General Motors Sustainability Report
2021 Sustainability Report ev erybody in.
Our vision of a world with zero crashes, zero emissions and zero congestion requires an everybody in approach. That’s why we’re accelerating our all-electric future and extending our technologies beyond our vehicles to meet the world’s growing demand for more zero-emissions solutions. Today, the GM team is working with an unprecedented sense of urgency, decisiveness, agility and breadth to take everyone on a journey to a more equitable, safe and all-electric future. On the Cover 2023 Cadillac LYRIQ Debut Edition available Summer 2022, by reservation only. Additional LYRIQ models available starting Fall 2022. See dealer for details. Vehicle not available for sale. Skip Navigation Introduction Reducing Emissions Design for Environment Technology Customers Safety Diverse Workforce Human Rights Supply Chain Communities Governance 2021 SUSTAINABILITY REPORT 1
About This Report General Motors is committed to publicly reporting on sustainability-related topics on an annual basis, discussing the opportunities and challenges that we encounter as we work to enhance performance and conduct business in the most responsible manner possible. This report has been prepared according to Global Reporting Initiative (GRI) Standards: Comprehensive Option and includes responses to the Sustainability Accounting Standards Board (SASB) framework—Transportation Standards and the Financial Stability Board Task Force on Climate-related Financial Disclosures (TCFD). Responses to sustainability-related frameworks and standards as well as assurance statements can be found in the 2021 Sustainability Supplement, which is available for download on gmsustainability.com. This report covers certain sustainability metrics and data for GM as of and during the year ended December 31, 2021, as applicable, unless otherwise stated. In instances where select information is provided from an earlier period or early 2022, that is noted in the report. The report is limited to automotive operations wholly owned and/or operated by GM. Unless otherwise stated, GM Financial, our financing services provider, and Cruise, our autonomous vehicle subsidiary, are not included in the report. In some instances, data has been included for operations in which GM’s interest is through joint ventures, including our automotive China joint ventures. In these instances, the inclusion of that data is noted. Dollar amounts presented within this report are stated in U.S. dollars. This report was published on April 28, 2022. We annually contract an independent third-party verification of a selection of greenhouse gas (GHG) and certain sustainability data assertions for our global operations. The verification statements and applicable data assertions can be found in the 2021 Sustainability Supplement. This report provides an overview of some of GM’s long-term goals and aspirations, and efforts in support of those goals and aspirations. Some material is derived from other company documents, and links are provided to those documents where appropriate. With respect to goals, commitments and aspirational or otherwise forward-looking statements in this report, actual results may differ, possibly materially. The report also includes certain numbers that are estimates or approximations and that may be based on assumptions. We believe that the estimates employed are appropriate and reasonable; however, due to inherent uncertainties in making estimates and assumptions, actual results could differ from the original estimates. Additional information with respect to forward-looking statements can be found on page 120 . Solely for convenience, trademarks and tradenames referred to in this report may appear without the ® or ™ symbols, but such references are not intended to indicate, in any way, that we will not assert, to the fullest extent under applicable law, our rights or the right of the applicable licensor to these trademarks and tradenames. Products Disclosure In this report, depicted vehicles and features may be simulated or preproduction and are subject to change. Additionally, certain products are not currently available or are subject to limited availability. For vehicle availability and feature use and limitations, including details relating to advanced safety and driver assistance features, consult the vehicle’s Owner’s Manual and brand’s website. IN THIS REPORT Introduction 1 Reducing Carbon Emissions 14 Designing for the Environment 31 Advancing Transformative Technologies 40 Earning Customers for Life 47 Keeping People Safe 52 Developing Talented & Diverse People 63 Upholding Human Rights 77 Supporting Supplier Responsibility 81 Building More Inclusive Communities 98 Ensuring Responsible Governance 104 Skip Navigation Introduction Reducing Emissions Design for Environment Technology Customers Safety Diverse Workforce Human Rights Supply Chain Communities Governance 2021 SUSTAINABILITY REPORT 2
MARY BARRA Leadership Message Earlier this year, I took a driverless ride through San Francisco in a fully electric Cruise autonomous vehicle (AV). It was one of the most inspiring moments of my career, and it reinforced my belief that our opportunity to change the world has never been clearer or closer. During a challenging 2021, a resilient and focused GM team continued to make significant progress toward our vision of a world with zero crashes, zero emissions and zero congestion. Our culture of innovation, which begins with our employees, is unlocking once-in-a-lifetime opportunities to create a better and safer future for all. We delivered to customers the GMC HUMMER EV supertruck and BrightDrop Zevo 600 van, the first-ever electric vehicles (EVs) featuring our Ultium platform, and we have since announced the Chevrolet Silverado EV and Chevrolet Equinox crossover EV—with many more to follow. Production of the sold-out Debut Edition of the Cadillac LYRIQ SUV is underway in Tennessee, and next month we will begin accepting orders for the next editions. Cruise is now at the cusp of commercializing accessible and zero-emissions ride-hailing services. Our transition to EVs and AVs is at the heart of our technology- and software-driven growth strategy. We will continue to increase our investments in these vehicles and new services as we progress toward decarbonizing our business. In fact, we are accelerating our work this year to meet increasing demand for our EVs. We are expanding our global EV manufacturing capacity to over 2 million vehicles by the end of 2025. Half of that will be in North America, where we have set a target to produce 400,000 EVs over the next 24 months—with the ultimate goal of becoming the EV market leader. Our commitments and investments reflect our sense of urgency to get everybody in an EV, and transform our vision into a reality. It’s also imperative that this future be inclusive, including our diverse Board, our workforce and our business partners. Industry-leading innovations like Ultium and Cruise are possible because of a culture at GM that encourages and values diverse ideas and perspectives. As part of our aspiration to be the world’s most inclusive company, we have also launched an internal Inclusivity Index to measure our progress, and we use the results to inform future actions. The brighter and more inclusive future we envision also extends to the communities where we live, work and play. Last year, to meet unique community needs, we provided more than $85 million in cash and in-kind donations to hundreds of local nonprofit partners, with a focus on education, skills and literacy training, climate equity programs and road safety. I am excited about the progress we are making toward reimagining how our customers and communities will move through the world, just as we did more than a century ago. I invite you to learn more in this report, and see why I am so optimistic about the road ahead. Mary T. Barra Chair and CEO I am excited about the progress we are making toward reimagining how our customers and communities will move through the world, just as we did more than a century ago.” Skip Navigation Introduction Reducing Emissions Design for Environment Technology Customers Safety Diverse Workforce Human Rights Supply Chain Communities Governance 2021 SUSTAINABILITY REPORT 3
Powering Growth With Purpose We pioneer the innovations that move and connect people to what matters General Motors is in the midst of a transformation that includes our accelerated transition to EVs and AVs. We are rethinking how and, in many cases, where we work. We are taking bold actions to make our business carbon neutral, and we are broadening our social impact by aiming to help create a zero-emissions future that is both inclusive and equitable. We are also laser-focused on our aspiration to become the most inclusive company in the world. For these reasons, the timing felt right to revisit the question of why we exist and to crystallize and articulate our Purpose. After extensive work by the Board, our Senior Leadership Team and a diverse, cross-functional global team of colleagues, we recently introduced our Purpose statement to our full team. For each and every one of us at General Motors, it’s the answer to why we exist: We pioneer the innovations that move and connect people to what matters. It’s a simple but powerful statement that honors our heritage of innovation, captures who we are today when we’re at our best and looks ahead. By defining our Purpose, it’s much easier to keep it front and center. Behaviors Our eight GM behaviors are the foundation of our culture and how we think and act in service of our Purpose. BE INCLUSIVE I create moments every day that value backgrounds, opinions and ideas that may be different than my own. THINK CUSTOMER I consider the customers’ needs in everything I do. INNOVATE NOW I see things not as they are but as they could be. LOOK AHEAD I make decisions now with the long-term view in mind, and I anticipate what lies ahead. ONE TEAM I collaborate cross-functionally to achieve enterprisewide results. BE BOLD I respectfully speak up, exchange feedback and boldly share ideas without fear. IT’S ON ME I take accountability for safety and my own actions, behaviors and results. WIN WITH INTEGRITY I have a relentless desire to win and do it with integrity. Skip Navigation Introduction Reducing Emissions Design for Environment Technology Customers Safety Diverse Workforce Human Rights Supply Chain Communities Governance
How GM Creates Value The needs of our customers are at the forefront of every decision we make. Today, we’re working to leverage our core business strengths to find new market opportunities that solve challenges for both individual customers and society at large. For example, we leveraged our Ultium battery platform to launch BrightDrop, which is focused on developing and commercializing smarter ways to deliver goods and services. And, Cruise is developing autonomous robo-taxis that we believe will reduce congestion in cities and improve safety. Our Vision ZERO crashes, ZERO emissions and ZERO congestion Our Growth Strategy This diagram shows an illustrative overview of some of GM’s performance indicators and is not meant to be inclusive of all key performance indicators (KPIs); rather, it is an example of how GM creates value for our stakeholders. Details on KPIs can be found in each of the corresponding sections. PRODUCT LEADERSHIP DRIVE EV/AV MONETIZE EXISTING & NEW BUSINESS DOMINANCE TRUCK & SUV ENTERPRISE LEVERAGE SCALE WORKPLACE OF CHOICE IMPACT SOCIAL SEGMENTS & SERVICES LAUNCH NEW PLATFORMS ADVANCE CUSTOMER EXPERIENCE REIMAGINE THE Deliver world-class customer interactions LEAD IN WORLD-CLASS DIGITAL CAPABILITY Inputs: GM Capital HUMAN CAPITAL • ~146,000 employees • 11 employee resource groups (ERGs) • 6 Global Diversity, Equity and Inclusion (DEI) Councils • 18,940 approximate global supplier count FINANCIAL CAPITAL • $128B automotive assets • $36.8B automotive liquidity • $7. 4B capital expenditures • $76B approximate supply chain spend INFRASTRUCTURE CAPITAL • 100+ facilities • 12,340 dealerships INTELLECTUAL CAPITAL • $ 7.9B R&D spend (inclusive of GM Financial and Cruise) • GM Global Innovation Team SOCIAL AND RELATIONSHIP CAPITAL • $50M Climate Equity Fund • $22M committed through the Justice and Inclusion Fund • $87M in cash and in-kind donations NATURAL CAPITAL • 25,304 ML water withdrawn • ~329,000 materials and services purchased • 45.2 GJ energy used Outputs: Value Created HUMAN CAPITAL: Our Employees • 2.9M+ training hours • 10,229 global salary promotions • Announced $7B investment in four Michigan manufacturing sites, expected to create 4,000 new jobs and retain 1,000 jobs FINANCIAL CAPITAL: Our Shareholders • $114B automotive net sales and revenue • $10B net income (inclusive of GM Financial and Cruise) • $ 9.7B net automotive cash provided by operating activities INFRASTRUCTURE CAPITAL: Our Customers • 6 .3M vehicles sold • 5 0 vehicle models with one or more Advanced Driver Assistance Systems (ADAS) • Increased EV charging infrastructure INTELLECTUAL CAPITAL: Our Customers • N ew solutions and services such as OnStar Guardian, BrightDrop, Ultifi, and Ultium batteries • S afety technologies SOCIAL AND RELATIONSHIP CAPITAL: Our Communities • 19 nonprofits received Climate Equity Fund grants • ~$ 6B North America Tier I and Tier II diverse supplier spend (including media) • $ 46M in grantmaking to support a portfolio of 364 U.S.-based nonprofit projects NATURAL CAPITAL: Our Planet • 1 .2M metric tons waste diverted from landfills and incinerators • 1 46,832 MWh renewable energy for electricity generated at our facilities (includes electricity generated from landfill gas sold to the grid for Orion and excludes on-site PPAs) • 4 .54 m3/vehicle water intensity reduction at our facilities • 3 1 Certified Wildlife Habitats Skip Navigation Introduction Reducing Emissions Design for Environment Technology Customers Safety Diverse Workforce Human Rights Supply Chain Communities Governance 2021 SUSTAINABILITY REPORT 5
2021 Sustainability Highlights 2040 Carbon neutral goal by 2040 and Science Based Target initiative (SBTi) approved targets for operations and products 1M+ Planned units of EV capacity in each of North America and China by 2025 $35B+ Planned investment from 2020 to 2025 in EVs and AVs 2035 Announced plan to eliminate tailpipe emissions from all new light-duty vehicles by 2035 $7B Announced investment in four Michigan manufacturing sites for a significant expansion of battery cell and EV assembly capacity in the United States 50% Manufacturing footprint in North America and China to be capable of EV production by 2030 100% Plan to source 100% renewable electricity at sites in the United States by 2025 and globally by 2035 $750M Planned investment of nearly $750 million through 2025 to expand access to EV charging in the United States and Canada $50M In early 2022, we doubled our Climate Equity Fund pledge to help ensure the people and communities most affected by climate change are not left behind Zevo 600 Delivered first all-electric delivery vans, with the Zevo 600 being the fastest vehicle to market in GM history 5K Expected to create 4,000 new jobs and retain 1,000 jobs in four Michigan manufacturing sites 3 Deployed three strategic pillars—DEI Maturity, Transparency and Talent Innovation—to drive DEI integration throughout the enterprise EEO-1 Published consolidated EEO-1 data for the first time 100K+ Ultium Charge 360 enables access, using GM mobile apps 1 , to more than 100,000 charging plugs throughout the United States and Canada 1 A vailable on select Apple and Android devices. Service availability, features and functionality vary by vehicle, device and the plan you are enrolled in. User terms apply. 2021 Recognitions Placed on the Bloomberg Gender Equality Index (GEI) 4th year in a row Diversity Inc Top 50 Companies for Diversity 6 years in a row 5th year for the World Index and 7th consecutive year as the only automaker on the North American index and a first-in-our-industry Gold Award Ranked 2nd among top U.S. auto companies in 2022 CDP Climate and Water Security A List 3rd year in a row 2022 World’s Most Ethical Companies ® 3rd year in a row and the only automotive original equipment manufacturer to be recognized on the list Skip Navigation Introduction Reducing Emissions Design for Environment Technology Customers Safety Diverse Workforce Human Rights Supply Chain Communities Governance 2021 SUSTAINABILITY REPORT 6
Our Climate Action Framework for an Equitable Transition Our future is electric and includes everyone. Climate change affects different communities in different ways. As we move toward a carbon neutral future, we must lead positive change and implement inclusive solutions that address everyone’s unique needs, especially those of the communities where we live and work. In 2021, we put forth a Climate Action Framework to help guide our actions as our industry and company undergo a fundamental shift in mobility. Building on our philanthropic commitment to equitable climate action, GM has announced that we will provide an additional $25 million through our Climate Equity Fund, dedicating a total of $50 million to help close equity gaps in the transition to EVs and other sustainable technologies. To date, grants have been made to 19 nonprofit organizations that are helping to implement inclusive solutions for a zero-emissions, carbon neutral future. Read more about GM’s impact through the Climate Equity Fund on page 101 . FOCUS AREAS Future of Work Current and future employees will have a role to play in GM’s transition to an EV portfolio, and we will invest in necessary training and reskilling to make that transition. EV Access Achieve through a wide range of EVs across most segments and price points. Infrastructure Equity Committing to accessible charging solutions that can help meet customers where they are and understanding the need to help address charging deserts and other scenarios that can hinder EV ownership. Climate Equity Funding organizations that are helping to close the climate equity gap at the community level. PRINCIPLES • Help make mobility safe, accessible and environmentally friendly for all. • Incorporate and normalize equity considerations across our business operations and program implementation efforts, including workforce strategy, sustainability efforts, and products and services. • Work with community-based stakeholders to identify their unique needs, assets and priorities as well as collaboratively assist impacted communities. • Advocate for inclusive and equitable climate change action, renewable energy and transportation-related policies at the federal, state and local levels. • Help support organizations that are providing equitable access to a more sustainable future. Skip Navigation Introduction Reducing Emissions Design for Environment Technology Customers Safety Diverse Workforce Human Rights Supply Chain Communities Governance 2021 SUSTAINABILITY REPORT 7
Sustainability Strategy GM’s sustainability strategy is led at the enterprise level to ensure a holistic approach across the company. Sustainability is overseen by the Board. GM’s sustainability strategy is led by senior leaders throughout the organization. Our chief sustainability officer is the enterprisewide leader of sustainability and directs initiatives through the Office of Sustainability. The Office of Sustainability has been strategically designed to ensure accountability for key sustainability targets and initiatives at the highest levels of the company; nurture a culture of sustainability across the organization; track and measure progress through transparent disclosure; and engage with both internal and external stakeholders on relevant matters. The Office of Sustainability leaders are charged with innovating and advocating as well as supporting social responsibility and transparent corporate practices. Our Sustainability Office uses a “team of teams” approach to help ensure that functional areas across the enterprise have accountability for their respective functions’ role in accelerating the company’s vision. Within each functional area, a single leader represents sustainability objectives and priorities, and owns sustainability goals and metrics. The teams focus on environmental and social aspects of sustainability. For example, a representative from engineering who sources cobalt for battery development works with the representative from supply chain to help ensure cobalt is sourced through strategic partnerships in an ethical manner that respects human rights. Sustainability Priority Assessment We prioritize sustainability topics by engaging with our stakeholders to understand those topics most relevant to them and our business, and those that offer the greatest opportunity to create meaningful shared value. This process is formally conducted through an assessment, and we performed our most recent assessment in 2021. We plan to conduct similar assessments every two to three years so that it takes into account emerging sustainability issues, macro events and current dynamics in the world around us. We performed our assessment in collaboration with a third party who guided us through a four-part process aligned with the GRI materiality principle for sustainability reporting. Identify a list of sustainability topics relevant to GM and the automotive industry. Understand stakeholder perspectives and priorities through an internal survey of more than 100 GM employees as well as 40 interviews with internal and external stakeholders. Score the topics based on quantitative and qualitative inputs. Prioritize the topics through the development of a tiered matrix as shown on the next page. Skip Navigation Introduction Reducing Emissions Design for Environment Technology Customers Safety Diverse Workforce Human Rights Supply Chain Communities Governance 2021 SUSTAINABILITY REPORT 8
SUSTAINABILITY STRATEGY CONT. The placement of priorities within three categories reflects a number of different stakeholder perspectives. The assessment identified six topics as highest priority and therefore urgent for the company to manage. Some topics were not deemed as urgent because stakeholders and management view them as a GM strength today. As an example, we have been working on operational waste, water and energy since 2010 and have robust management systems with a track record of performance in these areas. Still other priorities, such as autonomous technology and the associated ethics around it, are seen more as emerging issues that are likely to grow in importance over time. Through both the qualitative and quantitative inputs, several stakeholder themes emerged: • The safety of employees and vehicles remains a top priority and strength for GM as our business model shifts. • A changing and inclusive employee landscape calls for GM to focus on an equitable transition to an all-electric future that brings along all employees and customers around the world. • There is high ambition at GM. Both internal and external stakeholders are very supportive of the company’s vision of a world with zero crashes, zero emissions and zero congestion. • There is an imperative for standardizing the EV ecosystem, underscoring the intersection of such priorities as Product GHG Emissions and EV Infrastructure. • Responsible innovation should occur across the value chain as new advanced technologies create new business opportunities. Sustainability Priority Matrix Topics are listed in alphabetical order within each priority category and do not represent specific ranking within the category. Priority Biodiversity & Ecosystem Health Community Development Freedom of Association & Expression Operational GHG Emissions & Efficiency STEM Education Supplier Diversity Supply Chain Environmental Impacts Supply Chain Labor Conditions Sustainability-Related Compensation & Incentives Tax Payments Waste Management Water Management High Priority Autonomous Technology & Ethics Circular Economy Cybersecurity Employee Health & Well-Being Employee Recruitment, Engagement & Development Human Rights Occupational Health & Safety Responsible Use of Data Socially Responsible Innovation Highest Priority Business Ethics Climate Risk & Resilience Diversity, Equity & Inclusion EV Infrastructure Product GHG Emissions Vehicle Safety Supply Chain People Environment Products Governance Skip Navigation Introduction Reducing Emissions Design for Environment Technology Customers Safety Diverse Workforce Human Rights Supply Chain Communities Governance 2021 SUSTAINABILITY REPORT 9
KRISTEN SIEMEN A conversation with our Chief Sustainability Officer As climate transition strategies continue to make headlines, the focus on social issues is also on the rise. How is GM working to address an equitable transition? We know that, across the globe, no two communities are impacted by climate change in the same way. Last year, we announced our Equitable Climate Action initiative to ensure that our transition to an all-electric, carbon neutral future is an inclusive one for our current and future workforce, customers and communities that may be more likely to disproportionately experience the effects of climate change. This initiative is rooted in four key areas: the future of work, EV access, infrastructure equity and climate equity. It’s a fact that the realities of climate change aren’t the same in every community—and that means the solutions can’t be the same either. As we move to a carbon neutral future, it is on us to lead positive change and implement inclusive solutions that bring everyone along. What have been your priorities in your first year as CSO? Where do you intend to focus your efforts? In my first year as CSO, my priority has been to ensure our sustainability strategy connects to our overall corporate vision. Our commitment to a vision of a world with zero crashes, zero emissions and zero congestion positions us to become a leader in the industry. As we implement our growth strategy, we have an opportunity—and an obligation—to create a better future for everyone. The pursuit of a safe and sustainable world is a passionate movement within GM; one that’s gaining momentum as our technologies reveal their increasingly profound potential. As a leader, an engineer and a mom, I am here to help break down barriers and advance our plans toward creating a world with zero emissions for generations to come. What are the most critical challenges we are facing as an industry as we transition to all-electric vehicles, and how are we working toward achieving our carbon neutral ambition? Announcing our vision of a world with zero crashes, zero emissions and zero congestion has led to important business growth and innovation—primarily in our AVs and EVs. We have put in place a cohesive strategy and set science-based targets aligned with the Paris Agreement. Our goals include a plan to introduce more than 30 EV models globally by 2025, become carbon neutral in our global products and operations by 2040 and source 100% renewable electricity at sites in the United States by 2025 and globally by 2035. One of the most critical challenges we face is that we cannot reach the future we envision alone—we must continue to pursue opportunities for collaboration with stakeholders across the globe, including suppliers, dealers, policymakers, climate thought leaders and others. A shift this massive requires everybody in, working together toward a single goal—an inclusive, all-electric future. Because talent and recruitment have never been more important, how is GM fostering a culture of inclusion and integrating sustainability across the enterprise? When our CEO, Mary Barra, announced our ambition to be the most inclusive company in the world, it was intended to reflect our approach to shaping our own workplace culture, as well as how we want to impact the world on the journey to a more sustainable future. Our path to innovation starts and ends with our employees, who are fundamental to the vibrancy and success of our company. That is why we have established employee development programs that address both individual and business needs, as well as effective recruitment programs that reach out to diverse populations. In addition, we are continuing to evolve our hiring and employee engagement practices to attract, engage and develop critical skills and best-in-class talent with diverse backgrounds and experiences. “Everybody in” is the rallying cry of GM’s transition to an all-electric future. GM wants to put everyone in an EV, and our aspiration to be the most inclusive company in the world will accelerate that mission. Skip Navigation Introduction Reducing Emissions Design for Environment Technology Customers Safety Diverse Workforce Human Rights Supply Chain Communities Governance 2021 SUSTAINABILITY REPORT 10
Our Priorities Our topic areas reflect the priorities identified through our Sustainability Priority Assessment. The table shows the alignment between our priorities and our topic areas and provides a summary of our strategies and actions that are enabling us to work toward a more sustainable world. TOPIC AREA PRIORITIES STRATEGY & ACTIONS REDUCING CARBON EMISSIONS Product GHG Emissions Operational GHG Emissions & Efficiency Climate Risk & Resilience Advance our all-electric future by: • Planning to reach more than 1 million units of EV capacity in each of North America and China by 2025. • Planning to eliminate tailpipe emissions from new light-duty vehicles by 2035. • Investing more than $35 billion from 2020 to 2025 in EVs and AVs. • Building four battery cell manufacturing facilities through Ultium Cells LLC (an equally owned joint venture with LG Energy Solution) by mid-decade. • Planning to source 100% renewable electricity at sites in the United States by 2025 and globally by 2035. • Aiming to reduce operational energy intensity by 35% by 2035 against a 2010 baseline. • Committing to SBTi approved targets that include reducing absolute Scope 1 and 2 GHG emissions 72% by 2035 from a 2018 base year and Scope 3 GHG emissions from use of sold products of light-duty vehicles 51% per vehicle kilometer by 2035 from a 2018 base year. DESIGNING FOR THE ENVIRONMENT Circular Economy Waste Management Biodiversity & Ecosystem Health Water Management Pursue circular design in our products and Zero Waste in our operations by: • Aiming to reduce the carbon emission footprint of sourced materials in new GM vehicles by 2030. • Aiming to achieve over 90% waste diversion from landfills and incineration globally by 2025, with 86.4% achieved in 2021. • Partnering with strategic organizations on biodiversity and ecosystem health. • Aiming to reduce operational water intensity by 35% by 2035 against a 2010 baseline. ADVANCING TRANSFORMATIVE TECHNOLOGIES Socially Responsible Innovation EV Infrastructure Autonomous Technology & Ethics Pursue our path to EV leadership by: • Developing urban, last-mile delivery solutions through BrightDrop that help reduce carbon emissions and urban congestion. • Leading in the development and commercialization of AV technology with Cruise. • Increasing software-enabled services and subscriptions, including Ultifi and OnStar, to enhance the user experience for our customers. • Leveraging our HYDROTEC fuel cell platform to transform a variety of transportation modes, such as ships and planes, into all-electric products. • Taking our advanced driver assistance system Super Cruise to the next level by unveiling Ultra Cruise. Skip Navigation Introduction Reducing Emissions Design for Environment Technology Customers Safety Diverse Workforce Human Rights Supply Chain Communities Governance 2021 SUSTAINABILITY REPORT 11
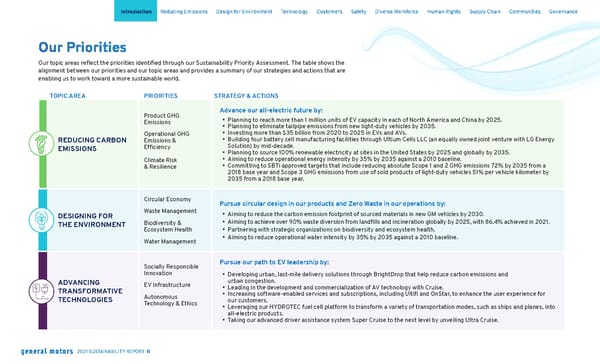
OUR PRIORITIES CONT. TOPIC AREA PRIORITIES STRATEGY & ACTIONS KEEPING PEOPLE SAFE Vehicle Safety Occupational Health & Safety Personal Safety Approach safety holistically by: • Creating a culture of safety through governance mechanisms and strategies that “Live values that return people home safely. Every Person. Every Site. Every Day.” • Applying safety advocacy, research and technology to focus on the safety of drivers, passengers and those outside the vehicle through our safety brand, Periscope. • Working with world-class research institutes to study how current safety technologies are making a real-world difference on the path to zero crashes. • Deploying various advanced driving technologies, such as forward collision alert, as standard equipment on select models across our product portfolio. • Providing our customers with OnStar safety services, in and beyond the vehicle, keeping them connected to 24/7 emergency support from specially-trained OnStar Advisors. DEVELOPING TALENTED & DIVERSE PEOPLE Diversity, Equity & Inclusion Employee Engagement, Retention & Development Freedom of Association & Expression Employee Health & Well-Being Advance our aspiration to be the most inclusive company in the world by: • Enhancing talent recruiting practices to attract a more diverse pool of candidates through programs that create new entry pathways into our workforce. • Building a positive work environment by creating a place where employees feel inspired to do their best work and feel valued for doing it. • Providing professional training and development opportunities for all employees at all levels to optimize their full potential. • Offering competitive benefits and promoting work-life balance by adopting new philosophies such as “Work Appropriately” to accommodate on-site, remote and hybrid work options. • Improving DEI through recommendations from our Inclusion Advisory Board of internal and external leaders, led by Chair and CEO Mary Barra. • Improving DEI maturity throughout our global business by leveraging ERGs, nearly all of which have executive-led advisory councils to help them advance and address issues and opportunities. • Supporting freedom of association and expression by working with 28 unions globally that represent 99% of our represented workforce and 61% of our total global workforce. UPHOLDING HUMAN RIGHTS Human Rights Respecting rights of all people within our value chain by: • Creating a strengthened Human Rights Policy , which was approved by the Board in 2021. • Utilizing the Cobalt Reporting Template, Mica Reporting Template and Conflict Minerals Reporting Template with our in-scope suppliers to support conflict mineral supply chain due diligence. Skip Navigation Introduction Reducing Emissions Design for Environment Technology Customers Safety Diverse Workforce Human Rights Supply Chain Communities Governance 2021 SUSTAINABILITY REPORT 12
OUR PRIORITIES CONT. TOPIC AREA PRIORITIES STRATEGY & ACTIONS SUPPORTING SUPPLIER RESPONSIBILITY Supply Chain Environmental Impacts Supply Chain Labor Conditions Supplier Diversity Build strong, transparent and trusted relationships with our suppliers in pursuit of an inclusive, zero-emissions future by: • Assisting suppliers in sourcing renewable energy for electricity through the GM Supplier Renewable Energy Solutions program. • Publishing the GM Sustainability Partner Guide and Framework for our Tier I suppliers to communicate our supply chain goals, priorities and processes. • Collaborating inside and outside the automotive industry to build sustainable and socially responsible supply chains by participating in programs such as Responsible Business Alliance, Responsible Minerals Initiative, Initiative for Responsible Mining Assurance and Global Platform for Sustainable Natural Rubber. • Spending of approximately $3.8 billion in 2021 with North America diverse Tier I suppliers for direct materials. • Inviting our Tier I suppliers to sign our Environmental, Social and Governance (ESG) Partnership Pledge. BUILDING MORE INCLUSIVE COMMUNITIES Community Development STEM Education Climate Risk & Resilience Create inclusive and sustainable solutions within the communities we live and work by: • Putting forth a Climate Action Framework for an equitable transition to help guide our actions as our industry and company undergo a fundamental shift in mobility. • Committing $50 million to a Climate Equity Fund to lead positive change and implement inclusive solutions that bring along everyone in the transition to an all-electric future. • Providing philanthropic support that helps develop community opportunities, support science, technology, engineering and mathematics (STEM) education and improve vehicle and road safety. • Promoting progress in our hometown of Detroit through a $50 million commitment to support nonprofits, education, employment and neighborhood revitalization efforts. ENSURING RESPONSIBLE GOVERNANCE Sustainability-Related Compensation & Incentives Business Ethics Ensure full transparency and ethical integrity throughout all operations by: • Enhanced Board oversight of ESG risk. • Integrating sustainability principles throughout the company’s business strategy, including management of climate change risk. • Incorporating robust cybersecurity and privacy protection policies and procedures as critical enablers of our digital transformation. • Creating and maintaining an ethical culture across all levels of our global workforce. • Adopting EV performance measures (including EV volume, launch timing and launch quality) for our long-term incentive plan to further align our executive compensation programs with our all-electric future and placing additional focus on GM’s growth and ESG performance. Skip Navigation Introduction Reducing Emissions Design for Environment Technology Customers Safety Diverse Workforce Human Rights Supply Chain Communities Governance 2021 SUSTAINABILITY REPORT 13
Reducing Carbon Emissions IN THIS SECTION The Journey to Zero Emissions 15 Accelerating an Inclusive All-Electric Future 16 Leveraging the Ultium Platform 17 Creating a Superior EV Ownership Experience 18 A Purpose-Built EV Portfolio 19 Growing the EV Market & Charging Infrastructure 21 Transforming a World-Class Manufacturing Footprint 22 Factory ZERO: How Our Future Looks 23 Reducing Emissions From ICE Vehicles 24 Conserving Energy in Our Facilities 25 Accelerating an All-Renewable Future 27 Our Strengths y Providing the talent, manufacturing scale, customer insights, as well as battery and software technology necessary to lead in an all-electric future y Changing consumer perceptions of what electric vehicles (EVs) can be by offering products across a range of price points and segments, from small crossovers to sport utility vehicles and trucks y Using our scale to help accelerate the renewable energy industry Our Opportunities y Helping consumers better understand, accept and adopt EVs as their choice for personal mobility y Achieving price and range parity between EVs and internal combustion engine (ICE) vehicles y Continuing to establish collaborative and coordinated public-private partnerships to help accelerate the buildout of charging infrastructure y Securing complementary national government policies to support charging infrastructure, renewable energy investments and EV adoption Edition 1 Pickup limited availability by waitlist. Additional GMC HUMMER EV models available Fall 2022. Skip Navigation Introduction Reducing Emissions Design for Environment Technology Customers Safety Diverse Workforce Human Rights Supply Chain Communities Governance 2021 SUSTAINABILITY REPORT 14
The Journey to Zero Emissions Our vision is a future with zero emissions to help create a more sustainable planet. GM plans to: Become carbon neutral in global products and operations by 2040. Achieve approved Science Based Target initiative ( SBTi) targets for operations and products. Meet our commitments under the Business Ambition Pledge for 1.5°C, an urgent call to action from a global coalition of United Nations agencies, businesses and industry leaders. Work with federal, state and local governments for implementation of supportive policies to move the United States closer to carbon neutrality consistent with the goals of the Paris Agreement. Collaborate with suppliers to set ambitious targets for the supply chain to reduce emissions, increase transparency and source more sustainable materials. Everybody in As we transition to an all-electric future, we will apply our climate equity framework to help ensure an equitable transition. 2% SCOPE 1 & 2 Strategic Plans • Plan to source 100% renewable electricity at sites in the United States by 2025 and globally by 2035. • Target a reduction in operational energy intensity by 35% by 2035 against a 2010 baseline. 14% SCOPE 3—Purchased Services and Supply Chain 2 Strategic Plans • Inviting our Tier I suppliers to sign the GM ESG Partnership Pledge to show their commitment to the principles of sustainability and human rights. • Monitor our suppliers' environmental and social progress through CDP and EcoVadis. • Leverage the GM Partner Sustainability Framework for suppliers to set goals. 84% SCOPE 3—Use of Sold Products 1 Strategic Plans • Take action to reach 1M+ planned units of EV capacity in each of North America and China by 2025. • Plan to achieve sales of 40% to 50% of annual U.S. volumes of EVs by 2030. • Plan to eliminate tailpipe emissions from new light-duty vehicles by 2035. From everybody in to everything in We have the opportunity to extend our electric and fuel cell technologies beyond light-duty vehicles to other transportation modes such as rail, shipping and heavy-duty trucks. Learn more . 1 A ligned with the SBTi for Scope 3, use of sold products. The SBTi standards require well-to-wheel (from fuel production to vehicle driving) for vehicle CO2 intensity (gCO2/km) calculations. We have revised our numbers for 2018 through 2020 for this requirement. Going forward, GM will use the SBTi standards in calculating vehicle CO2 intensity. 2 Inc ludes other Scope 3 categories. Skip Navigation Introduction Reducing Emissions Design for Environment Technology Customers Safety Diverse Workforce Human Rights Supply Chain Communities Governance 2021 SUSTAINABILITY REPORT 15
