 371 8897 3710 Beijing 12/F China Life Financial Center No. 23 Zhenzhi Road Chaoyang District Beijing 100026, PRC Tel: +86 10 8520 7788 Fax: +86 10 6508 8781 Changsha 20/F Tower 3, HC International Plaza No. 109 Furong Road North Kaifu District Changsha 410008, PRC Tel: +86 731 8522 8790 Fax: +86 731 8522 8230 Chengdu 17/F China Overseas International Center Block F No.365 Jiaozi Avenue Chengdu 610041, PRC Tel: +86 28 6789 8188 Fax: +86 28 6317 3500 Chongqing 43/F World Financial Center 188 Minzu Road Yuzhong District Chongqing 400010, PRC Tel: +86 23 8823 1888 Fax: +86 23 8857 0978 Dalian 15/F Shenmao Building 147 Zhongshan Road Dalian 116011, PRC Tel: +86 411 8371 2888 Fax: +86 411 8360 3297 Guangzhou 26/F Yuexiu Financial Tower 28 Pearl River East Road Guangzhou 510623, PRC Tel: +86 20 8396 9228 Fax: +86 20 3888 0121 Hangzhou Room 1206 East Building, Central Plaza No.9 Feiyunjiang Road Shangcheng District Hangzhou 310008, PRC Tel: +86 571 8972 7688 Fax: +86 571 8779 7915 Harbin Room 1618 Development Zone Mansion 368 Changjiang Road Nangang District Harbin 150090, PRC Tel: +86 451 8586 0060 Fax: +86 451 8586 0056
51 The Metaverse Overview : Vision, Technology, and Tactics | Preface
About Deloitte Deloitte refers to one or more of Deloitte Touche Tohmatsu Limited (“DTTL”), its global network of member firms, and their related entities (collectively, the “Deloitte organization”). DTTL (also referred to as “Deloitte Global”) and each of its member firms and related entities are legally separate and independent entities, which cannot obligate or bind each other in respect of third parties. DTTL and each DTTL member firm and related entity is liable only for its own acts and omissions, and not those of each other. DTTL does not provide services to clients. Please see www.deloitte.com/about to learn more. Deloitte is a leading global provider of audit and assurance, consulting, financial advisory, risk advisory, tax and related services. Our global network of member firms and related entities in more than 150 countries and territories (collectively, the “Deloitte organization”) serves four out of five Fortune Global 500® companies. Learn how Deloitte’s approximately 345,000 people make an impact that matters at www.deloitte.com. Deloitte Asia Pacific Limited is a company limited by guarantee and a member firm of DTTL. Members of Deloitte Asia Pacific Limited and their related entities, each of which are separate and independent legal entities, provide services from more than 100 cities across the region, including Auckland, Bangkok, Beijing, Hanoi, Hong Kong, Jakarta, Kuala Lumpur, Manila, Melbourne, Osaka, Seoul, Shanghai, Singapore, Sydney, Taipei and Tokyo. The Deloitte brand entered the China market in 1917 with the opening of an office in Shanghai. Today, Deloitte China delivers a comprehensive range of audit & assurance, consulting, financial advisory, risk advisory and tax services to local, multinational and growth enterprise clients in China. Deloitte China has also made—and continues to make—substantial contributions to the development of China's accounting standards, taxation system and professional expertise. Deloitte China is a locally incorporated professional services organization, owned by its partners in China. To learn more about how Deloitte makes an Impact that Matters in China, please connect with our social media platforms at www2.deloitte.com/cn/en/social-media. This communication contains general information only, and none of Deloitte Touche Tohmatsu Limited (“DTTL”), its global network of member firms or their related entities (collectively, the “Deloitte organization”) is, by means of this communication, rendering professional advice or services. Before making any decision or taking any action that may affect your finances or your business, you should consult a qualified professional adviser. No representations, warranties or undertakings (express or implied) are given as to the accuracy or completeness of the information in this communication, and none of DTTL, its member firms, related entities, employees or agents shall be liable or responsible for any loss or damage whatsoever arising directly or indirectly in connection with any person relying on this communication. DTTL and each of its member firms, and their related entities, are legally separate and independent entities. © 2022. For information, please contact Deloitte China. Designed by CoRe Creative Services. RITM1023439