Accelerating an Inclusive All-Electric Future Climate change needs to be addressed, and we want to be part of the solution by putting everyone in an EV. We accelerated our plans to transition to an all-electric future in 2021 when we announced increased investments in EV and autonomous vehicle (AV) development to more than $35 billion from 2020 through 2025 from our initial target of $20 billion. We also announced plans to introduce more than 30 EVs globally by the end of 2025, with more than two-thirds of these available in North America. These introductions, along with additional EVs being planned, should position us to have EVs represent 40% to 50% of annual U.S. sales volume by 2030. To reach this upper range, we will continue to work with federal, state and local governments for implementation of supportive policies to move the United States closer to carbon neutrality consistent with the goals of the Paris Agreement. In China, the world’s largest EV market, we will accelerate electrification through a plan in which 40% of new vehicles introduced through the end of 2025 will be EVs. This will build on our current market momentum in China. Based on our planned cadence of EV introductions, by the end of 2025, GM will have more than 1 million units of EV capacity in North America. This is in addition to more than 1 million units of EV capacity in China over the same time frame. Our EV portfolio is planned to be among the broadest in the industry with entries from affordable, high-volume market segments to top-of-the-line models and everything in between. The new all-electric GMC HUMMER EV and upcoming Cadillac LYRIQ , Chevrolet Silverado EV and Chevrolet Equinox EV feature the company’s Ultium platform, a combined EV architecture and propulsion system, which enables EVs at scale, across a broad set of lifestyles and price points. EVGRO is our dedicated team leading efforts to drive mass consumer adoption of EVs. This team combines startup agility with the broad strength of GM to minimize complexity and turn quick decisions into actionable programs across the enterprise, while leveraging cross-functional expertise and creativity. With projects spanning the EV ecosystem—from EV shopping to charging solutions—the team is working to reimagine the end-to-end customer experience by leveraging a broad array of collaborations and partnerships, including our dealer network, which represents a key competitive advantage. How We’re Driving EV Adoption The company’s Ultium platform, a combined EV architecture and propulsion system, enables EVs at scale, across a broad set of lifestyles and price points. EV education and engagement programs to maximize the ownership experience. A product lineup that complements a broad set of services to support residential and commercial energy options. Innovative energy solutions. Investments and collaborations in public and community charging networks. Reimagined service convenience. Creating a world-class digital retail experience. Connected services for a reimagined ownership experience, centered around the myBrand mobile app 2 . Turnkey services, such as home and fleet charging solutions. The Wuling Hong Guang MINIEV has been #1 in sales in the world’s largest new energy vehicle (NEV) market for 16 consecutive months from its launch in July 2020 to December 2021. The model also was the best-selling NEV model in the entire world for five months during 2021. 1 1 A ccording to EV Sales a market research organization. 2 A vailable on select Apple and Android devices. Service availability, features and functionality vary by vehicle, device and the plan you are enrolled in. User terms apply. 2023 Cadillac LYRIQ Debut Edition available Summer 2022, by reservation only. Additional LYRIQ models available starting Fall 2022. See dealer for details. Skip Navigation Introduction Reducing Emissions Design for Environment Technology Customers Safety Diverse Workforce Human Rights Supply Chain Communities Governance 2021 SUSTAINABILITY REPORT 16
Leveraging the Ultium Platform Our EV strategy leverages a highly flexible global EV platform powered by our proprietary Ultium propulsion system. GM’s Ultium-based EVs are powered by rectangular, pouch-style battery cells that are simple, lightweight and space-efficient. Our ability to stack the long pouch cells vertically or horizontally is unique in the industry and allows for a flat cabin floor and more interior room than comparable EVs that use cylindrical battery packs. This platform can power mobility across a broad range of price points from luxury vehicles to work trucks to high-performance vehicles. As a result, Ultium is enabling GM to compete on an entirely new level and pursue nearly every customer type and preference in the market. In 2021, we increased our vertical integration of key supply chains to accelerate technology adoption, drive down costs and mitigate supply chain risks. One of these initiatives includes next-generation silicon carbide devices that will be used in the integrated power electronics contained within Ultium Drive units in next- generation EVs. The device enables system efficiencies while lowering weight and conserving space. We also are working to reduce supply chain risks by improving supplies of heavy and light rare earth materials and magnets, copper and electrical steel—all critical components used in the manufacturing of electric motors for automotive and renewable power generation. As an example, we are forming a strategic relationship and commercial collaboration with Controlled Thermal Resources to secure local and low-cost lithium from the Salton Sea area of California. This lithium will be produced through a closed-loop, direct extraction process that results in a smaller physical footprint, no production tailing and lower carbon emissions when compared to traditional processes like pit mining or evaporation ponds. Importantly, the agreement positions us to source lithium through a U.S. supplier. These initiatives help us ensure availability of critical materials, drive supply chain innovation and, ultimately, deliver both higher-quality and more affordable vehicles to our customers. Ultium: A Revolutionary EV Platform Built on a flexible battery architecture for the production of EVs across different vehicle types with outstanding power, range and performance. 300+ miles 1 GM-estimated range of up to 300+ miles. 10 minutes 2 Level 2 and direct current (DC) fast charging with the capability to charge nearly 100 miles of range in 10 minutes. 50 to 200 kWh Battery energy storage ranging from 50 to 200 kWh. Ultium Drive Ultium Drive units to support front-wheel, rear-wheel, all-wheel and performance all-wheel drive applications. ~3 seconds GM-estimated acceleration of 0 to 60 mph in as little as approximately 3 seconds on the GMC Hummer EV. 1 A ctual range will vary based on several factors, including temperature, terrain, battery age, loading, use and maintenance. 2 GM-estimated. Actual charge times will vary based on battery condition, output of charger, vehicle settings and outside temperature. → Learn More about our Battery Chemistry Skip Navigation Introduction Reducing Emissions Design for Environment Technology Customers Safety Diverse Workforce Human Rights Supply Chain Communities Governance 2021 SUSTAINABILITY REPORT 17
LEVERAGING THE ULTIUM PLATFORM CONT. Ultium represents a milestone achievement in electrification, with battery pack costs nearly 40% lower compared to the previous generation, and we expect the second generation Ultium packs will cost nearly 60% less than the batteries used today 1 . We are committed to continuous manufacturing, materials and packaging efficiencies, high-energy cell design and increased vertical integration with local production that are expected to deliver greater energy density at a lower cost. We also are incorporating responsible battery recycling considerations. Today we refurbish, recycle or reuse 100% of batteries returned to us and apply the lessons in future design. Among the recycling initiatives that we are pursuing is a collaboration with the Department of Energy’s (DOE) U.S. Advanced Battery Consortium and recyclers to advance lithium-ion battery recycling. These projects are validating recycled materials as alternatives to mined materials for battery manufacturing with the goal of reducing future needs for mining. Learn more in Design for the Environment . Creating a Superior EV Ownership Experience In 2021, GM introduced Ultium Charge 360, a holistic approach that integrates charging networks, GM vehicle mobile apps, products and services to simplify the overall charging experience. Through Ultium Charge 360, GM Fleet, OnStar Business Solutions (where available) and BrightDrop, customers will be able to customize plans and select from preferred providers for their fleet electrification needs in the United States and Canada. 2 Ultium Charge 360 Capabilities • Access to Charging: GM continues to work with a variety of third parties, including charge point operators, electric utilities and government agencies to make home, workplace, public and fleet charging ubiquitous and easy for customers. • Mobile Apps: We will continue to update GM vehicle mobile apps to provide an even more intuitive mobile experience that simplifies navigating to a charging station, initiating charging sessions and paying for charging. • Products and Services: To help ensure a seamless EV transition, GM plans to offer EV owners charging accessories and installation services tailored to their lifestyle. A Holistic Solution for Fleets • A comprehensive solution to help new and existing fleet customers identify providers, tools and solutions required to plan, finance, deploy and operate charging infrastructure in fleet yards and depots. • Fleet and facility management tools. • Integration with GM’s fleet management solution, OnStar Vehicle Insight and the BrightDrop Software Platform. • Support for a wide range of fleet segments, including delivery, sales, utilities and motor pool. Convenient and Rewarding Ownership Experience • Implementing connected diagnosis and over-the-air programming with easy mobile service or dealer pick-up/drop-off options for service convenience. • Competitive battery warranty with battery performance monitoring. • A seamless, omnichannel customer experience with connected product offerings. • Make the myBrand apps as the “ownership hub” to access connected services, monitor battery health and energy status and plan routes. 2024 Chevrolet Equinox EV RS available Fall 2023. Availability of LT shown to be announced at a later date. 1 C ost reduction might vary by region and cell chemistry. 2 A vailable on select Apple and Android devices. Service availability, features and functionality vary by vehicle, device and the plan you are enrolled in. User terms apply. Skip Navigation Introduction Reducing Emissions Design for Environment Technology Customers Safety Diverse Workforce Human Rights Supply Chain Communities Governance 2021 SUSTAINABILITY REPORT 18
→ A Purpose-Built EV Portfolio The EV portfolio that we are building today is designed to meet the needs of a broad range of customers. We have the advantage of the most loyal customer base in the industry and intend to reward that loyalty with a convenient and seamless transition to an electric future. U.S. EV Models 2022 Chevrolet Bolt EV/EUV The 2022 Bolt EV and Bolt electric utility vehicle (EUV) both launched in summer 2021. The Bolt EUV has an EPA-estimated range of 247 miles on a full charge . 1 2022 GMC HUMMER EV Pickup 1, 2 As the world’s first zero-tailpipe-emissions, all-electric supertruck, the GMC HUMMER EV is built to navigate off-road conditions. A 24-module pack of Ultium battery cells offers a GM-estimated range of up to 329 miles. 2023 Cadillac LYRIQ 3 Cadillac’s introduction of its electric portfolio begins with the debut of the LY R I Q —a fully electric luxury crossover is expected to offer a GM-estimated range of over 300 miles per full charge. It will also offer the enhanced version of Super Cruise . 2022 BrightDrop Zevo 600 The BrightDrop Zevo 600 is an electric light commercial vehicle (eLCV) built for the delivery of goods and services over long ranges and is the fastest vehicle to market in GM’s history. 2024 Chevrolet Silverado EV 1, 4 The Silverado EV is expected to offer customers a GM-estimated range of 400 miles on a full charge and will feature an available fixed- glass roof for retail models, offering an experience of spaciousness. 2024 Chevrolet Equinox EV SUV and 2024 Chevrolet Blazer EV SUV Both models will be available in 2023. These two products, along with the Chevrolet Silverado EV, will place Chevrolet EVs in the industry’s two largest segments and one of the fastest-growing segments in the United States. Cadillac CELESTIQ 5 The Cadillac CELESTIQ will represent the ultimate expression of Cadillac innovation. The luxury sedan will offer all-wheel drive , four- wheel steering and a full-glass roof that allows each occupant of the vehicle to set their own level of transparency. 1 A ctual range will vary based on several factors, including temperature, terrain, battery age, loading, use and maintenance. 2 E dition 1 Pickup limited availability by waitlist. Additional GMC HUMMER EV models available Fall 2022. Available on EV3X based on a full charge. GM estimated. 3 2 023 Cadillac LYRIQ Debut Edition available Summer 2022, by reservation only. Additional LYRIQ models available starting Fall 2022. See dealer for details. 4 S ilverado EV RST GM-estimated range on a full charge based on current capability of analytical projection consistent with SAE J1634 revision 2017—MCT. Model year 2024 Silverado EV available Fall 2023. 5 C oncept vehicle. Not available for sale. Learn more about our Ultium effect Skip Navigation Introduction Reducing Emissions Design for Environment Technology Customers Safety Diverse Workforce Human Rights Supply Chain Communities Governance 2021 SUSTAINABILITY REPORT 19
China EV Models 2021 BAOJUN KiWi EV 1 The KiWi EV has a NEDC-estimated range of 305 kilometers on a full charge and supports DC fast charging , which enables it to be charged from 30% to 80% in one hour. Buick VELITE 6 EV 2 Range of up to 518 kilometers and supports fast charging from 30% to 80% capacity in just 30 minutes. 2022 Chevrolet Menlo The sporty-looking sedan is the brand’s first all-electric vehicle in China. The 2022 Chevrolet Menlo has an extended NEDC-estimated range of up to 518 kilometers on a single charge. 2022 Wuling Hong Guang MINIEV The Hong Guang MINIEV is China’s #1 selling EV, an affordable four-seat runabout that is fun to personalize. Rong Guang EV The Rong Guang EV is Wuling’s first electric minivan for the commercial vehicle market. 1 T he 2022 BAOJUN KiWi EV will be launched in the second half of 2022. 2 T he up to 518km range on a full charge is based on China Light-duty Vehicle Test Circle (CLTC). Actual fast-charging time may vary based on several factors, including temperature and external power environment. Skip Navigation Introduction Reducing Emissions Design for Environment Technology Customers Safety Diverse Workforce Human Rights Supply Chain Communities Governance 2021 SUSTAINABILITY REPORT 20
Growing the EV Market & Charging Infrastructure In the transition to an all-electric future, automakers must meet customer expectations relating to range, charging, battery and ownership. Our charging infrastructure strategy seeks to help solve these concerns. GM Charging Infrastructure Initiatives in the United States and Canada Nearly $750M planned investment through 2025 to expand charging for residences, workplaces and public areas. 3,250 EVgo DC fast charging (DCFC) stalls installed through 2025. 10 Signed agreements with major charging providers that include Blink Charging, ChargePoint, EV Connect, EVgo, FLO, Greenlots, EvGateway, EV Passport, PlugShare and SemaConnect. Up to 40,000 Level 2 EV chargers to be deployed as part of a Dealer Community Charging Program through 2025. This will help address gaps in public charging availability, including “charging deserts” in rural and underserved communities, by providing participating EV dealers up to 10 Ultium Level 2 charging stations. 100,000+ Ultium Charge 360 enables access, using GM mobile apps 1 , to more than 100,000 charging plugs. GM’s strategy to grow the EV market begins at the retail level, with initiatives to educate dealer partners, create a network of EV experts and engage customers to drive EV awareness, consideration and sales. Key pillars to GM’s strategy to grow the EV market include: • An all-new Electric Vehicle Experience Standards Program for participating dealerships. Through the program, each dealership designates an “EV Specialist” to champion the EV selling process at the store. • Access to “EV Academy” and dedicated EV training courses for the EV Specialist to help them navigate customers through the charging experience, all while maintaining GM standards for customer satisfaction. Training is expected to include quarterly training courses as identified by the GM Center for Learning, and enrolled specialists must achieve a 100% training percentage each quarter. • A new “gamification” microtraining platform to supplement EV training and drive EV literacy. • “EV Live,” a new platform to educate and guide dealers, customers, fleets and other parties with access to on-demand interactive training and consultation. • An “EV Learn” feature of the myBrand mobile apps 1 to allow shoppers insight into the EV ownership experience, including a cost savings calculator. • Innovative digital engagement tools, both in the physical and digital retail space, to guide customers through the shopping process. The Electric Vehicle Experience Standards Program provides dealers the opportunity to earn a monthly incentive for participating in initiatives designed to deliver on these customer experience objectives for EVs. 1 A vailable on select Apple and Android devices. Service availability, features and functionality vary by vehicle, device and the plan you are enrolled in. User terms apply. Skip Navigation Introduction Reducing Emissions Design for Environment Technology Customers Safety Diverse Workforce Human Rights Supply Chain Communities Governance 2021 SUSTAINABILITY REPORT 21
Transforming a World-Class Manufacturing Footprint We are building our electric future by leveraging our existing manufacturing footprint as well as building new plants for battery cell production. We plan to rapidly scale EV manufacturing. Globally, we are adding battery assembly/pack facilities to our existing sites in North America and China and converting some propulsion facilities to the manufacturing of drive units. Since 2020, we have announced investments totaling more than $14 billion in 10 sites across North America to increase our manufacturing capacity in the region to more than 1 million EVs annually by the end of 2025. This is a key step to deliver on our target to achieve carbon neutrality in our global products and operations by 2040. We believe that leveraging established assembly plants for EV production reduces capital expenditures up to $1.5 billion per assembly plant versus building an all-new plant and enables us to go into vehicle production in less than half the time required of a greenfield plant. GM is investing $7 billion in four Michigan manufacturing sites, significantly increasing battery cell and electric truck manufacturing capacity. This is the single largest investment announcement in GM history. The investment includes construction of a new Ultium Cells battery cell plant in Lansing, Michigan and the conversion of GM’s assembly plant in Orion Township, Michigan for production of the Chevrolet Silverado EV and the electric GMC Sierra, GM’s second assembly plant scheduled to build full-size electric pickups. In 2021, we also announced the Wallace Battery Cell Innovation Center, an all-new facility is expected to significantly expand our battery technology operations and accelerate the development and commercialization of longer- range, more affordable EV batteries. The Center, located at our Global Technical Center in Warren, Michigan, is slated to be completed in mid-2022. The latest addition of 50,000 square feet brings the Center to 85,000 total square feet as demand for EVs increases. Investing in an All-Electric Future (Projects completed, in progress or announced through the first quarter of 2022 in the United States as examples of our transformation) By the end of 2025, GM plans to have more than 1 million units of EV capacity in North America. This is in addition to more than 1 million units of EV capacity in China over the same time frame. Battery Cell Manufacturing 1 Lansing, Michigan New $2.6 billion plant to supply battery cells to Orion and other GM assembly plants. Factor y ZERO Detroit Hamtramck, Michigan Retooling of existing manufacturing facility, representing a $2.3 billion investment. Electric Motor Component Plant Lockport, New York Renovation and new equipment installation, a $154 million investment. Battery Cell Manufacturing 1 Lordstown, Ohio A $2.3 billion investment to mass-produce Ultium battery cells. EV Truck Assembly Orion, Michigan Retooling of existing manufacturing facility through a $4 billion investment. EV Assembly Spring Hill, Tennessee A $2.3 billion retooling of an existing manufacturing facility. Battery Cell Manufacturing 1 A $2.3 billion investment to supply batteries to the Spring Hill assembly plant. Die Casting Foundry Bedford, Indiana More than $51 million invested to support drive unit castings for Silverado EV. 1 B uilt through Ultium Cells LLC (an equally owned joint venture with LG Energy Solution) Our manufacturing investments in four Michigan manufacturing sites are expected to create 4,000 new jobs and retain 1,000 jobs in Michigan. Skip Navigation Introduction Reducing Emissions Design for Environment Technology Customers Safety Diverse Workforce Human Rights Supply Chain Communities Governance 2021 SUSTAINABILITY REPORT 22
Factory ZERO: How Our Future Looks Walk through the doors of Factory ZERO in Detroit, Michigan, and you’ll not only see the launchpad for GM’s multibrand EV strategy but also GM’s low carbon future. From sourcing renewable energy to power the all-electric vehicles it will produce, the retooling of this 36-year-old facility is reflective of the company that GM is becoming. SUSTAINABLE Reused or recycled a wide range of materials that came out of the facility during conversion. • Roads on the plant site are made from crushed concrete from the old floor. • All operations are expected to be powered by sourcing 100% renewable energy for electricity by 2023. • The in-plant fleet of forklifts, tuggers and Seegrid AVs is powered by hydrogen fuel cells–a first for a GM plant. • Treated stormwater will be used in cooling towers and a fire suppression system. • A 16.5-acre wildlife habitat is home to monarch butterflies, foxes and turkeys. ELECTRIC All Factory ZERO EVs will be built on the Ultium Platform, the heart of our EV product strategy. Among the vehicles that are expected to call the plant home: • 2022 GMC HUMMER EV pickup, which began production in late 2021 • 2024 GMC HUMMER EV SUV • Chevy Silverado all-electric pickup • GMC Sierra all-electric pickup • Cruise Origin INCLUSIVE Our target to bring everyone along on our EV journey has started here. • Redesigned employee experience for all plant employees incorporates newly developed orientations led by plant leaders and centered around GM behaviors. • Workspaces and gathering areas are designed to encourage a climate of collaboration among all groups and levels of responsibility. • Employees actively recognize and share success. • Site leadership and employees actively participate in an operational excellence project focused on actions to promote an inclusive environment. COMPETITIVE The retooled facility is a model for future GM facility renovations. • Retooling requires only two-thirds of the capital required to build a greenfield plant. • GM projects that it will avoid up to $15 billion in capital costs by 2030 through the renovation of existing manufacturing facilities versus ground-up construction. • Through virtual tools and working in parallel with production engineering teams, manufacturing launch time is reduced from two years to less than one, as opposed to up to four years for greenfield planning and construction. Skip Navigation Introduction Reducing Emissions Design for Environment Technology Customers Safety Diverse Workforce Human Rights Supply Chain Communities Governance 2021 SUSTAINABILITY REPORT 23
Learn more about fuel efficiency and emissions regulation in the Public Policy section of this report. → Reducing Emissions From ICE Vehicles As we move closer to our vision of an all-electric portfolio, we also are improving the efficiency of ICE vehicles. Continual improvements in vehicle engine and transmission efficiency, as well as vehicle weight, have helped us to eliminate excess materials use in manufacturing, while reducing fuel use and costs for customers. For example, the 4WD Crew Cab Silverado has seen an improvement in tailpipe CO2 emissions of 25% from 2000 through 2020. 3 Within GM, we have institutionalized extensive governance processes that predict, plan, measure and assess our fleet’s fuel efficiency and emissions performance according to established government test procedures on a dynamic and country-by-country basis. Well-to-Wheel CO2 Emissions per Light-Duty Vehicle 1, 2 (gCO2e/km) 2018 2019 2020 USA 287 293 280 China 220 208 206 Brazil 200 198 195 Weighted Average 245 243 240 U.S. Light-Duty Fuel Economy Technologies Across the Fleet Percent of Total U.S. Light-Duty Volume Stop-Start (reduces fuel usage when the vehicle is stopped) 74% MY21 Engine/Transmission Thermal Management (warms up engine and transmission faster to reduce friction and losses) 56% MY21 Aero-Shutter (reduces aerodynamic drag) 83% MY21 High-Efficiency Alternators (72%+) (reduce losses from electricity generation) 88% MY21 1 2 021 data will be available mid-2022. 2 D ata has been restated to align with SBTi for Scope 3, Use of Sold Products. The SBTi standards require well-to-wheel (from fuel production to vehicle driving) for vehicle CO2 intensity (gCO2e/km) calculations. We have revised our numbers for 2018 through 2020 for this requirement. Going forward, GM will use the SBTi standards in calculating vehicle CO2 intensity. Numbers are inclusive of EV portfolio. 3 D ata prior to July 2009 corresponds to General Motors Corporation. Skip Navigation Introduction Reducing Emissions Design for Environment Technology Customers Safety Diverse Workforce Human Rights Supply Chain Communities Governance 2021 SUSTAINABILITY REPORT 24
Conserving Energy in Our Facilities Our goal to become carbon neutral in our operations will be achieved in part through an ambitious energy conservation and renewable energy program. An important pillar in GM’s carbon reduction strategy for Scope 1 & 2 emissions is to focus on energy efficiency. Globally, our plants continue to work on improving energy efficiency and reducing GHG emissions through the use of an energy management system (EnMS). In addition to our Science-Based Target goal for GHG emissions, GM expanded our energy intensity goal for operations to 2035 with a 35% reduction from a 2010 baseline. Following are some of the programs and strategies that we deploy to conserve energy in our operations. U.S. DOE 50001 Ready Program In 2021, 27 GM U.S. manufacturing facilities, or 93% of our U.S. manufacturing footprint, implemented the U.S. DOE 50001 Ready program. GM has implemented 50001 Ready at 27 manufacturing and two nonmanufacturing facilities—more than any other participating company. In 2021, we expanded the program to two nonmanufacturing sites in the United States, two plants in Canada and one in Mexico. We plan to expand this program to all manufacturing facilities globally to continuously monitor and improve our EnMS. Better Buildings Low Carbon Pilot We are participating in the DOE Better Buildings program to demonstrate pathways to achieve low or zero carbon in the operation of buildings and manufacturing plants. Energy Star’s Building Portfolio Manager (BPM) GM uses data analytics to measure and track energy consumption globally. BPM is an example of a tool that allows us to benchmark performance and make continuous improvements. 2021 Energy Star Certifications for Superior Energy Management • IT Innovation Centers in Texas and Arizona • Enterprise Data Centers (2) in Michigan • Flint Assembly • Fort Wayne Assembly GM Energy Strategy Increasing Energy Efficiency Reduce energy consumption at our facilities. Sourcing Renewables Source through direct investments, green tariffs and power purchase agreements. Addressing Intermittency Mitigate against gaps in renewable energy for electricity transmission. Policy Advocacy Work to drive down costs and increase renewable energy for electricity opportunities. Goal: Plan to source 100% renewable electricity at sites in the United States by 2025 and globally by 2035. Skip Navigation Introduction Reducing Emissions Design for Environment Technology Customers Safety Diverse Workforce Human Rights Supply Chain Communities Governance 2021 SUSTAINABILITY REPORT 25
CONSERVING ENERGY IN OUR FACILITIES CONT. Energy Star Challenge for Industry This continuous improvement program has recognized 69 GM plants multiple times over the past 10 years for a total of 130 recognitions. The Challenge is to reduce energy intensity by 10% within a five-year period. In 2021, five plants met the Challenge with an average 15% reduction over three years. The five plants were Qingdao Assembly, Baojun Assembly and Dongyue Engine, all in China, Silao Assembly in Mexico and Flint Assembly in the United States. Energy Star certifications provide a benchmark system for energy efficiency, identifying buildings and auto assembly plants within the top 25th percentile of operating efficiency. Energy OnStar This tool (unrelated to GM’s OnStar service), is a continuous commissioning system that monitors the performance of our HVAC equipment in real time. Approximately one-third of our operational energy use is heating and cooling, and the system allows us to quickly identify when a unit is malfunctioning and easily find opportunities for improvement. The Energy OnStar tool helped us optimally manage plant shutdowns in 2021 during the semiconductor shortage. Energy Star Treasure Hunts Through this process, we can engage nearly 100 team members to uncover quick ways to save energy. In 2021, we conducted 17 on-site and virtual energy treasure hunts, covering 61 million square feet of space, and found 175 opportunities that could potentially save the company $5 million. We also extended this approach to our suppliers during the year, including rolling out a Virtual Energy Treasure Hunt process. Learn more in Supporting Supplier Responsibility . A More Energy-Efficient Plant One of our energy efficiency projects in 2021 was at Fort Wayne Assembly, where we manufacture the Chevrolet Silverado and GMC Sierra full-size trucks. The 35-year-old plant generated steam with large natural gas boilers to heat the building and manufacturing processes. The Powerhouse also generates six megawatts of renewable electricity from landfill gas, a renewable fuel that would normally be flared, which we instead use to generate renewable electricity as part of our RE-100 target. The remainder of the plant’s electric loads are served by wind and solar and are 100% powered by renewable energy. The project will eliminate steam, an inefficient heating method, by using the waste heat from the landfill gas engines to supply most of the building heat and converting other steam loads to direct or indirect natural gas. Additional energy conservation measures include the installation of ultraviolet lamps in air handling units, lighting and dock heater controls. GM was recognized by the Michigan Battle of the Buildings in 2021 for manufacturing resiliency in the face of rapidly changing dynamics during the pandemic. In 2021, GM received recognition from Energy Star for Sustained Excellence in Energy Management for the 10th year, confirming our continuous improvement activities. Skip Navigation Introduction Reducing Emissions Design for Environment Technology Customers Safety Diverse Workforce Human Rights Supply Chain Communities Governance 2021 SUSTAINABILITY REPORT 26
Accelerating an All-Renewable Future In 2021, we accelerated our timeline for sourcing 100% of our electricity from renewable sources for our U.S. sites to 2025, five years earlier than previously announced and 25 years ahead of our initial target set in 2016. In doing so, we also will help drive growth in the renewable energy sector. Just as GM has the scale to promote widespread adoption of EVs, we also have the scale to help bring about a transition to renewable power sources across the United States. We are the 12th largest offtaker in the world 1 , and largest in the automotive industry, of renewable power purchase agreements by capacity. Reducing our own operational carbon footprint and setting up the grid for a future in which EVs can charge using renewable power for electricity is an essential part of our zero-emissions vision. By accelerating our renewable energy for electricity goal, GM aims to avoid 1 million metric tons of carbon emissions that could have been produced between 2025 and 2030. The accelerated U.S. goal will position us to continue working toward our goal of sourcing 100% renewable energy to power global operations by 2035. This U.S. goal builds upon approval of our targets. In 2021, the SBTi assessed GM’s official submission against the Call to Action’s eligibility criteria. The target submission for Scope 1 and 2 emissions is a reduction of absolute emissions of 72% by 2035 from a 2018 base year, which meets the minimum ambitions for a 1.5°C pathway. We are currently on track to meet the target by 2035 with 25% of our global electricity powered by renewable energy in 2021. Quantifying the Impact 5 the number of years we have accelerated our goal to source 100% renewable energy to supply electricity for our U.S. sites. 1M metric tons of potential carbon emissions avoided if we meet our goal by 2025 instead of 2030. The GHG emissions equivalent of 125,963 homes’ energy use annually. 1 BloombergNEF Skip Navigation Introduction Reducing Emissions Design for Environment Technology Customers Safety Diverse Workforce Human Rights Supply Chain Communities Governance 2021 SUSTAINABILITY REPORT 27
ACCELERATING AN ALL-RENEWABLE FUTURE CONT. GM Renewable Energy for Electricity Initiatives 1 MI—Consumers Energy G r e e n Ta r i f f 100 MW MI—DTE G r e e n Ta r i f f 447 MW IN—On-Site Landfill Gas Fort Wayne Assembly—6.4 MW MI—On-Site Landfill Gas Orion Assembly—8 MW Toledo, OH On-Site Solar 1.8 MW Rochester, NY On-Site Solar 0.345 MW Rancho Cucamonga, CA Solar PPA (Rooftop) 3 MW Hilltopper, IL Wind PPA 100 MW Trishe, OH Wind PPA 103 MW Bowling Green, KY On-Site Solar 0.85 MW Cactus Flats, TX Wind PPA 50 MW Newport, AR Solar PPA 180 MW TN , KY—T VA G r e e n Ta r i f f 128 MW Hidalgo, TX Wind PPA 30 MW 1 F igure includes both operating and executed agreements. Total Capacity of Renewable Electricity 14.4 MW Landfill Gas 313.995 MW Solar 830 MW Wind Skip Navigation Introduction Reducing Emissions Design for Environment Technology Customers Safety Diverse Workforce Human Rights Supply Chain Communities Governance 2021 SUSTAINABILITY REPORT 28
Our Energy & Emissions Progress Absolute Scope 1 & 2 Emissions (million metric tons CO2e) 2018 2020 2021 2019 Energy Intensity (MWh/Vehicle) (Energy used in GM’s operations) 2018 2020 2021 2019 2.31 2.13 2.06 2.25 1.50 Goal 2018 BASELINE 2019 2020 2021 2035 Renewable Energy as a Percentage of Global Electricity Use 2018 2020 2021 2019 2021 3% 22% 23% 25% 55% 1 2018 BASELINE 2019 2020 2021 2025 100% Goal 2035 21,489,324 Electricity Consumption (including cooling) Energy Consumption by Source (GJ) 21,048,701 Fuel Consumption From Nonrenewable Sources (including heating) 1,713,704 Fuel Consumption From Renewable Sources (including heating) 938,548 Steam Consumption ACCELERATING AN ALL-RENEWABLE FUTURE CONT. Energy intensity is a global calculation. 2021 performance was higher than prior years due to lower vehicle production driven by semiconductor shortages and other COVID-related constraints. 1 B ased on estimated forecasted global renewable energy sourced through currently executed agreements, subject to change depending on actual future electric usage in operations, and actual future renewable generation. Skip Navigation Introduction Reducing Emissions Design for Environment Technology Customers Safety Diverse Workforce Human Rights Supply Chain Communities Governance 2021 SUSTAINABILITY REPORT 29
ACCELERATING AN ALL-RENEWABLE FUTURE CONT. Climate Innovation Goes the Extra Mile As we move toward an all-electric future, it is on us to lead positive change and implement inclusive solutions. In 2021, we committed to several capital and philanthropic ventures to support our zero-emissions future. It is imperative that we bring everyone along and go beyond our more than $35 billion investment in EV and AV development. We have joined Breakthrough Energy Catalyst, a collaborative public-private partnership to help advance the commercialization of green technology. Focus Areas • Direct Air Capture • Green Hydrogen • Long Duration Energy Storage • Sustainable Aviation Fuel Our Role • Founding Anchor Partner • Member of Catalyst Leadership Council GM has joined TPG Rise Climate, designed to grow the wide range of commercially viable climate technologies that have been incubated by the research community, early-stage investors and other climate innovation accelerators. Focus Areas • Clean Energy • Enabling Solutions • Decarbonized Transport • Greening Industrials • Agriculture and Natural Solutions Our Role • Corporate Coalition Member • Insights into a wide range of sustainability strategies, technologies and investment opportunities Climate Equity Fund GM has established a $50 million Climate Equity Fund to assist community-based organizations with helping to close equity gaps in the transition to EVs and other sustainable technology. Learn more on page 101 . Focus Areas • Increase the Number of People Qualified for Clean Energy Careers • Increase Awareness and/or Access to Sustainable Transportation Solutions • Increase Programs that Mitigate the Effects of Climate Change, Assist with Climate Adaptation and/or Community Resilience Our Role • Established in 2021 • Committed an additional $25 million in funding in 2022 to bring the total fund to $50 million • 19 beneficiaries in first year Skip Navigation Introduction Reducing Emissions Design for Environment Technology Customers Safety Diverse Workforce Human Rights Supply Chain Communities Governance 2021 SUSTAINABILITY REPORT 30
Designing for the Environment IN THIS SECTION Sourcing & Engineering More Sustainable Materials 32 Pursuing Zero Waste 36 Nature Conservancy Programs 38 Reducing Water Intensity 39 Our Strengths y Developing innovative sustainable design solutions while delivering outstanding customer- and brand-focused products y Developing materials that involve a less resource-intensive manufacturing process and do not result in as much end-of-life (EoL) waste y Educating employees, supply chain partners and stakeholders about the benefits of sustainable materials and circular economy processes y Creating end-markets for waste and other discarded materials that would otherwise go to landfills or incinerators y Adopting construction and manufacturing processes that minimize resource consumption and promote circularity Our Opportunities y Finding the right tools and methodologies to measure environmental impacts of our materials and products y Identifying markets for repurposing opportunities, such as for plastics and metals y Reducing GM operational water intensity through innovative methods Skip Navigation Introduction Reducing Emissions Design for Environment Technology Customers Safety Diverse Workforce Human Rights Supply Chain Communities Governance 2021 SUSTAINABILITY REPORT 31
Sourcing & Engineering More Sustainable Materials A sustainable vehicle goes beyond being electric and incorporates responsible materials and a design to minimize environmental impact at end-of-life. As we transform our business to support production of electric vehicles (EVs), we are not only considering EoL reusability and recyclability but also working to ensure the use of sustainable materials in our vehicles from inception. This will be accomplished through a comprehensive commodity management plan, which includes purchased steel, aluminum, plastics, EV battery cell materials, textiles and more. These materials—that represent more than 90% of the CO2 emissions generated by materials in our vehicles—have been identified as part of our implementation strategy. The plan drives collaboration with our suppliers and applies data-driven strategies that can be customized to the specific attributes of each commodity. Plastics We are collaborating with our plastics suppliers to advance circular economy practices and support the responsible utilization of resources. Some of their strategies to achieve those commitments include switching to renewable energy for electricity in their manufacturing processes, continued recycling efforts, incorporating biomaterials, improving processes in their own business and utilizing carbon capture technologies and carbon offsets. Our plastics suppliers are working to overcome common challenges in this industry, which include increasing costs, scaling issues and the quality of available feedstocks. Natural Rubber GM is a founding member of the Global Platform for Sustainable Natural Rubber, a multistakeholder initiative whose goal is to transition the natural rubber supply chain to a more sustainable model. The initiative now has more than 100 members, including Original Equipment Manufacturers (OEMs); tire manufacturers; rubber producers, processors and traders; nongovernmental organizations; and smallholder farmers. All members are expected to adopt a sustainability policy framework, which covers economic, social and environmental aspects of sustainability and will help protect ecological health, local livelihoods and fundamental human rights. Steel and Aluminum We are engaging with our direct materials suppliers regarding how to make these materials more sustainable. We expect supplier carbon-emissions reductions to be achieved using process innovation, recycled materials, renewable energy for electricity and carbon capture utilization and storage. GM will work to secure supply of low-CO2 metals and materials ahead of their availability at scale. Beginning in the first quarter of 2022, we became the inaugural customer of a Nucor Corp. line of net-zero carbon steel products called Econiq. EV Battery Materials The EV battery materials commodity management plan uses a combination of supply chain carbon reduction, the incorporation of recycled materials and third-party partnerships to help ensure responsible sourcing. While utilizing critical recycled minerals is a significant focus for GM, the advancement of the EV landscape will continue to depend on the use of raw materials until the EV circular economy reaches maturity. Read more about our work with the Responsible Minerals Initiative on page 93 . Tex tile s Together with our suppliers, we are developing dozens of new textile materials from items such as recycled plastic bottles. We are committed to developing 35% recycled content on seat insert fabrics and 100% recycled yarn for future seat bolster fabrics, overhead fabrics, floor carpets, floor mats and more in our upcoming vehicles. Beyond textiles, we are continually researching new and innovative materials, including bio-based alternatives, lower-impact leather tanning practices and alternatives to chrome plating. Our Materials Commodity Management Plan aims to procure increasingly sustainable materials via carbon emissions reductions through process innovation, recycled material content, renewable and fossil free energy for electricity and carbon capture utilization and storage. Skip Navigation Introduction Reducing Emissions Design for Environment Technology Customers Safety Diverse Workforce Human Rights Supply Chain Communities Governance 2021 SUSTAINABILITY REPORT 32
SOURCING & ENGINEERING MORE SUSTAINABLE MATERIALS CONT. 2021 Recycled Content in GM Vehicles GM is working to increase the sustainable materials used to make our vehicles. While these materials are not all available on all vehicles, each improvement provides valuable insights and brings us closer toward our goal. >17M pounds of recycled plastic was used in GM vehicles Fans and Fan Shrouds 165,375 pounds Generator Covers 7,000 pounds Wiper Shields 89,000 pounds Hood Seals 6,000 pounds Center Console 1.8M pounds HVAC Ducts 2M pounds POSTCONSUMER NYLON Window Support Brackets 1.3M pounds Tow Hook Covers 28,500 pounds Underbody Shields 644,341 pounds Wheelhouse Liners >11M pounds water bottles recycled 2023 Cadillac LYRIQ Debut Edition available Summer 2022, by reservation only. Additional LYRIQ models available starting Fall 2022. See dealer for details. Skip Navigation Introduction Reducing Emissions Design for Environment Technology Customers Safety Diverse Workforce Human Rights Supply Chain Communities Governance 2021 SUSTAINABILITY REPORT 33
SOURCING SUSTAINABLE MATERIALS CONT. SOURCING & ENGINEERING MORE SUSTAINABLE MATERIALS CONT. Sustainable Battery Life Cycle: Battery Reuse and Recycling GM’s EV battery life cycle management (LCM) is a crucial element in GM’s commitment to an all-electric and a zero-emissions future. Since the introduction of the GM Volt plug-in hybrid electric vehicle, we have developed a robust battery LCM program that spans from design, manufacturing and service to EoL and supports our sustainability goals. Ensuring proper LCM can help reduce energy and materials requirements throughout the battery supply chain and is key to minimizing sustainability impacts. We have created an ecosystem that ensures all batteries returned to GM are reused or recycled. In addition, GM continues to evaluate opportunities for the reuse of EoL EV batteries for second life, non-EV uses. Examples of past demonstrations include our collaboration with Oak Ridge National Laboratory to evaluate and test a stationary storage system built with EoL batteries against various use cases including solar integration and back-up power. Stationary storage units were also installed at the General Motors data center office at the Milford Proving Grounds re-using Volt batteries, as well as at a SAIC-GM-Wuling facility using Baojun E100 and E200 batteries. GM is developing stationary storage and energy-efficient solutions within multiple manufacturing facilities with the ability to provide up to 15 megawatts of on-site power capacity. In parallel, GM’s Global Purchasing and Supply Chain Team seeks to strengthen local supply of raw battery materials. As an example, we have announced work with Controlled Thermal Resources for the supply of locally sourced, low-cost lithium, and with POSCO chemicals to strengthen our own cathode active materials supply chain and localize its processing to North America. When it comes to vehicle EoL, we recognize the importance of enabling GM EV batteries to be disposed of properly. Today, GM’s recyclemybattery.com website provides vehicle dismantlers with valuable information for disabling and removing battery packs from GM EVs. A list of EV battery recyclers is provided along with information on how to safely store and ship used EV battery packs. We will continue to develop guidelines that support safe handling, storage and transport of EV batteries by EoL processors and to evaluate opportunities to enable recycling of all EoL batteries. Battery Recycling Initiatives We will continue to evaluate opportunities for second-life use of batteries. However, battery recycling is our primary focus today and a key enabler to more sustainable battery supply chains. Recycling efforts in which GM is actively engaged include: • Collaboration with the Department of Energy’s U.S. Advanced Battery Consortium and recyclers to advance lithium-ion battery recycling. These projects are validating recycled materials as alternatives to mined materials for battery manufacturing with the goal of reducing future needs for mining. • Strategic sourcing of recycled materials from multiple companies utilizes new hydrometallurgical processes that produce battery materials with approximately a 30% lower carbon footprint than when mined. These processes are used for all returned GM EV batteries as well as all battery material waste generated at GM and Ultium plants. • Continuous collaborations with suppliers in effective ways of using recycled battery materials in our own supply chain. Skip Navigation Introduction Reducing Emissions Design for Environment Technology Customers Safety Diverse Workforce Human Rights Supply Chain Communities Governance 2021 SUSTAINABILITY REPORT 34
Construction of Factory ZERO SOURCING & ENGINEERING MORE SUSTAINABLE MATERIALS CONT. Using Sustainable Packaging We have established a sustainable materials working group that is dedicated to sustainable packaging. The group is working closely with suppliers and external partners to innovate around current practices and embed circular economy principles in packaging procurement and design. As part of this work, GM has partnered with WestRock as the preferred supplier for all consumer-facing packaging. WestRock prioritizes recycled content input in their sourcing, averaging 35% to 55% recycled content in corrugated boxes and 100% recycled content in coated boards. Our plan is for any virgin materials used in our packaging produced by WestRock to be certified by the Sustainable Forestry Initiative. In 2021, approximately 8,000 parts for GM Customer Care & Aftersales were packaged in WestRock’s sustainable consumer-facing packaging. Sustainable Construction Practices GM’s commitment to sustainability extends into global construction projects. In 2021, GM recycled over 140,000 tons of wood, metal, concrete and plastic produced in construction projects and found reuse initiatives for over 105,000 tons of concrete, soil, asphalt and other materials. We reduced our construction-driven CO2 impact by installing CarbonCure concrete at two GM projects in Spring Hill, Tennessee. Concrete using CarbonCure Technology’s process has a lower carbon footprint than traditional concrete through their CO2 sequestering process. One of the best examples of our sustainable construction practices is GM’s Factory ZERO Detroit-Hamtramck Assembly Center, which has been retooled, upgraded and expanded to serve as a launchpad for GM’s multi-brand all-EV strategy. During its conversion, we reused or recycled a wide range of materials that came out of the former factory, including crushed concrete from the floor that was repurposed for temporary roads around the facility. Factory ZERO Construction Recycling (in tons) 63,208 concrete 3,282 steel 13 wood 126,416 soil 4,804 asphalt Read more about Factory ZERO in the Reducing Carbon Emissions section of this report. → Skip Navigation Introduction Reducing Emissions Design for Environment Technology Customers Safety Diverse Workforce Human Rights Supply Chain Communities Governance 2021 SUSTAINABILITY REPORT 35
Pursuing Zero Waste As part of our “Zero Waste” ambition, we aim to divert 90% of GM’s operational waste generation from landfills and incineration, with or without energy recovery, by 2025. Our Zero Waste program was designed to be as comprehensive as possible, incorporating in its scope all solid waste, containerized liquids and hazardous waste. With this program we are helping to drive innovation in the recycling industry, supporting all elements of circular economy. A great example is our innovative project to reuse foundry sand. Our casting plant in Defiance, Ohio, ships their used sand to be reused in our Saginaw Metal Casting Operations (SMCO) in Michigan. The SMCO team tested multiple samples of the used sand from Defiance. In mid-2021, the first load of sand was delivered for a pilot test and the product met all the quality standards. A full reuse program was launched, enabling SMCO to avoid purchasing more than 1,120 tons of new sand. Other benefits include less mining of sand and lower dependency on natural resources, which increases resiliency in our supply chain. GM received 34 environmental sustainability awards recognizing various achievements, including implementing good manufacturing practices. 86.4% 1 2021 Zero Waste performance 1 G M Zero Waste represents the percentage of waste diverted from landfill, incinerators and energy recovery compared to a three-year average (2017–2019) baseline of total operational waste generated. Waste Reduction Across the Enterprise Sustainability is considered everyone’s responsibility at GM. Employees across our business units are highly engaged in our Zero Waste program. For example, at our global headquarters in Detroit, the GM Company Store is our branded merchandise hub for visitors, including auto enthusiasts. In 2021, the store created innovative ways to participate through packaging and environmentally sustainable merchandise, two areas that could have an immediate impact on the store’s environmental footprint. The store implemented environmentally friendly alternatives for all the materials used for packaging and shipping customer purchases. Recycled plastic bags replaced plastic bags; more biodegradable paper tapes replaced plastic tapes; and crinkled recycled craft paper replaced bubble wrap for wrapping fragile items such as coffee mugs. Finally, shipping boxes will contain only recycled cardboard going forward. In sustainable merchandise, the store was proud to launch its first T-shirt featuring the new GM “everybody in” logo on a T-shirt made from 100% recycled fabric. As in the past, innovation, adoption of new technologies and engagement with suppliers both upstream and downstream help us adapt and be a steward in this area. Skip Navigation Introduction Reducing Emissions Design for Environment Technology Customers Safety Diverse Workforce Human Rights Supply Chain Communities Governance 2021 SUSTAINABILITY REPORT 36
PURSUING ZERO WASTE CONT. External Engagement and Partnerships Waste minimization and landfill diversion require partnerships and collaborations throughout the industry. Current partnerships include: • The United States Automotive Materials Partnership LLC (USAMP) Chemical Recycling of Automotive Shredder Residue (ASR) Project has teamed with Eastman Chemical Company and PADNOS to demonstrate that plastics recovered from shredded EoL vehicles can be chemically recycled and used to make new automotive components. USAMP is a subsidiary of the United States Council for Automotive Research LLC, the collaborative technology company of Ford Motor Company, General Motors and Stellantis. The project will strive to minimize mechanical recycling and processing of ASR to prepare it for use as a feedstock for Eastman’s Carbon Renewal Technology processes. • Through the Automotive Industry Action Group (AIAG) and Suppliers Partnership for the Environment, GM leads working groups with other automotive OEMs, including the Sustainable Materials and Packaging Teams. Together, we are defining key terminology and supporting the development of key performance indicators. • The Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) America Recycles Day pledge, for which we collaborate with the EPA and other signatories to enhance the U.S. recycling system, helps to create a resilient path for circular economy to protect the environment. Aiming Higher in South America Our Zero Waste target is more stringent in regions that have already met the 90% goal. For example, the target for GM South America (GMSA) is 95% diversion by 2025. As a leading region in the Zero Waste program, GMSA has achieved this high level of performance through engagement with several internal departments and local suppliers. The strategy involves an advanced environmental sustainability awareness program, reduction of waste, increase in waste sent for recycling, promotion of circular economy, containerization optimization and continuous improvement on manufacturing processes. Corporate Sustainability Employee Engagement In September 2021, a new team was formed to support education and engagement globally. With the goal of empowering employees to champion sustainability in their unique position at GM, the team works with cross-functional subject matter experts and supports internal and external engagement opportunities. One key initiative established in 2021 to drive engagement at GM is the Sustainability Ambassador Program (SAP). The SAP is a diverse group of employees spanning 10 countries and 200 unique GM organizations. Employees in this program have a proven passion and have dedicated time to support GM Sustainability aspirations and the United Nations Sustainable Development Goals (UN SDGs). These employees are advocates for sustainability culture advancement throughout the organization, local sustainability strategists across teams and disrupters of institutional processes. These employees use the network to grow their skill set, support sustainability projects across the company and learn about new teams and initiatives. Ambassadors also include sustainability leads from each of the 11 employee resource groups. The Sustainability Ambassadors meet monthly for fireside Q&As with leaders across the company to learn about advancements and challenges being overcome. To date, leaders from EV battery recycling, Global Purchasing and Supply Chain, Communications, Market Research and more have come to answer questions at this forum. In 2022, there will be more working groups forming through this platform to support sustainability projects across the enterprise. Our global facilities participated in over 200 focused local outreach events supporting environmental education to nearby schools, cleaning up local green spaces like nature preserves and watersheds, and planting native species in their communities. Learn more about other ways GM is engaging our employees . → Skip Navigation Introduction Reducing Emissions Design for Environment Technology Customers Safety Diverse Workforce Human Rights Supply Chain Communities Governance 2021 SUSTAINABILITY REPORT 37
Nature Conservancy Programs We understand the value that natural ecosystems provide, not only to our operations, but also to our lives. To truly embrace our everybody in culture, we develop solutions to preserve biodiversity and restore ecosystems at our facilities and in surrounding communities. These innovations have been implemented through engagements with multiple partners, such as the Wildlife Habitat Council (WHC), the National Wildlife Federation (NWF) and the Living Lands & Waters group. GM has published a Biodiversity by Design catalogue with the WHC that shares construction practices and ideas that support wildlife conservation. As an example, a parking lot at our GM Technical Center in Warren, Michigan, was converted into a green space and planted with native vegetation and pollinators to attract butterfly species. Since 2007, Living Lands & Waters has planted and distributed over 1.6 million trees throughout the Midwestern United States and beyond. GM has sponsored Living Lands & Waters for the past five years and supported its goal to plant more than 1 million trees, increase biodiversity, reduce erosion, improve water and air quality as well as mitigate the impacts of climate change. Since 2017, GM sites across the United States and Canada have received 63,058 trees and planted them on-site, in local green spaces and/or in locations chosen by employees and community partners. WHC certifies land areas that promote wildlife conservation to their set of standards. Through our WHC partnership, GM has achieved: 31 certified programs, the largest within the automotive industry and fourth largest among leading WHC member companies. 17 of those active sites are certified gold programs, the most gold programs of any organization in WHC. Total of 124 biodiversity projects, focusing on educating and avian protection. National Wildlife Federation Our longstanding partnership with the NWF through the GM Eco-Green Schools program provides resources to hands-on environmental projects. Students across the United States participate in wildlife habitat restoration, recycling programs, water preservation and many other sustainability programs. In 2021, more than 2,622 students participated in these projects. GM employees contributed more than 400 volunteer hours to help teachers and mentor students to complete their projects. Thirty-one trees were planted on the George Washington Carver Elementary School campus for Arbor Day with assistance from Arizona Public Service and other community partners. All trees were intentionally picked for their drought resistance and ability to thrive in the desert ecosystem and provide future shade. In 2021, GM celebrated the United Nations (U.N.) World Environment Day by engaging in 103 events globally, involving 33 schools and 2,160 community members. Pictured above is our Bupyeong complex at GM South Korea celebrating World Environment Day. During Earth Day, we launched 62 events globally, engaging with 791 members of the community. One of those events was planting a native species sample at GMSA’s Joinville complex. Skip Navigation Introduction Reducing Emissions Design for Environment Technology Customers Safety Diverse Workforce Human Rights Supply Chain Communities Governance 2021 SUSTAINABILITY REPORT 38
Reducing Water Intensity Water is a scarce resource that we must manage efficiently, especially in water-stressed areas. While GM’s operations are not overly water- intensive, we do use water in the vehicle manufacturing process and make it available for the people in our facilities. We are committed to responsibly using water while taking actions that preserve water quality and support conservation across our operations, in our supply chain and in the communities in which we operate. Our commitment to water stewardship has been recognized by GM being named to CDP’s 2021 Water A List for the third time. GM engages with over 300 suppliers through CDP Water Security Supply Chain and other organizations like AIAG. GM is also a signatory to the CEO Water Mandate—a U.N. Global Compact Initiative— joining other global business leaders to address key challenges around water security and further aligning to the UN SDGs. We are mapping our water progress and achievements against the mandate’s six core target areas: Direct Operations; Supply Chain and Watershed Management; Collective Action; Public Policy; Community Engagement; and Transparency. We are working toward our goal to reduce the water intensity of our operations by 35% by 2035, compared to a 2010 baseline. This target builds on the water conservation work we have done in our GM facilities over the past decade. In 2021, our water intensity was 4.54 cubic meters per vehicle, which is higher than our projected path to meeting our 2035 goal. This was due to lower vehicle production at GM facilities driven by semiconductor shortages and other COVID-related constraints. There is a fixed amount of water that our operations need to run, regardless of the number of vehicles we produce so lower production impacts our water intensity measures. Our water conservation work continues to tackle that underlying water usage and drive down total water usage. GM Water Stewardship Managing water on a local basis whereby each facility sets its own targets for annual improvement according to the level of water stress in their local area. Using the World Resources Institute’s Aqueduct tools that map water risks—floods, droughts and stress—to annually identify risks in current operations with either alternate supply, conservation or water reuse. Focusing on areas within our operations with the greatest water impact, such as vehicle painting operations. SGMW Chongqing plant in China improved their utilization of reclaimed water by expanding use from irrigation and roof cooling to also using the water in their painting operations. Evaluating water usage at the vehicle component level to identify parts that have the highest life cycle water impacts such as structures, seats and drivelines, and working with suppliers to help unlock opportunities for improvement. Engaging employees at manufacturing facilities through water treasure hunts, focused activities where groups come together to seek out new ways to reduce consumption. The GM Tonawanda facility reduced cooling water by over 55,000 cubic meters in 2021 after participating in a water treasure hunt. Water Intensity 1 (m3/vehicle) 2018 2020 2021 2019 1 W ater intensity is a global calculation. 2021 performance was higher than prior years due to lower vehicle production driven by semiconductor shortages and other COVID-related constraints. Goal: Aiming to reduce the water intensity of our operations by 35% by 2035, compared to a 2010 baseline. Skip Navigation Introduction Reducing Emissions Design for Environment Technology Customers Safety Diverse Workforce Human Rights Supply Chain Communities Governance 2021 SUSTAINABILITY REPORT 39
Advancing Transformative Technologies IN THIS SECTION Our Path to EV Leadership 41 Super Cruise and Ultra Cruise Driver 42 Assistance Technology Commercializing Self-Driving Vehicles 43 Urban Solutions for Last-Mile Delivery 45 Our Strengths y Deploying all-electric, self-driving shared vehicles in fleets, through Cruise y Integrating multiple mobility breakthroughs— such as autonomy, sharing and electrification— into a single vehicle, accelerating the acceptance and adoption of each y Creating new urban mobility solutions, such as last-mile delivery and other transportation- related businesses y Advocating for regulations to address the advent of commercial self-driving technologies Our Opportunities y Building trust and understanding among customers for automated driving systems y Developing commercially viable business models for shared mobility solutions Skip Navigation Introduction Reducing Emissions Design for Environment Technology Customers Safety Diverse Workforce Human Rights Supply Chain Communities Governance 2021 SUSTAINABILITY REPORT 40
Image is computer generated Our Path to EV Leadership Transformation and innovation have been part of GM’s DNA for more than 100 years. Today, as we pursue our vision of zero crashes, zero emissions and zero congestion, GM is once again delivering technologies that redefine how people and goods are moved. Our business growth model is predicated on leveraging leading positions in electrification, hydrogen fuel cell, autonomy and connected vehicles—positions that are enabling GM's path to EV leadership. As an example, our new software platform, Ultifi, is made possible by the investments made in GM’s vehicle intelligence platform and position us to scale new software, and services rapidly and securely across our entire fleet. Through software, we expect to unlock new opportunities and experiences for our customers, similar to the way smartphone applications use cameras and sensors to deliver a new communications experience. A vehicle like the Cadillac LYRIQ has up to 15 cameras and more than 100 sensors on board. With Ultifi, we can develop new features and functions that redefine the vehicle experience. This platform is expected to be a key part of our strategy to keep improving our gas-powered portfolio while also helping to create experiences that attract customers to our growing portfolio of electric vehicles (EVs). Currently our Global Innovation Team is conducting a pilot project for a software-enabled platform, currently internally called Future Roads, which provides risk scoring, crash hot spots and seatbelt usage insights leveraging anonymized vehicle data. With these actionable insights, governments can take more effective and cost-efficient steps to create safer and better maintained communities. Over the next few years, we plan to release additional products such as road weather reporting, pothole locations, road roughness and more. Everything In Our advanced propulsion technology platforms present the potential to electrify everything—going well beyond today’s on-road vehicle application. The unique modularity and flexibility of the Ultium platform opens opportunities beyond our own vehicles. Ultium, together with our HYDROTEC fuel cell platform, gives GM the potential to transform a variety of transportation modes into zero-emission products. In 2021, GM made the following moves to extend all-electric solutions beyond automotive vehicles: In early 2022, GM announced plans for multiple HYDROTEC fuel cell-based power generators that provide mobile DC fast charging capability for EVs without imposing on the grid. These HYDROTEC fuel cell generators could ultimately replace gas- and diesel-burning generators with zero-emissions technology in a variety of places, as well as provide backup power during power disruptions. GM has taken a strategic stake in Pure Watercraft, which specializes in creating all-electric boating solutions. The collaboration is expected to leverage Pure Watercraft’s innovative marine propulsion technology and experience in the commercial marine industry with GM’s battery technology, engineering, supply chain and manufacturing capabilities. GM and Liebherr Aerospace signed a joint development agreement to co-develop hydrogen fuel cell-powered aeronautics technology. The companies are expected to work toward the creation of an electrical power generation system that demonstrates how hydrogen fuel cell-based power systems could be used in aircrafts. We have an agreement to supply HYDROTEC fuel cell power cubes to Navistar for use in its production model fuel cell electric vehicle (FCEV)—the International ® RH™ Series. The FCEV is expected to receive energy from two GM HYDROTEC fuel cell power cubes. GM and Lockheed Martin entered an agreement to develop a Lunar Mobility Vehicle to enable astronauts to explore the lunar surface farther than ever before as part of NASA’s Artemis program to send humans back to the moon. GM and Wabtec Corporation have entered into a nonbinding memorandum of understanding to leverage our Ultium battery and HYDROTEC fuel cell technologies for Wabtec locomotives. Skip Navigation Introduction Reducing Emissions Design for Environment Technology Customers Safety Diverse Workforce Human Rights Supply Chain Communities Governance 2021 SUSTAINABILITY REPORT 41
Super Cruise and Ultra Cruise Driver Assistance Technology 1 GM’s strong leadership position in vehicle electrification and connectivity platforms is matched by a similarly strong position in advanced driver assistance technologies, some of which enable hands-free driving under compatible driving conditions. 22 vehicles offered with Super Cruise globally by the end of 2023 10M+ miles have been driven using Super Cruise to date The technologies to support these systems provide the building blocks to leverage across other important applications, including the development of advanced vehicle safety features and fully autonomous technologies. Our move toward such systems began with Super Cruise, the world’s first truly hands-free driver assistance technology, which was introduced in 2017 with the 2018 Cadillac CT6 and provided drivers with more than 140,000 miles of compatible roads in the United States and Canada. In 2019, the road network was expanded to 200,000 miles. Super Cruise will be available on 22 vehicles globally by the end of 2023, including the 2022 Chevrolet Bolt EUV, the GMC HUMMER EV, Cadillac Escalade and many other models. In 2021, we unveiled Ultra Cruise, which will take advanced driver assistance systems (ADAS) technology to the next level. Ultra Cruise is designed to enable door-to-door, hands-free driving in 95% of driving situations, including city streets, subdivision streets and paved rural roads, in addition to highways. Eventually, the technology is expected to expand to every paved road in the United States and Canada. We expect that Ultra Cruise will be one of the premier and most capable ADAS features in the market. Both Super Cruise and Ultra Cruise are expected to leverage the Ultifi software platform and Vehicle Intelligence Platform to enable continuous improvement as each system evolves over time, with more frequent updates adding features, services and functions over-the-air. While Ultra Cruise is expected to be available on select vehicles, Super Cruise is planned to be offered more broadly across GM’s portfolio, expanding access to more customers. 1 A lways pay attention while driving and when using Super Cruise. Do not use a hand-held device. Requires active Super Cruise plan or trial. Terms apply. Automatic Lane Change and Lane Change on Demand are not available while trailering. Skip Navigation Introduction Reducing Emissions Design for Environment Technology Customers Safety Diverse Workforce Human Rights Supply Chain Communities Governance 2021 SUSTAINABILITY REPORT 42
Commercializing Self-Driving Vehicles GM’s path to autonomous vehicles (AVs) is key to achieving our aspiration of enabling a world with zero crashes, zero emissions and zero congestion. GM and Cruise are pursuing what we believe to be the most comprehensive path to autonomous mobility in the industry. Since GM’s 2016 acquisition of Cruise, GM’s majority-owned autonomous startup, Cruise has been developing its core AV technology with safety as its gating metric, while refining its operations to enable its autonomous ride-hail and goods delivery business. In October 2020, Cruise became one of the first California companies permitted by the California Department of Motor Vehicles to test AVs without a trained test driver in the vehicle, and the first company to do so in the complex driving environment of San Francisco. In June 2021, Cruise became the first company to receive a permit from the California Public Utilities Commission (CPUC) to provide passenger test rides in its AVs without a trained test driver in the vehicle. As the first company to receive such a permit, Cruise has been conducting fully driverless rides with the public—completing hundreds of such test rides by the end of 2021. Pending final approval from the CPUC, Cruise is one permit away from being able to commercialize its fully autonomous ride-hail business within its operational design domain in San Francisco. Cruise remains on track to begin charging for fully driverless ride-hail operations in the coming months. Cruise is also continuing to expand its collaboration with Walmart, which invested in Cruise in 2021. Last year, Cruise and Walmart launched a fully autonomous commercial delivery service in Scottsdale, Arizona, with more than 3,000 deliveries completed by the end of 2021. Walmart customers in the area are now able to opt-in to autonomous delivery services and track their order through the Cruise web app 1 . GM and Cruise continue to gain technological expertise and experience, leveraging software and technology innovation combined with GM’s innovation and vast automotive design, engineering, manufacturing, testing, validation and proven quality methods. Together, GM and Cruise’s work is expected to advance both company’s integrated AV strategy while providing maximum flexibility to pursue the most value-accretive path to commercializing and unlocking the full potential of AV technology. Cruise has attracted funding from various third-party investors, including Microsoft and Walmart. GM recently acquired SoftBank's $2.1 billion stake in Cruise, and, separately, invested an additional $1.3 billion, leveraging the strength of our balance sheet to capitalize on the opportunity to increase our equity investment in Cruise and advance our integrated autonomous vehicle strategy. Investment in China China, the world’s largest automotive market, is embracing electrification and autonomous technology faster than anywhere else in the world. In 2021, GM announced a $300 million investment in Momenta to accelerate the development of next-generation self-driving technologies for future GM vehicles in China. GM is collaborating with companies around the world, such as Momenta, to build its technology capabilities and support diverse consumer choices across the globe. Launch timing for the next-generation ADAS technologies that will be deployed in China and other details will be shared closer to production. 1 A vailable on select Apple devices. Service availability, features and functionality vary by vehicle, device and the plan you are enrolled in. User terms apply. Concept vehicle shown. Not available for sale. Skip Navigation Introduction Reducing Emissions Design for Environment Technology Customers Safety Diverse Workforce Human Rights Supply Chain Communities Governance 2021 SUSTAINABILITY REPORT 43
COMMERCIALIZING SELF-DRIVING VEHICLES CONT. Concept vehicle shown. Not available for sale. Shared Mobility Through the Cruise Origin GM and Cruise continue to make progress on the Cruise Origin, a purpose-built, all-electric, fully autonomous vehicle—the result of collaborative efforts among GM, Honda and Cruise. The Cruise Origin represents several aspirations for the future of safe mobility: a vehicle that is shared, autonomous and electric. The Cruise Origin is designed to operate without a steering wheel, pedals or a driver. The vehicle will have more space for passengers and goods. GM and Cruise are working together to create economies of scale that lower costs and increase quality. In the process, this will help enable us to offer a more inclusive mobility option for people such as senior citizens, those with disabilities or those who do not currently have access to reliable transportation. We believe shared mobility offers significant potential to reduce urban congestion. The global population, particularly in cities, is growing rapidly. By 2030, the world is projected to have 41 megacities with 10 million inhabitants or more . Currently, ride-hailing represents only a small fraction of vehicle miles driven in the United States, and most privately owned vehicles spend most of their time unused. By encouraging passengers to ride together in shared cars and shuttles, ride-hailing can further increase efficiency and reduce congestion. Another potential benefit of the Cruise Origin is more affordable transportation. A fully autonomous vehicle eliminates certain expenses associated with traditional, conventional ride-hailing with a human driver. With a lower cost structure, an autonomous ride-hail and delivery service can charge less and be available for more communities. GM currently is manufacturing pre-production of Cruise Origin at GM’s Global Technical Center in Warren, Michigan, and is on track to begin production by the first quarter of 2023 at GM’s Factory ZERO in Detroit, Michigan. Skip Navigation Introduction Reducing Emissions Design for Environment Technology Customers Safety Diverse Workforce Human Rights Supply Chain Communities Governance 2021 SUSTAINABILITY REPORT 44
1 G M estimate of up to 250 miles on a full charge, subject to change. GM estimated range based on current capability of analytical projection consistent with Society of Automotive Engineers J1634 revision 2017—MCT. Actual range may vary based on several factors, including temperature, terrain, battery age, loading, and how the vehicle is used and maintained. BrightDrop Zevo 600 vehicle used by FedEx Express. Urban Solutions for Last-Mile Delivery The World Economic Forum estimates that demand for urban last-mile delivery, fueled by e-commerce, will grow by 78% by 2030, leading to a 36% increase in delivery vehicles in the world’s top 100 cities—further exacerbating urban congestion and pollution. This increase in demand is expected to cause delivery-related carbon emissions to rise by 21% and add 11 minutes to each passenger’s commute. Third-party logistics companies, which manage fleets of many thousands of vehicles, are on the front lines of these challenges, rising to meet demand while addressing the associated increases in emissions and congestion. In addition, these companies are faced with labor shortages and occupational injuries due to the physical strain of handling packages. Curb management is also a safety consideration. On congested urban streets, a parked delivery vehicle can create traffic hazards, while the manual unloading of packages can clog sidewalks and bike lanes, and present bicyclist and pedestrian safety concerns. Our solution to these challenges is BrightDrop, an internal startup devoted to decarbonizing last- mile deliveries through an ecosystem of electric products, software and services that empower companies to move goods more efficiently. BrightDrop is designed to help businesses lower their ownership and operating costs, maximize labor productivity and improve employee safety and freight security—all while operating with products that work together intelligently and with zero operating emissions. BrightDrop launched publicly in 2021 and introduced its first products, the Zevo 600, an electric light commercial vehicle (eLCV) built for the delivery of goods and services over long ranges 1 , and the Trace. The Trace is a smart, electrically propelled cart that helps reduce time and physical effort required for couriers to get goods from the delivery van to customers. A customer field test demonstrated 25% improvement in package delivery volumes per route, enabling the reduction of total vehicles in use. The Trace can also enable multimodal delivery models where vehicles drop off the Traces and foot or bike couriers can then complete the final delivery, further reducing congestion and operational costs. The Trace can be used as a standalone product or can be coupled with the Zevo 600. 25% improvement in package delivery volumes per route, based on a customer field test Skip Navigation Introduction Reducing Emissions Design for Environment Technology Customers Safety Diverse Workforce Human Rights Supply Chain Communities Governance 2021 SUSTAINABILITY REPORT 45
URBAN SOLUTIONS FOR LAST-MILE DELIVERY CONT. The Zevo 600 is the fastest vehicle program to market in GM’s history Record-setting development timeline of just 20 months enabling delivery of our first units in December 2021 BrightDrop completed the first production builds of the Zevo 600 in September 2021, making the Zevo 600 the fastest vehicle program to market in GM’s history. The record- setting development timeline of just 20 months was made possible by leveraging the highly flexible Ultium battery platform, innovative virtual development processes established by the GMC HUMMER EV program and an agile approach to manufacturing development. The timetable enabled delivery of the first few of 500 eLCVs to FedEx Express, BrightDrop’s first customer, in December. Also in 2021, BrightDrop unveiled the Zevo 400, a smaller eLCV. Verizon, one of the largest fleet operators in the United States, is the first customer slated to integrate the Zevo 400 into its field maintenance and service fleet. The Zevo 400 combines many of the same features of the Zevo 600, but its smaller size enables enhanced curb management, maneuverability and the ability to fit into a standard-size parking space—a benefit for customer operations and a key feature to help reduce street congestion in urban areas. In early 2022, BrightDrop also added Walmart as a customer, with the retailer reserving 5,000 units of BrightDrop’s Zevo 600 and smaller Zevo 400 electric delivery vans to be ordered. The units will support Walmart’s last-mile delivery network and goal of operating an all-electric logistics fleet by 2040. BrightDrop is an example of how we are leveraging technology platforms into new markets while also leveraging GM’s ability to execute at scale. We are converting our CAMI manufacturing plant in Ingersoll, Ontario, to produce the BrightDrop eLCVs. Skip Navigation Introduction Reducing Emissions Design for Environment Technology Customers Safety Diverse Workforce Human Rights Supply Chain Communities Governance 2021 SUSTAINABILITY REPORT 46
Cadillac CT6 EV Earning Customers for Life IN THIS SECTION Customer Experience 48 Customer Trust & Satisfaction 49 Quality Assurance 50 Dealer Quality Programs 51 Our Strengths y Building upon strong performance where customers are willing to recommend our brands based on their experiences y Continuing to leverage digital solutions to simplify interactions, increase value and deliver world-class experiences y Continuing to strengthen our commitment to building quality vehicles Our Opportunities y Helping dealers and employees to adjust to automotive trends, such as the transition to selling electric vehicles (EVs), in order to meet customer expectations y Ensuring the same high-level quality vehicles as we deploy increasing levels of advanced technology y Maintaining consistent experiences across thousands of customer interactions worldwide Skip Navigation Introduction Reducing Emissions Design for Environment Technology Customers Safety Diverse Workforce Human Rights Supply Chain Communities Governance 2021 SUSTAINABILITY REPORT 47
Quotes are sourced from Clarabridge customer feedback management tool and are intentionally anonymized. Customer Experience Our Customer Experience (CX) Team’s purpose is to create safe and effortless experiences that customers actually love. We aim to deliver experiences that feel simple, convenient, human, satisfying, and beautiful. I appreciate the courteous, knowledgeable customer service representative who addressed my questions and provided me with a year-long plan at a better rate. 03/23/2022 Love this BUICK app 1 easy to use and has all my car’s information. 11/02/2021 Fleet Opps Advisers always do a great job of helping me do my job! 03/23/2022 In 2021, the CX Team, working cross-functionally with our internal and external partners, have designed, developed and launched more than 2,000 customer-impacting improvements touching digital customer interfaces, contact centers, brand sites and GM’s loyalty program. A few of those improvements include new dynamic content in the mobile app 1 , an all new e-commerce platform allowing customers to purchase replacement parts online and a customer self-service hub built into the brand websites. We also make great efforts to ensure our customers can share their feedback with us through the GM Customer Assistance Center. Our Customer Assistance Center is integrated with our U.S. dealer network, field organization, technical and parts assistance, engineering, product quality teams and OnStar and Roadside teams. GM customers can easily report a suggestion, concern or comment through the web channel, email address or phone hotline. This highly dedicated global team supports over 2.5 million interactions monthly to quickly account for feedback and help resolve concerns. In addition to listening to customers through the Customer Assistance Center, GM has launched a new customer feedback management tool that aggregates millions of comments from customers across all channels. The intelligence of this tool allows us to listen to customers, identify opportunities and proactively reach out to support customers as well as continually feed the insights internally to improve our products, services and experiences. Rewarding Loyalty My GM Rewards program, the most comprehensive automotive loyalty program, allows enrolled members to earn and redeem points on eligible purchases, including new GM vehicles, parts, accessories, paid dealer services and OnStar and Connected Services plans. In 2022, we launched an all new rewards program featuring three membership tiers and new ways to earn and redeem. ~6M cumulative members enrolled in the My GM Rewards program. 2 1 A vailable on select Apple and Android devices. Service availability, features and functionality vary by vehicle, device and the plan you are enrolled in. User terms apply. 2 2 018–2021 year-end. Skip Navigation Introduction Reducing Emissions Design for Environment Technology Customers Safety Diverse Workforce Human Rights Supply Chain Communities Governance 2021 SUSTAINABILITY REPORT 48
Customer Trust & Satisfaction We put customers at the center of everything we do and strive to deliver the highest possible levels of product quality. Our focus on product quality and our customers aligns the entire company behind the goal of exceeding customer expectations and providing them with the best overall experience. GM brands, products and services aim for benchmarks in studies measuring product quality and consumer satisfaction. Vehicle Development Process Our focus on the customer defines how we develop, engineer and manufacture our vehicles with quality and durability goals in mind, starting with the vehicle development process. We harness customer feedback from global markets to help shape our customers’ product experience, using our GM Compass customer survey to gather preferences on a variety of issues—from performance and efficiency to how people interact with their vehicles. The Global Vehicle Development Process is rooted in a cultural commitment to design, engineer and build quality vehicles. Building upon GM’s “Who We Are” and “How We Behave” foundational statements, employees are committed to a goal of delivering quality as a value supported by key initiatives and behaviors. This commitment involves three elements: Product Safety , which includes our Speak Up For Safety program, Safety Field Investigation processes, Prevent Repeat Defects process and Safety Incident Protocols. The Speak Up For Safety program and Safety Field Investigation processes help identify and investigate potential issues. Prevent Repeat Defects is one of the approaches we use to help confirm field learnings are captured in our standard work to prevent the issue from reoccurring. Systems Engineering , which uses a systems approach to translate our customers’ needs into industry-leading vehicle designs. IT-based systems help map, flow and trace requirements across engineering organizations to help ensure our products are safe, reliable and win in the marketplace. Quality Chain is an integrated approach to connecting quality tools and methods that enables cross-functional team collaboration to mitigate defects from reaching our customers. This is executed by connecting vehicle-level requirements to system, subsystem and component levels. This helps drive enterprisewide engagement so design and process issues can be mitigated across all systems and processes. We also emphasize systems engineering companywide. This includes requiring all people to practice the discipline of systems thinking, understanding how their individual roles contribute to the bigger picture, rather than thinking in silos. GM also has quality tools that work as interconnected processes and cross system and organizational boundaries. Using these tools together helps us build discipline into our process for identifying and addressing failure modes. These product development centric elements are foundational and complemented by our Launch Excellence initiative. The initiative uses affinity diagrams to help teams focus on what must be true in terms of process and discipline to successfully navigate vehicle development. Beginning with 2022 model year vehicles, a new warranty was announced in the United States and Canada that will provide coverage for any seatbelt or airbag system for six years or 72,000 miles, whichever comes first. Skip Navigation Introduction Reducing Emissions Design for Environment Technology Customers Safety Diverse Workforce Human Rights Supply Chain Communities Governance 2021 SUSTAINABILITY REPORT 49
Quality Assurance Our quality policies and philosophy of continuous improvement help us shape our customers’ product experience. All GM suppliers are required to be ISO 9000 certified—a set of international standards on quality management and quality assurance. Likewise, all manufacturing operations that require International Organization for Standardization (ISO) 9001:2015 certification by certain regions/countries have done so. Globally, we have transitioned to the new ISO 9001:2015 standard, which is aligned with the most recent trends. Fifty-two operations have completed the transition and certification through 2021. We have nine component plants certified to the International Automotive Task Force (IATF) 16949 standards. We also maintain a Global Manufacturing System that incorporates all ISO and IATF requirements, guides quality aspects of our business and has more rigorous standards, in some cases, than external ones. A focus of our quality assurance programs is “initial quality,” which refers to vehicle issues that customers may experience in the first months of ownership. In recent years, customer convenience features, such as user-friendly infotainment systems, seat comfort or placement of knobs and handles, have emerged as top initial quality issues rather than component-related issues. We measure our performance in this area through a key metric: J.D. Power Initial Quality Study (IQS) Problems Per Hundred. Vehicle Quality and Satisfaction Recognitions J.D. Power 2021 IQS Segment Award Winners Cadillac CT5 (Midsize Premium Car) and Chevrolet Corvette (Premium Sporty Car) J.D. Power 2021 U.S. Automotive Performance, Execution and Layout Study Segment Award Winners Cadillac CT5 (Midsize Premium Car), Chevrolet Corvette (Premium Sporty Car), Chevrolet Blazer (Midsize SUV), Chevrolet Tahoe (Large SUV) and GMC Sierra HD (Large HD Pickup) J.D. Power 2022 Vehicle Dependability Study Segment Award Winners Buick Encore (Small SUV), Buick Envision (Compact SUV), Chevrolet Impala (Large Car), Chevrolet Suburban (Large SUV) and Chevrolet Silverado HD (Large HD Pickup) Skip Navigation Introduction Reducing Emissions Design for Environment Technology Customers Safety Diverse Workforce Human Rights Supply Chain Communities Governance 2021 SUSTAINABILITY REPORT 50
Dealer Quality Programs Putting customers at the center of everything we do extends to the experience they have when visiting GM dealerships. It is foundational that dealerships deliver a consistent level of sales and aftersales excellence to earn and maintain customer trust. We also maintain the Mark of Excellence program, which annually recognizes high- achieving dealers, as well as specific employees and teams at dealers. Out of GM’s 4,048 Chevrolet, Buick, GMC and Cadillac dealerships across the United States, 3,165 dealers and 68,403 dealer employees were enrolled in the 2021 Mark of Excellence program. We provide both technical and nontechnical training to help our dealers meet or exceed their customers’ expectations. This training includes modules for sales, finance, front office and management staff; apps for sales and service; both online and hands-on training for technicians; and interactive job aids or reference documents to help reinforce what they’ve learned. Departments within the dealership relating to sales must maintain a certain level of training performance each quar ter. Training requirements for service technicians include third-party Automotive Service Excellence certification, an industry-standard and customer-recognized seal of quality. In addition, technicians who have achieved GM World Class Technician status have completed over 435 hours of training. U.S. Dealer Quality Programs 1 There are two elements of quality management systems that help us achieve this consistency across dealers: facility/customer experience conformance and sales performance. These elements are measured over five Dealer Quality programs: The Standards for Excellence (SFE) program Measures dealers’ and sales consultants’ sales performance. Out of GM’s 3,855 Chevrolet, Buick and GMC dealerships, 3,343 dealers and more than 26,378 sales consultants were enrolled in the 2021 SFE program. The Essential Brand Elements (EBE) program Measures a dealer’s conformance to a defined facility image as well as conformance to specific customer-related brand standards. Out of GM’s 3,855 Chevrolet, Buick and GMC dealerships, 3,044 dealers were enrolled in the 2021 EBE program. The EV Experience (EVX) Provides CX standards to assist dealers in offering EV customers an educational and transparent experience in their shopping and purchase of an EV. Includes specific training, equipment, tools and advertising guidelines. The EVX program also includes a sales performance opportunity for the EV specialist at the dealership. Out of GM’s 3,834 dealers that have either a Chevy and/or GMC franchise, 2,867 are enrolled. The Parts and Service Excellence (PASE) incentive Designed to pull together many key aftersales metrics under one program to win customers for life. Out of GM’s 4,048 dealerships, there are 3,780 enrolled in the PASE program. Project Pinnacle The goal of Project Pinnacle is to drive dealer engagement in providing a customer experience in line with the luxury competitive set. Out of GM’s 564 Cadillac dealerships, there are 523 enrolled in the Cadillac Pinnacle program. 1 E nrollment in these programs is voluntary, and enrollment numbers change periodically based on dealer participation. The variable compensation of each dealership depends on the level of achievement under the SFE and EBE programs. Skip Navigation Introduction Reducing Emissions Design for Environment Technology Customers Safety Diverse Workforce Human Rights Supply Chain Communities Governance 2021 SUSTAINABILITY REPORT 51
Keeping People Safe IN THIS SECTION Vehicle Safety 53 Developing Safe Products 54 Culture of Safety 59 Our Strengths y Putting forth our safety brand, Periscope, which integrates advocacy, research and technology to help illustrate the importance we place on vehicle safety y Broadening our internal view of safety to include other aspects of well-being, including physical health, mental health and inclusion y Applying workplace best practices and educating GM leaders and team members on the power they have to affect safety outcomes by modeling safe behaviors and business practices y Continued engagement from a global workforce on the topics of vehicle and personal safety Our Opportunities y Addressing driving behaviors that are often beyond our control, such as driver distraction and impairment y Educating consumers on the benefits and features of the advanced driver assistance systems (ADAS) on their vehicles to encourage greater adoption Skip Navigation Introduction Reducing Emissions Design for Environment Technology Customers Safety Diverse Workforce Human Rights Supply Chain Communities Governance 2021 SUSTAINABILITY REPORT 52
Vehicle Safety Our safety brand, Periscope, helps customers see how GM looks at safety, holistically. Periscope is how we engineer for safety through a human lens—focusing on driver behaviors and the driving environment, and developing features and technologies that can assist the driver and help keep customers safe. Periscope brings together safety research, advocacy and technology to focus on the safety of drivers, passengers and those outside the vehicle. Part of our safety research is work with world-renowned universities and institutes, including the Virginia Tech Transportation Institute (VTTI) and the University of Michigan Transportation Research Institute (UMTRI). Our safety advocacy supports nonprofit organizations, including Safe Kids Worldwide. And, our development of in-vehicle technologies can help drivers avoid crashes, reduce injuries and save lives. A Holistic Approach to Vehicle Safety Periscope embodies safety from three perspectives Zero Crashes The Vehicle Engineering advanced technologies and features. The Driver Education and advocacy to help reduce driver error and risky driving behaviors. The Environment Leveraging renowned research partnerships to help influence vehicle and driving policies to make city and community infrastructures safer. GM has a rich history of safety innovation—from the first production airbag systems in the 1970s to today’s Super Cruise feature, which uses a series of escalating alerts (including a steering wheel light bar) to prompt the driver to pay close attention to the road ahead (monitored by a Driver Attention System face camera) and take steering control whenever take-over requests are issued. Chevrolet safety engineer helping her teenage daughter learn to drive using Chevrolet teen driver technology. Skip Navigation Introduction Reducing Emissions Design for Environment Technology Customers Safety Diverse Workforce Human Rights Supply Chain Communities Governance 2021 SUSTAINABILITY REPORT 53
→ Developing Safe Products As we continue to transform mobility through new technology platforms, we are committed to incorporating safety every step of the way. The safety of our employees and customers is of the utmost importance. Decision-making for safety issues includes executives at the highest levels of the company and engages employees at every level to identify potential vehicle safety issues. The vice president of global product safety and systems leads the product safety organization and is accountable for developing GM’s vehicle safety systems, confirming and validating our vehicle safety performance, identifying emerging issues and conducting field actions, including recalls. Global Product Safety Management Process INVESTIGATE & ANALYZE Robust teams of internal product investigators and safety forensic engineers help identify and investigate potential vehicle safety issues. A data analytics team merges multiple inputs—such as Speak Up For Safety submissions and dealer service records—to build a unique, comprehensive database. Through statistical analysis and machine learning models, potential issues are identified early by linking key information from disparate data sources. REVIEW Appropriate levels of management, up to senior leadership, review issues. When a decision is made for a recall, a cross-functional team initiates all necessary actions to inform appropriate government agencies, dealers and customers. EXECUTE The team supplies a remedy to the customer free of charge and provides follow-up communication to customers to encourage them to get the repair. Completion rates are monitored and shared where appropriate with government agencies. Meanwhile, Global Product Safety and Systems improves cross-system integration and addresses functional safety and compliance in the vehicle development process. GM Safety & Noncompliance Recalls (Number of Recalls) Number of Global Recalls with <10,000 Vehicles Global recalls that involve fewer than 10,000 vehicles are one way we measure the effectiveness of our safety quality management process. The ability to catch more issues early—with a relatively low volume of vehicles affected—and act swiftly is positive. The data above is also included in the total vehicle volume of safety and noncompliance recalls. GM Safety & Noncompliance Recalls (Vehicle Volume in Millions) 2020 2021 1 2019 2018 2017 1.8 1.6 8.6 7.3 4.2 2.2 2.1 1.4 9.7 9.3 Global North America 1 Includes 7M Takata airbag-related recalls. Learn more about our product development process in Earning Customers for Life . Skip Navigation Introduction Reducing Emissions Design for Environment Technology Customers Safety Diverse Workforce Human Rights Supply Chain Communities Governance 2021 SUSTAINABILITY REPORT 54
Speak Up For Safety Our Speak Up For Safety program is designed to give employees, customers, suppliers and dealers an easy, consistent and unfiltered way to report potential vehicle safety issues and suggest improvements. Concerns can be submitted through a toll-free phone number, a smartphone app, email or the Speak Up For Safety website . We view Speak Up For Safety submissions by our employees as a measure of employee engagement in safety issues. Additionally, to reinforce a sense of personal accountability, employees’ performance is evaluated in part on a demonstrated commitment to safety. Our dedicated safety team funnels concerns to the appropriate departments where they are evaluated, addressed and, where necessary, escalated. By building a culture of safety, we attempt to find issues sooner and reduce the number of impacted vehicles. For more information see the Global Product Safety Management Process table . Externally, GM maintains an open dialogue with the National Highway Traffic Safety Administration (NHTSA), including regularly scheduled meetings with senior agency officials. Expedited discussions, as needed, cover field investigations, safety recalls and other identified issues. GM also participates in meetings with NHTSA and other stakeholders to advance safety discussions that benefit the industry as a whole. Engineering Advanced Technologies and Features In our pursuit of a world with zero crashes, we will continue to provide foundational vehicle safety through crash performance, thoughtful reminders, technology to help avoid or mitigate crashes and other safety innovations. Even with the latest advancements in vehicle safety technology, seat belts remain the primary occupant restraint in the vehicle and can help save lives when properly worn. 1 In 2020, NHTSA estimated that front seat belt use is about 90% 2 in the United States, yet almost half of in-vehicle fatalities are unbelted occupants. For this reason, increasing seat belt use remains a priority at GM, and we are expanding our Buckle to Drive feature to more models. When turned on, this feature can prevent the vehicle from being shifted into gear for up to 20 seconds while reminding unbelted drivers to buckle their seat belt through a chime and a visual message. 1 A lways use seat belts and child restraints. Children are safer when properly secured in a rear seat in the appropriate child restraint. See the Owner’s Manual for more information. 2 Visit https://www.nhtsa.gov/risky-driving/seat-belts for more details. DEVELOPING SAFE PRODUCTS CONT. 4,103 average annual from 2018–2021 35,842 since program inception 2,979 in 2021 Speak Up For Safety submissions Skip Navigation Introduction Reducing Emissions Design for Environment Technology Customers Safety Diverse Workforce Human Rights Supply Chain Communities Governance 2021 SUSTAINABILITY REPORT 55
DEVELOPING SAFE PRODUCTS CONT. Helping drivers avoid crashes is another GM priority. ADAS innovations are already available today that represent significant steps toward avoiding crashes. For example, under certain conditions, Automatic Emergency Braking (AEB) 1 can help avoid or reduce the harm caused by striking the rear end of a detected vehicle ahead. AEB automatically provides hard emergency braking or enhances the driver’s hard braking if the system detects such a collision is imminent under certain conditions. Similarly, Lane Keep Assist with Lane Departure Warning 1 provides gentle steering wheel turns to help keep the driver from inadvertently leaving their lane. Through building-block changes such as these, drivers are increasingly aided in helping to avoid or mitigate the harm caused by common crashes. Global Deployment of ADAS 1 Number of models with these technologies available or as standard equipment out of 71 total models 50 Forward Collision Alert 26 Safety Alert Seat 43 Lane Keep Assist With Lane Departure Warning 29 HD Surround Vision 10 Lane Departure Warning 41 Rear Cross Traffic Alert 33 Adaptive Cruise Control 45 Front Pedestrian Braking 47 Enhanced Automatic Emergency Braking or Automatic Emergency Braking 42 Lane Change Alert With Side Blind Zone Alert or Side Blind Zone Alert Education and Advocacy GM recognizes the need to continue building public awareness of roadway safety risks by promoting safe driving behaviors and a safe roadway environment. We invest in nonprofit relationships and initiatives to promote good behaviors such as seat belt usage and educate on the dangers of impaired and distracted driving. Examples of current relationships and initiatives include: For more than 20 years, GM and Safe Kids Worldwide have collaborated to help keep kids safe in and around vehicles through many programs, like the GM-funded Buckle Up Program. The Buckle Up Program works through a nationwide coalition to provide inspection stations and free car seat check-up events throughout the year. In fact, over 30 of our own GM employees are trained as certified Child Passenger Safety Technicians and also volunteer their time to support these car seat check-up public events. Directed toward the teen driver, GM partners with National Organizations for Youth Safety to implement the annual Seat Belts Save (SBS) Challenge. SBS is a four-week campaign designed to educate teens about the dangers of riding in a vehicle without wearing a seat belt and to increase the number of teens who regularly wear a seat belt while driving or riding in a vehicle. America Walks is leading the way in advancing safe, equitable, accessible and enjoyable places to walk and move by giving people and communities the resources to effectively advocate for change. GM supports America Walks to ensure pedestrians are equipped with resources to remain safe when sharing roadways with motorists, bicyclists and others. In 2021, GM provided grant funding in support of Project Look Out, a U.S.- based media campaign aimed at preventing distracted driving. GM support aided Project Look Out in moving from its development phase to its implementation phase. Learn more. 2023 Cadillac LYRIQ Debut Edition available Summer 2022, by reservation only. Additional LYRIQ models available starting Fall 2022. See dealer for details. 1 S afety or driver assistance features are no substitute for the driver's responsibility to operate the vehicle in a safe manner. The driver must remain attentive to traffic, surroundings and road conditions at all times. Visibility, weather and road conditions may affect feature performance. Read the vehicle's owner's manual for more important feature limitations and information. Skip Navigation Introduction Reducing Emissions Design for Environment Technology Customers Safety Diverse Workforce Human Rights Supply Chain Communities Governance 2021 SUSTAINABILITY REPORT 56
DEVELOPING SAFE PRODUCTS CONT. Leveraging Renowned Research Periscope’s focus on research identifies which technologies may have a significant impact on reducing crashes and injuries. GM works with world-class research institutes to study how safety technologies currently available in vehicles are making a real-world difference on the path to a world with zero crashes. We have collaborated with organizations such as NHTSA, UMTRI, Insurance Institute for Highway Safety and the Highway Loss Data Institute. Following a landmark police report study conducted in 2019, GM continued to work with UMTRI to analyze the field effectiveness of a wide range of GM ADAS and headlighting technology in addressing rear-end striking, pedestrian, lane departure, lane change and backing crashes. In the latest study, UMTRI performed an analysis using over 10.9 million GM Model Year 2013–2020 vehicles along with police reports from 14 states. After comparing the crash instances involving vehicles with and without ADAS features, the study provided further evidence that much of this technology is making a proven impact, with statistically significant results, to help reduce crashes or mitigate injuries when crashes do occur. (Please see UMTRI-2022-2 report for further details.) Because a key purpose of ADAS features is to alert the driver to potential crashes, how the driver is alerted and how the driver responds also play an important role to help ensure feature effectiveness in the field. 1 GM has conducted significant research to determine how best to communicate those alerts to the driver so that they can take action to help avoid a crash threat. For example, the GM-exclusive Safety Alert Seat 1 was developed with research conducted by TNO in the Netherlands, as well as with the VTTI. The Safety Alert Seat provides directional seat vibrations to help alert drivers of the direction of potential crash threats detected by various active safety systems. This haptic alert supplements provided visual alerts and has been shown to be preferred by our customers and to increase usage of ADAS that employ the technology. To learn more about UMTRI please visit https://www.umtri.umich.edu Effectiveness of ADAS Front Pedestrian Braking 1 reduced frontal pedestrian crashes by 23% IntelliBeam 1 , or auto high beam highlighting, reduced a combined set of frontal animal, pedestrian and bicyclist crashes by 22% Lane Keep Assist with Lane Departure Warning 1 reduced roadway departure crashes by 17%, and reduced such crashes with reported suspected minor injury or higher injury severities for anyone in the crash by 21% AEB 1 (or Forward Automatic Braking 1 ) with Forward Collision Alert 1 reduced rear end striking crashes by 41%, and reduced such crashes with reported suspected minor injury or higher severities for anyone in the crash by 55% Lane Change Alert with Side Blind Zone Alert 1 reduced lane change crashes by 16% The Reverse Automatic Braking 1 feature, combined with Rear Vision Camera, 1 Rear Park Assist 1 and Rear Cross Traffic Alert 1 reduced backing crashes by 83% 1 S afety or driver assistance features are no substitute for the driver's responsibility to operate the vehicle in a safe manner. The driver must remain attentive to traffic, surroundings and road conditions at all times. Visibility, weather and road conditions may affect feature performance. Read the vehicle's owner's manual for more important feature limitations and information. Edition 1 Pickup limited availability by waitlist. Additional GMC HUMMER EV models available Fall 2022. All results shown are from a research study conducted with UMTRI . 2022 GMC HUMMER EV Pickup Skip Navigation Introduction Reducing Emissions Design for Environment Technology Customers Safety Diverse Workforce Human Rights Supply Chain Communities Governance 2021 SUSTAINABILITY REPORT 57
DEVELOPING SAFE PRODUCTS CONT. OnStar Safety Innovation Periscope’s holistic view of safety extends to OnStar, our safety and security service. For years, OnStar has helped customers primarily by responding to crashes or vehicle issues. Today, the service is expanding beyond both the vehicle and GM customers through the OnStar Guardian mobile phone app 1 . The app enables customers to access certain OnStar support services whether at home, out walking or in any vehicle, regardless of brand or ownership. In 2021, we expanded the availability of the app to GM customers in Mexico and made it available to anyone in the United States and Canada with a compatible Apple or Android device. Also in 2021, OnStar and RapidDeploy, a public safety technology company working to accelerate Next Generation 911, launched a first-of-its-kind program to supply every 911 call center in California with OnStar’s Automatic Crash Response notifications. The certified emergency OnStar advisor will coordinate with the appropriate 911 center for rescue and response. In addition, GM invested in RapidDeploy, which will enable the company to improve the public safety community’s situational awareness with a cloud-native, data-driven solution. This investment underscores GM and OnStar’s commitment to working with the public safety community to support and accelerate Next Generation 911. Incorporating Safety Into Electric and Autonomous Vehicles (EVs and AVs) Safety is of equal priority and importance in the design of both EVs and internal combustion engine (ICE) vehicles. We have a dedicated high-voltage battery safety team that works to help protect the battery in a crash, which is similar to how we approach protecting fuel systems in ICE-powered vehicles. Our batteries are packaged below the seating area and are designed to be an integral part of the vehicle structure safety cage that helps to protect the occupants in the event of a crash. We assess the crash performance of the unique characteristics of a high- voltage battery system, and our vehicles are designed to shut down and isolate the electrical system in the event of a crash or flood to avoid the risk of electrical shock. We play key roles in leading standards committees on battery safety through organizations like the Society of Automotive Engineers International and intend to remain an industry leader in this area. Our safety research and development extends to self-driving autonomous technology. AV development reflects all 12 safety elements in the NHTSA voluntary guidance, Automated Driving Systems 2.0—A Vision for Safety. Across the country, state and federal regulators and legislators are actively considering how to help foster and shape the evolution of AVs. GM is engaged with policymakers to advance AV-enabling legislation and regulations. In particular, we are focused on discussing our mobility offerings with city officials across the United States and around the world, given that urban settings are the environment in which our AVs will first launch commercially. 1 A vailable on select Apple and Android devices. Service availability, features and functionality vary by vehicle, device and the plan you are enrolled in. User terms apply. Skip Navigation Introduction Reducing Emissions Design for Environment Technology Customers Safety Diverse Workforce Human Rights Supply Chain Communities Governance 2021 SUSTAINABILITY REPORT 58
A Culture of Safety Our workplace safety vision is to “Live values that return people home safely. Every person. Every site. Every day.” This vision is guided by our safety policy, which applies to all employees and others working at our sites, including consultants, agents, sales representatives, distributors, independent contractors, third-party suppliers who work on GM premises and contract workers when performing work for GM. Workplace safety is governed at the highest levels of the company through monthly operating reviews with global functional senior leaders, including the CEO and the Global Safety Leadership Council (GSLC), which comprises more than 20 senior global leaders. The GSLC determines strategic global safety direction and approves workplace safety initiatives, both of which are the responsibility of the vice president, Global Workplace Safety, who also provides a bimonthly update on the company’s safety performance to the Board. Enterprise workplace safety risks and control initiatives are reviewed on an annual basis, and updates are provided to the Board’s Risk and Cybersecurity Committee. Workplace safety reviews are also a part of every meeting of the full Board. In 2021, COVID-19 continued to be a major focus of workplace safety management. We continued to align our practices with the protocols of each country where GM operates. GM employees were also encouraged to receive the COVID-19 vaccine, and GM partnered with health systems, local health departments and national pharmacies to offer and administer the vaccine to employees. GM also published a vaccine guide for employees and continues to update a COVID-19 Employee Guide, which contains preparedness measures and a response plan for all employees. All employees are required to undergo training for COVID-19 protocols. Additionally, applying the “work appropriately” philosophy has helped us reduce employee exposure to COVID-19. Where the work permits, employees have the flexibility to work where they can have the greatest impact on advancing our goals. Skip Navigation Introduction Reducing Emissions Design for Environment Technology Customers Safety Diverse Workforce Human Rights Supply Chain Communities Governance 2021 SUSTAINABILITY REPORT 59
A CULTURE OF SAFETY CONT. Global Workplace Safety (GWS) Strategy Our comprehensive GWS strategy highlights five key focus dimensions, seen at left, that will enable us to achieve our vision to return people home safely as we aspire to zero injuries and fatalities. We have a five- year plan for each of these dimensions, which is refreshed annually with new initiatives to help us continuously improve and make progress toward this vision. The five dimensions include: Culture: An Enterprise Safety Culture We strive for a culture where each person decides to keep themselves and their team members safe. In 2021, we continued our focus on how senior management can lead safety. To help create mindsets where people consider safety and health in all that we do, a new process called Safety and Health In Everyday Leadership Discussions (SHIELD) was implemented for use by senior leaders in meetings where strategic business decisions are made. During safety moments, in lieu of a traditional message, senior leaders ask probing questions within agenda topics of discussion to help create awareness and understanding of potential safety impacts. Using the SHIELD process has increased safety engagement during meetings and in overall decision-making. The Manufacturing Leadership Team is also focused on improving the effectiveness of High-Risk Global Performance Standards, which address pedestrian/vehicle interaction, electrical safe work practices, lockout energy control and fall protection practices. Senior leaders visited 26 manufacturing and nonmanufacturing sites and conducted small group discussions and floor walks. As a result of these visits, senior leaders gained a deeper understanding of how standards are being applied and provided additional support to strengthen relationships and grow our safety culture. The Employee Safety Concern Process is the most efficient way to identify and resolve workplace safety concerns. The process provides a structure for employees at manufacturing sites and office environments to report potential safety issues . Knowledge: Hazard and Risk Identification We aim for every person, at every site, to be able to recognize hazards, understand risk levels and feel empowered to address safety concerns. In 2021, learning topics that impact serious injuries and fatalities (SIF) potential (e.g., Pre-task Planning, Management of Change and Lockout Energy Control) were conducted in more interactive, conversational forums versus traditional classrooms. Overconfidence, normalization of deviance and other biases which often lead to perceptual distortion and poor judgment were explained and openly discussed. This helps employees recognize situations where they may be inadvertently putting themselves or others in harm’s way. Systems: Workplace Safety Systems Our global safety management system, Workplace Safety System (WSS), drives continuous improvement in all five global workplace safety dimensions: Culture, Risk Mitigation, Systems, Data and Knowledge. The system is aligned with our continuous improvement philosophy and with internationally recognized standards such as ISO 45001. In 2021, our sites continued maturing and improving their WSS. Additionally, a cross- functional team collaborated to improve our safety governance system to align and interconnect site, regional and global safety boards. Efforts were focused on reducing SIF potential and supporting our performance assurance processes. In 2021, we emphasized continued improvement on safe decision-making skills at the site level. Following a global effort in 2020 to conduct site culture assessments at major manufacturing facilities, we provided personalized, one-on-one coaching for more than 500 leaders at Ramos Arizpe Assembly in Mexico and at Spring Hill Assembly in Tennessee. Additional site culture assessments were conducted at our powertrain plant in Toledo, Ohio, GM Silao site in Mexico and other sites. Workplace Safety System Governance Skip Navigation Introduction Reducing Emissions Design for Environment Technology Customers Safety Diverse Workforce Human Rights Supply Chain Communities Governance 2021 SUSTAINABILITY REPORT 60
A CULTURE OF SAFETY CONT. As we transition to EVs, we continue to ensure our procedures and policies are updated to address any potential risks associated with new technologies. GM has formed a cross-functional team to help protect our employees. The team uses research, benchmarking and professional networking to create standards and develop training to support a safe environment for everyone working with EV components and vehicles. Although we are at the beginning of our journey, our team is already collaborating with others in the industry in the transition to an all-electric future. Data: Data-Driven Decisions Accessible, easy-to-analyze global safety data promotes data-driven decisions. A data management system is used to report, collect and analyze all safety information, including incident reports, audit findings, inspections, corrective actions and risk mitigation data. This data provides us meaningful information to develop risk mitigation plans that address issues, like hazards, with the most repetitive exposure, the most repetitive type of injuries and the most repetitive gaps detected during safety tours. In 2021, we introduced a new SIF metric globally that allows GM to analyze exposure data and identify opportunities to proactively ensure safety. SIF subject matter expert teams were established at site, regional and global levels to validate accurate reporting and drive actions at the more effective levels of hierarchy (e.g., elimination, substitution and engineering). In 2022, GM will set specific improvement targets around leading SIF metrics to promote more effective control methods and monitor our exposure reduction efforts. Any loss of life or serious injury in the workplace is unacceptable. Our target is zero, so that every person who enters a GM facility leaves safe and unharmed. GM has a robust prevention program developed to promote the reporting and control of events that could result in severe harm or a fatality. Through the program we identify critical activities and develop global performance standards with mandatory safety controls. In 2021, we expanded our program and transitioned to tracking global performance through our new SIF metric and have established additional corrective actions focused to reduce SIF exposure and drive continuous improvement. Risk Mitigation We aspire to do business with companies and contractors that share the same commitment to returning people home safely. Historically, most SIF events occurring on GM sites have involved contract labor. In order to manage the impacts of COVID-19 on our represented workforce, we temporarily leveraged contract labor at a higher rate than in past years. We work to provide contractors and temporary employees the necessary safety and process training to prevent safety occurrences and build a culture of safety among everyone. In 2021, we updated our Safety Contract Management calibration method to include a series of assessments to measure the engagement and safety culture of our contractors. We also expanded our attention to supplier pre-screening and on-site safety culture validation processes for suppliers to ensure they also share our value for people and safety. Skip Navigation Introduction Reducing Emissions Design for Environment Technology Customers Safety Diverse Workforce Human Rights Supply Chain Communities Governance 2021 SUSTAINABILITY REPORT 61
A CULTURE OF SAFETY CONT. Global Workplace Safety Performance 1 Lost Workday Case Rate 2 (GM Employees) Number of lost workday injuries and illnesses per 1,000,000 work hours. This key performance indicator focuses on those injuries and illnesses that resulted in employees and contract labor losing days from work. This helps us identify areas and processes where we should center our focus to improve our safety controls. Lost Workday Case Rate 2 (Contractors) Number of lost workday injuries and illnesses per 1,000,000 work hours. This key performance indicator focuses on those injuries and illnesses that resulted in contractors losing days from work. This helps us identify areas and processes where we should center our focus to improve our safety controls. Fatalities (GM Employees and Contractors) A work-related incident resulting in death. Our target is zero, so that every person who enters a GM facility leaves safe and unharmed. Recordable Incident Rate (GM Employees and Contractors) Number of incidents that resulted in injuries or illnesses that required medical treatment beyond simple first aid treatment per 1,000,000 work hours. This metric helps to identify hazards, eliminate risks and drive reporting for all incidents so that we can identify and assess areas for improvement. Global Calls to Action Closed on Time Percent of Global Calls to Action closed on time. A Global Call to Action is a list of lessons learned and required corrective actions to be performed by each GM site globally in response to serious incidents that occurred on any GM site. 1 I n 2021, we are no longer tracking Sentinel Events Proactive as we transition tracking the potential for SIF. 2 L ost workday case rate is defined as an incident that resulted in an injury or illness that required a worker to be away from work for one full work day or more after the date of injury. Skip Navigation Introduction Reducing Emissions Design for Environment Technology Customers Safety Diverse Workforce Human Rights Supply Chain Communities Governance 2021 SUSTAINABILITY REPORT 62
Developing Talented & Diverse People IN THIS SECTION A Team That Includes Everybody 64 Diversity, Equity & Inclusion 67 Total Rewards 73 Labor Relations 75 Our Strengths y Global workforce practicing behaviors aligned with our vision to become the most inclusive company in the world y Integrating new technology to better connect and engage with current and prospective talent y Providing a broad range of development opportunities to meet employees’ diverse needs, including training for new skills, education reimbursement and stretch assignments y Leveraging our diverse network of employees, including our employee resource groups (ERGs) and newly established diversity, equity and inclusion (DEI) committees to help attract and retain employees and achieve business results Our Opportunities y Competing for highly sought-after tech talent in critical skilled areas such as software development and engineering, user design and interface and advanced driver assistance systems (ADAS) y Continuing to increase the representation of qualified women and people from traditionally underrepresented groups on our teams and in our succession planning processes y Driving greater equity throughout our business practices and talent management processes Skip Navigation Introduction Reducing Emissions Design for Environment Technology Customers Safety Diverse Workforce Human Rights Supply Chain Communities Governance 2021 SUSTAINABILITY REPORT 63
A Team That Includes Everybody People are our greatest asset and the reason behind our success. They are the key to realizing our vision of a world with zero crashes, zero emissions and zero congestion. To continue making strides in our cultural transformation and to reach an all-electric future, we must recruit the most qualified diverse talent and foster great employee experiences in a culture where individuals can learn, develop and thrive. We gladly continue our journey of building a world-class diverse, equitable and inclusive organization at GM. Employee experiences begin before joining GM, and we take that very seriously. Recruitment provides us with the largest opportunity to build a workforce with the diversity of thought and essential technical skillsets that are critical to achieving a better, safer and more equitable world for everyone. By starting with a diverse mix of candidates at the onset of our recruiting efforts, we are better positioned to advance the aspirations we have set for becoming the most inclusive company in the world. A key objective of our talent recruitment and assessment processes is to foster a mindset of inclusion and provide an experience that enables the most qualified pool of diverse candidates to find opportunities at GM. We are committed to increasing the variety of highly skilled employees and recognize that there are many pathways to success. We know from one candidate to another high- quality talent is innately diverse: Everyone has their own unique background and brings their own unique experiences to a role—and we are consistently architecting better ways for each candidate to shine in their own light during the application and interview processes. The GM Talent Acquisition Team combines their expertise in recruitment with various outreach strategies, including market analysis, sourcing, talent marketing and communications, to generate relevant, effective candidate interactions that contribute to GM’s hiring of highly qualified and diverse talent aligned with our growth strategy. We aim to provide inclusive job descriptions that focus on the capabilities and skills needed for the role. As candidates move through the recruitment process, they participate in structured interviews that help provide an objective platform to assess skill and behavioral alignment with the specific job needs. We also strive to create diverse teams of interviewers who reflect an inclusive mindset and provide different perspectives when assessing a candidate. Skip Navigation Introduction Reducing Emissions Design for Environment Technology Customers Safety Diverse Workforce Human Rights Supply Chain Communities Governance 2021 SUSTAINABILITY REPORT 64
A significant shift in our ability to attract diverse talent has been the adoption of our “Work Appropriately” philosophy. This approach accommodates on-site, remote and hybrid work options, depending on the role, and underscores the trust that we have in our employees to do their best work wherever they can have the greatest impact on achieving our goals. Leveraging “Work Appropriately” has provided us with a tremendous advantage in talent recruitment, as it enables many potential candidates to experience the opportunities that exist at GM without having to move. Engaging Every Employee We strive every day to engage our employees in a meaningful way so that everyone feels connected to and united by our common Purpose, Vision and Values . We measure engagement through our global Workplace of Choice survey, which goes to all employees. The full survey is conducted every two years in addition to shorter pulse surveys throughout the year. In 2021, more than 75,000 global salaried and represented employees provided feedback. We strive for continuous improvement in engagement scores. To this end, GM’s Senior Leadership Team and senior executives have aspirational engagement targets. All leaders also have a common annual performance management goal to emphasize their role in creating an engaged workplace culture that embraces feedback and recognition. >75,000 global salaried and represented employees participated in our Workplace of Choice pulse survey A TEAM THAT INCLUDES EVERYBODY CONT. Learn more about other ways we are engaging our employees . → Skip Navigation Introduction Reducing Emissions Design for Environment Technology Customers Safety Diverse Workforce Human Rights Supply Chain Communities Governance 2021 SUSTAINABILITY REPORT 65
A TEAM THAT INCLUDES EVERYBODY CONT. Developing Everyone’s Potential Growth and development are top priorities for GM employees around the world. Learning continues to be a significant enabler of employees’ growth and development. GM subscribes to a 70-20-10 philosophy of learning, where 70% of learning ideally occurs through on-the-job experiences, including stretch projects. The next 20% occurs through exposure activities, coaching, mentoring, participation in ERGs and other social activities. And the final 10% of learning happens through formal educational resources. Learning and development opportunities are available to employees at all levels across the enterprise. We believe learning is an experience that needs to be extended to employees in the course of their daily work. How We Learn at GM Rather than be prescriptive about learning, we encourage employees to build skills and seek out diverse experiences that interest them most through a variety of programs and tools. PROGRAM DESCRIPTION Degreed (Global) A learning experience platform introduced in 2021 to support employees’ learning during the flow of work. Enables self-assessment of skills proficiency prioritization of 2,500 learning pathways. Access to 9,700 social learning groups. DEI pathways are integrated with our monthly DEI microlearnings, initiated in 2021, so employees can continue exploring and practicing new knowledge. AGM Technical Learning University (United States) Manufacturing labs at our Global Technical Center campus for skilled trades workers and salaried manufacturing engineers from across the United States to hone their skills using next-generation equipment such as automation and robotics. The Professional Managers Network (North America) Open to front-line people leaders as a resource to help engage and motivate their teams. SYNAPSE (Global) An annual innovation competition hosted by our innovation lab, iHub, where teams of employees stretch beyond their roles to create, develop and pitch ideas to leadership. iHub Idea Incubator. A place for GM employees to submit their innovation ideas related to GM’s core business. Talent Spotting Framework (Global) To continually spot and grow our talent, more than 5,000 people leaders were trained globally in 2021 to leverage this comprehensive framework. Employee Cards and Talent Profiles (Global) Part of our Workday platform, employees can input their own strengths and career aspirations into this human resources (HR) tool, which results in greater visibility and connections to opportunities. Workday Mentoring Program (Global) Hosted through our Workday platform, this program encourages employees to establish mentoring relationships with more than 2,000 mentors available to guide and support them in their career journeys. Executive Leadership Development (Global) Collaborations with academic institutions such as Stanford University and the University of Michigan support employee capability development efforts by keeping employees up-to-date on emerging trends in business and society. People Leader Basics (Global) Modularized people leader training designed to establish foundational expectations, upskill manager capabilities and further drive the GM leadership competencies across the enterprise. Learn more about employee opportunities for mentorship and growth on our GM Careers website . → Getting Everybody in the Know As we accelerate our all-electric future, it’s important that all GM employees are knowledgeable about our growing electric vehicle (EV) products and services. In 2021, we launched several new internal channels to increase awareness, including: • A g lobal microsite accessible on the home page of our intranet with the latest EV news, learnings tools and available resources. • A D egreed course dedicated to cultivating employee understanding of key areas of GM’s electrification strategy. • A Y ammer channel dedicated to internal EV conversations, questions and engagements. Skip Navigation Introduction Reducing Emissions Design for Environment Technology Customers Safety Diverse Workforce Human Rights Supply Chain Communities Governance 2021 SUSTAINABILITY REPORT 66
Diversity, Equity & Inclusion In 2020, GM announced its intention to become the most inclusive company in the world—from attracting and retaining a diverse workforce to providing developmental opportunities so every employee can realize professional growth throughout their career with GM. Accountability for DEI begins at the highest levels of the company and extends throughout the organization. Every year, GM’s chief diversity, equity and inclusion officer presents a review of DEI to the Board. We also have an Inclusion Advisory Board (IAB) that is comprised of internal and external leaders and is led by our Chair and CEO. The IAB provides advice and recommendations to GM’s Senior Leadership Team on DEI and cultural competence. Our chief DEI officer is responsible for the creation and execution of our strategy as well as helping drive and coordinate cross- functional DEI initiatives across all regions and all levels of the company. Meet our Inclusion Advisory Board . → Our Journey...to Become the Most Inclusive Company in the World At General Motors, we recognize our journey to becoming the most inclusive company in the world is one that must be rooted in transparency, accountability and a commitment to cultivating a workforce that reflects the communities in which we live and work. We continue to take deliberate actions to ensure all areas of our business are supportive of a world-class, inclusive, equitable and diverse organization. Building DEI Maturity Across the Enterprise In June 2020, GM Chair and CEO Mary Barra, announced our mission to become the most inclusive company in the world and commissioned the IAB. In August 2020, “Be Inclusive” became the eighth GM behavior. Expanding critical conversations on DEI with employees around the globe. Increasing capacity of the DEI Center of Excellence (COE) to accelerate reach and impact; global senior leaders leading DEI integration into the enterprise. Growing global ERG impact while engaging functional DEI committees to help operationalize strategies on a local basis. We are focused on simplifying our processes and procedures to enable us to move faster—we want to embed DEI into every aspect of our business. Skip Navigation Introduction Reducing Emissions Design for Environment Technology Customers Safety Diverse Workforce Human Rights Supply Chain Communities Governance 2021 SUSTAINABILITY REPORT 67
In addition to the IAB, other diversity-focused councils within our organization include: • GM Supplier Council • ERG Leader Council • Minority Dealer Development Council • Women’s Dealer Advisory Council • One DEI Council We are working consistently and diligently to integrate DEI in everything we do throughout the business and build DEI maturity across the enterprise by engaging in critical conversations with leaders and employees to bring everybody in on our journey to inclusion. We recognize our journey must be rooted in transparency, accountability and a commitment to cultivate a culture of innovation where everyone can be their true self, do their best work, feel valued and know that their voice matters. Our DEI Strategy As we pursue our path to EV leadership, we are focused on three DEI strategic pillars: DEI Maturity, Transparency and Talent Innovation. Our DEI strategy is aligned with and integrated into our growth strategy. We continue to heavily invest in and strengthen our COE for DEI, increasing areas such as business intelligence and insights, growth of ERG impact, internal and external partnerships, global reach and scale and workforce design and innovation. Driving DEI Maturity We are working with our leaders at all levels of the organization and with all employees to foster an inclusive culture, with an inclusive mindset, that continuously improves our interpersonal interactions with each other and our customers, suppliers and communities. For example, GM recognizes that unconscious bias is one of the key impediments to building an inclusive culture, so we provided 1,300+ global leaders with live, interactive unconscious bias training in 2021. In addition, more than 125 global leaders received training to facilitate unconscious bias workshops in their respective workplaces around the world, setting up additional opportunities for live, interactive engagement and training. We also shared DEI Toolkits with 9,000 people leaders to help them drive dialogue on DEI topics with their staffs and introduced a new DEI people leader module for our learning platform, Degreed. Skip Navigation Introduction Reducing Emissions Design for Environment Technology Customers Safety Diverse Workforce Human Rights Supply Chain Communities Governance DIVERSITY, EQUITY & INCLUSION CONT. 2021 SUSTAINABILITY REPORT 68
DIVERSITY, EQUITY & INCLUSION CONT. Increasing Transparency Inclusivity demands transparency. We are committed to holding ourselves accountable and demonstrating progress to our internal and external stakeholders through data collection, analysis and disclosure. Publicly sharing certain information is an important part of accountability, for us and other companies, which is why we disclosed our consolidated Equal Employment Opportunity (EEO)-1 Report for the first time in 2021 for 2020 data and committed to make similar disclosures in the future. Data collection and analysis is also an important part of transparency. We recognize the importance of understanding where we are today in order to continue our progress. We have launched an Inclusivity Index as part of our global Workplace of Choice survey. In addition, we believe that transparency reaches beyond data. We also aim for transparency in professional communications and encourage open discussion of our DEI journey. We have amplified internal communication around DEI and we regularly share inclusive moments that matter. GM’s DEI progress is regularly reviewed by the Senior Leadership Team and the Board for progress against key metrics: Inclusivity Index score, diversity in the overall GM population and diversity in the overall executive population. We also measure hiring, promotions, performance assessments, candidate pools and attrition as indicators of equity. In 2021, we were pleased to report that our efforts yielded increases in representation among several underrepresented groups, including women and racial and ethnic minorities. Leveraging Talent Innovation Innovation is at the heart of transforming GM technologies, and we are bringing that same innovative mindset to our HR processes and systems to improve equity. A skills-based approach to hiring and a focus on new pathways to enter our workforce are key. Some examples include: Being a founding member and Detroit-area lead of the OneTen coalition, 60 companies and leaders that aim to train, hire and advance 1 million Black Americans over a 10-year period into family-sustaining jobs with opportunities for advancement. In year one, we hired 400+ individuals associated with this partnership, exceeding our OneTen hiring commitment. Re-introducing our career re-entry program, Ta ke 2 that targets anyone who has two or more years of experience in a field of work and has taken a break from that field for two or more years. Recruiting recent college graduates from more than 500 different U.S. colleges and universities. Providing opportunities for more than 600 students annually through our paid college summer intern and co-op program, which has been recognized as one of the Top 100 Internship Programs. Collaborating with organizations such as the Society of Women Engineers; the Society of Hispanic Professional Engineers; American Indian Science and Engineering Society; Out in Science, Technology, Engineering and Mathematics; National Society of Black Engineers; AfroTech and many other organizations that help provide us with a diverse slate of potential new hires. Skip Navigation Introduction Reducing Emissions Design for Environment Technology Customers Safety Diverse Workforce Human Rights Supply Chain Communities Governance 2021 SUSTAINABILITY REPORT 69
DIVERSITY, EQUITY & INCLUSION CONT. Creating an Inclusive Culture When the goal to become the world’s most inclusive company was announced, our DEI efforts intensified, and our sense of urgency accelerated. Today, the cultural transformation taking place within our company is as significant as the technology transformation driving our business growth. Indeed, the two are interrelated; at the intersection of these transformations is the potential for innovation, and significant and consistent innovation is required for GM to reach its zero, zero, zero vision. Key builders of this culture are the employees in our ERGs—global voluntary, employee- led groups that serve as a resource for their constituent members and allies. ERGs help GM improve DEI maturity throughout our global business. We have 11 ERGs, with many chapters across the United States and the world. Importantly, ERGs are fully open to anyone interested in participating. Nearly all ERGs have executive-led advisory councils to help them advance and address issues and opportunities. We’re proud that all GM ERGs experienced growth in members and allies during 2021. We are complementing the work of ERGs through the establishment of DEI cultural ambassadors as well as inclusion committees. This distributed model of DEI ensures that we are addressing DEI from both local and centralized perspectives. These ambassadors and committees are critical to our ability to address local opportunities as well as to scale certain DEI initiatives across the company. Furthermore, this approach enables everyone to lead DEI efforts—not just as people leaders, but at the individual level. GM Women Making an Impact Around the World In 2021, GM Women ERGs engaged in a variety of activities to support each other, dealer networks and their communities. United States Focused on wellness, development and partnerships to encourage everyone to become their own unique leader. Mexico Created a program, WOMENPOWER, emphasizing the elimination of cultural career stallers and stoppers. South America Launched Women in Action, a continuous learning program for women at all levels to understand and overcome bias. United Arab Emirates Formed DEI Committee to build a thriving, equitable and inclusive environment that supports leaders of diverse backgrounds. Egypt Celebrated International Women’s Day by highlighting female talent and holding a session on inclusion. Philippines Held a webinar on women in traditionally male-dominated jobs. Korea Shifted to a Diversity Council to ensure men and women were brought together to address issues and drive solutions that would benefit all. China Introduced a mentoring program to create two- way learning and broaden networking among women employees. Employee Resource Groups Skip Navigation Introduction Reducing Emissions Design for Environment Technology Customers Safety Diverse Workforce Human Rights Supply Chain Communities Governance 2021 SUSTAINABILITY REPORT 70
GM’s HR and leadership team in South America announce final candidate selections. DIVERSITY, EQUITY & INCLUSION CONT. Promoting Equity GM has long been a global leader in advocating for women’s equity in the workplace. In 2021, women were in 31.9% of our top management positions within two levels of the CEO. The Bloomberg Gender-Equality Index is among the organizations that have recognized GM as a leader in gender equity. We are committed to equal pay practices. Our commitment to the Equal Pay Pledge reflects the value we place on gender pay equity and our shared belief that employees’ protected characteristics, including gender, should not factor into compensation decisions. As part of this commitment, GM has a rigorous annual process that involves measuring pay equity and making adjustments whenever unaccounted-for discrepancies are found. GM has a strong antidiscrimination policy that extends to all groups. We believe everyone deserves to work in an environment where they can be proud of who they are. GM ERGs help guide our strategy and understanding of important issues surrounding equity. GM Plus, our ERG focused on LGBTQ+ employees, for example, encourages allyship as one of the ways people can support the LGBTQ+ community, with about half of its over 1,000 members identifying as allies. In addition, the president of the GM Able ERG leads our disability advisory council. Diverse Recruitment Successes During 2021, we took a number of actions to increase diversity within our workforce. When we restarted our Oshawa Assembly plant in Ontario, we recognized the opportunity to rebuild our approximately 1,200-person workforce to achieve gender parity. Through a recruitment process that helped to eliminate gender bias, the plant was able to re-open with women making up roughly half of the new workforce. Similarly, GM Brazil held a successful Technical Rotation and Career Knowledge (TRACK) program aimed at accelerating inclusion of Black professionals in our workforce, especially in leadership positions. The TRACK program is GM’s talent pipeline for future leaders. More than 5,700 candidates applied initially. Candidates went through a three-month multiphased process that ranged from online assessments to an everybody in session with GM leaders. Ultimately, 16 professionals—seven of whom were female—joined the GM Brazil team, with backgrounds ranging from engineering to psychology. The project concluded with onboarding activities at GM’s plant in São Caetano. 31.9% women in top management positions within two levels of the CEO 2021 Diversity Recognition Skip Navigation Introduction Reducing Emissions Design for Environment Technology Customers Safety Diverse Workforce Human Rights Supply Chain Communities Governance 2021 SUSTAINABILITY REPORT 71
Extending Inclusivity Into the Market Our business seeks to support and foster diversity and inclusion within the global communities where we operate to provide the best customer experience and positively impact our broader society. Dealer Diversity We are proud that the coming year will see us celebrate the 50th anniversary of GM’s Minority Dealer Development (MDD) Program. Established in 1972, it continues to serve as the longest running, industry-leading minority dealer program. In addition, GM is the first and only original equipment manufacturer to have a Women’s Retail Network (WRN). This network is dedicated to growing a performance-driven, customer-focused and profitable dealer network by connecting highly qualified women dealers. General Motors works diligently toward increasing the number of qualified diverse dealers; reaching a level of operational effectiveness that consistently meets or exceeds the general dealer population; encouraging and attracting diversity into retail organizations as dealer operators, managers and employees; and advocating that all GM dealerships provide a respectful environment for diverse customers and employees. In 2021, we made DEI training available to more than 100,000 dealer team members. We are proud that our MDD and WRN programs consist of almost 600 diverse dealer partners in our dealer network, over 100 more than any other manufacturer. Our diverse dealers consistently outperform all other GM dealers in many key performance indicators and are among the most profitable of our retail partners. Justice & Inclusion Fund We are driving generational change and impact through the Justice and Inclusion Fund with investments focused on health, education, economic empowerment and policy. Through the end of 2021, we committed $22 million to organizations such as The Martin Luther King Jr. Memorial Foundation; Asian Pacific American Institute for Congressional Studies; the Smithsonian Latino Center; and other organizations doing critical racial justice work. With these actions, we hope to impact 2.6 million people. Using Our Voice We believe that everyone has the responsibility to speak up in the presence of bias and injustice. We speak out, and will continue to do so, on social and racial equity issues. Our alignments in support of justice include signing a letter in support of the COVID-19 Hate Crimes Act. We are also signatories for many DEI efforts, including: • CEO Action for Diversity & Inclusion Pledge • Coalition for the American Dream • Business Coalition for the Equality Act • The Dialogue Project • Gender and Diversity KPI Alliance GM also has a robust engagement with the Business Roundtable , of which GM Chair and CEO Mary Barra became the Chair at the start of 2022. Learn about GM’s Supplier Diversity Program here . → GM Justice & Inclusion Fund $22M committed 2.6M people expected to be impacted In 2021, we extended DEI training to 100,000+ dealer team members. DIVERSITY, EQUITY & INCLUSION CONT. Skip Navigation Introduction Reducing Emissions Design for Environment Technology Customers Safety Diverse Workforce Human Rights Supply Chain Communities Governance 2021 SUSTAINABILITY REPORT 72
Total Rewards Offering competitive pay and benefits and promoting work-life balance further helps us to attract and retain an engaged and diverse workforce that enables the greatest possible returns on our investments in talent. Total Rewards Program GM provides a comprehensive Total Rewards program to support our employees and their families around the globe. We prioritize a holistic approach to well-being, which includes support for employees’ physical, emotional and financial wellness. Besides offering competitive wages, GM’s benefit packages, which vary by country, may include health insurance, access to employee assistance program(s), life insurance, short- and long-term disability benefits, profit sharing, retirement and savings plans, paid time off, tuition assistance, vehicle discounts for employees and their family members and various other benefits employees can voluntarily elect. Recognition Program Recognition is an important part of the GM culture, and our salaried recognition program provides an online platform where employees across the globe can recognize and be recognized for living our company values and behaviors and for their contributions. This program is leveraged by 99% of our salaried employees. In 2021, there were approximately 1 million recognitions sent, 1.75 million recognitions received and 1.2 million comments shared. Additionally, we are working with our union partners to find new ways to recognize and engage represented employees. United States Paid Family Leave/Disability Leave GM provides salaried employees up to 12 weeks of paid family leave per year to care for a family member with a serious health condition or to bond with a child added to their family through birth, adoption or foster care placement. In 2021, 1,919 employees took an average of 37 days of Paid Family Leave. This leave is provided in addition to the six to eight weeks of disability leave available to birth mothers. Employees are also eligible to apply for unpaid time off under GM’s Dependent Care Leave policy, which provides job protection for up to 12 months. GM provides short-term disability benefits for up to one year with wage replacement ranging from 60% to 100% of base pay. In 2021, 12,587 employees took short-term disability leave, 14% of the U.S. workforce. After short-term disability benefits cease, company-provided long-term disability benefits are available to employees. Long-term disability benefits are payable up to age 65, depending on seniority and employee type, and provide for wage replacement at a rate between 50% to 60% of base pay. Employee/Family Assistance The Family Care Assistance program provides salaried employees access to back-up child/elder care, a subscription to Sittercity.com to source care needs and elder care support, and a program to provide specialized assistance to support employees with children with developmental needs. Additionally, GM salaried employees are eligible to utilize a combined lifetime maximum benefit of up to $40,000 to reimburse for expenses associated with fertility treatments, adoption and/or surrogacy. Plus, personalized navigation assistance can be provided to find the best clinical care, adoption or donor-assisted reproduction support teams. Retirement, Savings and Profit Sharing Represented employees, based on their service date, are eligible either to accrue service in the GM Represented-Rate Employees’ Pension Plan or to receive a 6.4% GM Retirement Contribution and $1 per hour contribution, up to 40 hours per week (and up to 2,080 hours per year), to their GM Personal Savings Plan account (401(k)). The salaried workforce receives a 4% retirement contribution and the opportunity for a 4% matching contribution to their 401(k) account. Employees are also eligible for represented profit-sharing or salaried bonus payments tied to the company’s achieving specific targets. In 2021 ~ 1M recognitions sent 1.75M recognitions received 1.2M comments shared Skip Navigation Introduction Reducing Emissions Design for Environment Technology Customers Safety Diverse Workforce Human Rights Supply Chain Communities Governance 2021 SUSTAINABILITY REPORT 73
Canada Pregnancy and Parental Leaves In conjunction with government benefits, employees are eligible for up to 75% of their base salary for up to 12 months, based on the qualifications for that specific leave type. Pension and Savings GM provides a Defined Contribution Pension Plan for employees. The hourly plan requires a 4% employee contribution, and GM provides a 4% company contribution. If an employee contributes an additional 1%, GM will contribute an additional 2% of pensionable earnings. The salaried plan offers a 4% company contribution and the opportunity for a 4% match contribution toward a registered pension plan. All contributions are capped at current income tax limits. Tuition Assistance Salaried employees are eligible for tuition reimbursement up to a maximum of $8,000 CAD per calendar year for undergraduate, graduate or doctorate-level education. After eight years of service, hourly employees can receive tuition assistance of $1,300 annual reimbursement for each eligible dependent enrolled in a full-time or certificate program at an accredited U.S. or Canadian university or community college. Mexico Pension and Savings GM provides salaried employees with a Defined Benefit Pension Plan provided they meet certain service and age requirements. In addition, all salaried and hourly employees can contribute up to 13% of their salary (or the legal cap) into a Savings Fund each pay period. GM matches the amount up to the legal cap on an annual basis. Other Benefits Salaried employees with at least two years of seniority, and with leadership approval, may be reimbursed for up to 90% of their tuition costs (capped at MXN $100,000/year) based on class performance up to a maximum of three years. GM also provides a scholarship program for hourly employees’ children in the amount of MXN $2,400 to MXN $6,000 per year, depending on the location. In addition, employees receive a food coupon up to a legal cap or 11% of salary, whichever is greater. GM subsidizes a portion of the employees’ meal costs at the on-site cafeteria, as well. For all sites, GM provides a subsidized transportation/bus service for hourly employees. For hourly and salaried employees, GM provides additional vacation days above regulatory requirements and pays above the mandatory requirements for the Christmas bonus and Sunday/ vacation time for certain locations. Brazil Paid Time Off/Additional Assistance Female employees receive 180 days of maternity leave and are eligible for childcare assistance; according to the collective agreement of their locality. Female employees are entitled to a breastfeeding leave for two half-hour periods during the working day, or eight consecutive days after maternity leave until the child is six months old and 30 days of paid rest in the event of a miscarriage; according to the collective agreement of their locality. Tuition Assistance Tuition is paid at 50% for employees’ undergraduate, graduate or doctorate-level education. This is subject to certain requirements, provided there is applicability to their current role and development plan. GM also offers discounts for employees for language schools and universities. Pension and Savings GM provides a Defined Contribution Plan for employees earning a specific base salary. Employees can contribute to the plan, and GM matches 50% of the total basic contribution. In addition, GM provides an additional general contribution for employees earning a specific base salary. China Paid Time Off/Additional Assistance Marriage leave is provided for wedding preparation and honeymoon. Employees can also apply for unpaid personal leave to handle private matters. Employees can use up to 158 days maternity leave. Paternity leave is offered within three months after the birth of a child/children. Employees also receive five days of leave, per child, each year until their child turns three. Sick leave of five or 10 days, based on length of service, is also provided. Local Chinese employees in Beijing can get a winter heating allowance of up to 1,800 yuan per person per year. Employees will also receive a clothing allowance of 500 yuan at the anniversary date of employment. Additionally, an internal housing fund is paid to local employees to support them in purchasing or renting a house. TOTAL REWARDS CONT. Skip Navigation Introduction Reducing Emissions Design for Environment Technology Customers Safety Diverse Workforce Human Rights Supply Chain Communities Governance 2021 SUSTAINABILITY REPORT 74
Labor Relations At GM, manufacturing is our competitive advantage in building our all-electric future. That means the future of our business, as well as the future of mobility, rests largely in the hands of our represented employees. Their success and the growth of our business are inextricably linked. As we transition to an all-electric future, collaboration with our union partners and support for our represented employees underscore the competitive and unmatched business advantage they bring to GM. This experienced and skilled workforce comprises more than 95,000 industrial problem-solvers on our manufacturing team, who, collectively, have 1.4 million years of experience. It is critical to bring this workforce along on our EV journey . Since the beginning of 2021 (through March 2022), GM has announced the creation or retention of almost 7,000 jobs as part of our investment in America. Our commitment was clearly demonstrated in early 2022 when GM announced a $7 billion investment in four Michigan manufacturing sites, expected to create 4,000 new jobs and retain 1,000 jobs. The investment includes a new battery cell plant, the conversion of an assembly plant to EV production and upgrades in production capabilities for two other assembly plants. Equally as important as investments in facilities are investments in our workforce to ensure they possess the required skills to successfully launch our future EVs and AVs. As an example, the GM Automotive Manufacturing Electrical College is a new immersive training program providing participants the opportunity to train in both classroom and hands-on settings for a future role on a launch team at one of GM’s vehicle assembly facilities. We also restructured the Electrical Apprentice Program to include the latest technologies focusing more on Programmable Logic Controllers, robotics and vision systems. The goal is to equip participants with the technical skills needed to perform electrical-based job duties before they reach the floor of a manufacturing site. Working Collaboratively With Union Partners Healthy union relationships are built on effective communication. We engage with our union partners daily and provide opportunities for them to offer input into our processes. An ongoing priority is to ensure that our represented employees feel empowered as members of our global manufacturing and operations team and that their voices and ideas are heard on topics such as safety and quality improvement. GM announced a $7B investment in four Michigan manufacturing sites, expected to create 4,000 new jobs and retain 1,000 jobs Skip Navigation Introduction Reducing Emissions Design for Environment Technology Customers Safety Diverse Workforce Human Rights Supply Chain Communities Governance 2021 SUSTAINABILITY REPORT 75
LABOR RELATIONS CONT. We also strive to understand and address represented workforce concerns to capitalize on opportunities for them. In 2019, GM ratified a new four-year labor agreement covering employees at 55 United Auto Workers (UAW)- represented sites across the United States. This agreement provides GM-represented workers with a world-class wage, benefit and profit- sharing package, rewarding their hard work and supporting families and communities across the United States. Importantly, the agreement also establishes a National Committee on Advanced Technology, made up of both union and management representatives. We have covered technologies such as additive manufacturing, autonomous robots and drones and unique operator interfaces in our most advanced assembly facilities. These opportunities have been implemented to upskill our workforce in the area of electrification. The committee meets at least quarterly to discuss the impact of electrification and other advanced technologies on our represented workforce. In addition, the agreement outlines collaborative initiatives to enhance the health and safety of manufacturing employees as well as other aspects of the production process. Supporting Represented Employees Through Business Challenges The global pandemic and associated supply chain shortages during the past two years have been challenging for our operations. Throughout, GM has prioritized taking care of our represented employees by ensuring the health and safety of all who are on the job. In particular, we have had to creatively manage the complex and fluid global semiconductor shortage. This has called for inventive ways to sustain production and prioritization of our highest-demand, capacity- constrained products—all while developing sustainable, long-term supply chain solutions. Our responsible employment philosophy extends to when workers are displaced because of a plant production adjustment. During recent adjustments, we have supported workers through various measures, including on-the-job training programs and various types of paid leave and supplemental unemployment insurance. As the pandemic extends into its third year, we continue to support all of our employees in innovative ways with initiatives ranging from mailing masks to employees’ homes for their families for holiday gatherings and holding vaccination clinics at many of our facilities for employees, to providing paid time off for certain quarantine situations. Union Partnerships GM works with about 28 unions globally, representing approximately 99% of our represented workforce, or 61% of our total global workforce, who are covered by collective bargaining agreements. GM’s relationships with labor unions are healthy and stable partnerships aimed at optimizing the outcomes for both the employees and the business. We manage our labor relations regionally, with a global focus. The labor relations responsibility is held by the global manufacturing leader, with partnerships that go to the highest level of the GM organization. Regular meetings are held with our union partners, starting with quarterly meetings between our CEO and UAW leadership. Regional vice presidents of manufacturing conduct face-to-face meetings with the unions when visiting the manufacturing sites; manufacturing directors meet with the local unions at plant sites regularly; and plant managers around the globe discuss business issues daily with local unions. These meetings provide critical input for making business decisions in a dynamic environment where schedules, economic swings and products are ever changing. GM leadership devotes time to work productively with our union partners and ensure they are updated on the business and pertinent issues. We work continuously with our union partners around the world to address unique issues within their respective markets. During 2021 alone, examples included: • In the United States, renovating the former Detroit-Hamtramck assembly plant to reopen as Factor y ZERO following a $2.2 billion investment to build a variety of all-electric trucks and SUVs (Grand Opening was November 17, 2021). • In Korea, rebuilding GM factories to support the introduction of new models, which included visiting our plants in the United States and Mexico to better share learnings. • In Mexico, working on compliance issues around the U.S.-Mexico-Canada free trade agreement. Skip Navigation Introduction Reducing Emissions Design for Environment Technology Customers Safety Diverse Workforce Human Rights Supply Chain Communities Governance 2021 SUSTAINABILITY REPORT 76
Upholding Human Rights Our Strengths y Committing to respect all internationally recognized human rights and human rights defenders y Working cross-functionally to understand and manage human rights risks and impacts y Sharing our commitments with our global workforce across a range of platforms y Deepening relationships with stakeholders worldwide and seeking out ways to collaborate Our Opportunities y Promoting protection of human rights across our global operations, joint ventures and supply chain Skip Navigation Introduction Reducing Emissions Design for Environment Technology Customers Safety Diverse Workforce Human Rights Supply Chain Communities Governance 2021 SUSTAINABILITY REPORT 77
Human Rights GM is committed to bring everyone along as our business, industry and world make the transition to a lower-carbon future. This includes respecting the human rights of all people. As described in the United Nations Guiding Principles on Business and Human Rights (UNGPs), governments have a responsibility to protect the human rights of their people, and businesses such as GM have a responsibility to respect the human rights of people. A key part of this is recognizing and addressing potential adverse impacts a business can have on people throughout its enterprise, and taking steps to prevent, mitigate and, where appropriate, remediate those impacts . At GM, we understand that long-term success starts with a company’s value system and a principled approach to doing business. In 2021, the Board’s Governance and Corporate Responsibility Committee approved an updated and strengthened Human Rights Policy . The Board also formally added human rights oversight to the Governance and Corporate Responsibility Committee’s annual responsibilities. It regularly reviews GM’s human rights-related policies and strategies and conducts an annual review of GM’s human rights practices and responsible sourcing practices. Other committees of the Board, including the Executive Compensation Committee, the Risk and Cybersecurity Committee and the Audit Committee, also engage with human rights-related matters as needed. For example, when relevant, the Executive Compensation Committee addresses certain human capital management matters, the Risk and Cybersecurity Committee addresses supply chain risks and the Audit Committee oversees GM’s ethics and compliance program. Human rights is an important issue addressed both by the Board and cross-functionally by senior leaders across the company. Our chief sustainability officer is responsible for GM’s Human Rights Policy and works cross- functionally with GM’s Human Resources; Diversity, Equity and Inclusion; Labor Relations; Ethics and Compliance; and Global Purchasing and Supply Chain Teams, among others, to understand and address potential human rights risks and impacts. Highlights from GM’s updated Human Rights Policy include: • A commitment to respect all internationally recognized human rights, including those described in the United Nations Global Compact (UNGC), Universal Declaration of Human Rights, the International Labour Organization’s (ILO) Declaration on Fundamental Principles and Rights at Work (the ILO Core Conventions), and the Organisation for Economic Cooperation and Development Guidelines for Multinational Enterprises. • A commitment to respect the rights of human rights defenders, people who speak up on behalf of those whose rights may be threatened. The policy states that GM will “neither tolerate nor knowingly contribute to threats, intimidation or attacks against human rights defenders in relation to our operations” and encourages our suppliers to make the same commitment. • An underscored commitment to respect the rights of people who may be particularly vulnerable—Indigenous peoples, women, children, migrant workers and people with disabilities, among others, and our expectation that suppliers share in this commitment. The Policy applies to all of GM’s global operations, including joint ventures in which we have managerial control, and also contains obligations for suppliers and contractors. The Policy includes ethical recruitment practices, diversity, antiharassment, prohibition of unlawful discrimination, support of women’s rights and equal pay, individual privacy, GM is a member of the UNGC, which endorses a framework of principles in the areas of human rights, labor, the environment and anticorrup- tion. We are committed to these principles and are actively implementing them. Visit the 2021 Sustainability Supplement for more information. Skip Navigation Introduction Reducing Emissions Design for Environment Technology Customers Safety Diverse Workforce Human Rights Supply Chain Communities Governance 2021 SUSTAINABILITY REPORT 78
HUMAN RIGHTS CONT. reporting and nonretaliation policies. Suppliers and business partners we contract with are expected to make commitments to human rights as well, including the ILO’s Core Conventions against forced labor, child labor, discrimination and harassment, and protecting freedom of association and the right to collective bargaining. Suppliers are also expected to comply with laws on safety and working conditions. GM’s zero-tolerance policy against the use of child labor, and all forms of modern slavery and forced labor, is stated in our Supplier Code of Conduct and Conflict Minerals Policy . Our Supplier Code of Conduct details our expectations for contacted suppliers and business partners to comply with all laws, including safety, data, freedom of association and collective bargaining laws. The Supplier Code of Conduct also states that suppliers and business partners we contract with will not harass or discriminate against employees, nor tolerate corrupt business practices. Suppliers are expected to cascade similar expectations through their own supply chains. Communicating Our Commitments Our goal is to have our entire global workforce understand our commitments, including awareness of our Human Rights Policy and how to access it. To that end, together with our Internal Communications Team, we’ve developed a global communications strategy for our Human Rights Policy that leverages our internal company site (Socrates), our internal announcement and discussion platform (Yammer), our employee resource groups, leadership at each of our global plant locations and location-specific private Facebook pages as channels to reach as much of our global workforce as possible. The Human Rights Policy is available in eight languages to promote ease of access and understanding. Identifying Potential Impacts In order to effectively prevent and mitigate potential impacts to people, the UNGPs identify what those potential impacts could be and prioritize them by determining which are the most severe and most likely, in a process known as a human rights saliency assessment. Salient human rights issues for a company are those that are most at risk of the most severe impacts through a company’s activities and business relationships. GM is engaged in a saliency assessment process. In 2021, as a part of this process, we conducted desktop research, reviewed industry analyses and began connecting with external stakeholders. We also held a series of interactive internal capacity building and exploratory workshops with leaders from across the enterprise and our geographic footprint in order to identify and prioritize potential human rights-related impacts. In the series of workshops with a cross- functional working group, we looked at our value chain, considered potential impacts to people throughout our value chain, and then considered the severity and likelihood of each impact. Through this process, the working group arrived at an initial set of potential impacts to consider. In 2022, GM will refine and validate the potentially salient human rights impacts with internal and external stakeholders. While we recognize that nearly all of the potential impacts identified are by nature systemic and not limited to GM or even the automotive industry, we take seriously our responsibility to work to identify, prevent, mitigate and remediate potential human rights impacts to which we may contribute, as detailed in our Human Rights Policy. The results from our initial saliency assessment workshops are an important jumping off point that we will build upon. We recognize that effective, regular stakeholder engagements are an important part of identifying and addressing potential human rights impacts. We view the saliency assessment process as an ongoing exercise with impacts and prioritizations that may, and likely will, change over time. Saliency Assessment Process E VA L UATE Consider, through a cross-functional workshop, severity and likelihood of potential impacts to people across our value chain. VA L I DATE Develop and refine potentially salient human rights impacts with internal and external stakeholders. COMMIT Act to prevent, mitigate and remediate potential human rights impacts to which we may contribute, as detailed in our Human Rights Policy. Skip Navigation Introduction Reducing Emissions Design for Environment Technology Customers Safety Diverse Workforce Human Rights Supply Chain Communities Governance 2021 SUSTAINABILITY REPORT 79
→ → HUMAN RIGHTS CONT. Preventing and Mitigating Impacts Historically, we have relied on trainings as a tool to prevent human rights-related issues from arising, as well as robust reporting and internal review mechanisms to rapidly identify and respond to issues, if and when they arise. We will use the findings from our saliency assessment to further strengthen our strategy as we continue to evolve our management of potential human rights impacts. In the near future, we plan to take a closer look at our salient issues to gain additional understanding of the risks. In parallel with developing action plans, we intend to build out management systems to enhance understanding, ownership and accountability over our salient issues. Engaging With Stakeholders Stakeholder engagement is an important part of addressing human rights matters. We value the relationships that we have formed with many of our stakeholders and look forward to future opportunities to connect, learn and collaborate. We engage with stakeholders through many forums. We believe it is important to hear directly from stakeholders, or their representatives, who may be impacted by our business. It is through these conversations that trust is built, and they provide an invaluable opportunity for us to learn and to co-create potential solutions, when appropriate. For example, through dialogues facilitated by the Development Partnership Institute, we engaged with representatives of Indigenous mining communities in a number of countries, including Australia and Canada. From these conversations, we heard concerns that Indigenous interests and perspectives were frequently not included in sustainability-related frameworks, despite claims of inclusivity and comprehensiveness. We also heard that Indigenous people appreciate opportunities to engage in and more fully understand the value chain. In response, we are actively exploring opportunities to build relationships and communication channels with communities closer to the origin of our supply chains. One example of this is our engagement with multistakeholder initiatives such as the Global Platform for Sustainable Natural Rubber, which includes smallholder farmers from sourcing regions in Asia and Africa. We are also working to further bolster our due diligence processes and have announced a new partnership with the Initiative for Responsible Mining Assurance to promote comprehensive third-party assessments and certifications, in addition to continuing to work closely with the Responsible Minerals Initiative, as discussed in the Supply Chain section . Additionally, we are updating our Supplier Code of Conduct to emphasize our expectation that all suppliers share in our commitments to respect human rights. We are also expanding our compliance efforts to gain more insight into whether suppliers are living up to expectations. In 2022, we plan to launch a new platform that will help educate and build supplier capacity around human rights and other critical sustainability areas. Read GM’s Anti-Slavery and Human Trafficking Statement . Learn more in Supporting Supplier Responsibility section. Skip Navigation Introduction Reducing Emissions Design for Environment Technology Customers Safety Diverse Workforce Human Rights Supply Chain Communities Governance 2021 SUSTAINABILITY REPORT 80
Supporting Supplier Responsibility IN THIS SECTION Why Supplier Relationships Matter 82 Sourcing Strategic Raw Materials 83 Supply Chain Engagement 84 Industry Collaboration 85 Integrating Sustainability Into Our Supply Chain 86 Supply Chain Compliance 91 Supply Chain Disruption 92 Responsible Sourcing of Raw Materials 93 Supporting Diverse Suppliers 95 Our Strengths y Expanding work with our suppliers to utilize EcoVadis and CDP as sustainability platforms to collect data and gain further insight into their sustainability and compliance practices y Continuing to collaborate and share best practices with our suppliers to strengthen progress toward shared goals y Creating new relationships and leveraging existing relationships to bring innovative ideas and new approaches to our supply chain Our Opportunities y Accelerating the pace of change within our supply chain to address sustainability risks and opportunities y Enhancing visibility into the lower tiers of our supply chain to further mitigate social and environmental risks y Sourcing sustainable materials at greater scale that are critical to the continued development and widespread deployment of electric vehicles (EVs) Skip Navigation Introduction Reducing Emissions Design for Environment Technology Customers Safety Diverse Workforce Human Rights Supply Chain Communities Governance 2021 SUSTAINABILITY REPORT 81
Why Supplier Relationships Matter Our goal of a zero-emissions future is dependent on the broad-scale commercialization of EVs. That future begins with a supply chain that can provide us with the components and materials necessary to produce EVs, including advanced batteries and other technologies. This makes supplier relationships more critical than ever to fulfill our vision. Our global supply chain spans thousands of businesses and is built on strong, transparent and trusted relationships. These relationships, which our Global Purchasing and Supply Chain (GPSC) organization manages, are critical to ensuring product quality, availability and affordability for our customers. By seeking to be the customer of choice for suppliers, we strive to improve business competitiveness, mitigate business risks, improve quality and efficiency in our value streams, and maximize our influence in addressing societal concerns. Our supply chain strategy flows from GPSC's Priority Wheel, pictured at right. The Priority Wheel is a well- established set of priorities aligning supply chain objectives, with customer focus at the core. It also encourages us to gain supplier input on major process improvements and other issues that may affect them. Our vice president of GPSC is responsible for executing the objectives in our Priority Wheel. We have made significant progress in strengthening our supplier relationships as shown in Plante Moran’s 2021 annual Working Relations Index , where we achieved a score of 289, a 20-point improvement compared to the previous year. Supply Chain Scale & Scope #3 ranking in North American Automotive OEM-Supplier Working Relations Index ® $76B approximate supply chain spend 18,940 approximate global supplier count 329,000 approximate materials and services purchased Local Sourcing 1 as a Percentage of Regional Spend 2 73% International and South America 92% North America 96% China 1 Local spend tracks local sourcing at a regional level. 2 Percentages are approximate. Skip Navigation Introduction Reducing Emissions Design for Environment Technology Customers Safety Diverse Workforce Human Rights Supply Chain Communities Governance 2021 SUSTAINABILITY REPORT 82
Sourcing Strategic Raw Materials The semiconductor supply shortage that impacted the global economy and caused widespread supply chain issues throughout 2021 and beyond underscores the importance of strategically evaluating every level and tier of our supply chain. This is especially important as it relates to our expanding EV programs, where improving visibility and traceability in the supply chain is critical. GM is prioritizing development of a resilient and sustainable supply chain of raw materials to manufacture our battery chemistry, which requires cobalt, battery-grade nickel and lithium, as well as other minerals. We are proactively and aggressively pursuing responsibly sourced materials at strategic tiers of the supply chain and exploring where investment and partnerships can yield benefits and GM’s Wallace Battery Cell Innovation Center Image is computer generated untapped value that lowers costs of advanced technologies. In 2021, we have advanced several initiatives, including: • A strategic supplier agreement with Wolfspeed, Inc. to develop and provide silicon carbide power device solutions for GM’s EV programs. The devices are expected to enable more efficient EV propulsion systems to extend EV range. • A nonbinding Memorandum of Understanding with GE Renewable Energy to evaluate opportunities to improve supplies of heavy and light rare earth materials and magnets, as well as copper and electrical steel, used in manufacturing of both EVs and equipment that generates renewable energy for electricity. The initial focus of the collaboration will be on creating a North America and Europe based supply chain of vertically integrated magnet manufacturing that both companies will use in the future. Metal alloys and finished magnets produced from rare earth materials are critical components used in manufacturing electric motors for automotive and renewable power generation. The companies will also work together to help establish new supply chains for additional materials, such as copper and eSteel, that are used in automotive traction motors and renewable power generation. • A strategic relationship and commercial collaboration with Controlled Thermal Resources to support development of U.S.-sourced, low-cost lithium from the Salton Sea area of California. The lithium will be produced through a closed-loop, direct extraction process that results in a smaller physical footprint, no production tailing and near-zero carbon dioxide emissions when compared to traditional processes such as pit mining or evaporation ponds. • A long-term supply agreement with MP Materials , the owner of America’s only active and scaled rare earth production site in California. GM has agreed to support MP Materials’ efforts to become a vertically integrated, technically qualified and approved North American manufacturer of advanced magnets. • GM and POSCO Chemical have agreed to create a joint venture to build a factory in North America to manufacture Cathode Active Material (CAM), a key battery material that is the most significant determinant of cell costs, quality and performance. GM and POSCO share a vision and are leveraging our combined experience, scale and expertise to develop a sustainable, ethically sourced and competitive supply chain for CAM inputs to support the launch of a North American CAM manufacturing facility. Skip Navigation Introduction Reducing Emissions Design for Environment Technology Customers Safety Diverse Workforce Human Rights Supply Chain Communities Governance 2021 SUSTAINABILITY REPORT 83
Supply Chain Engagement GPSC advances how GM and our suppliers achieve mutual success by providing better product quality, cost and durability to our customers. PROGRAM DESCRIPTION GM Supplier Business Council (SBC) The GM SBC consists of 20 suppliers who meet quarterly with our GPSC Leadership Team. Within the SBC, the Sustainability Sub-Council serves as a sounding board for GPSC’s sustainability strategy. The Sustainability Sub-Council consists of SBC and non-SBC members who are recognized for their work in sustainability and a team of cross-functional GM employees. We look to this Sub-Council as the voice of our greater supply base on topics of sustainability. GM Supplier Business Meetings GM Supplier Business Meetings are held regularly throughout the year as a global webcast where GM global topics are shared. GM Chair and CEO Mary Barra addresses this group annually. Suppliers who participate in this webcast represent approximately 85% of our annual purchases for parts and services. GM Supplier Safety Council The Supplier Safety Council serves as an open and collaborative forum to exchange safety policies and share best practices across the supply base. Any GM supplier is welcome to access the Council’s database to learn safety practices that can be shared within their own operations and supply base. GM SupplyPower GM SupplyPower is an internet portal used by GM to share information, including sustainability event information, policies, guidelines, standards and reports, and best practices with suppliers. It includes a section devoted to sustainability. We encourage suppliers to facilitate discussions with their organizations on important information posted in SupplyPower. Supplier of the Year Our Supplier of the Year program recognizes top performers. In 2021, 135 suppliers from 16 countries were awarded and recognized, including 17 first-time winners. The 2021 program also included a new Overdrive Award with criteria including supplier sustainability innovation. Communication Tools Communication tools—AwareLine, Speak Up For Safety and others—are used by suppliers and our own employees to raise concerns, including those relating to potential human rights and environmental violations. Speak Up!, GM’s Non-Retaliation Policy , protects GM employees from retaliation as a result of raising concerns. Our Supplier Code of Conduct prohibits suppliers from retaliating or harassing their employees for utilizing grievance mechanisms. Across the globe, we hold various webinars and work with third parties to provide external training to improve supplier operations, primarily in the areas of environmental management, workplace conditions, sustainability, ethics and human rights. In 2021, we conducted 18 supplier educational sessions covering topics that included energy reduction, conflict mineral reporting template requirements, supplier sustainability goal-setting and sustainable logistics. 2021 OVERDRIVE AWARD FOR SUSTAINABILITY WINNERS 2020 OVERDRIVE AWARD FOR SUSTAINABILITY WINNERS Skip Navigation Introduction Reducing Emissions Design for Environment Technology Customers Safety Diverse Workforce Human Rights Supply Chain Communities Governance 2021 SUSTAINABILITY REPORT 84
Industry Collaboration We collaborate with, and are active members of, organizations inside and outside the automotive industry to develop sustainable and socially responsible supply chain programs. We work closely with many industry- and supply chain-focused organizations, including the Automotive Industry Action Group (AIAG), where we actively participate in the Responsible Materials Work Group, along with several of its subgroups, and sit on the Corporate Responsibility Steering Committee. GM has partnered with the AIAG, of which we are a member, to provide training to our employees and suppliers through their Supply Chain Sustainability eLearning. The training reflects the Automotive Industry Guiding Principles, which are comprised of three pillars: Business Ethics, Environment, and Human Rights & Working Conditions. Human rights training topics include child labor and young workers, wages and benefits, working hours, forced labor, freedom of association, health and safety, harassment and nondiscrimination. In 2020, 400 GM employees took the AIAG training; this number increased to 475 in 2021, covering 17 different countries within GM’s global footprint. In Spring 2022, AIAG will be launching a more robust sustainability eLearning platform that expands on the content of the current training. This interactive and comprehensive platform will engage trainees in scenario-based learning that references specific challenges within the sustainability sphere. GM is serving as a sponsoring company to help finance the tool, and, as a result, training will be free to suppliers. GM expects to begin rolling out the AIAG sustainability eLearning platform to a portion of our supply base mid-year 2022. Compliance with IATF 16949 Quality Standards (IATF 16949) is a requirement for GM Tier I suppliers. This third-party certification requires suppliers to employ responsible supply chain practices and to have policies on employee code of conduct, antibribery and ethics escalation policy (“whistle-blowing”). Learn more in the Upholding Human Rights section of this report. → 475 GM employees in 2021 received AIAG’s Supply Chain Sustainability eLearning training, which highlights fundamental principles of responsible working conditions. 89% of approximately 4,000 supplier locations are third-party certified to the IATF 16949 Quality Standard. Key Industry Collaborations Skip Navigation Introduction Reducing Emissions Design for Environment Technology Customers Safety Diverse Workforce Human Rights Supply Chain Communities Governance 2021 SUSTAINABILITY REPORT 85
Integrating Sustainability Into Our Supply Chain GM is driving toward an all-electric future with a vision of everybody in. This vision extends beyond GM and includes our suppliers. We know that only with our suppliers’ commitment will we achieve our vision of zero crashes, zero emissions and zero congestion. We take pride in knowing that many of our suppliers are dedicated to protecting our planet and fostering healthy work environments. In recognition of this commitment, in 2021, we began inviting Tier I suppliers to sign General Motors’ Environmental, Social and Governance (ESG) Partnership Pledge. Our ESG Partnership Pledge embraces sustainability in a holistic manner, focusing on commitments related to environmental, social and governance topics. Suppliers pledging to improvements in these three pillars helps us all accomplish our shared goals of reducing economy-wide carbon emissions and serving our communities. For the environmental pillar, we ask suppliers to commit to carbon neutrality for their Scope 1 and Scope 2 emissions relevant to products or services a supplier provides to GM. The timeline for a supplier to reach carbon neutrality is based on their industry, listed at right. GM selected the listed carbon neutrality dates for each supplier industry based on the technology available to achieve a realistic yet ambitious glidepath. For the social pillar, we ask suppliers to achieve or exceed a threshold score within the EcoVadis system in the areas of Labor and Human Rights as well as Ethics. Likewise in the governance pillar, suppliers are asked to achieve or exceed a threshold score in the area of Sustainable Procurement within EcoVadis. These scores show a supplier’s commitment to developing a comprehensive social responsibility program as well as robust environmental and social programs within their own supply chains. Timeline to Achieve Aspirational Carbon Neutrality by Supplier Category By 2025 or sooner Professional Services Suppliers working predominantly in offices providing software/ nonmaterial goods By 2035 or sooner Manufacturing Suppliers providing vehicle components and purchased equipment By 2038 or sooner Raw Materials/ Logistics Suppliers in carbon-inten- sive industries providing raw materials or primary resources and services that are focused on freight and transportation We ask suppliers to provide near-term results by obtaining a minimum score of 50 in the EcoVadis Human Rights, Ethics and Sustainable Procurement Pillars. Skip Navigation Introduction Reducing Emissions Design for Environment Technology Customers Safety Diverse Workforce Human Rights Supply Chain Communities Governance 2021 SUSTAINABILITY REPORT 86
INTEGRATING SUSTAINABILITY INTO OUR SUPPLY CHAIN CONT. The cross-functional GPSC Sustainability Team is leading efforts to integrate sustainability into all aspects of our supply chain. Focus areas include culture and communication; energy; finance; strategy and policy; supplier engagement; supplier performance and reporting; supply chain; packaging and logistics; and sustainable materials. We recently announced the GM Supplier Renewable Energy Solutions program in collaboration with Shell Energy. This innovative energy pilot program offers certain suppliers special pricing on renewable energy for electricity, along with other benefits such as complementary carbon tracking. All participants in the program will receive 5% Renewable Energy Credits (RECs) matched to their energy use, and CO2 tracking. Plus, they have the option to purchase additional RECs to help address their carbon footprint efforts. Another key achievement in 2021 was the publication of a GM Sustainability Partner Guide and Framework to our Tier I suppliers, which communicates our supply chain goals, priorities and processes. The guide outlines GM’s approach to sustainability and includes increasing levels of engagement from our suppliers with four distinct levels: compliance, commitment, growth and leadership. Both the guide and framework are available to suppliers through SupplyPower, the GPSC sustainability portal. The framework addresses environmental, social and governance topics and allows for supplier-specific goals based on their materiality assessments. Some goals are universal for all suppliers, such as year-over-year carbon reduction targets . The framework also contains requirements that support GM’s vision for more sustainable materials in our products, packaging and logistics, as well as overall supplier sustainability within their own operations. GM’s Supplier Sustainability Framework defines how we measure sustainability goals within our supplier purchasing program. GM’s Supplier Sustainability Framework enables us to assess sustainability within our Tier I supplier community, including Strategic Supplier Engagement (SSE) and key indirect and logistic suppliers. Additionally, it creates a pathway for GM suppliers to take increasingly bold steps toward a more sustainable future. The framework is comprehensive and inclusive of our Tier I suppliers, allowing each supplier to be recognized for supporting GM’s sustainability goals. Assessing Performance In 2021, we furthered our commitment to create a more sustainable supply chain by working with EcoVadis to rate and understand the sustainability performance of our supply base. EcoVadis allows us to gain visibility of the management systems suppliers have in place to support advancement of the environment, labor and human rights, ethics and sustainable procurement. Working with our suppliers and EcoVadis through their platform, scorecard and performance improvement tools in 2021, we have established a sustainability performance benchmark representing 83% of GM’s Direct Tier I strategic spend. The average score of all GM’s rated suppliers is 51.7 out of 100, which is 15% (or 8.1 points) higher than the average of all suppliers rated by EcoVadis in 2021. Moving into 2022 and beyond, with the integration of EcoVadis in 2021, GM is setting expectations to drive rapid supplier sustainability improvement to meet our ambitious supply chain sustainability goals. General Motors Sustainable Purchasing Program Supplier Goals Framework Level 0 Compliance GM’s baseline requirements for our suppliers. 1 Commitment Making sustainability a priority, creating alignment, setting goals and achieving results. 2 Growth Furthering commitment while expanding sustainability into one’s supply chain. 3 Leadership A true accomplishment, recognizing a supplier as a pacesetter in sustainability. All Tier 1 Suppliers Terms and Conditions Supplier Code of Conduct Materiality assessment Goals in all 3 sustainability pillars (relevant, impactful, transparent, improving, United Nations Sustainable Development Goal (UN SDG) linked) ≥ 4% year-over-year absolute CO2 reduction (Scope 1 & 2) Sustainable procurement program Supplier to cascade goals into own supply base Minimum ratings (CDP, EcoVadis) Industry Leader Leading innovator Ambitious targets (Scope 1, 2 & 3, SBTi, Zero Waste) Proactive actions Life cycle assessment (full) Enrolled Suppliers* Score in EcoVadis CDP participation Industry specific participation (e.g. GPSNR) ≥ 3% year-over-year absolute CO2 reduction (Scope 1 & 2) Actively support GM’s commitment to sustainable materials and packaging Strong social sustainability commitment * Initial enrolled suppliers to include SSE suppliers, key indirect and key logistics suppliers. Skip Navigation Introduction Reducing Emissions Design for Environment Technology Customers Safety Diverse Workforce Human Rights Supply Chain Communities Governance 2021 SUSTAINABILITY REPORT 87
CDP Supply Chain Response INTEGRATING SUSTAINABILITY INTO OUR SUPPLY CHAIN CONT. Climate Response 99% response rate from enrolled suppliers 50% of suppliers engaging their own suppliers $2B annual monetary savings from emissions reductions 61% reporting active targets 465.27M (metric tons) estimated annual CO2e savings Water Response 78% response rate from enrolled suppliers 25% of suppliers engaging their own suppliers 48% reporting any water-related policy 76% reporting active targets and/or goals 70% reporting water accounting As we are all met with the realities and consequences of climate change, our deep relationships with suppliers will help us innovate to find industry solutions. The issues we face today cannot be solved by one company, or even one nation, which is why at GM we are taking an ‘everybody in’ approach that includes each one of our suppliers.” SHILPAN AMIN GM Vice President, Global Purchasing and Supply Chain—Introduction of GM Sustainability Partner Guide and Framework (2021) CDP Supply Chain Initiative GM has participated in the CDP supply chain since 2013. We are working with CDP and our suppliers to accelerate action on the environmental front. CDP supports companies in measuring and managing their impacts on climate change, deforestation and water-related risks. GM’s participation in CDP goes beyond our own operational footprint to include information from select suppliers. Enrolled suppliers in the CDP initiative include all direct material strategic suppliers, a subset of indirect suppliers who are mainly manufacturing-based suppliers and our top strategic logistics suppliers. This group represents more than 80% of our supply chain spend. During the past two years, we have set a goal of increasing participation among in-scope SSE and key logistic suppliers year-over-year. In 2021, our response rate rose to more than 99% of surveyed suppliers, exceeding previous years for the Climate Change questionnaire. We aim to achieve 100% participation for targeted suppliers in 2022. Skip Navigation Introduction Reducing Emissions Design for Environment Technology Customers Safety Diverse Workforce Human Rights Supply Chain Communities Governance 2021 SUSTAINABILITY REPORT 88
INTEGRATING SUSTAINABILITY INTO OUR SUPPLY CHAIN CONT. Managing Supply Chain Impact Through Life Cycle Analysis Life cycle analysis, using environmental extended input/output analysis from the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (U.S. EPA) EEIO 2.0 database, allows us to estimate the environmental impacts of our 18,936 suppliers. The analysis is broken down by industry and tier to identify which products in our supply chain contribute to greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions, water consumption and land use. GHG Impact by Supplier Tier & Industry In our supply chain, the largest GHG and water impacts occur among Tier II suppliers. Purchased goods and services represent 13% 2 of our total carbon emissions which we are working to reduce. We analyze environmental supplier impacts at the vehicle component level to identify potential priority areas for carbon reduction. This helps us monitor and manage sustainability trends within our supply base as automotive technologies change. Supplier GHG Impact by Vehicle Component 1 TIRES & WHEELS 6% POWERTRAIN 35% GLASS 1% BODY 28% INTERIOR 26% S E AT S 4% 1 G HG Data is for calendar year 2020 and represents our most recent analysis. The analysis excludes our Joint Ventures. 2 Inc ludes purchased goods and services Scope 3 category one. Skip Navigation Introduction Reducing Emissions Design for Environment Technology Customers Safety Diverse Workforce Human Rights Supply Chain Communities Governance 2021 SUSTAINABILITY REPORT 89
Supplier Engagement and Training on GM Environmental Standards The GPSC Sustainability Team employs multiple avenues for supplier engagement on environmental topics, as the following examples demonstrate. Energy Treasure Hunts We conduct energy treasure hunts with suppliers to drive energy- and water-reduction efforts at Tier I and Tier II supplier facilities. The program’s success is embedded in its collaborative framework, identifying potential energy reduction and financial savings opportunities at suppliers’ manufacturing facilities. In 2021, GM conducted this analysis with five suppliers: Lear, Kongsberg Automotive, Superior Industries, Tenneco and Adient. These treasure hunts collectively provided recommendations to save 3,300 MWh of energy and 6,660 cubic meters of water, as well as eliminating 3,158 metric tons of CO2 emissions. Sustainable Steel Summit As we continue to examine our environmental impact, we recognize steel is a major contributor to carbon emissions. In order to address this impact, GM hosted our first Sustainable Steel Summit focused on engaging key steel suppliers in a collaborative discussion about the industry’s most pressing issues, including carbon emission reduction strategies. The Summit began with a leadership kickoff message, followed by emerging renewable energy for electricity technology, a look into GM supplier sustainability and a carbon neutral roadmap. It concluded with a moderated discussion with all attendees. GM leadership facilitated the discussion topics around the challenges of moving toward “green steel” and next steps in developing a shared sustainability plan with GM material partners. The summit helped solidify GM’s partnership with steel supplier Nucor, effectively becoming the first customer for Econiq, Nucor’s new range of net zero carbon steel products. Energy Symposium Also in 2021, we held an Energy Symposium focused on renewable energy and carbon neutrality. The two-day event provided insight into renewable energy for electricity as a sound business decision. The GPSC Sustainability Team, suppliers and stakeholders discussed carbon neutrality and highlighted immediate tangible opportunities and resources available to accelerate action. The first day was open to the public; employees, suppliers and stakeholders invested or interested in carbon neutrality and renewable energy were invited to join. The second day was directed toward energy conservation practitioners—site energy leaders and utility managers. Sustainability in Logistics GM participates in various freight sustainability programs, including the EPA’s SmartWay Partnership, which we have been a proud member of since 2013. In 2021, we increased our engagement with the SmartWay program by encouraging all our eligible logistics suppliers to join. As a result, participation in the program increased by one-third, with a commitment from U.S. and Canadian carriers that represents 99% of our truck and rail spend. Through participation in Transporte Limpio, a freight efficiency program administered by Mexico’s Secretariat of Environment and Natural Resources, we are expanding freight efficiency efforts to include Mexican truck carriers. Our GM Logistics Team aggressively evaluates our logistics network for optimization opportunities, studying methods for improving efficiency and emissions reduction through redesigning routes, changing modes and adjusting frequency. In 2021, the team implemented a program to include emissions metrics in business case analyses. The integration of carbon calculation methodology allows for increased visibility of CO2 emissions when reviewing and considering various network scenarios. Our GM Logistics Team is also focused on increasing collaboration with our carriers, industry leaders and peers. In 2021, GM held its first Global Logistics Sustainability Workshop with approximately 500 attendees from 150 logistics suppliers. Also in 2021, the EPA invited our GM Logistics Team to speak at a SmartWay webinar to share our sustainability journey with more than 100 companies from a range of industries. As we build on this progress and drive toward a more sustainable and efficient logistics network, our goals include: • Increasing supplier participation in freight sustainability programs, including engagement from our ocean and airfreight carriers • Incorporating sustainability metrics into sourcing decisions and carrier scorecards • Collaborating with carriers on emissions reductions and green technology adoption • Promoting the development of innovative strategies, best practice sharing and top-performing carrier recognition INTEGRATING SUSTAINABILITY INTO OUR SUPPLY CHAIN CONT. Skip Navigation Introduction Reducing Emissions Design for Environment Technology Customers Safety Diverse Workforce Human Rights Supply Chain Communities Governance 2021 SUSTAINABILITY REPORT 90
Supply Chain Compliance We place high expectations of excellence and ethical conduct on our suppliers, who are expected to act in a way that is consistent with our principles and values. Our Supplier Code of Conduct and purchase contract Terms and Conditions set forth expectations for ethically responsible social, business and environmental practices. Our Terms and Conditions clearly state our prohibition against any use of child labor or any other form of forced or involuntary labor, abusive treatment of employees or corrupt business practices in the supplying of goods and services to GM. Our contracts lay out expectations for lawful compliance within the following areas: data protection and privacy, wages, hours and conditions of employment, subcontractor selection, antidiscrimination and occupational health and safety. GM also expects suppliers to cascade our Supplier Code of Conduct or a code with similar requirements throughout their own value chain. We are committed to upholding human rights across our network of suppliers and have several policies in place, including our Human Rights Policy and Conflict Minerals Policy. Our strong focus on supplier sustainability influences sourcing decisions. We strive to utilize ethical and sustainable suppliers who share our values to work together to reach mutual sustainability goals. When sourcing, criteria including meeting conflict mineral reporting requirements, CDP participation and EcoVadis scores are reviewed. High-scoring suppliers may be rewarded with the potential for new or extended contracts. When we become aware of violations or alleged violations of our Supplier Code of Conduct, we respond swiftly and appropriately, up to and including the termination of business relationships. GM conducts annual self- verification surveys to validate adherence to the Code and contractual obligations. Material noncompliance disclosed in surveys or otherwise identified is addressed directly with suppliers. In 2021, survey responses were collected from 3,900 suppliers spanning production, logistics, customer care and after sales support. Supplier responses to the survey are reviewed and, if required, are escalated to remediate risk and noncompliance. GM requires our Tier I suppliers that provide production parts for vehicles across the globe to mandate that their direct suppliers meet all GM’s quality standards. The foundation of this process is our Built in Quality Supplier (BIQS), consisting of IATF 16949 certification and Quality Performance Metrics. This foundation allows them to cascade quality standards through the tiers of our supply base. We aim for all GM Tier I suppliers to achieve BIQS Level 5, the highest level possible. BIQS compliance also encourages these Tier I suppliers to uphold the same quality standards within their own supply bases, since issues here can ultimately affect their quality performance. To support monitoring, suppliers’ IATF 16949 certification status is part of our Sourceability Report, which is a compilation of metrics used to make informed sourcing decisions and support supplier engagement. Suppliers found not conforming to the IATF standard are required to implement corrective actions. After implementation, the certification body reaudits the supplier to ensure conformance. 3,900 suppliers participated in supplier compliance surveys in 2021. Skip Navigation Introduction Reducing Emissions Design for Environment Technology Customers Safety Diverse Workforce Human Rights Supply Chain Communities Governance 2021 SUSTAINABILITY REPORT 91
Supply Chain Disruption Supply chain visibility is key to identifying and mitigating sustainability risk and impacts and achieving proactive avoidance. We utilize an industry-leading, in-house customized supply chain visibility tool that integrates GM plants, Tier I suppliers, reported Tier II suppliers and logistics nodes. This tool gives our organization the capability to map geographic locations and relationships across the global GM supply chain. The tool also incorporates 24/7 monitoring and global incident mapping of supply chain disruptions and potential human rights issues including those affecting members of our supply chain worldwide. Through our monitoring process, GM can identify suppliers potentially involved in human rights events. If identified, GM’s Supply Chain Risk Management Team reacts swiftly to notify the appropriate GM global supply chain crisis response teams. These crisis teams are then able to work cross-functionally with Tier I suppliers and GM’s functional purchasing, logistics and engineering teams to respond. This collaboration enables GM to mitigate any human rights or sustainability risks potentially identified. How We Monitor & Manage Supply Chain Risks • Senior leadership review at least four times per year • Cross-functional meetings • Board Risk & Cybersecurity Committee • Risk Advisory Council • Quarterly risk dashboard updates • Annual CEO business unit reviews • Annual global risk assessment • Senior Leadership Team interviews Supply Chain Monitoring • Use innovative tools and real-time data analysis to monitor catastrophic events (e.g., earthquake, hurricane) and isolated disruptions (e.g., factory fire, labor strike). • Report all potential impacts to regional command center. • Receive information on suppliers and supply chain tiers through third-party services. • Factor risk scores into sourcing process. • Develop mitigation plan for high-risk areas. Skip Navigation Introduction Reducing Emissions Design for Environment Technology Customers Safety Diverse Workforce Human Rights Supply Chain Communities Governance 2021 SUSTAINABILITY REPORT 92
Responsible Sourcing of Raw Materials Many of the advanced technologies in our portfolio may use minerals and materials that are potentially mined in conflict-affected and high-risk areas. To identify and mitigate human rights risk in the sourcing of these raw materials, our due diligence practices undertaken in connection with our Responsible Materials Program and our Conflict Mineral Program are aligned with the Organization for Economic Co-operation and Development Due Diligence Guidance for Responsible Supply Chains of Minerals from Conflict-Affected and High-Risk Areas. We enjoy strong management support for conflict mineral supply chain due diligence. A compliance committee comprised of cross-functional GM leaders and an executive steering committee provide leadership and direction for the program. Third-party cobalt and mica mining activities in certain regions of the world have been associated with potential human rights violations. To help mitigate this risk, we annually request all Tier I direct vehicle component suppliers with cobalt product content to complete the Cobalt Reporting Template, the Mica Reporting Template (MRT) and the Conflict Minerals Reporting Template (CMRT) to help GM map the supply chain for components containing these minerals. Similarly, we annually utilize the CMRT to survey 100% of Tier I suppliers with products containing tin, tungsten, tantalum and gold (3TG) to gain visibility of the smelters or refiners (SORs) of these minerals in our supply chain. In 2021, 2,602 supplier locations were considered in-scope for GM’s Conflict Minerals Program, and we received responses from 94% of these suppliers. After SORs are identified, they are validated to determine whether they have passed the Responsible Minerals Assurance Process (RMAP). This process, administered through the Responsible Minerals Initiative (RMI), employs a risk-based approach to validate SORs’ processes in place for responsible mineral procurement. Those SORs that have passed this assessment are considered conformant to the RMAP. Supporting Supplier Communities GM is committed to supporting communities in which we source minerals. For example, we recently became members of the Pact Youth Apprenticeship Program in the Democratic Republic of the Congo. Pact implements various programs in the Lualaba province with the aim of reducing child labor in mining. These activities include community sensitization, positive parenting training, coordination of community stakeholders and strengthening of civil society organizations. Since 2017, Pact has assisted youth in the Kolwezi area to thrive in alternative livelihoods to mining by equipping them with vocational and business skills. Pact analyzes the feasibility and profitability of trades within a specific community through a market study. Then, Pact identifies mentors from the selected trades and chooses them based on their good character, solid professional experience, proof of legal establishment and a workshop in the target community. Finally, adolescent miners, from 15 to 17 years old, are selected to undergo a six-month intensive apprenticeship in a trade. Skip Navigation Introduction Reducing Emissions Design for Environment Technology Customers Safety Diverse Workforce Human Rights Supply Chain Communities Governance 2021 SUSTAINABILITY REPORT 93
RESPONSIBLE SOURCING OF RAW MATERIALS CONT. We work with our suppliers regularly to provide education and awareness, including training, webinars and supplier bulletins. We are active in the AIAG Responsible Materials Work Group, which works on common automotive industry solutions with other original equipment manufacturers (OEMs) and suppliers regarding conflict minerals and high-risk materials. In 2021, we joined the Initiative for Responsible Mining Assurance, a third-party certification of industrial mine sites for mined materials, and RCS Global Better Mining Initiative for small and artisanal mines. It is our aim to work with suppliers through the tiers of our supply chain to identify nonconformance to our policies and code of conduct and remedy nonconformance. If we cannot find an avenue to mitigate the risk, we reevaluate the business relationship. We are an active participant within the RMI and corresponding RMI working subgroups. The Smelter Engagement Team is one of these subgroups that enables us to have direct SOR engagement. We have found that coordinated outreach to nonconformant SORs can be effective at encouraging RMAP participation. Likewise, GM has participated in RMI-sponsored SOR RMAP pre-audit visits, with the most recent visit being in 2019 with an Indian gold refiner. If SORs have not been validated as conformant to the RMAP, we encourage them to participate in this third-party assessment. GM sent communications to 10 3TG SORs during the 2021 calendar year. Due to COVID-19 concerns and restrictions, GM did not conduct on-site SOR visits in 2020 or 2021. The extraction of cobalt, a component of lithium- ion batteries, raises industrywide concerns around the use of child labor. Through efforts and membership in RMI, we are working to mitigate human rights risk in the cobalt supply chain by: • Identifying and assisting with the disposition of cobalt refiners to determine if these companies meet RMI’s industry specification for an eligible cobalt refiner. • Performing outreach to cobalt refiners that are not conforming to the RMI industry standards to encourage them to go through the RMAP for cobalt. • Functioning as a single point of contact on behalf of RMI for several cobalt refiners, assisting them in their pursuit to join the RMAP. We are working collaboratively within RMI’s mica subgroup to proactively develop processes to reduce human rights risk in the mica supply chain. The RMI subgroup is working with the Responsible Mica Initiative in the following areas: • Identifying processors of mica in the supply chain using a company identification questionnaire. • Creating a joint due diligence standard for these processors. • Dispositioning processors of mica using RMI methods and adding them to the RMI smelter/ refiner database. These efforts will allow us to expand our due diligence scope to mica. In 2021, we requested MRTs from all suppliers with mica content in their products. Doing so will allow GM to gain visibility of mica processors in our supply chain to identify risk and conduct due diligence to reduce human rights and environmental harm in the mica supply chain. Skip Navigation Introduction Reducing Emissions Design for Environment Technology Customers Safety Diverse Workforce Human Rights Supply Chain Communities Governance 2021 SUSTAINABILITY REPORT 94
→ Supporting Diverse Suppliers GM continues to build upon our legacy of leadership by helping diverse suppliers advance. In 1968, we became the first OEM to establish a formal supplier diversity program. We have continued to contribute to many community initiatives in collaboration with diverse suppliers. GM strives to achieve equitable and sustainable supply chain inclusion goals that establish long-term viability for our diverse supply base. For over a decade, GM utilized our annual Supplier Connections event to strengthen existing relationships, enhance our business acumen and identify new sourcing opportunities, which has attracted thousands of attendees. COVID-19 has challenged us and our diverse business communities, driving us to stay connected virtually in 2021. We supported multiple virtual conferences with our advocacy partners, such as the National Minority Supplier Development Council, as they focused on preparing, positioning and propelling minority business owners to the next level of achievement, despite the impact of the global pandemic. GM received Top Corporation Platinum Award Winner by the Women’s Business Enterprise National Council— their highest distinction for corporations that have demonstrated a sustained commitment to the inclusion of women-owned businesses in their supply chains. In 2021, we invested over $250,000 in technical assistance programs, reaching more than 100 diverse businesses through key partnerships. GM was the first automaker to join the National Gay & Lesbian Chamber of Commerce, which supports and certifies LGBTQ+ owned and operated businesses. 39% Asian Pacific/Indian 26% Women, Nonminority 22% African American 7% Hispanic 3% Canadian Aboriginal 3% Native American Our Vision Achieve equitable and sustainable supply chain inclusion goals that ensure long-term viability for our diverse supply base. Our Mission We serve as bridge builders, connecting an ecosystem of diverse suppliers, communities, advocacy organizations and customers. Our Aim To ensure that our connections drive lasting business relationships, customer loyalty and world-class parts and services that support our long-term viability. $3.8B Approximate spend with North America diverse Tier I suppliers for direct materials $2.2B Approximate spend with North America diverse Tier II suppliers for direct materials Learn more about GM’s robust Diversity, Equity & Inclusion program in the Developing Talented & Diverse People section of this report. Skip Navigation Introduction Reducing Emissions Design for Environment Technology Customers Safety Diverse Workforce Human Rights Supply Chain Communities Governance 2021 SUSTAINABILITY REPORT 95
Our Supplier Diversity Mission: Drive I.D.E.A.S. SUPPORTING DIVERSE SUPPLIERS CONT. I MPACT Economic & Community Impact • Annual Tier I & II spend targets and performance management • Sourcing inclusion and supplier sustainability goals • Health Check Assessment D EVELOPMENT • Dartmouth College partnership: Tuck Executive Education—Diverse Business Programs (Advisory Board Chair and 19 scholarship awards in 2021) • Inner City Capital Connect Detroit Cohort Anchor Sponsor: ○ Strategic partnership that offers a tuition-free program focusing on executive education, training and mentorship to Detroit’s small business owners • Women Entrepreneur Leadership Lab Detroit Cohort Sponsor: ○ Technical assistance and networking program that has a strategic focus on developing African American women entrepreneurs at various stages in their business journey • Member of the Automotive Industry Group— National Minority Development Council ○ Comprised of 16 OEM companies with the following core objectives: ➞ Benchmarking of World Class Suppliers leading to enhanced sourcing opportunities across the automotive industry ➞ Enhancing our members’ skill sets and related processes • Partnered with Women’s Business Enterprise (WBE) six-time Emmy Award winner, Shawne TV, to help drive new relationships, engage in discussion and deliver strategic content via social media with diverse audiences and organizations E DUCATION • National Association of Black Suppliers (five scholarships awarded to high school students) • Sponsored four Cristo Rey High School student internships that support two local advocacy organizations • Sponsored Black United Fund, which is committed to supporting, developing and implementing youth empowerment programs in underrepresented communities A DVOCACY • Active memberships and sponsorships with more than 20 national and regional organizations • Partnered with the Asian Pacific American Chamber of Commerce (APACC) to support the Asian American Pacific Islander (AAPI) small business community by helping approximately 70 AAPI-owned small businesses and individual professionals gain access to APACC membership, resources and programming S UPPLIERS • Partnered with a WBE company, Diversity Spend Solutions (DSS), to create and track Tier I diverse spend • In partnership with DSS, Supplier Diversity executed an assessment to our internal procurement teams and strategic diverse supply base that aids in driving shared accountability of Supplier Diversity key performance indicators across our enterprise • GM Supplier Council representation (six of 20 members are diverse business owners) • In addition to our GM Supplier Council, our Supply Chain organization commenced a Supplier Inclusion Board assembled of our 13 supplier partners who demonstrate a similar level of DEI commitment as we do by sharing best practices. The Supplier Inclusion Board’s mission is to enlighten, promote and improve DEI by collaborating with other suppliers, and the overall industry, to be the automotive manufacturer of choice reflecting our diverse customer base. Skip Navigation Introduction Reducing Emissions Design for Environment Technology Customers Safety Diverse Workforce Human Rights Supply Chain Communities Governance 2021 SUSTAINABILITY REPORT 96
SUPPORTING DIVERSE SUPPLIERS CONT. Diverse Media Suppliers General Motors remains committed to our approach to diverse relationships through our stated action plan, which enables engagement, economic empowerment and sustainable growth with diverse media. The action plan is realized through five components: 1. Strengthened Commitment ○ Increased Diverse Media Spend—In 2021, General Motors achieved our stated goal of investing 8% in Total Diverse Owned and Targeted media, and we expect to meet our goal of investing 10% in Total Diverse Owned and Targeted media in 2022. 2. Deeper Engagements ○ Diverse-Owned Media Summit—GM hosted our first Diverse-Owned Media Summit in May 2021, with over 200 diverse media owners in attendance to demonstrate our commitment to build relationships with diverse-owned media providers through communication and collaboration. We will host our 2nd Annual Summit in May 2022. ○ We encouraged attendees at the Summit to submit an overview of their business for GM’s consideration for deeper engagements beyond the summit. ○ Adding to the Annual Summit, in 2022 we expect to introduce a series of quarterly connects designed to aid in continuous dialogue, information sharing and inspiration with diverse owners. 3. Sustainable Growth ○ Diverse Marketing Incubator Fund—GM plans to allocate $50 million over 10 years to support and scale diverse marketing companies. This investment is expected to support sustainable growth and is incremental to GM’s media spend. 4. Increased Flexibility ○ Revisited Payment Terms—General Motors was an early adopter to shorten payment terms for its diverse-owned marketing companies by modifying our standard payment terms and reducing payment timing from 60 days to 30 days to help give diverse suppliers greater flexibility. This underscores GM’s priority, in collaboration with diverse media, to create a win-win for diverse media companies and GM. 5. Expanded Opportunities ○ Prospective Partnering Analysis—GM expects its media buying agencies to follow a multifactor analysis for selection of diverse media. The analysis requires new criteria for assessing capabilities, reach and analytics and is expected to drive more opportunity for diverse media. Achieved our goal of 8% in Total Diverse Owned and Targeted media in 2021 Expect to meet our goal of 10% in 2022 Skip Navigation Introduction Reducing Emissions Design for Environment Technology Customers Safety Diverse Workforce Human Rights Supply Chain Communities Governance 2021 SUSTAINABILITY REPORT 97
Building More Inclusive Communities IN THIS SECTION An Inclusive Social Impact Strategy 99 Funding to Support an Equitable Transition 100 Climate Equity Fund: Year 1 Highlights 101 Investing in Our Hometown 101 Community Relations 102 Our Strengths y Contributing our time and talents to benefit underserved communities y Building positive relationships in communities that strengthen our social license to operate y Using the power of our voice to advocate internally and externally, for a future with equity and inclusion for all y Ensuring an equitable transition to an all-electric future Our Opportunities y Continuing to work to make sure that everyone in our communities has an equitable chance to succeed y Measuring social impact in a meaningful and statistically rigorous way y Supporting communities that are disproportionately affected by climate change through our Climate Equity Fund and other initiatives Skip Navigation Introduction Reducing Emissions Design for Environment Technology Customers Safety Diverse Workforce Human Rights Supply Chain Communities Governance 2021 SUSTAINABILITY REPORT 98
An Inclusive Social Impact Strategy Our social impact strategy focuses on philanthropic investments that create inclusive and sustainable solutions to common social issues. We prioritize programs that create equitable opportunities for minority populations. Our social impact framework encompasses four focus areas with outcomes that we strive to achieve. Learn more about our focus areas in our Social Impact Report . STEM EDUCATION Advance Education in Science Technology, Engineering and Mathematics (STEM) VEHICLE & ROAD SAFETY Fuel Safer Practices in and Around Vehicles COMMUNITY DEVELOPMENT Improve Neighborhoods and Empower Residents CLIMATE EQUITY Equitable Access to a More Sustainable Future INDICATOR # of students with employable labor skills for careers in STEM # of vehicle-related injuries and deaths reduced # of individuals whose socioeconomic opportunity is improving # of closed equity gaps related to climate change SOCIAL OUTCOMES Increase in students who earn a degree in STEM that matches market needs Increase seat belt and restraint usage Increase basic literacy, essential technical skills and living wage employment opportunities Increase in number of people qualified for clean energy careers Increase presence, achievement and persistence for underrepresented minorities in STEM fields Decrease impaired and distracted driving Increase access to necessities, including food, housing, transportation and financial education Increase in awareness and/or access to sustainable transportation solutions Increase number of qualified teachers trained in STEM subjects Increase in awareness of safe road environments Increase in innovative and collaborative community improvements Increase in programs that mitigate the effects of climate change, assist with climate adaptation and/or community resilience TARGET POPULATION K-12th grade and college students with an emphasis on women and minorities All road users with an emphasis on children and teens Individuals in underserved communities Individuals in underserved communities with emphasis on Black, Indigenous and people of color (BIPOC) Skip Navigation Introduction Reducing Emissions Design for Environment Technology Customers Safety Diverse Workforce Human Rights Supply Chain Communities Governance 2021 SUSTAINABILITY REPORT 99
Funding to Support an Equitable Transition The changes driving the transition of our business to an all-electric future represent a seismic shift in our industry. Shifts of this magnitude have a history of leaving communities behind. As we accelerate that future, we must listen, learn and apply an equity lens to our actions. We understand that climate change does not impact every community equally, and that sustainable technology alone is not enough for everyone to benefit from an all-electric future. In its first year, the Climate Equity Fund disbursed grants to 19 nonprofit organizations. One recipient was a novel EV project, the St. Louis Vehicle Electrification Rides for Seniors (SiLVERS) program sponsored by Forth Mobility. SiLVERS provides EVs to two community centers that offer nonemergency rides to elders and distribute food to homebound seniors in North and South St. Louis. The program supports historically underserved communities with electric technologies to offset tailpipe emissions from fossil fuel-powered trips. Our understanding of community challenges associated with climate change has led to the establishment of a $50M Climate Equity Fund that provides philanthropic support to community-based organizations. We have doubled our investment since an initial $25 million in 2021. Grants are focused toward furthering the four areas of GM’s Climate Action Framework for an Equitable Transition : • future of work • electric vehicle (EV) access • EV infrastructure equity • climate equity Engaging with Stakeholders Our everybody in approach to an all- electric future extends to engaging with stakeholders on key topics. In 2021, Ceres convened a diverse group of stakeholders to provide recommendations to GM to help inform our role in an equitable transition to clean mobility within the United States. The discussion centered around three themes: • Defining equitable clean mobility, which may differ among communities and their historic context; • Economywide obstacles such as affordability of vehicles and access to charging infrastructure; and • Viable solutions in which GM can play a role such as charging and car share opportunities. In addition, other transition considerations were discussed, such as the impact on today’s workers and the need to prepare the next generation of workers for an EV future. Skip Navigation Introduction Reducing Emissions Design for Environment Technology Customers Safety Diverse Workforce Human Rights Supply Chain Communities Governance 2021 SUSTAINABILITY REPORT 100
Program Highlights Climate Equity Fund: Year 1 Highlights 1 605 individuals better qualified for clean energy jobs 19 nonprofits funded 94,287 individuals impacted 11,600 students, educators and mentors to implement sustainability projects 82,367 individuals to be impacted by climate change mitigation programs The Heat, Health and Equity Initiative (HHEI) addresses the disparate effects of extreme heat, one of the deadliest impacts of climate change, on low-income communities and communities of color throughout Northern Manhattan. The HHEI works to ensure the community is aware of the impact of extreme heat, and how to access benefits and programs, while also working to advance community-driven policy recommendations to improve federal and state programs. Valley CAN estimates only 20% of the needed zero-emissions- vehicle (ZEV) maintenance technicians receive training. Valley CAN partnered with community college automotive programs and the California New Car Dealers Association and their members to expand a successful ZEV maintenance pilot, creating a job pipeline for graduates and preparing to implement ZEV maintenance training curriculum statewide. A grant from GM will help RMI identify EV “charging deserts” in low-income communities across major North American cities. With this support, it will also create a large government, industry and community stakeholder effort to streamline residential and public EV charging infrastructure permitting, creating more opportunities to bring EVs to low-income neighborhoods. Investing in Our Hometown Another key focus of our corporate giving strategy is the city of Detroit, home to GM’s global headquarters. In 2021, we announced a $50 million investment in Detroit-based nonprofit programs that expand access to education and employment opportunities and strengthen city neighborhoods. We’ve aligned these specific areas of focus to address the needs of Detroit and its residents. Last year, we funded 53 projects that will impact 173,490 individuals. Portfolio highlights include: • 1.25 million pounds of fresh and shelf-stable food provided to families. • 129 individuals to enroll in paid training, internship and full-time employment opportunities. • $150,000 in grants awarded to 10 local small businesses. 10TH ANNIVERSARY OF GM STUDENT CORPS A paid summer internship program for high school students in underserved Michigan communities that offers life-skills training, college and work readiness, team building and community service. 1,570 students engaged since 2013 1 G eneral Motors awards grants for a one-year term. Therefore, grants awarded throughout 2021 may still be in progress in 2022, and some impact numbers may be estimates. Skip Navigation Introduction Reducing Emissions Design for Environment Technology Customers Safety Diverse Workforce Human Rights Supply Chain Communities Governance 2021 SUSTAINABILITY REPORT 101
Community Relations GM has 118 facilities in the United States, located in 27 states. In many of the communities where we live and work, we are a major employer and significant contributor to the local tax base. In turn, these communities are a source of local talent and resources that enable our operation. This symbiotic relationship is part of our business strategy, and we are committed to ensuring these relationships are built on trust and accountability. That means positive and sustainable engagement with key individuals, groups and organizations in each community where we live and work. As our industry and world transform, we aim to strengthen and fortify these grassroots relationships in order to build resiliency in both our business and our communities. In 2021, GM leaders at both the local and corporate level prioritized local community engagement and dialogue that centered on collaboration, problem solving and sharing of best practices. This communication included the launch of 10 unique external newsletters in 25 different communities to share quarterly local and corporate news. GM has longstanding positive relationships with local public health departments. The pandemic provided an opportunity to strengthen our collaboration through vaccination, contact tracing and other activities. As vaccines became available early in the year, GM developed an internal campaign to promote the benefits of vaccination. In GM communities where vaccination rates were lower than the state average, we partnered with local chambers of commerce to share our voice as a community business leader and our own approach to vaccination efforts. We also helped amplify this message through TV and radio interviews across multiple states and penned an op-ed from our chief medical officer and workplace safety lead, titled “Working Together for a Safe Return to Work,” that we shared with local publications. It’s particularly important for us to ensure local communities understand GM’s business transformation. Following our Investor Event in October, our executive vice president of manufacturing and sustainability hosted community webinars with key stakeholders to share more about GM’s growth strategy and electrification journey. He underscored that manufacturing is a competitive advantage for GM and outlined how we intend to bring our people and our communities along on our journey, and how we can support that journey by advocating for EV charging infrastructure and helping to build the workforce of the future. Corporate Giving Heat Map (U.S. Giving by State, 2021) Skip Navigation Introduction Reducing Emissions Design for Environment Technology Customers Safety Diverse Workforce Human Rights Supply Chain Communities Governance 2021 SUSTAINABILITY REPORT 102
1 S ubject to change annually based on investment portfolio priorities. 2021 GM Giving At-a-Glance 1 STEM IMPACT Tot al 1.7M individuals 74 nonprofits engaged To learn more about 2021 funding breakdown by focus area, download our 2021 Social Impact Report . FUNDING BY UNDERREPRESENTED POPULATION 39% Black/African American 19% Hispanic/Latino 8% Other underrepresented populations GM COMMUNITY IMPACT GRANTS DISBURSED $3M in grants 148 nonprofits 112,000 estimated people impacted COMMUNITY DEVELOPMENT IMPACT 76,230 total individuals 12 BIPOC-owned small businesses received a grant and technical assistance 11,827 free rides to alleviate transportation barriers 2,000 women of color to receive entrepreneurship education GM CARES Our employee volunteer force Time valued at $3M for 364 nonprofits 15,284 employee volunteers 95,648 volunteer hours 17 states and 9 countries VEHICLE & ROAD SAFETY IMPACT 36,000 individuals committed to the Safe Driving Pledge Tot al 900,000 individuals 153 high schools provided road safety programming 483,000 individuals to receive education on seat belt use Employee Participation Skip Navigation Introduction Reducing Emissions Design for Environment Technology Customers Safety Diverse Workforce Human Rights Supply Chain Communities Governance 2021 SUSTAINABILITY REPORT 103
Ensuring Responsible Governance Our Strengths y Using our Purpose, Vision, Values and Core Behaviors as a guide for how we conduct ourselves in all areas of business y Leading our industry regarding ethical business practices as one of Ethisphere’s World’s Most Ethical Companies ® y Maintaining Board committees that enhance the Board’s oversight of corporate social responsibility and sustainability Our Opportunities y Engaging with and incorporating the insights of institutional shareholders y Addressing emerging cybersecurity risks related to business and customer security and privacy y Ensuring environmental compliance at facilities across the world with varying requirements and resource constraints y Holding all employees and third parties accountable to our Code of Conduct and appropriately investigating concerns raised IN THIS SECTION Corporate Governance 105 Cybersecurity & Privacy 109 Environmental Management & Compliance 111 Ethics 114 Public Policy 118 Edition 1 Pickup limited availability by waitlist. Additional GMC HUMMER EV models available Fall 2022. Skip Navigation Introduction Reducing Emissions Design for Environment Technology Customers Safety Diverse Workforce Human Rights Supply Chain Communities Governance 2021 SUSTAINABILITY REPORT 104
Corporate Governance GM is governed by its Board of Directors that meets throughout the year. The Board is elected by GM’s shareholders to oversee and provide guidance on GM’s business and affairs. It is the ultimate decision-making body of the company, except for those matters specifically reserved to shareholders. Among other things, the Board oversees company strategy and execution of the strategic plan. In addition, it oversees management’s proper safeguarding of the assets of the company, maintenance of appropriate financial and other internal controls, compliance with applicable laws and regulations and proper governance. The Board is committed to sound corporate governance policies and practices that are designed and routinely assessed to enable GM to operate its business responsibly, sustain our success and build long-term shareholder value. The Board also works with management to integrate environmental, social and governance (ESG) principles into the company’s business strategy. This includes agenda items and discussions related to ESG topics at Board and committee meetings. Leadership Structure Currently, the Board is led by our Chair and CEO, Mary Barra, whose role as Board Chair is complemented by that of our Independent Lead Director, Patricia Russo. The Board is comprised of 13 members, all but one of whom—Ms. Barra—are independent, as defined by the Board’s Corporate Governance Guidelines, which reflect the independence standards of the New York Stock Exchange and the U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission. The Board has the flexibility to decide when the positions of Board Chair and CEO should be combined or separated and whether a GM executive or an independent director should be Board Chair. This allows the Board to choose the leadership structure that it believes will best serve the interests of our shareholders at any particular time. At this time, the Board continues to believe that Ms. Barra’s in-depth knowledge of GM’s business and vision for the future bring focused leadership to the Board. Therefore, combining the role of Chair and CEO and electing a strong Independent Lead Director results in the optimal Board leadership structure for GM at this time. Governance Best Practices and Shareholder Protections The Board has adopted governance structures and policies that it believes promote Board independence and protect the interests of shareholders. These structures and policies include, among others: • Independence of 12 out of 13 directors. • Strong Independent Lead Director empowered with clearly delineated duties. • Annual election of all directors. • Majority voting with director resignation policy in uncontested elections. • Annual review of the Board’s leadership structure by the independent directors. • Proxy access and shareholder right to call special meetings. • No poison pill or dual-class shares. Skip Navigation Introduction Reducing Emissions Design for Environment Technology Customers Safety Diverse Workforce Human Rights Supply Chain Communities Governance 2021 SUSTAINABILITY REPORT 105
Board Diversity GM’s Board is composed of directors who bring diverse viewpoints and possess a variety of skills, professional experience and backgrounds, including with respect to ESG. 54% of our directors are women, and 31% of our directors identify themselves as racially/ethnically diverse. In addition, 67% of Board committees are chaired by women. Read more about the Board in our 2022 Proxy Statement . CORPORATE GOVERNANCE CONT. 2021 Board Composition 6 Male 7 Female Male 7 6 Female 9 White 4 Diverse Race or Ethnicity White 4 9 Diverse race or ethnicity 6 0-5 years 4 >5-10 years 3 >10 years 0-5 years 4 6 >5-10 years 3 >10 years 3 50s 9 60s 1 70s 50s 9 3 60s 1 70s Committee Structure and ESG Governance The Board has six standing committees: Audit; Executive; Executive Compensation; Finance; Governance and Corporate Responsibility; and Risk and Cybersecurity. Other than the Executive Committee, all standing committees of the Board consist entirely of independent directors. Through the Board as a whole and each of its committees, the Board is committed to overseeing the company’s integration of ESG principles throughout GM’s business and managing the related risks and opportunities. The key responsibilities, recent activities and focus areas of each committee can be found in our 2022 Proxy Statement . Each committee has a written charter setting forth its purpose, authority and duties. Overall, the committees enhance the Board’s oversight of areas that are critical to GM’s corporate responsibility and sustainability efforts, including: transparent and reliable financial reporting; risk identification and mitigation (including climate change and other ESG issues); ethics and compliance; product and workplace safety; supply chain and human rights; pay-for- performance; data security; diversity, equity and inclusion; Board and management succession planning; consideration of shareholder proposals; and political and lobbying priorities and expenditures. 67% of committees chaired by women (4 out of 6) 63 average age of directors Range: 52—71 4 new directors over past three years Skip Navigation Introduction Reducing Emissions Design for Environment Technology Customers Safety Diverse Workforce Human Rights Supply Chain Communities Governance 2021 SUSTAINABILITY REPORT 106
Board Committees and ESG Each year, in connection with the review of its committee charters, the Board updates the committees’ oversight responsibilities as necessary. In 2021, the Board updated each charter to delegate specific ESG responsibilities to each committee. Below is a summary of these charter updates along with other highlights of the committees’ ESG-related responsibilities and practices: CORPORATE GOVERNANCE CONT. Governance and Corporate Responsibility Committee • Responsible for ESG initiatives, strategies and policies that have a material impact on the company. • Tracks an ESG scorecard and conducts annual reviews of ESG reporting standards, lobbying activities, corporate philanthropy and human rights (including responsible sourcing practices and policies). • Responsible for the Board’s shareholder engagement program. • Starting in 2022, reviews and approves the Sustainability Report. Audit Committee • Beginning in 2021, reviews the disclosure process and control procedures over ESG disclosures. • Starting in 2022, reviews and approves the Sustainability Report. • Oversees the Internal Audit Function, General Motors Audit Services (GMAS), which provides independent, objective assurance on the effectiveness of risk management, internal controls and governance processes within GM. GMAS’ annual audit plan includes coverage of controls around ESG disclosures as well as workplace and vehicle safety, ethics and compliance, environmental and cyber risks. Executive Compensation Committee • Starting in 2022, will (i) make an annual determination as to whether the company’s ESG and sustainability goals and milestones are effectively integrated into the compensation programs; (ii) review compensation plans for executives to confirm the alignment related to GM’s sustainability risks and opportunities; and (iii) with respect to the annual shareholder say-on-pay vote, consider shareholder feedback relative to the alignment of GM’s sustainability goals. Finance Committee • Reviews changes to our shareholder composition, including the impact of ESG- oriented investors. Risk and Cybersecurity Committee • Reviews GM’s strategic, operational and cybersecurity risks, including workplace safety, vehicle cybersecurity safety, climate change and privacy risk. • Considers climate change as part of its key strategic and operational risk management framework. Skip Navigation Introduction Reducing Emissions Design for Environment Technology Customers Safety Diverse Workforce Human Rights Supply Chain Communities Governance 2021 SUSTAINABILITY REPORT 107
Shareholder Engagement Members of the Board and senior management regularly engage with institutional shareholders. These engagements help the Board and management gain feedback on a variety of topics, including strategic and financial performance; operations; products; executive compensation; and Board composition and leadership structure; as well as on important environmental and social issues. The constructive insights, experiences and ideas exchanged during these engagements have helped the Board evaluate and assess key initiatives during GM’s ongoing transition to an all-electric future. GM also has a history of engaging with shareholders who submit proposals for inclusion in our proxy statement for consideration at our annual meeting. In the past, these constructive engagements have led to shareholders withdrawing their proposals following discussion and action on the part of GM. Learn more about the Board’s engagement with shareholders and other stakeholders in our 2022 Proxy Statement . → CORPORATE GOVERNANCE CONT. Board Oversight of Risk Management The Board discharges its risk oversight responsibilities, in part, through delegation to its committees. The company’s risk governance is facilitated through a top-down and bottom- up communication structure, with the tone established at the top by Ms. Barra, the Board Chair and CEO, who also serves as Chief Risk Officer, and other members of management, namely the Senior Leadership Team. The Senior Leadership Team also utilizes our Risk Advisory Council, an executive-level body with delegates from each business unit, to discuss and monitor the most significant enterprise and emerging risks in a cross-functional setting. They are tasked with championing risk management practices and integrating them into their functional or regional business units. Corporate Political Contributions and Lobbying Expenditures The Board has an active role in overseeing GM’s participation in the political process and believes it should have a role in helping to shape public policy and address legislation that impacts the company, our industry and our shareholders and other stakeholders. GM has supported and will continue to support public policies that drive the achievement of our long-term, sustainable growth. The following are highlights of the Board’s role: • To guide activities, the Board has adopted a U.S. Corporate Political Contributions and Expenditures Policy ( Political Contributions Policy ). • The Governance and Corporate Responsibility Committee oversees the Political Contributions Policy and annually reviews the company’s engagement in the public policy process. • The Governance and Corporate Responsibility Committee also annually reviews all corporate political contributions, GM Political Action Committee contributions (which are funded entirely by voluntary employee contributions) and the process by which they are made. The committee receives multiple updates each year regarding the company’s direct and indirect lobbying activities and expenditures. • The Governance and Corporate Responsibility Committee annually conducts a benchmarking exercise to confirm its political contribution and lobbying expenditure disclosures align with those of our peers and discusses emerging shareholder expectations. The Board also receives a monthly report on the most pressing public policy issues. It uses this report to continuously assess which issues are important to the company’s long-term interests and which organizations the company is working with to advance those interests. Learn more about GM Lobbying guidelines in our Public Policy Supplement . Skip Navigation Introduction Reducing Emissions Design for Environment Technology Customers Safety Diverse Workforce Human Rights Supply Chain Communities Governance 2021 SUSTAINABILITY REPORT 108
Cybersecurity & Privacy Transformative innovations—self-driving vehicles, combined with electrification and connectivity—are changing the nature of transportation and our relationships to the vehicles that move us. As the automotive industry continues to mitigate risks in the physical world, such as crashes, emissions and congestion, new risks are emerging in the virtual world, including cybersecurity and privacy risks. Cybersecurity and data protection are critical to the digital transformation of the auto industry. Cybersecurity Risks Software and connected services are key to GM’s vision of zero crashes, zero emissions and zero congestion, and with the increasing connectivity of GM vehicles, cybersecurity risks continue to evolve. Already, GM offers OnStar and connected services to more than 22 million connected vehicles globally through subscription-based and complimentary services. Safely and securely delivering these services has been possible due to a strong cybersecurity focus and priority throughout the company. GM’s organizational focus and oversight of cybersecurity is well-developed. This structure includes a dedicated Risk and Cybersecurity Committee of the Board, cybersecurity leadership tied directly to the CEO and Senior Leadership Team and a vice president of global cybersecurity who serves as a single- point senior executive. This vice president leads a dedicated organization that focuses on protecting against unauthorized access to vehicle safety systems and customer data. Leveraging well-established risk frameworks and standards, GM is focused on cybersecurity risk throughout the entire company, including information technology and intellectual property protection, vehicle and connected services, manufacturing safety and operations, supply chain and third-party security, merger and acquisition risks and the secure integration of all new business models. Cybersecurity remains a core focus and a high priority at GM in the development of advanced driving features, semi and autonomous systems, in-market enhancements, connected services and many other software-defined services. Hardware and software protective measures are employed and a key focus of our Product Cybersecurity organization. Privacy Protection GM relies upon information technology systems and networked products, some of which are managed by third parties, to process, transmit and store electronic information, and to manage or support a variety of our business processes, activities and products. Additionally, GM collects and stores sensitive data, including personally identifiable information of our customers and employees, in data centers and across information technology networks. Robust privacy policies and processes are critical to protecting GM’s employees and customers, and our business. GM’s Privacy Center publishes a Global Privacy Policy that covers all GM operations. We also have a Third-Party Information Security Requirements Exhibit and Privacy Exhibit with specific additional privacy obligations that are required for all contracts involving personal information (PI). Our contracts lay out requirements for compliance with data protection and privacy laws and regulations, and for managing PI in a manner that reinforces customer and employee trust and confidence in GM and our products and services. We keep these documents updated to address changes in laws and regulations, changes in our business and products, and changes in consumer expectations. In addition, the Board has approved the adoption of Global Privacy Principles, and GM continues to be committed to the Alliance for Automotive Innovation’s Consumer Privacy Protection Principles. Privacy Program The Privacy Center has a privacy program framework that focuses on policies, procedures, tools, guidance and training. This framework also includes a Privacy-by-Design program that requires all data-dependent initiatives to receive a privacy-focused consultation through their life cycle. The Privacy Center resides within our legal staff, and additional non-legal resources Skip Navigation Introduction Reducing Emissions Design for Environment Technology Customers Safety Diverse Workforce Human Rights Supply Chain Communities Governance 2021 SUSTAINABILITY REPORT 109
CYBERSECURITY & PRIVACY CONT. are leveraged on a functional, regional and product/program basis to instill best practices in a consistent manner across the global enterprise. In certain cases, external reviewers have been engaged to ensure use of industry best practices. The goal of our collaborative privacy practice is to ensure that the collection, use and sharing of employee and customer PI is secure and compliant, and that it reinforces employee and customer trust and confidence. Our greatest resources in protecting PI are our employees and processes. Privacy compliance is part of GM’s annual Corporate Required Training (CRT), which emphasizes the importance of privacy to our business and the high priority the company places on employee and consumer privacy. In addition to GM’s annual training, the Privacy Center conducts awareness training on emerging privacy laws and regulations with key areas of our business. Privacy Practices Our Information Security program is aligned to the National Institute of Standards and Technology Cyber Security Framework and International Organization for Standardization (ISO) Standards and includes elements to protect the confidentiality, integrity and availability of information. We have a robust Information Lifecycle Management (ILM) Policy and record retention schedule that applies globally to all GM employees and other individuals or entities (e.g., contract workers, purchased services, etc.) that create or manage GM records. The ILM Policy requires that we properly retain only those records needed to meet business, fiscal and legal requirements. GM requires an online Privacy Impact Assessment to be completed, reviewed and approved by a Privacy Center member prior to the implementation of any new product, service or process, or any change to the foregoing, involving the use of PI. Additionally, Information Security Risk Management creates a PI risk score for systems containing PI. Systems with high risk are required to have additional information technology controls. We have instituted a cross-functional data export review process that evaluates the privacy, security and business risks of proposed data exports outside GM. Unless a proposed export is approved by the cross-functional team, it does not leave GM. Incidents GM has a robust process for employees to report an incident involving possible wrongdoing, a violation of GM’s Code of Conduct—Winning with Integrity, an IT or other cybersecurity event, PI incident or other concerns. This includes reporting through our toll-free GM Awareline hotline and a robust process for reviewing and investigating all alleged incidents. An employee who violates our Privacy Policy or Code of Conduct may be subject to discipline, including warnings, suspension with or without pay and/or termination of employment. GM also has a dedicated cyber intelligence team that continuously monitors publicly available information for cyber incidents or data spills that may impact GM or our suppliers. Customer Privacy GM’s privacy statements are publicly disclosed on consumer-facing websites such as our corporate, vehicle brand and OnStar sites. We utilize an opt-in approach for the collection, use and sharing of consumer PI where legally required or appropriate, based on the nature of the data collected and its intended use. We also offer customers opt-out options where appropriate. GM complies with all privacy regulations, such as General Data Protection Regulation and the California Consumer Privacy Act. We honor data subject requests under these regulations, including requests to access, make corrections to and delete data. In addition, we do not allow the use of customer PI for secondary usage if it is not disclosed in the Privacy Statement or otherwise consented to by the customer. In 2021, we did not have any material customer privacy complaints. Skip Navigation Introduction Reducing Emissions Design for Environment Technology Customers Safety Diverse Workforce Human Rights Supply Chain Communities Governance 2021 SUSTAINABILITY REPORT 110
Environmental Management & Compliance GM facilities around the world vary in function, geography, size and surrounding natural environments, which gives rise to varying concerns such as resource scarcity and different levels of environmental compliance requirements. Although GM-owned and -operated facilities have their own operating plans depending on their location, all function under a common Global Environmental Policy , which provides an effective foundation for environmental stewardship. GM has a robust process to enhance the integration of environmental sustainability practices into daily business decisions and to: • Comply with applicable environmental laws and regulations globally. • Monitor our performance according to GM’s own Environmental Performance Criteria (EPCs), which are universal corporate performance requirements designed to protect human health and the environment in accordance with the GM Global Environmental Policy. • Conform to key sustainability performance indicators and environmental performance metrics. Each GM manufacturing site has one or more environmental leaders, who are supported by a GM regional environmental leader and a team of subject matter experts in regional central offices. We also have an annual business planning process, known as Business Plan Deployment (BPD), to strengthen the management of environmental performance. This process links our Global Manufacturing salaried employees and their annual compensation to GM Sustainability Commitments. Performance on BPD metrics and goals is monitored monthly at all GM manufacturing sites. Action plans are developed as needed to ensure we keep performance on track. Environmental Compliance As a responsible corporate citizen, GM’s Global Environmental Policy and Guiding Environmental Commitments provide guidelines to help reduce the impact of our activities on the environment. Our global guidelines play a significant role in our overall environmental compliance, ensuring that local plant policies: • Are appropriate to the nature, scale and environmental impacts of each plant’s activities, products or services. • Reinforce a commitment to comply with applicable laws and regulations and with other relevant environmental requirements. • Include a commitment to continuous improvement and pollution prevention. • Provide the framework for setting and reviewing environmental goals and targets. • Are documented, implemented, maintained and communicated to all employees. Statutory, regulatory and permit programs administered by various governmental agencies in different jurisdictions impose numerous environmental requirements on our facilities and products. Compliance with applicable environmental requirements is an organizational imperative. Compliance issues occasionally arise, and each allegation of noncompliance is treated seriously by GM. In 2021, GM received 15 Notices of Violation, 12 in the United States and three outside the United States. GM paid one penalty over $10,000 in 2021, at a cost of $10,500. GM’s Guiding Environmental Commitments are the foundation of our Global Environmental Policy. The Commitments serve as a guide for all GM employees worldwide, encouraging environmental awareness in both daily conduct and in the planning of future products and programs. Skip Navigation Introduction Reducing Emissions Design for Environment Technology Customers Safety Diverse Workforce Human Rights Supply Chain Communities Governance 2021 SUSTAINABILITY REPORT 111
ENVIRONMENTAL MANAGEMENT & COMPLIANCE CONT. 2019 Conducted benchmarking of industry best practices associated with ISO 14001 certification models. Began redesign of GM’s EMS ISO 14001 program in the United States from individually conforming programs to a holistic, global enterprise conformance model. 2020 Aligned North American manufacturing sites under a common ISO 14001 framework and developed a construct to transition global facilities into this common EMS framework. 2021 Conducted third-party audits of GM’s Global ISO 14001 Enterprise Program resulting in one Minor Finding issued by the Registrar auditing company. 2022 Global Enterprise ISO 14001 Certificate was issued to GM on February 21, 2022. Expanding the global ISO 14001 enterprise program to include new manufacturing operations and additional nonmanufacturing sites. St. Catharines Propulsion Plant in Ontario was the winner of the 2021 GM Manufacturing Sustainability Recognition Award for their renewable energy project, Gold Certified Wildlife Habitat and many sustainability initiatives. Environmental Management System (EMS) All manufacturing facilities that GM owns and operates, and a majority of our nonmanufacturing sites around the world, have implemented an EMS. GM’s EMS combines elements of ISO 14001 and management system elements that are unique to our operations. From 2019 through 2022, GM developed and implemented an aligned, global, third-party certified ISO 14001 enterprise program. This integration ensures we achieve our environmental commitments as a normal part of our business activities. GM continues to expand our EMS programs into other company entities when and where there is a recognized identified benefit. Environmental Performance Implementation of our Guiding Environmental Commitments is facilitated by GM EPCs that apply to our global facilities and major technology centers. The EPCs are internal performance requirements for the management of environmental matters at our facilities. In many cases, they supplement applicable legal requirements by setting minimum standards for environmental management and performance practices that may be more stringent than those required by law. As a result, we work to ensure that a base level of environmental performance is achieved, regardless of where a facility is located or whether a particular jurisdiction has an environmental regulatory program in place. In 2020, we expanded our tracking of environmental compliance and sustainability performance in manufacturing operations by leveraging the Manufacturing Excellence Indexes (MEI) system. Created by Manufacturing, MEI is an internal GM scoring tool to benchmark GM operations performance against internal facilities. The use of real-time data provides the organization a strategic and common method to measure performance, assess risk and drive continuous improvement. Managing Substances of Concern Responsibly GM has established policies, procedures and supplier engagement to monitor banned substances and to ensure global compliance and protect the health of our customers. We receive supplier data monthly that is cross-referenced with known restricted substances lists to ensure compliance with regulations around the world. Our Vehicle Chemical Regulatory Compliance Team evaluates all materials and components/ parts to verify that they do not contain substances that are prohibited or restricted through GM internal standards, approval databases, the Global Automotive Declarable Substance List and the International Material Data System. Skip Navigation Introduction Reducing Emissions Design for Environment Technology Customers Safety Diverse Workforce Human Rights Supply Chain Communities Governance 2021 SUSTAINABILITY REPORT 112
ENVIRONMENTAL MANAGEMENT & COMPLIANCE CONT. Employee Environmental Training Our people are key stakeholders in our environmental stewardship and are critical to our environmental performance. We strive to have the best-trained environmental professionals in the world. Although most environmental training is specific to a facility, country or region, we continually provide strategic training and guidance to our environmental professionals to help them keep pace with evolving environmental issues, changing regulations and best practices. Our training addresses a variety of areas specific to the regulatory requirements for air quality, waste management, water quality and other environment-related topics. Environmental professionals develop training goals through Workday , the company’s human capital management portal, and seek personal and professional development through internal and external conferences, webinars and lunch and learns. In North America, environmental professionals attend focused sessions over a period of a week where speakers, both internal and external to the company, educate on a variety of topics. Outside North America, environmental professionals take a Global Environmental Certification and Training Program focused on GM’s Guiding Environmental Commitments, our internal EPCs and industry best practices. Skip Navigation Introduction Reducing Emissions Design for Environment Technology Customers Safety Diverse Workforce Human Rights Supply Chain Communities Governance 2021 SUSTAINABILITY REPORT 113
Ethics The foundation of GM’s business is: Our Core Behaviors help drive our business decisions and activities worldwide. GM is committed to creating and maintaining an ethical culture and conducts ethical culture surveys across our global workforce to monitor our progress every few years. Our 2020 third-party survey results show that internal perceptions of GM’s ethical culture continue to increase and are higher than the third-party’s 2018–2019 benchmark, which includes responses from over 500,000 individuals across 32 companies. In 2022, for the third year in a row, General Motors was also the only original equipment manufacturer automaker recognized as one of the World’s Most Ethical Companies ® by Ethisphere, a global leader in defining and advancing the standards of ethical business practices. Winning with Integrity is one of our Core Behaviors, and the World’s Most Ethical designation is a testament to our ethical leadership as we continue to transform our company and industry. An ethical business starts at the top. Chair and CEO Mary Barra and other members of our Senior Leadership Team regularly issue messages to all employees emphasizing the importance of our Code of Conduct and their expectation that every employee strive to do the right thing, even when it is difficult. The Board is also committed to upholding the highest legal and ethical conduct in fulfilling its responsibilities. All Board members, officers and employees are expected to act ethically at all times and to adhere to the law, our Code of Conduct and any applicable company policies. The Board, in addition to our eligible salaried employees (e.g., everyone other than those on excused leave), also completes GM’s Code of Conduct training. The Board’s Audit Committee has oversight responsibility for GM’s ethics and compliance program, which promotes a culture of high performance with high integrity by advocating and helping implement the principles of GM’s Code of Conduct—Winning with Integrity. The Global Ethics and Compliance Center (GECC) is led by the assistant general counsel and chief compliance officer, who reports to the executive vice president of global public policy, general counsel and corporate secretary, and indirectly to the Board’s Audit Committee. The chief compliance officer provides regular updates to the Audit Committee. The chief compliance officer meets with the Audit Committee in private sessions without other members of management present at least once per year. The GECC prevents, detects and helps correct violations of law and corporate policies and helps promote our ethical business culture. The GECC seeks to align GM’s ethics and compliance program with the recognized elements of an effective compliance program and primarily manages GM’s Code of Conduct; Non-Retaliation Policy; conflict of interest disclosure process; investigations; ethics and compliance training and communications; global policy development; compliance assurance; risk-based third-party due diligence; whistleblower line; anti-corruption compliance assurance in GM strategic transactions; and other anti-corruption risk areas. Regional compliance officers are established in each of GM’s operating regions to help ensure compliance and ethics globally. We also have a network of compliance liaisons, as well as other compliance personnel located throughout GM who provide guidance to employees and answer ethics and compliance questions. Additional global structures and oversight are in place for safety, export compliance, antitrust compliance, data/cybersecurity compliance, records management compliance and other risk areas. The Role of Ethics Compliance Liaisons In 2021, we launched a new Compliance Liaison program to help further localize compliance into business units and to serve as an additional knowledgeable resource for identifying compliance issues. Compliance liaisons are GM team members supporting business units and regions who help detect, prevent and resolve potential compliance issues across the company. Our Vision A World with Zero Crashes, Zero Emissions and Zero Congestion Our Core Values Customers, Excellence, Relationships and S e ek Tr u th Our Eight Core Behaviors Be Inclusive, Think Customer, Innovate Now, Look Ahead, One Team, Be Bold, It’s On Me, and Win with Integrity Skip Navigation Introduction Reducing Emissions Design for Environment Technology Customers Safety Diverse Workforce Human Rights Supply Chain Communities Governance 2021 SUSTAINABILITY REPORT 114
Code of Conduct GM’s Code of Conduct —Winning with Integrity— reinforces our commitment to a work environment founded on mutual respect, trust and accountability. It outlines the policies and obligations that guide our business conduct, and includes employee guidance on various reporting mechanisms available to report safety and other concerns (e.g., Speak Up For Safety, Awareline). Our Code of Conduct also emphasizes GM’s Non-Retaliation Policy . It applies across our company, at every level, including supervisors, senior leaders and Board members, and extends to subsidiaries that GM controls. We expect third parties, including suppliers, to act in a manner that is consistent with the principles and values outlined in our GM Supplier Code of Conduct when conducting business with, and on behalf of, GM. We expect GM employees working with our third parties to hold third parties accountable. Our Code of Conduct is available in nine languages (including English); our Supplier Code of Conduct is available in 13 languages (including English); and certain compliance policies are available in multiple languages to ensure they are understood by employees and third parties in all locations where GM does business. Our Code of Conduct governs how our employees are expected to act: displaying integrity in the workplace, in the marketplace and in their communities when representing GM, and it guides the conduct of our daily business ETHICS CONT. practices worldwide. In 2022, we refreshed the Code of Conduct to add our “Be Inclusive” behavior, a new CEO leadership message and other relevant and timely content. To ensure the effectiveness of our Code of Conduct, we regularly conduct independent third-party assessments of GM’s compliance program against the Department of Justice and other applicable laws, regulations and rules. We also regularly conduct compliance risk assessments. Our Code of Conduct publicizes various points of contact for employees with questions or concerns, including local leadership, Human Resources, labor representatives, the GECC, Legal Staff, GM Audit Services and our Awareline. GM maintains a robust conflict of interest disclosure process that applies to all salaried employees and members of the Board. Employees are required to complete an electronic conflict of interest questionnaire at least once during their employment and keep it updated as their personal circumstances change. Board members who are not employees provide written disclosure of any actual or potential conflicts of interest at least once a year. To ensure compliance awareness continues throughout the year, our GECC team develops compliance and ethics messages on a regular basis, underscoring the importance of these topics. Skip Navigation Introduction Reducing Emissions Design for Environment Technology Customers Safety Diverse Workforce Human Rights Supply Chain Communities Governance 2021 SUSTAINABILITY REPORT 115
ETHICS CONT. Reporting Concerns GM encourages our employees to speak up and provides resources to do so. An internal “Report Concerns” site makes it easy for employees to identify the most effective way to quickly report their concern. In cases where an individual is uncomfortable reporting through other established internal channels, we maintain a global toll-free hotline. The Awareline is operated by an independent third party and allows employees and others to confidentially report concerns of misconduct by the company, our management, supervisors, employees or agents. Reports can be made in more than a dozen languages, 24 hours per day, 7 days per week, by phone, web or email. Reports may be made anonymously, where permitted by law. In 2021, GM received 4,170 reports to the Awareline, of which 3,048 were classified as allegations, and the remaining reports were suggestions, inquiries or other miscellaneous issues. GM tracks all reports of misconduct— whether made to the Awareline or through some other channel—in a case management system that facilitates efficient investigation, follow- up and compliance trend analysis. The case management system allows GM to follow up with individuals who submit Awareline reports anonymously, while preserving the reporter’s anonymity, to help GM better investigate and remediate anonymous allegations. Allegations of misconduct are reviewed and prioritized based on a number of factors, including the type of misconduct, the position of the alleged wrongdoer within the company and whether the allegation entails any potential violations of law. High-priority cases receive special scrutiny and review; a cross-functional committee meets monthly to discuss their investigative progress and resolution. There is also a quarterly review process to determine which cases, if any, require reporting to the Board or Audit Committee, as well as processes in case a particular allegation requires more immediate reporting. The chief compliance officer also provides regular updates to the Audit Committee on key GECC priorities and accomplishments and trends in Awareline submissions and Investigations. Speak Up!, GM’s Non-Retaliation Policy, protects GM employees from retaliation when they raise a concern in good faith. GM’s most recent Ethical Culture Survey, as well as industry benchmarking data, shows that the majority of misconduct reports are made to an employee’s manager. To help our GM managers in such circumstances and to provide additional guidance regarding GM’s Non- Retaliation Policy, the GECC has developed a website that provides helpful compliance tools for managers, including compliance toolkits on various topics, compliance moments to use at meetings, quick reference compliance guides and other materials. GM also makes available a scenario-based “What Would You Do?” course for managers. In 2021, the GECC developed and is piloting a post-investigation antiretaliation survey to initiate outreach to known reporters following an investigation to identify and respond to potential retaliation and improve the investigative process. These materials help GM managers create a safe and open reporting environment for their teams. Supplier Due Diligence GM’s success depends in part on building positive business relationships with reputable and ethical suppliers that meet our business needs. GM maintains a Supplier Code of Conduct that sets forth our expectations for ethical conduct as well as a risk-based due diligence program for our suppliers and business partners. GM’s due diligence activities consider, among other things, safety, reputation, human rights, integrity, business requirements, compliance with laws and GM’s expectations for adherence to Winning with Integrity. We engage in continuous risk assessment, using a variety of tools and cross-functional resources to better understand and mitigate risk. We provide resources to our suppliers through our GM SupplyPower portal and other channels to ensure open communication and to help suppliers understand our expectations and improve their operations. Learn more in Supporting Supplier Responsibility . 2021 Types of Allegations Received CATEGORY PROPORTION OF ALLEGATIONS Accounting, Auditing and Financial Reporting Fraud relating to accounting procedures, internal controls or auditing matters 0.1% Business Integrity Examples: Fraud, conflicts of interest, corruption 5.6% Human Resources, Diversity and Workplace Respect Examples: Interpersonal conflicts, harassment, discrimination, retaliation 66.8% Environment, Health and Safety Examples: Threats and violence, substance abuse, environmental concerns, workplace safety 13.3% Misuse, Misappropriation of Corporate Assets Examples: Theft, property damage, information or IP loss, computer misuse 14.2% Skip Navigation Introduction Reducing Emissions Design for Environment Technology Customers Safety Diverse Workforce Human Rights Supply Chain Communities Governance 2021 SUSTAINABILITY REPORT 116
Ethics Training and Education ETHICS CONT. Training is a critical aspect of reinforcing our ethical culture because it educates our employees on how to apply the standards and principles set forth in our policies in their work activities. Every year, all eligible salaried employees are required to review the Code of Conduct and complete CRT. All CRT courses are available to global employees in eight languages (including English). New or refreshed courses are deployed annually, often with new content, new scenarios and exercises. We use adaptive technology that tailors the courses to an individual’s job responsibilities. GM’s Compliance Training and Communications Group within the GECC oversees the process of regularly updating the CRT. Once the annual program and policy certification requirements are approved by the CRT governance board, a cross-functional group that includes senior leaders from human resources, the course owners and subject matter experts draft the course objectives and content based on company risk analysis and any new compliance regulations. We follow guiding principles of trust, respect and accountability as we select vendors, determine how many courses to offer, set completion deadlines and make other course-related decisions. For example, we ensure courses are relevant to our employees’ roles, keeping courses concise and setting consistent content standards. CRT in 2021 included: • GM Code of Conduct: Winning with Integrity • Cybersecurity • Export and Sanctions Compliance • Antitrust and Competition Law Compliance Once employees complete the Code of Conduct training, they are required to certify that they agree to comply with the policies contained in the Code; that they have disclosed any new potential conflicts of interest; and that they have reported any violations of the Code and any vehicle or workplace safety issues. In 2021, GM achieved a 100% completion rate among eligible salaried employees for both our CRT and Code of Conduct Certification Program. Beyond distributing our Code of Conduct and requiring annual training on ethics- and compliance-related topics, we use risk-based principles to provide live and/or “virtual” training to thousands of employees each year. For example, the Compliance Team conducted live training sessions to targeted audiences on topics that included export compliance, antitrust, Foreign Corrupt Practices Act, privacy, working with third parties, winning in the marketplace without sacrificing our values and other relevant compliance topics. The GECC also utilizes on-demand microlearning modules so that employees can access refresher training on gifts and entertainment and conflicts of interest processes as needed. Finally, we recognize a companywide Compliance and Ethics Week in which we engage employees through interactive games, leadership messages, compliance toolkits, employee recognitions and other measures to promote our Winning with Integrity behavior. By keeping ethical behaviors top of mind for all GM employees throughout the year, we continue to win with integrity in our dealings with suppliers, governments and other third parties. 2021 Ethics & Compliance Training By-the-Numbers ~364,000 total online courses delivered ~64,000 employees and select contractor workers who completed ethics and compliance training ~6,000 in-person advanced compliance training modules delivered 4 required courses for employees 1 customized contract worker course Skip Navigation Introduction Reducing Emissions Design for Environment Technology Customers Safety Diverse Workforce Human Rights Supply Chain Communities Governance 2021 SUSTAINABILITY REPORT 117
→ Model year 2024 Silverado EV available Fall 2023. Public Policy We have consistently and publicly advocated for climate action and awareness, as well as policies that address climate change through economy-wide, market-based carbon pricing mechanisms. Our global commitment to an all-electric, zero- emissions future is unwavering, regardless of the prevailing vehicle emissions standards in any region in which we operate. We advocated for passage of the Infrastructure Investment and Jobs Act (IIJA) by the U.S. Congress in 2021, as we believe it puts the United States on the path toward strengthening the economy and advancing innovation. The IIJA also lays the foundation for sustainability policies that will help address climate change and improve environmental quality and resiliency. GM supports those goals and, critically, we support those provisions, such as electric vehicle (EV) charging infrastructure, that accelerate the adoption of EVs and help to establish the United States as a global leader in electrification today and into the future. In August 2021, GM announced our plan to achieve sales of 40-50% of annual U.S. volumes of battery electric vehicles by 2030 in order to move the nation closer to a zero-emissions future consistent with the Paris Agreement. Demonstrating our readiness to engage in the climate policy debate, GM joined 41 other leading U.S. companies in signing a statement organized by the Center for Climate and Energy Solutions as part of its Climate Innovation 2050 initiative. The statement called upon the Biden Administration and Congress in 2021 to enact ambitious, durable and bipartisan climate solutions. We believe this should include an economywide market-based approach that puts a value on carbon, as well as transformative levels of federal investment in the country’s infrastructure—including EV chargers and the grid—to prepare for an electrified future. It is critical that EV mandates are matched to appropriate complementary policies that accelerate EV adoption and put the United States in a leadership position to transform the auto industry and supply chain. We are encouraged by the provisions on EV infrastructure, EV supply chain and EV battery manufacturing and recycling development contained in the IIJA. Several of the provisions contained within the bill are consistent with aspects of GM’s proposed National Zero Emissions Vehicle Program, first suggested by GM in 2018. We look forward to working with federal, state and local stakeholders to assist in the efficient distribution and use of these IIJA funds. To stimulate the rapid uptake of EVs, we continue to strongly support the extension and expansion of federal and state consumer rebates and tax incentives for new and used light- and heavy-duty EV purchase and lease, and charger installation. Global Fuel Economy and Emissions Regulation Emissions requirements have become more stringent around the world, driven by policy requirements in areas such as air quality, energy security and climate change. It is important that governments update their legacy regulations, like the Corporate Average Fuel Economy standards in the United States, to reflect the rapidly changing transportation and mobility landscape. Properly designed standards will allow the entire global industry to accelerate the pace of innovation and better prepare for an all-electric future. Learn more about GM’s public policy advocacy in our Public Policy Supplement . Skip Navigation Introduction Reducing Emissions Design for Environment Technology Customers Safety Diverse Workforce Human Rights Supply Chain Communities Governance 2021 SUSTAINABILITY REPORT 118
PUBLIC POLICY CONT. Addressing Congestion Through Public Policy GM envisions a future where we can all enjoy the benefits of vehicle use—freedom, convenience and comfort—while minimizing congestion. And, we are working on the technologies and engaging in the policy discussions that will make this future possible. GM has a well-established track record of engagement with innovative city and mobility initiatives such as the deployment of sustainable last-mile solutions. In Seattle, BrightDrop participated in one of the nation’s first zero operating-emissions, last-mile neighborhood delivery hubs. In New York City, the integration of BrightDrop’s Trace allowed couriers to remove one on-road vehicle from the delivery route and cut delivery vehicle curbside dwell time in half, when used on routes in a high-density, vertical urban environment—all while reducing physical strain on couriers. Thoughtfully designed last-mile urban delivery solutions, such as BrightDrop, are a timely and critical component as competition for curb space creates safety and quality-of-life issues. As cities continue to explore ways to tackle congestion in their communities, GM looks forward to building on this foundation through partnerships and constructive dialogue with stakeholders, pilot projects and other efforts that seek to leverage public policy to realize our vision of a future in which people can enjoy the freedom, convenience and comfort of vehicle use in cities with zero congestion. Many cities and states are already exploring these policies, finding that there could be a variety of ways to improve mobility for their residents. GM does not endorse any one approach but recognizes that cities and states are exploring all of these and believes a comprehensive strategy incorporating one or more policy levers could be successful. GM is prepared to engage with these debates to advance our zero congestion vision while bolstering our credibility as a messenger and stakeholder in this issue area. A combination of autonomous vehicle (AV) technology, new mobility solutions and policy will enable reductions in congestion through safety improvements, greater efficiencies in road use and reductions in traffic volumes. As we explore future markets for our AV and fleet offerings, we work closely with communities to find solutions together. Gains in efficiency and safety not only create opportunities for more equitable access to health care, education and employment, but can alleviate the negative effects of transportation networks. GM is optimistic that innovations in vehicle connectivity will help optimize traffic flows and reduce traffic crashes, ultimately easing congestion. We are focused on deploying advanced driver assistance technologies, such as Super Cruise and Ultra Cruise, and self-driving technology, through applications such as the Cruise Origin that we believe can help achieve these objectives. GM has a well-established track record of engagement with innovative city and mobility initiatives. Skip Navigation Introduction Reducing Emissions Design for Environment Technology Customers Safety Diverse Workforce Human Rights Supply Chain Communities Governance 2021 SUSTAINABILITY REPORT 119
Forward-Looking Statements Cautionary Note on Forward-Looking Statements: This report may include “forward-looking statements” within the meaning of the U.S. federal securities laws. Forward-looking statements are any statements other than statements of historical fact. Forward-looking statements represent our current judgement about possible future events. In making these statements, we rely upon assumptions and analysis based on our experience and perception of historical trends, current conditions and expected future developments, as well as other factors we consider appropriate under the circumstances. We believe these judgments are reasonable, but these statements are not guarantees of any future events or financial results, and our actual results may differ materially due to a variety of factors, many of which are described in our most recent Annual Report on Form 10-K and our other filings with the U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission. We caution readers not to place undue reliance on forward-looking statements. Forward-looking statements speak only as of the date they are made, and we undertake no obligation to update publicly or otherwise revise any forward- looking statements, whether as a result of new information, future events or other factors that affect the subject of these statements, except where we are expressly required to do so by law. Skip Navigation Introduction Reducing Emissions Design for Environment Technology Customers Safety Diverse Workforce Human Rights Supply Chain Communities Governance 2021 SUSTAINABILITY REPORT 120
300 RENAISSANCE CENTER DETROIT, MI 48265-3000